Lecture 23: Myosin and Muscle
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
actin networks at the front and back of the cell
Lamelopodia and filopodia at the leading edge, stress fibres at the back
what creates the different zones of Rho activity?
extracellular signalling, chemotactic gradient
what does myosin protein do?
generate force through a conformational change with phosphate release (ATP to ADP)
what are muscles made of?
billions of contractile bundles
bundle of muscle fibres → myofibril → sarcomere
what is a sarcomere?
basic unit of muscle contraction, made from tightly packed arrays of actin filaments and myosin filaments
what are Z disk, I band and A band?
Z disk → where myosin filaments extend from
A band → myosin bundles
I band → distance between Z disk and A band

what happens with muscle stimulation?
sarcomeres undergo rapid contraction (50 ms! 5-10 ms for period between signal and start of contraction, 40-45 ms for contraction phase from fully elongated to fully contracted)
Crossbridge cycle
1 ATP hydrolysis = 1 “power stroke”
ATP binds to myosin head and it is released from actin
Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi, head rotates to cocked state
Myosin head binds actin filament
“Power stroke” : release of Pi and elastic energy strains myosin, moving actin filament left
ADP released and repeat step 1

How is Rigor Mortis caused?
from failure of myosin to detach in the absence of ATP, causing stiffness
neck domain of lever arm
if the arm is longer, there will be a larger swing, moving actin faster
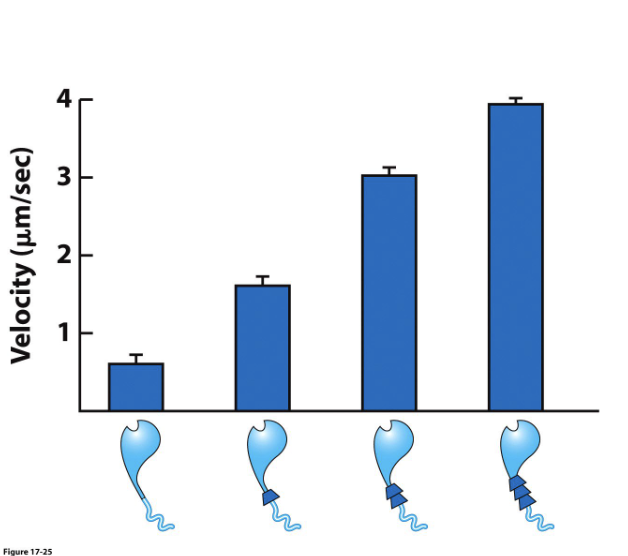
myosin force produced
~ 5 pN of force over a length of ~ 10 nm (50 pN nm of work)
design challenges that muscles face
prevention of continuous contraction
activation of contraction
Freezing the structure of the sarcomere (to hold steady)
what determines the structure of the sarcomere?
nebulin, titin, and capping proteins

what does tropomyosin do?
it blocks the binding site for myosin on the actin filament.
what happens to tropomyosin in the presence of Ca2+?
It rotates the tropomyosin to reveal the myosin-binding site of actin
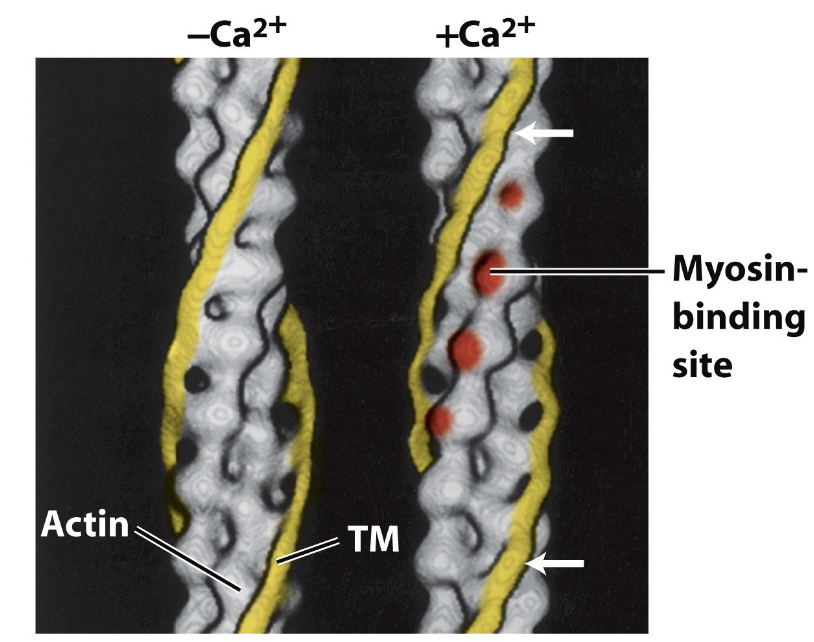
How is muscle contraction activated?
From motor neurons that receive signals from the brain and transmit them to the muscle
what happens when motor neurons are stimulated?
a rapid spike in Ca2+ concentration in the muscle fibres
what does the sarcoplasmic reticulum do?
it stores Ca2+
What does troponin do?
it binds calcium and pulls tropomyosin out of the way, allowing myosin to bind
muscle contraction is stimulated by what?
presence of calcium