chemistry - key concepts in chemistry: ionic bonding (1.21 - 1.27)
1.21 how are ionic bonds formed?
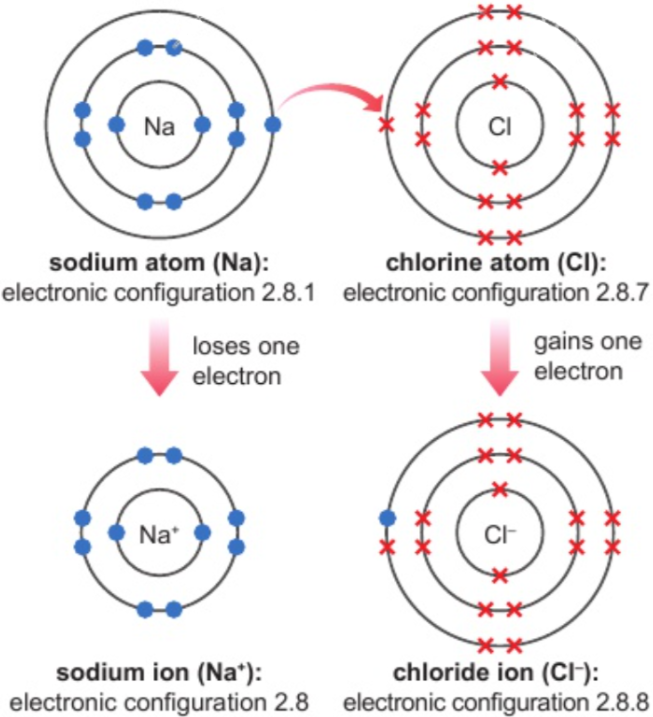
electrons transferred between metal & non-metal atoms
strong ionic bond - strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
metal atoms lose electrons - form cations (+ve ions)
non-metal atoms gain electrons - form anions (-ve ions)
1.21 dot & cross diagrams
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
1.21 how are ionic bonds formed?
electrons transferred between metal & non-metal atoms
strong ionic bond - strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
metal atoms lose electrons - form cations (+ve ions)
non-metal atoms gain electrons - form anions (-ve ions)
1.21 dot & cross diagrams

1.22 ion definition
atom/group of atoms with positive/negative charge
1.23 calculate numbers of protons, neutrons & electrons in simple ions given atomic number & mass number
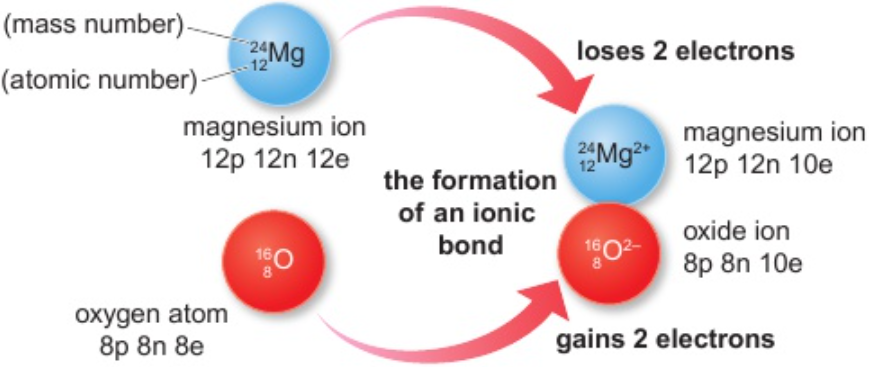
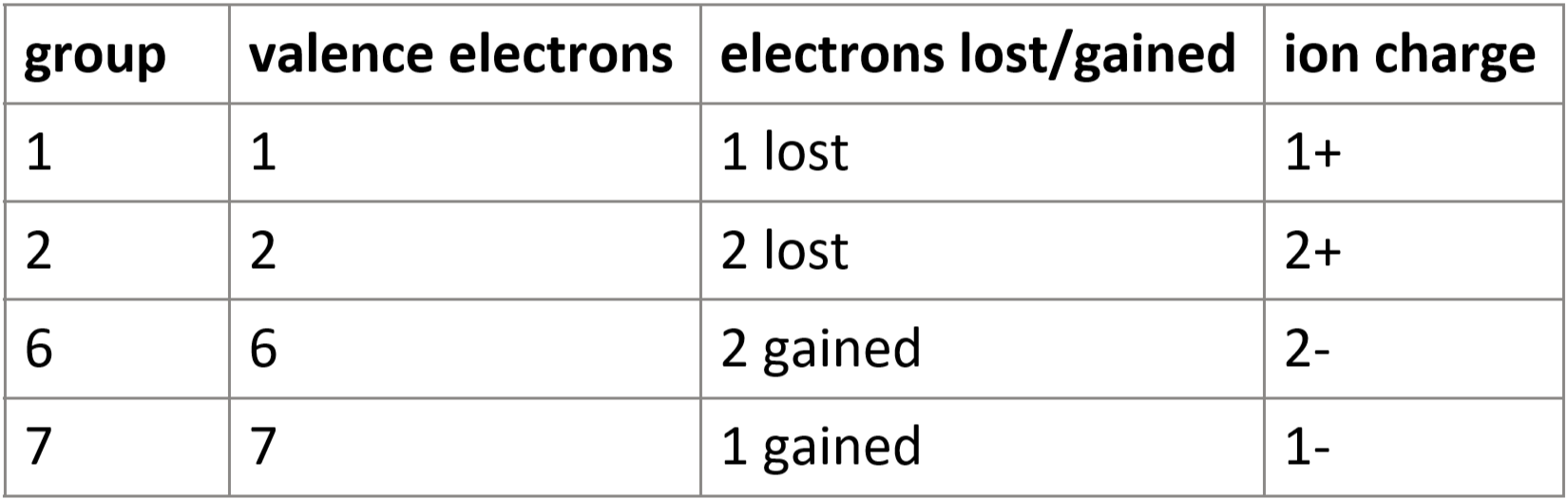
1.24 formation of ions - groups 1, 2, 6 & 7
1.25 endings -ide & -ate (names of compounds)
-ide: contains 2 elements; e.g. iron (II) sulfide (FeS)
-ate: contains 3/more elements, 1 is oxygen; e.g. iron (II) sulfate (FeSO4)
1.26 ionic formulae - oxide, hydroxide, halide, nitrate, carbonate, sulfate
oxide = O2-
hydroxide = OH-
halide = (group 7)-
nitrate = NO3-
carbonate = CO32-
sulfate = SO42-
1.26 deduce formula of ionic compounds given formula of ions
e.g. Na+ + Cl- → NaCl
e.g. Na+ + CO32- → Na2CO3
1.27 structure of ionic compound
lattice structure
regular arrangement of ions
held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction (ionic bonds) between oppositely charged ions