lesson1(recap, atomic radius, nuclear reaction)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
another term for proton number
atomic number
another term for nucleon number
mass number/atomic mass
what do cations and anions do
lose + and gain electron -
what does the nucleus of an atom consist of
protons and neutrons
what does it mean by nuclear charge
number of protons in the nucleus
what is the nuclear charge of hydrogen( must indicate +)
+1
what is the nuclear charge of oxygen
+8
what force causes nucleus of an atom to be attracted to the electrons
electromagnetic force
what components of atoms take part in chemical reactions
valence electrons and neutrons
What is the octet rule?
atoms tendency to have 8 valence electrons (lose or gain)
what is duplet rule and how is it different to octet rule
want 2 valence electrons instead of 8
how can one determine atom identity
by its proton(atomic)number
what is natural abundance
percentage of how abundant the isotope is of a particular element
what happens when you add all the natural abundance of every isotope together
get 100%
formula of relative atomic mass
(nucleon number x natural abundance)+...../100
(everything divide 100 for percentage)
what to do if only have relative atomic mass with isotopes nucleon number and want to find out natural abundance of each isoptope
use variable x for natural abundance so 1 is x 1 is 100-x
what is common for all respective groups
same number of valence electrons (thus similar chemical properties)
what is common for respective periods
same number of electron shells
which group has alkali metals
group 1
which group has alkaline metals
group 2
which group has halogens
group 7 /17(in other periodic tables)
difference between alkaline and alkali metals
alkaline metals is less reactive
what is shielding effect
decrease in FOA exerted by nucleus on valence electrons due to Prescence of inner shells
what happens to FOA in atoms as inner shells increasse
decrease
due to shielding effect what happens to atomic radius when inner electron shells increase
atomic radius increase(valence electrons not held tightly)
across a period does atomic radius increase or decrease
decrease(proton increase =electron increase -more inner shells)
across a period does atomic radius increase or decrease
decrease
(still same number of electron shell but increase electrons hence more attracted to nucleus so atomic radius decrease)
what is electronegativity
ability to draw shared electrons to itself
how to know if an element has stronger electronegativity
increase across period
Why electronegativity increases across a period
greater nuclear charge smaller atomic radius
why electronegativity decreases down a group
going down atom increase size (more electron shells)
what is electromagnetic radiation
light like alpha beta...
what happens during alpha decay
a pair of protons and pair of neutrons bind together (helium atom)
check how to write equation
what is beta decay
one neutron change to proton
(gain electron- another element-check how to write in one note)is -1
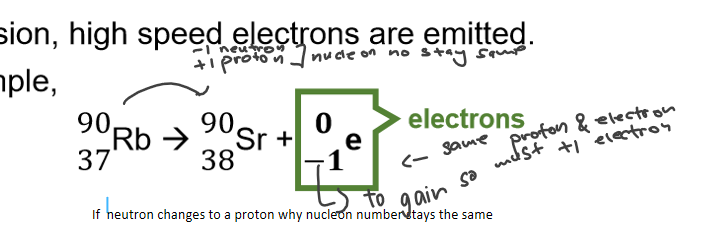
what is positron emission
proton to neutron(liek cation so +1
what is electron emission/capture
electron react with proton form neutron
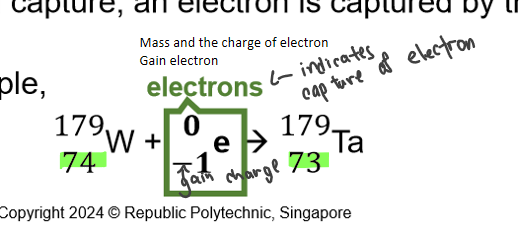
what determines stability of nuclei
ratio of protons and neutrons
what happens when nuclei is unstable
undergo radioactive decay