Vaccine delivery 1+2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the main purpose of vaccines?
To induce protective immunity without full infection.
Name three main types of viral vaccines
Inactivated, live attenuated, subunit.
Why do inactivated vaccines require boosters?
They confer weaker immunity.
Which vaccine type is contraindicated in immunocompromised patients?
Live attenuated vaccines.
What is a viral vector vaccine?
A harmless virus engineered to express pathogenic proteins.
Difference between replicating and non-replicating viral vectors?
Replicating can multiply; non-replicating cannot.
What are adjuvants?
Compounds enhancing immune response to antigens.
Role of adjuvants in subunit vaccines?
Strengthen immune response.
Main challenge of recombinant vaccines?
Poor stability and weaker immune response.
Advantage of intranasal delivery?
Needle-free, mucosal immunity
What is the main advantage of microneedle patches?
Thermostability, painless, self‑administration.
What carrier is used in mRNA vaccines?
Lipid nanoparticles.
what are polyplexes
Complexes formed between polymers and nucleic acids
Cationic polymers are the best, due electrostatic attraction to negatively charged oligonucleotides/genetic materials and cellular membranes
what was an issue faced with Polyplex made of PEI & mRNA encoding influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) & nucleocapsid
Toxicity which is a common issue with many cationic compounds. This is due to positively charged polymer could electrostatically interact with the negatively charged membrane which could impact the integrity of the membrane which can lead to osmotic lysis
how are dendrimers synthesised
Synthesised from a polyfunctional core, which dictates the three-dimensional shape & size of the molecule
how is structure of dendrimer is adapted for function and targeting
Interior core suitable for encapsulation of antigenic cargo, while the exterior layer can be functionalised by targeting moieties
why can dendrimers act as adjuvants
Exhibit immune-stimulating properties, thus can act as adjuvants
what are nanocapsules and explain their structure
Composed of an inner lipid core stabilised by phospholipids & an external polymeric shell.
Opportunity to load hydrophobic adjuvant molecules in the core
While antigen cargos are displayed on the surface, associated with the external polymers
why are nano capsules suitable for efficient lymphatic drainage
optimisation of particle size
surface charge
selection of different coating polymers
what is shingrix?
(herpes zoster subunit vaccine, HZ/su): is an adjuvanted recombinant subunit vaccine
the ONLY clinically approved liposome-based vaccine
what are lipoplexes
complexes formed by lipids (mainly cationic) & nucleic acids. Studies for mRNA vaccine delivery. Early stage of research
what is the composition of lipid nanoparticles
-Cationic Lipids (for mRNA complexation)
-Ionisable Lipids (facilitate in vivo delivery and endosomal escape)
-Phospholipids, Cholesterol & PEGylated Lipids (improve NP properties such as stability, tolerability and biodistribution)
what is the purpose of ionisable lipids in lipid nanoparticles
Nano carries are engulfed by cells by endocytosis forming endosome. If carrier is trapped in endosome for a long time it will be hydrolysed by lysozymes. So need mechanism to release carrier (ionisable lipids )
what adverse effect can PEGylated lipid component lead to?
Allergic reactions
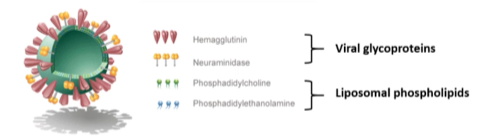
what are hybrid systems?
Virosomes/VLPs are non-replicating “artificial virus” composed of a liposome covered/functionalised with the viral glycoprotein envelop
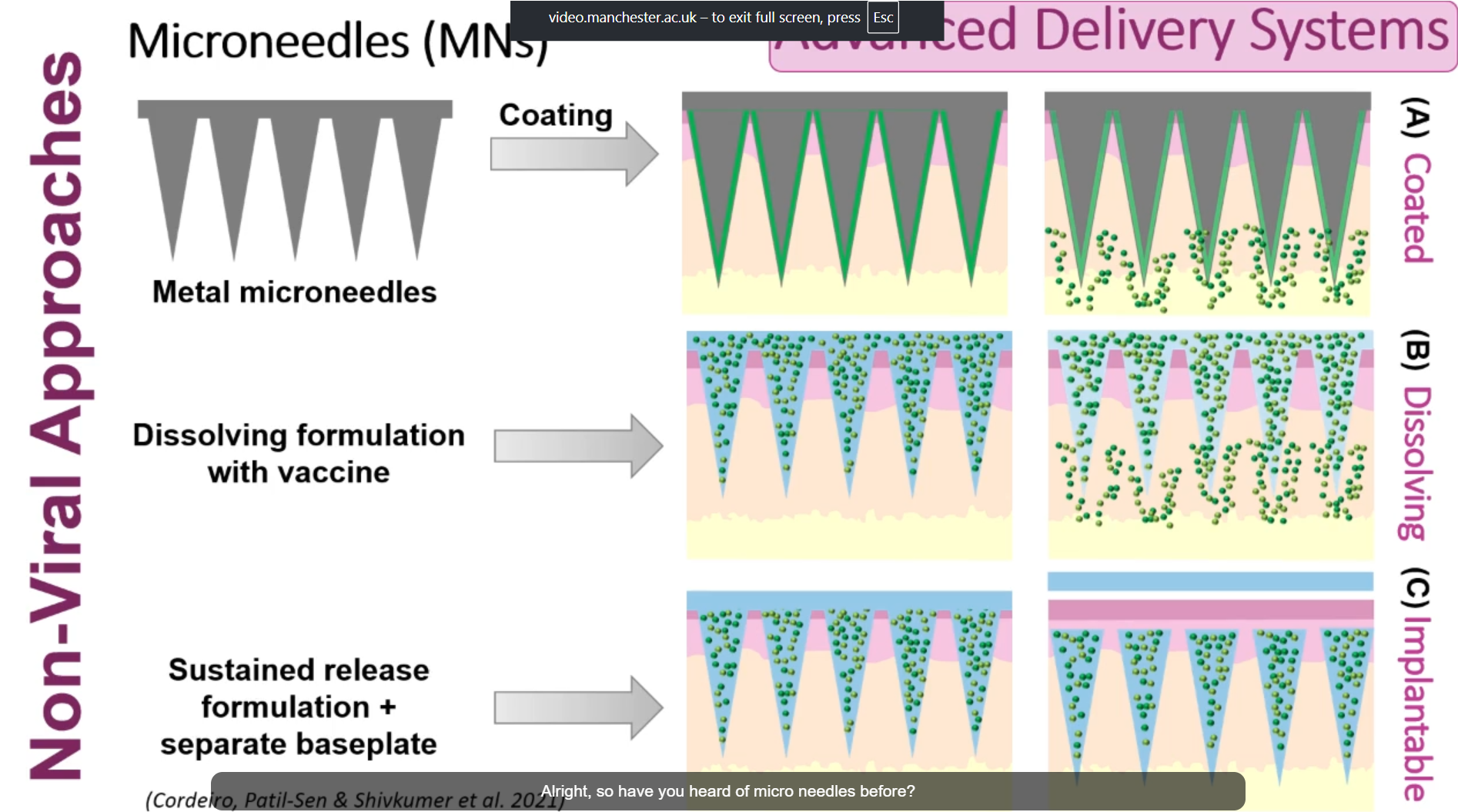
what are the different types of microneedles
Metal (coating)
dissolving formulation with vaccine
sustained release formulation + separate baseplate
describe formation of hydrogels and advantages
Hydrophilic polymers will entangle to form a net in water resulting in gel formation
Biocompatible and degradable because 85% water
Viscous but sheer thinning so injectable
Mucoadhesive so can be delivered though Musco nasal route
Very amenable systems
Not in market currently under research
what is electroporation and why is it needed?
DNA not easily up taken by cells, exposing cells to short high voltage pulses (electroporation) temporarily disrupts cell membrane forming pores for a short period of time which allows DNA to enter cell