Art History Terminology Weeks 1-5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
iconography
from Greek “writing of images” refers to the content/subject of a price of artwork and includes, symbolic, often religious, the meaning of objects, persons, or events depicted in art
2
New cards
formal analysis
Analysing an object’s shape, form, and structure, can include composition, material, technique, line, color, and texture, but NOT what is depicted/context
3
New cards
provenance
History of Ownership
4
New cards
objective dating technique
A technique that can help clarify the actual age of an object. Absolute dating methods mainly include radiocarbon dating, dendrochronology, and thermoluminescence.
5
New cards
stylistic analysis
Analyzing an artwork in connection to other work from the artist and potentially the artist’s biographical information.
* ***Period Style-*** Refers to the characteristic manner of a specific time (ie. mannerisms)
* ***Regional Style-*** Describes changes in style connected to geography (ex. Italian Renaissance)
* ***Personal Style-*** Distinctive manner of individual artists or architects/designers.
* ***Period Style-*** Refers to the characteristic manner of a specific time (ie. mannerisms)
* ***Regional Style-*** Describes changes in style connected to geography (ex. Italian Renaissance)
* ***Personal Style-*** Distinctive manner of individual artists or architects/designers.
6
New cards
additive sculpture techniques
Adding substance to a medium (ex. adding clay)
7
New cards
subtractive sculpture techniques
Removing substance from a medium (chiseling, cutting, etc) (like risen and sunken reliefs)
8
New cards
composite view/twisted perspective
Convention of representing part of the figure in profile and another part of the same figure frontally
9
New cards
chthonian
of or relating to Earth mother goddess images, ex. Woman of Willendorf figurine
10
New cards
shamanism
Practice involving a shaman, a “seer” or wizened one, who metaphorically dies or is transformed so as to be able to journey to another world, the true primordial world, where illnesses can be fixed, catastrophes avoided, animals or other humans placated, people cured.
Jean Clottes (1990s) – adds the shamanism piece to explain a minority of human hybrid
images in the caves
Jean Clottes (1990s) – adds the shamanism piece to explain a minority of human hybrid
images in the caves
11
New cards
henge
An arrangement of megalithic stones in a circle, often surrounded by a ditch.
12
New cards
megalithic
adj. from the Greek for "great stone," meaning of large, roughly hewn stone, especially in prehistoric construction
13
New cards
post-and-lintel construction
two uprights supporting a spanning element
14
New cards
tenise and morten joint
mortise hole into which a tenise tongue fits snuggly
15
New cards
corbelling
vault formed by the piling of stone blocks in horizontal courses cantilevered inward until the walls make an arch
16
New cards
Cave in Alta Mira, Spain
c. 12,000 BCE - Bison paintings
17
New cards
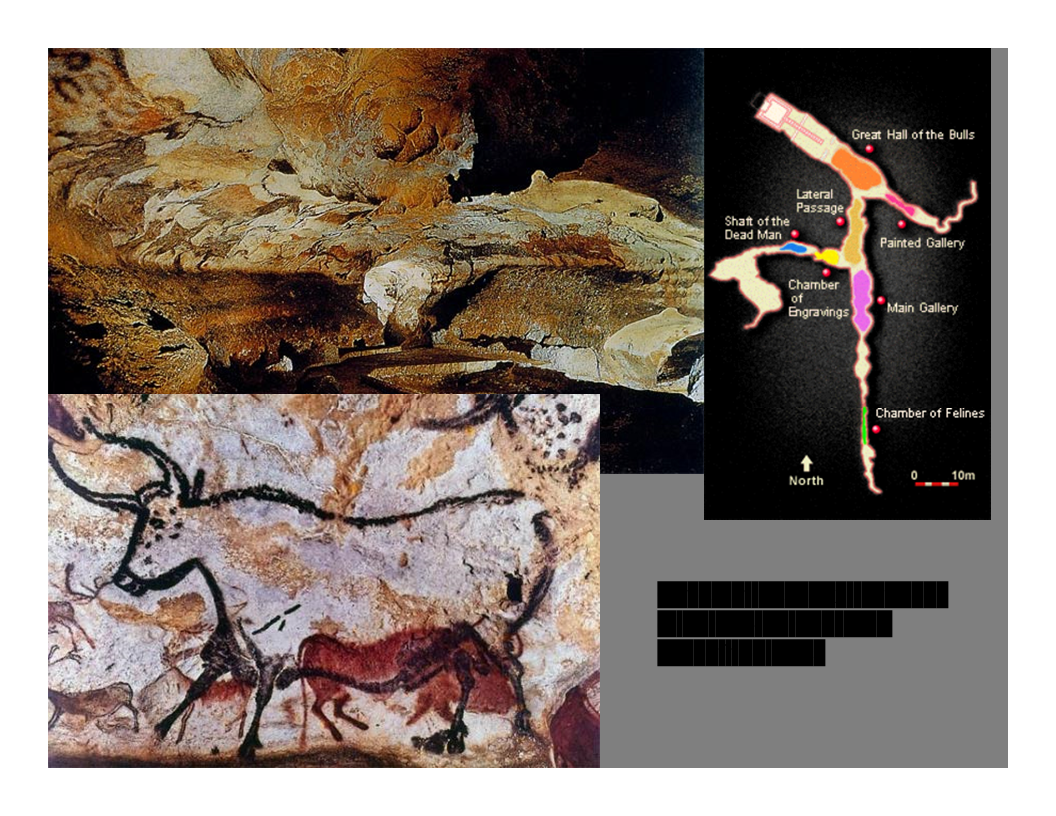
Caves at Lascaux, France
15,000-13,000 BCE - Hall of the Bulls: Bull and Red Ox
\
Annette Laming-Emperaire (1950) – minute observations about groupings, animals, gender,
human handprints to suggest interpreting horses, bisons, and women, as prehistoric
symbols of perhaps calm, peace, or harmony.
\
Annette Laming-Emperaire (1950) – minute observations about groupings, animals, gender,
human handprints to suggest interpreting horses, bisons, and women, as prehistoric
symbols of perhaps calm, peace, or harmony.
18
New cards

Cave at Pech-Merle, France
c. 22,000 BCE - Spotted horses and negative hand prints
19
New cards
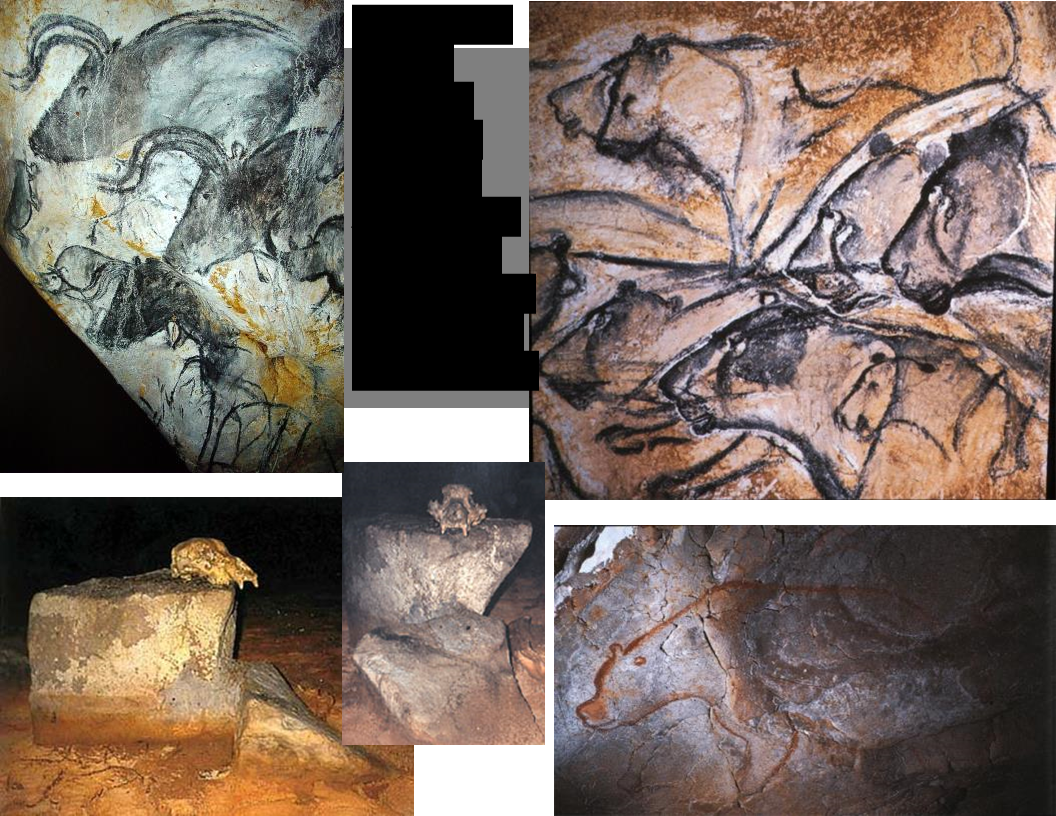

Cave at Chauvet, France
c. 28,000 BC - Aurochs and Rhinoceros Predator Cats Hall of Bears
\
SolomonReinach (1909) – sympathetic magic/hunting & Abbie Henri Breuil (1920) – sites of
religious worship/initiation
\
SolomonReinach (1909) – sympathetic magic/hunting & Abbie Henri Breuil (1920) – sites of
religious worship/initiation
20
New cards
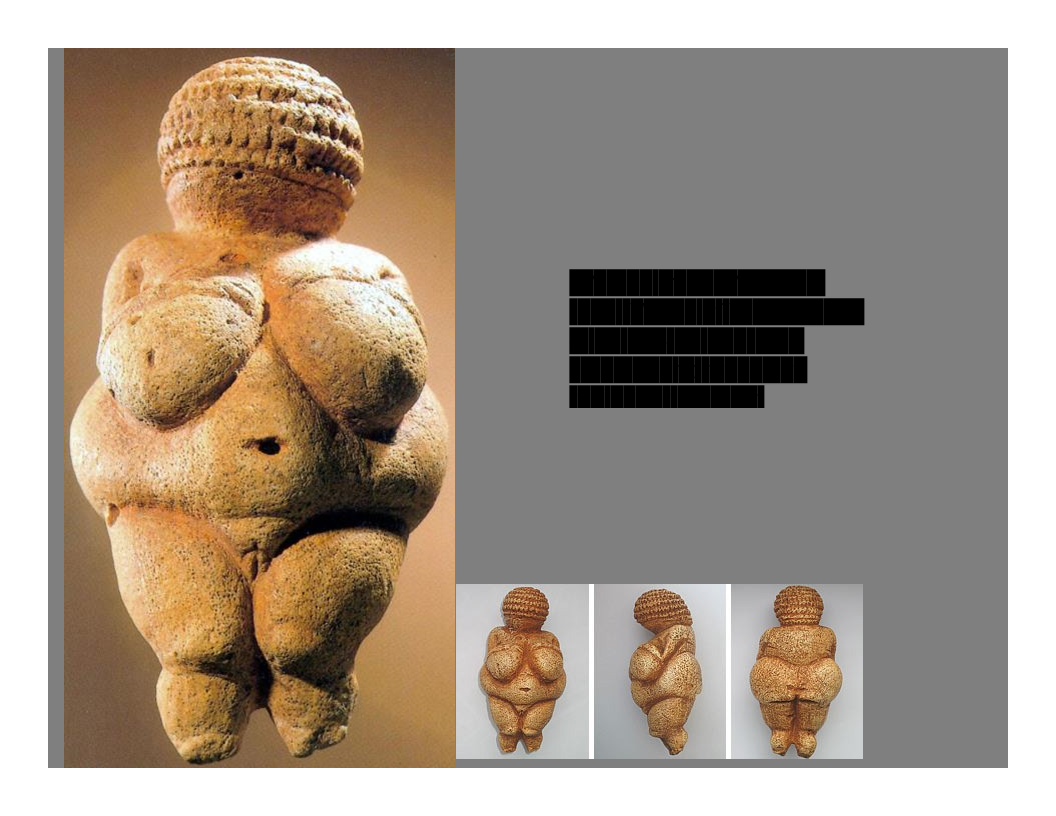

Woman from Willendorf (aka “Venus of Willendorf”),
c. 28,000-25,000 BCE
limestone w/ traces of red ocher pigment
limestone w/ traces of red ocher pigment
21
New cards

Caves at Lascaux, France, c. 15,000-13,000 BCE
Shaft of the Dead Man: Bird-Headed Man with Bison
22
New cards
Paleolithic
40,000-9,000 BCE
23
New cards
Mesolithic period
9,000-8,000 BCE
24
New cards
Neolithic period
8,000-2,300 BCE
25
New cards
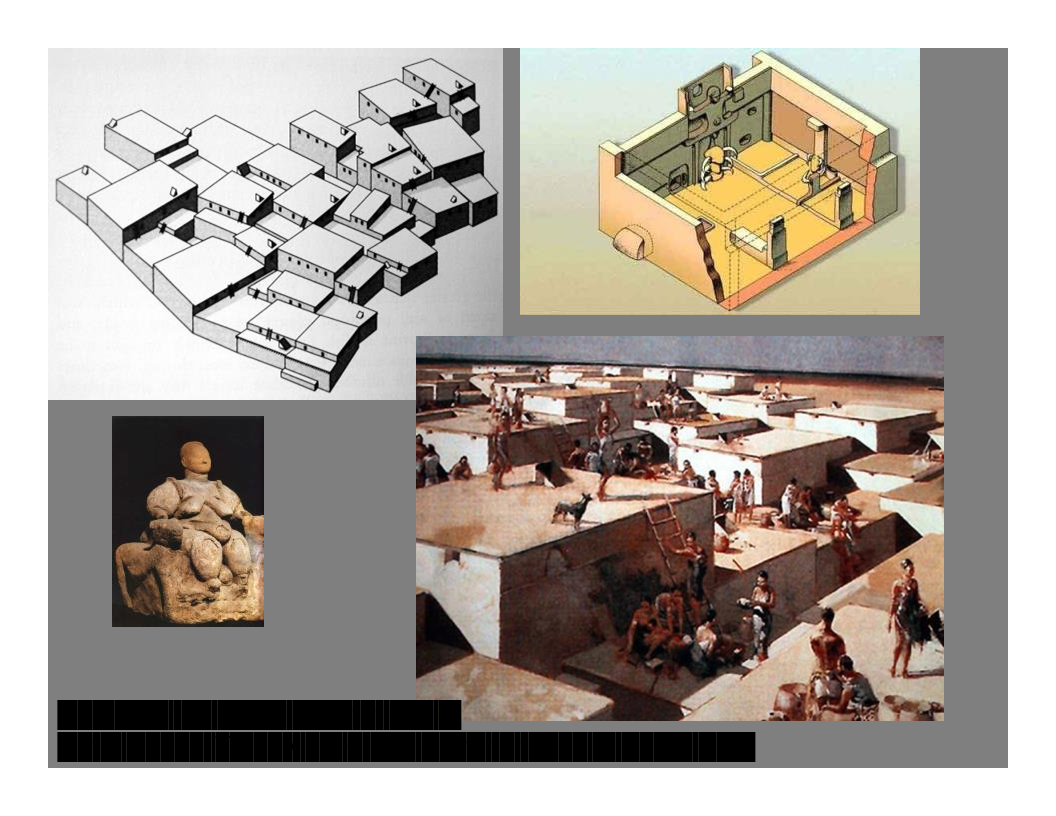

Çatal Höyük, Turkey
ca. 6,000 BC – average pop. 7,000-5,000 people
* Builds houses out of mudbrick, builds connecting outer walls for defensive skills.
* Had to enter house through ladder from roof
* Had domesticated doggos
* Builds houses out of mudbrick, builds connecting outer walls for defensive skills.
* Had to enter house through ladder from roof
* Had domesticated doggos
26
New cards

Skara Brae, Scotland
ca. 3,100 BC – average pop. 40-50 people
* Covered by sea storm, which preserved it until later sea storm in the 1800s uncovered it
* urbanism grows and profits from defense (in this case from the elements)
* A fired iron bar for protection
* Fishing society
* Corbelling- vault formed by the piling of stone blocks in horizontal courses cantilevered inward until the walls make an arch
* Covered by sea storm, which preserved it until later sea storm in the 1800s uncovered it
* urbanism grows and profits from defense (in this case from the elements)
* A fired iron bar for protection
* Fishing society
* Corbelling- vault formed by the piling of stone blocks in horizontal courses cantilevered inward until the walls make an arch
27
New cards

Stonehenge
Salisbury Plain, England, c. 2550-1600 BCE
* 2550- BCE potentially began in 31,000 BCE in a circle. The structure came along a few hundred years later
* Alignment of Heel Stone with the summer solstice- Sun rises over the heel stone
* 2550- BCE potentially began in 31,000 BCE in a circle. The structure came along a few hundred years later
* Alignment of Heel Stone with the summer solstice- Sun rises over the heel stone
28
New cards
ziggurat
A monumental platform for a temple (in mesopotamian architecture)
29
New cards
Stele (pl. stelae)
a carved stone slab used to mark graves or commemorate historical events
30
New cards
Hierarchy of scale
artistic convention in which greater size = greater importance
31
New cards
registers/friezes
bands of a pictorial narrative, or the particular levels on which motifs are placed
32
New cards
relief carving
figures carved to project from a background of which they are part
33
New cards
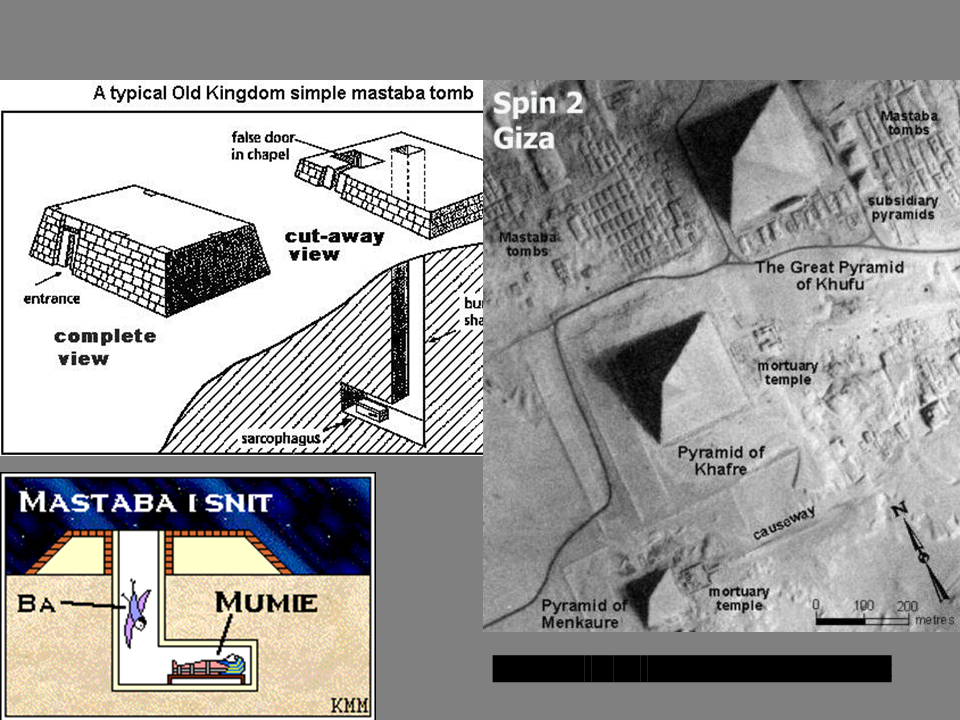
mastaba
Arabic for “bench”; a rectangular structure with sloping sides erected over a subterranean tomb and connected to the outside with a shaft
34
New cards
ka
Ka— Life force, must have a body to occupy even after death, soul?
35
New cards
Akhenaton & changes to Egyptian belief, artistic conventions, and the royal court
* renames himself Akhenaton “One who is effective on behalf of Aton”
* Amarna or Aketatan- City
* Husband of Nefertiti
* More stylistic representation than before- changed proportions,
* Steele- Familial scene in an unfamiliar way. stylized hands from Aton the Sun God
* Double-jointed fingers in art stick around after his rule
* Amarna or Aketatan- City
* Husband of Nefertiti
* More stylistic representation than before- changed proportions,
* Steele- Familial scene in an unfamiliar way. stylized hands from Aton the Sun God
* Double-jointed fingers in art stick around after his rule
36
New cards
Minoan (King Minos)
Minoan Culture— Crete
37
New cards
labyrinth
a complicated irregular network of passages or paths in which it is difficult to find one's way; a maze.
Greek myth potentially based on a network of storage rooms underneath palace
Greek myth potentially based on a network of storage rooms underneath palace
38
New cards
minotaur
half-man half-bull
39
New cards
fresco
a painting done rapidly in watercolor on wet plaster on a wall or ceiling, so that the colors penetrate the plaster and become fixed as it dries.
40
New cards
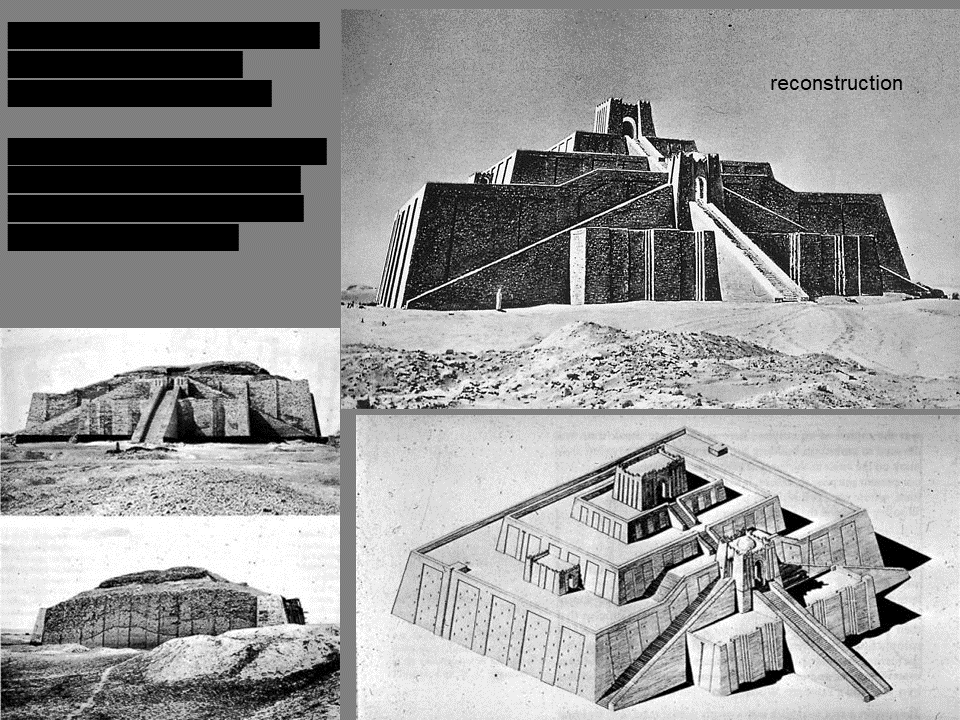
Ziggurat at Ur (modern Iraq)
ca. 2100 BCE Sumerian
* tiered structure, built of mudbrick. Temple at the top, waiting room for the gods.
* Built it high to avoid flooding from rivers
* Mentioned in the Epic of Gilgamesh
* tiered structure, built of mudbrick. Temple at the top, waiting room for the gods.
* Built it high to avoid flooding from rivers
* Mentioned in the Epic of Gilgamesh
41
New cards
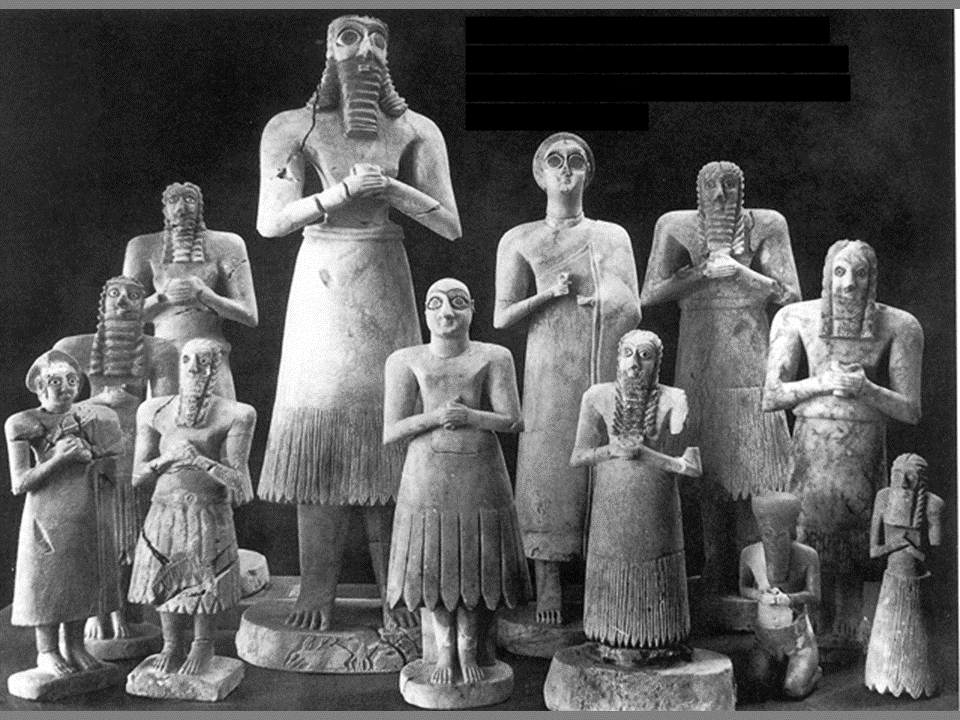

Statuettes from Square Temple at Eshnunna (modern Iraq)
2700 BCE Sumerian
* Placed in temples so individuals can communicate with Gods
* Most hold either an offering bowl or a scroll
* Wide Eyes— artistic convention, attendant to the Gods was meant to stay alert forever
* Men have fringed skirts, women have simple dresses
* Made either of a dark stone or lapis lazuli
* Placed in temples so individuals can communicate with Gods
* Most hold either an offering bowl or a scroll
* Wide Eyes— artistic convention, attendant to the Gods was meant to stay alert forever
* Men have fringed skirts, women have simple dresses
* Made either of a dark stone or lapis lazuli
42
New cards
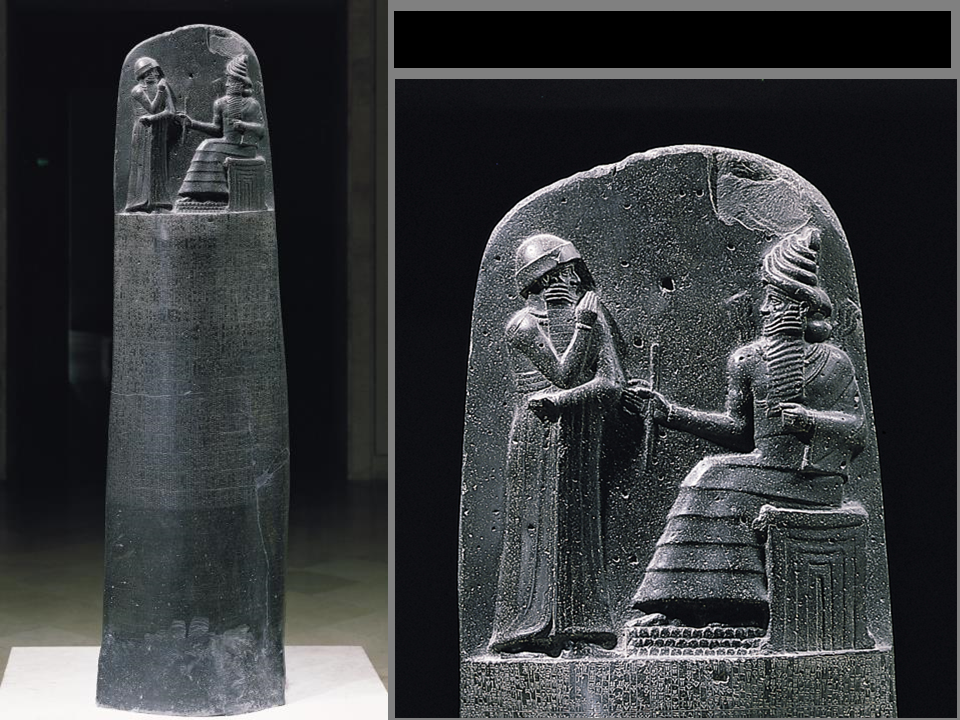

*Stele of Hammurabi*
7'4" tall, basalt, c. 1780 BCE Babylonian Egypt: Pre-Dynastic - only the palette of Narmer (ca. 3000 BCE)
* cuneiform law code
* Contains the Code of Hammurabi
* Hammurabi is the figure standing, having an audience with the seated Sun God
* Two basic types of law found that we still have: retribution & restitution
* cuneiform law code
* Contains the Code of Hammurabi
* Hammurabi is the figure standing, having an audience with the seated Sun God
* Two basic types of law found that we still have: retribution & restitution
43
New cards

*Palette of King Narmer*
ca. 3000-2920 BCE (slate)
* Used for Eye-makeup but not for human scale
* Raised Relief
* Hierarchy of Scale— King Narmer is in the center, bigger than all the other figures We know it’s Narmer because it’s actually labeled
* Used for Eye-makeup but not for human scale
* Raised Relief
* Hierarchy of Scale— King Narmer is in the center, bigger than all the other figures We know it’s Narmer because it’s actually labeled
44
New cards

The Great Pyramids
(from left: Menkaure - smallest; Khafre - w/ cap; and Khufu-
largest), Giza, ca. 2551-2472 BCE
* Pyramid accomplished during the Old Kingdom
* Built by peasant workers or seasonal laborers but not slaves
* Built using ramps, rope, clay water
* Every block in the Khufu pyramid is cracked but it is still standing
* **Khufu’s Pyramid=** largest of the great pyramids, know the specifics of size and construction
* difference between smaller and longer sides is seven inches, >400’ tall
* Elaborate anti-theft protocols
* Workers who sealed it needed to dig until a tunnel below was reached
* diverted stress from pressure to allow for the pharaoh's chamber to not collapse
* all about the long-term/ afterlife
* ***Khafre’s Pyramid-*** Cap is what remains of the pyramids of Giza’s polished, white limestone casing.
* Sphynx is in front of it in the causeway— smaller than Khufu
* Statues still remain
largest), Giza, ca. 2551-2472 BCE
* Pyramid accomplished during the Old Kingdom
* Built by peasant workers or seasonal laborers but not slaves
* Built using ramps, rope, clay water
* Every block in the Khufu pyramid is cracked but it is still standing
* **Khufu’s Pyramid=** largest of the great pyramids, know the specifics of size and construction
* difference between smaller and longer sides is seven inches, >400’ tall
* Elaborate anti-theft protocols
* Workers who sealed it needed to dig until a tunnel below was reached
* diverted stress from pressure to allow for the pharaoh's chamber to not collapse
* all about the long-term/ afterlife
* ***Khafre’s Pyramid-*** Cap is what remains of the pyramids of Giza’s polished, white limestone casing.
* Sphynx is in front of it in the causeway— smaller than Khufu
* Statues still remain
45
New cards
![*Khafre* \[ka statue; sculpture portrait\]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/476fc12f005048e993cc75f0ba7e7a4b.jpeg)
*Khafre* \[ka statue; sculpture portrait\]
from Giza, ca. 2500 BCE, blueish diorite stone
* ***Kafre*** \[*ka*. statue: sculpture portrait\] from Giza, ca. 2500 BCE, blueish diorite stone
* Only one can see blue in Sunlight, blue is associated with Horus
* Stone imported from Nubia
* The throne has relief sculptures of plants from Upper & Lower Egypt
* Horus watching the back of his head
* ***Kafre*** \[*ka*. statue: sculpture portrait\] from Giza, ca. 2500 BCE, blueish diorite stone
* Only one can see blue in Sunlight, blue is associated with Horus
* Stone imported from Nubia
* The throne has relief sculptures of plants from Upper & Lower Egypt
* Horus watching the back of his head
46
New cards
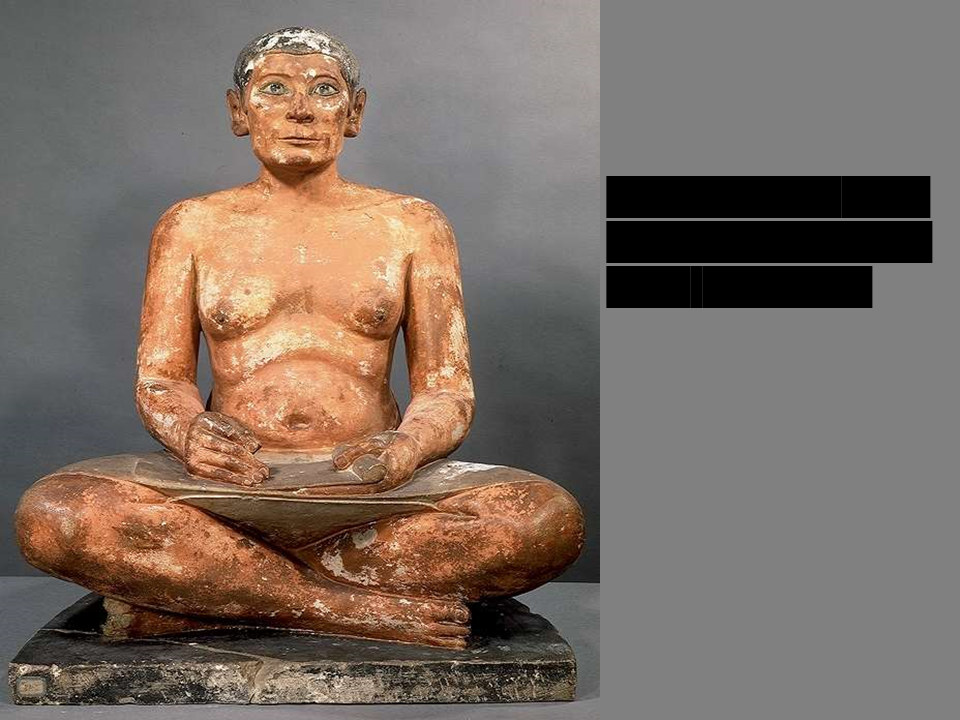

*Seated Scribe*
Old Kingdom, Giza, ca. 2575-2450 BCE
* painted limestone, less idealized than sculptures of kings.
* More realistic eyes, body rolls
* The lower you were socially, the more naturalistic your portrait was
* Hands were made close to the body / not holding anything to avoid hands breaking off from grave robbers
* painted limestone, less idealized than sculptures of kings.
* More realistic eyes, body rolls
* The lower you were socially, the more naturalistic your portrait was
* Hands were made close to the body / not holding anything to avoid hands breaking off from grave robbers
47
New cards

*Stele with Akhenaton, Nefertiti, and three daughters*
New Kingdom from Amarna, ca. 1340 BCE
* More stylistic representation than before- changed proportions,
* Steele- Familial scene in an unfamiliar way. stylized hands from Aton the Sun God
* Double-jointed fingers in art stick around after his rule
* Aton reaching out with hands
* More stylistic representation than before- changed proportions,
* Steele- Familial scene in an unfamiliar way. stylized hands from Aton the Sun God
* Double-jointed fingers in art stick around after his rule
* Aton reaching out with hands
48
New cards
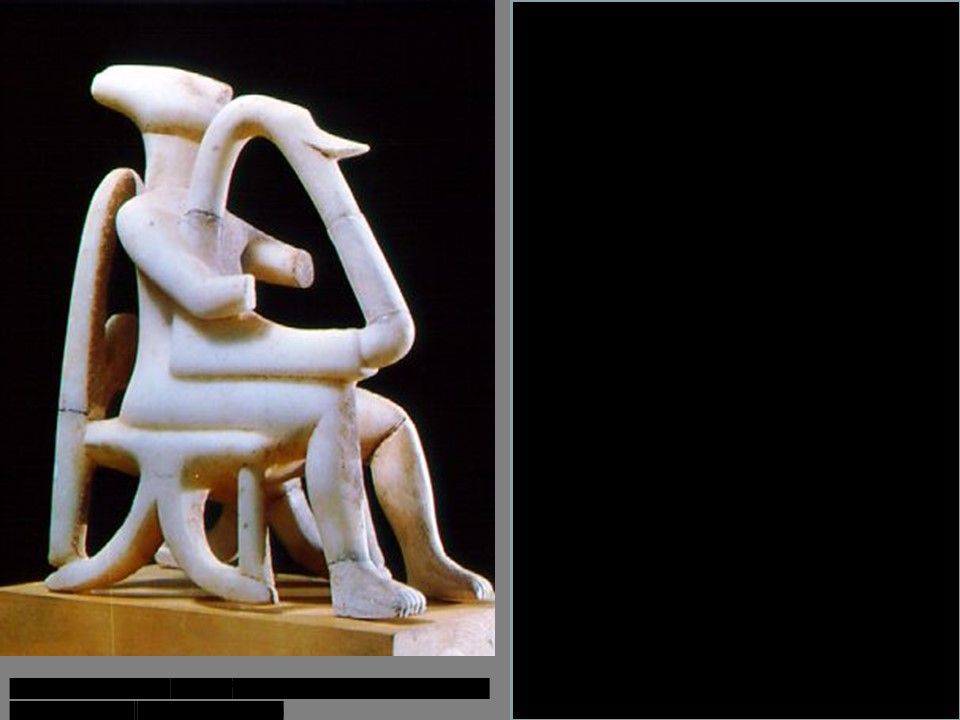

Cycladic sculpture, *Harpist (no hands)*
c. 2400 BCE, Athens, National Archaeological
49
New cards
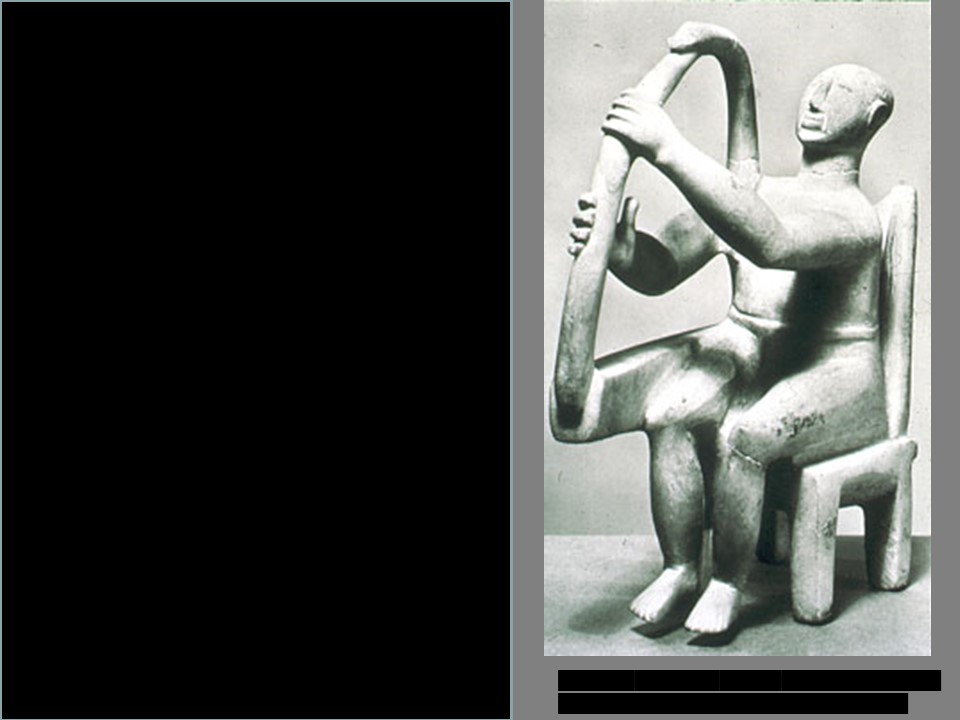

Cycladic sculpture, *Harpist*
c. 2400 BCE, New York, Metropolitan Museum of Art (marble)
50
New cards
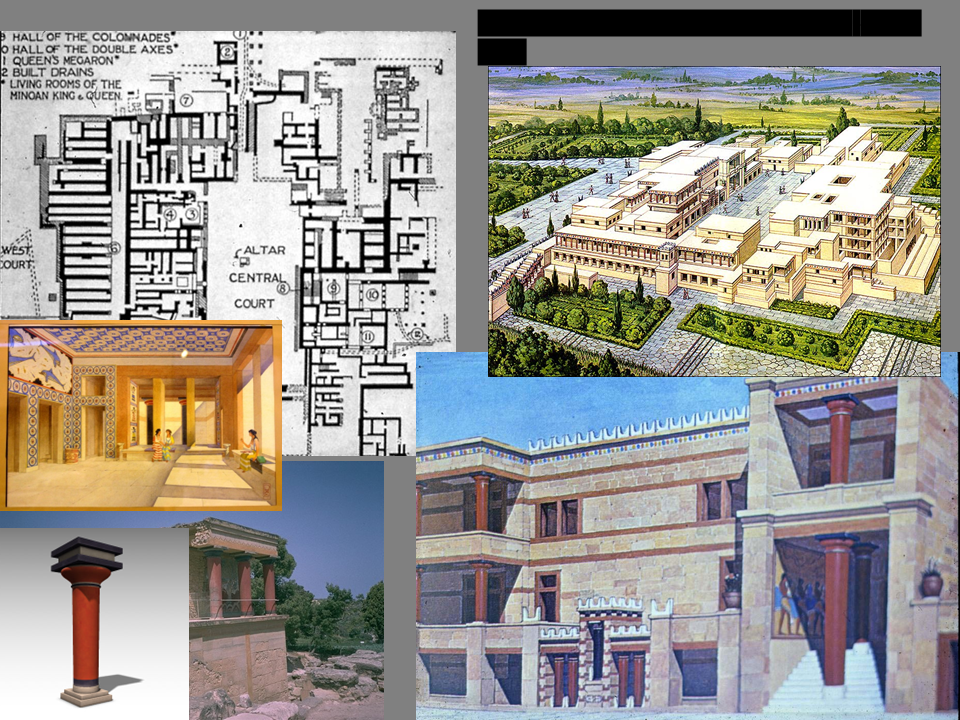
Palace of Knossos, Crete
ca. 1700-1400 BCE
* Excavated during the 1900s (or 19th century)
* Women, Bulls, and Minoan Civilization,
* Network of storage rooms underneath palace— connected through literature by the MINOTAUR!!!!
* Castle has a lack of defensive structure, the defense were ships on the sea
* The danger was from fire or Earthquakes
* Excavated during the 1900s (or 19th century)
* Women, Bulls, and Minoan Civilization,
* Network of storage rooms underneath palace— connected through literature by the MINOTAUR!!!!
* Castle has a lack of defensive structure, the defense were ships on the sea
* The danger was from fire or Earthquakes
51
New cards
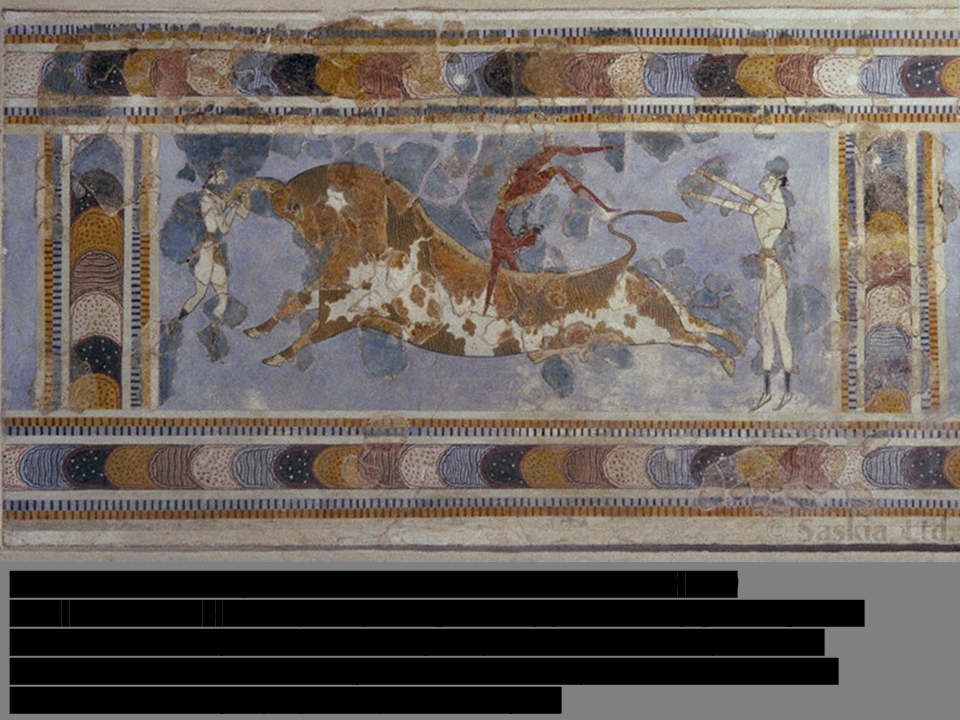

*Fresco of the Bull Leapers*, Palace of Knossos, Crete
ca. 1450-1400- buon / true fresco –
Artistic conventions represented males deep red and females white with black hair. Bull jumping in the palace courtyard.
Artistic conventions represented males deep red and females white with black hair. Bull jumping in the palace courtyard.
52
New cards

Geometric krater from the Dipylon cemetery,
Athens, ca. 740 BCE (Geometric)
53
New cards
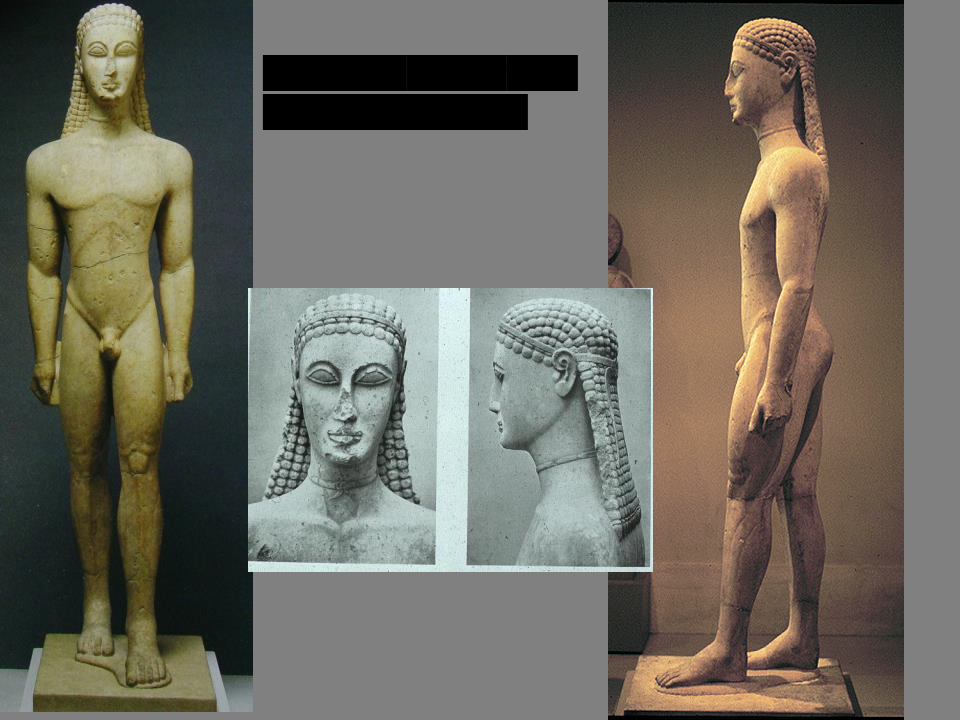

New York *Kouros*
ca. 600 BCE (Archaic)
54
New cards

*Doryphoros*
Polykleitos, ca. 450-440 BCE The ‘Canon’ of human proportion (High Classical), Roman copy in marble of the Bronze Greek original
55
New cards
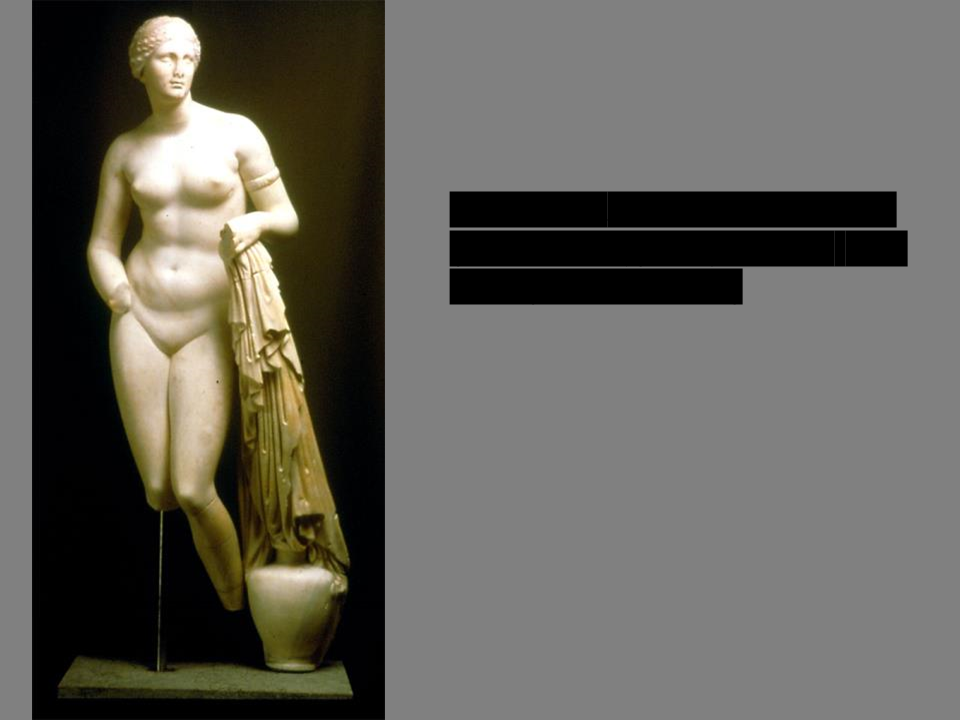

*Aphrodite of Knidos* (Roman copy)
Praxiteles, original 350-340 BCE (Late Classical)
56
New cards
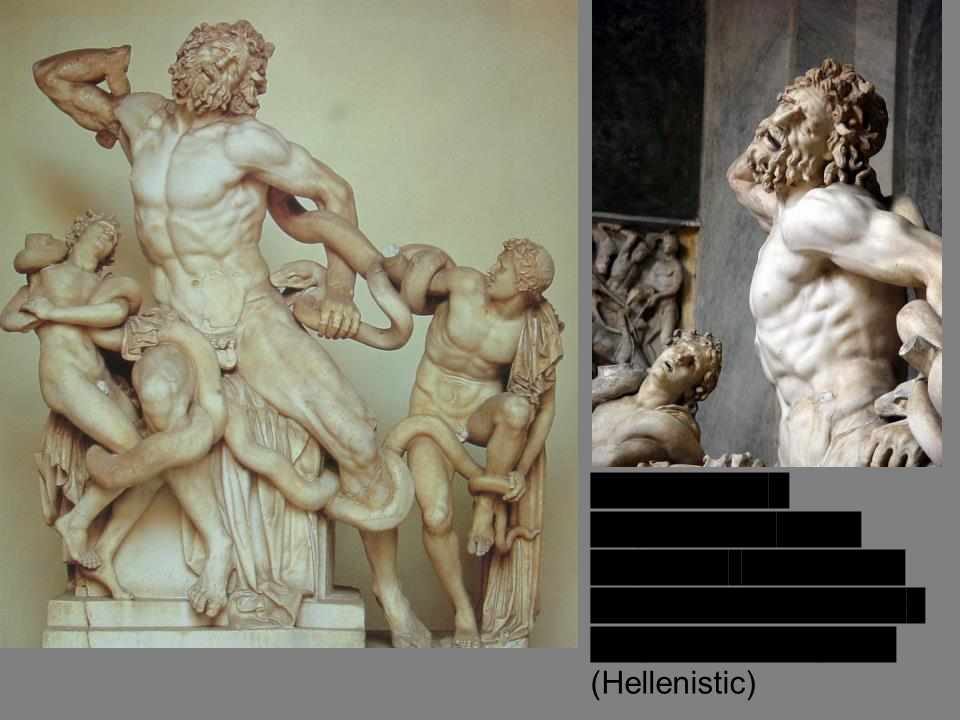

*Laocoön and his Sons*
Athanadoros, Hagesandros, and Polydoros of Rhodes, early first century CE (Hellenistic)
57
New cards
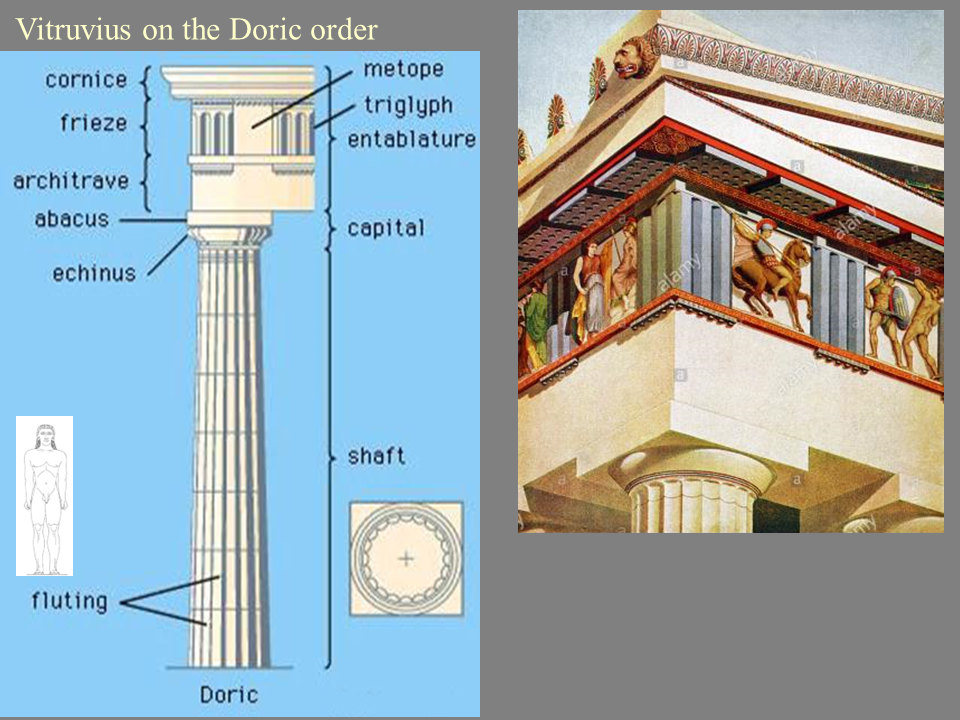
*entasis*
subtle adjustments/ optical refinements (swelling) that give beauty to a temple (i.e. Temple at Paestum or Parthenon)
58
New cards
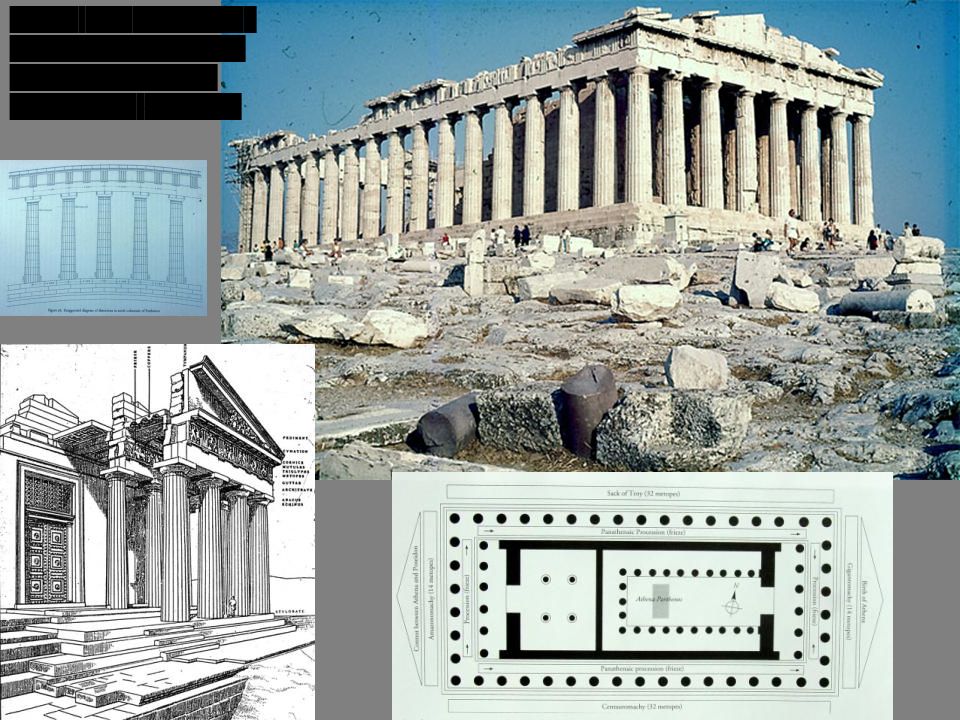
Parthenon (Temple of Athena)
Iktinos and Kallikrates, Acropolis, Athens, 447-438 BCE
Know who commissioned and with what funds; what is a sanctuary? Acropolis?
\
describe what the visual experience inside the Parthenon would have been like.
white marble approachable from all sides
Know who commissioned and with what funds; what is a sanctuary? Acropolis?
\
describe what the visual experience inside the Parthenon would have been like.
white marble approachable from all sides
59
New cards
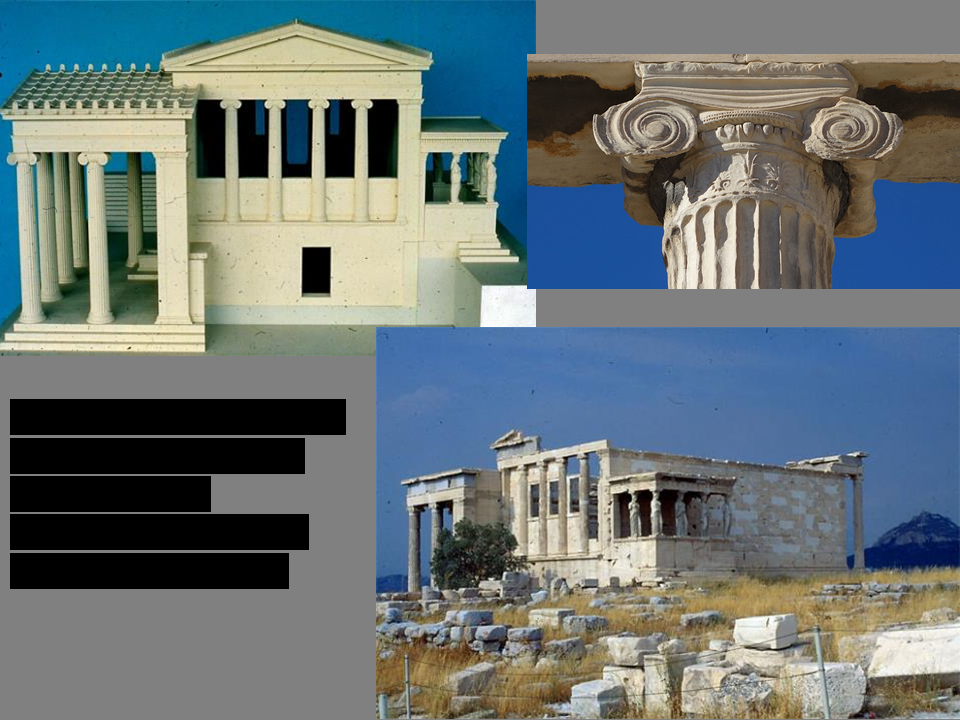

Erechtheion
Acropolis, Athens ca. 421-405 BCE (on the Erectheion: Caryatid Porch on the south)
60
New cards
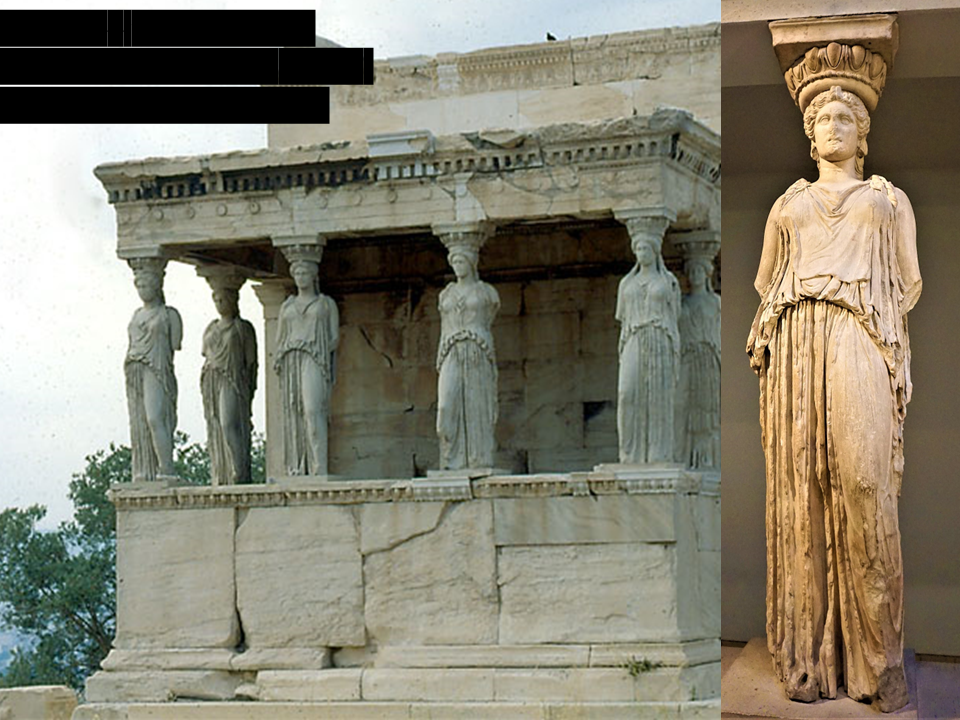

Caryatids
women of the Peloponnesian town of Karyai (prisoners of the Athenians)
61
New cards
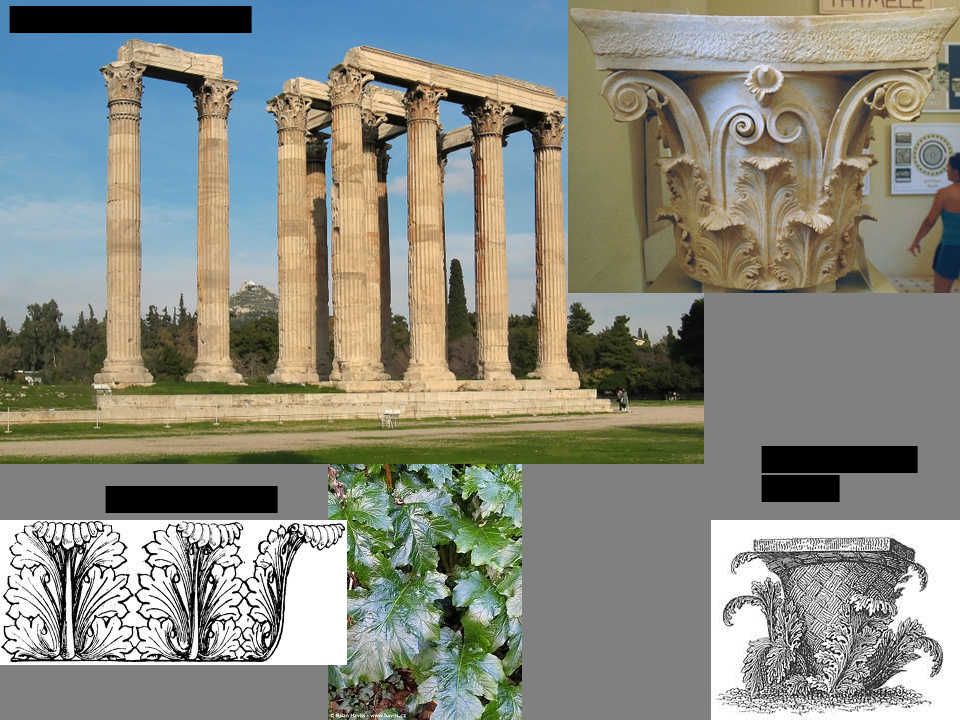

Corinthian order
62
New cards
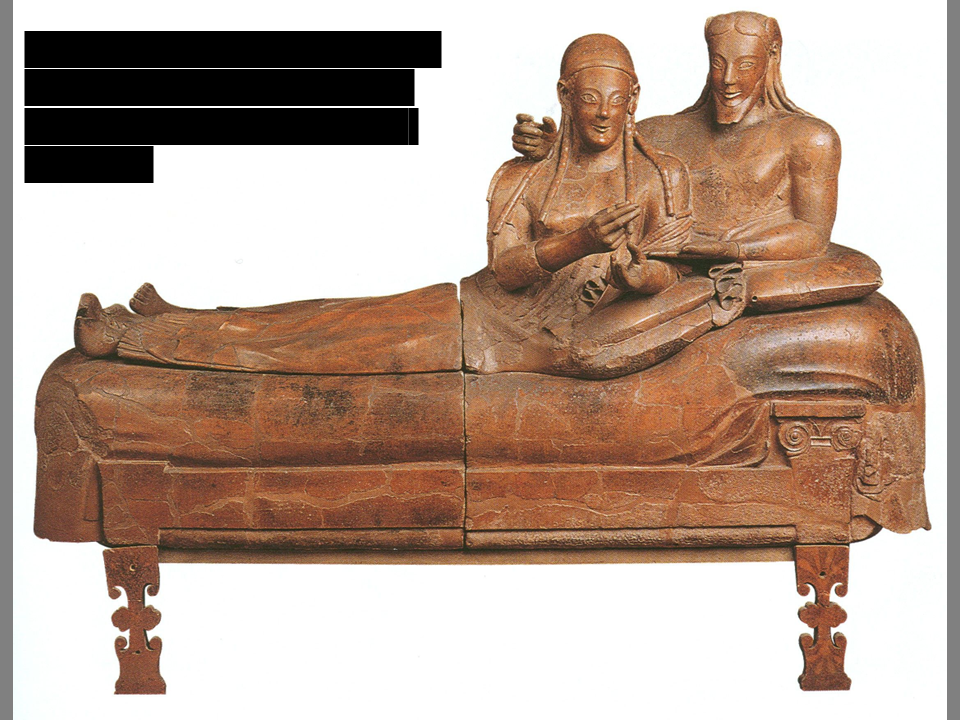

Sarcophagus w/ reclining couple
Painted terracotta (baked clay) Ca. 520 BCE Etruscan (ca750-
509 BCE)
509 BCE)
63
New cards
peripteral –
row of columns all around pedimental statues
*cella* in 2 parts algebraic ratio of proportions x=2y + 1
*cella* in 2 parts algebraic ratio of proportions x=2y + 1
64
New cards
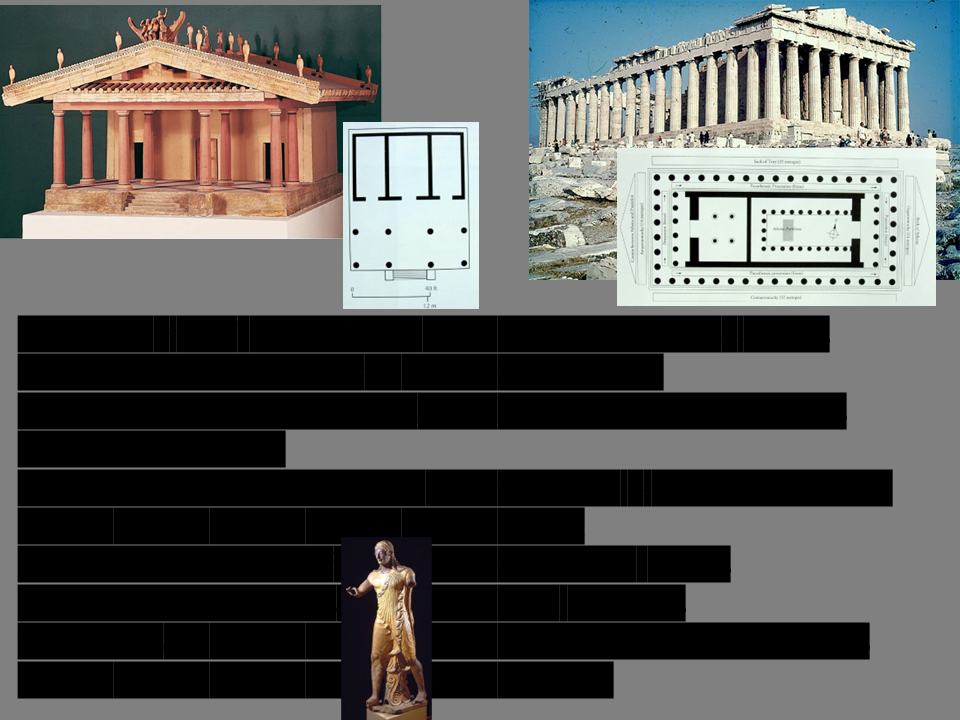
Etruscan 6th-century temple model
wood, sun dried brick, clay front entrance, columned porch one main side (front)
colonnade porch + exterior wall
colonnade porch + exterior wall
65
New cards
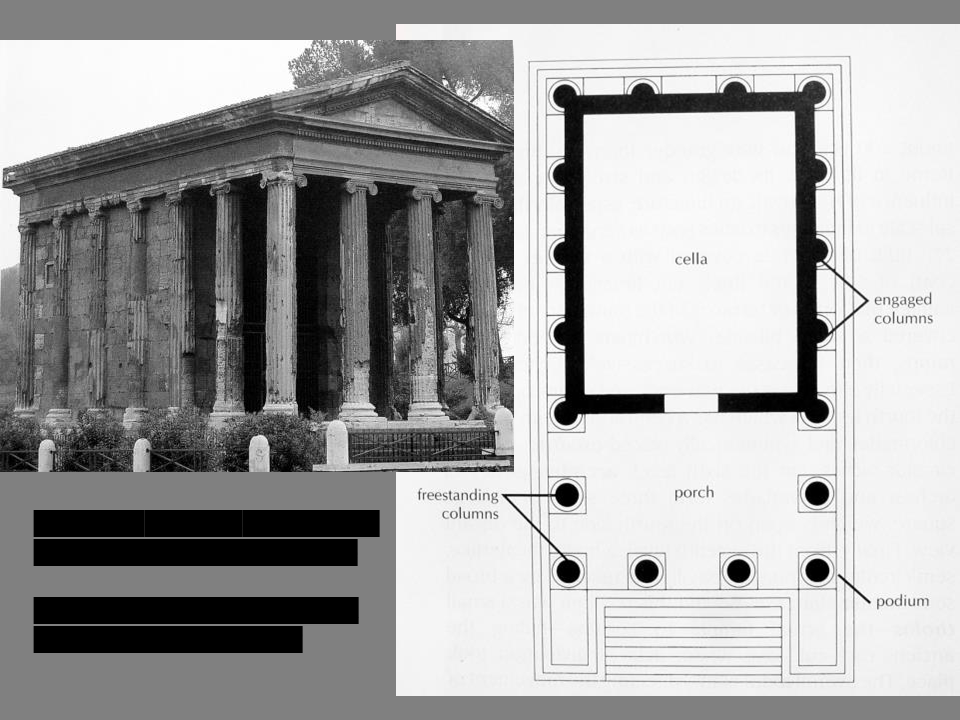
Temple of Portunus
Rome, Italy,
ca. 75 BCE Republican, Rome
\
What elements are Etruscan &
what are Greek inspired?
ca. 75 BCE Republican, Rome
\
What elements are Etruscan &
what are Greek inspired?
66
New cards
Veristic
(truthful) portraits of powerful Republican Roman men
67
New cards
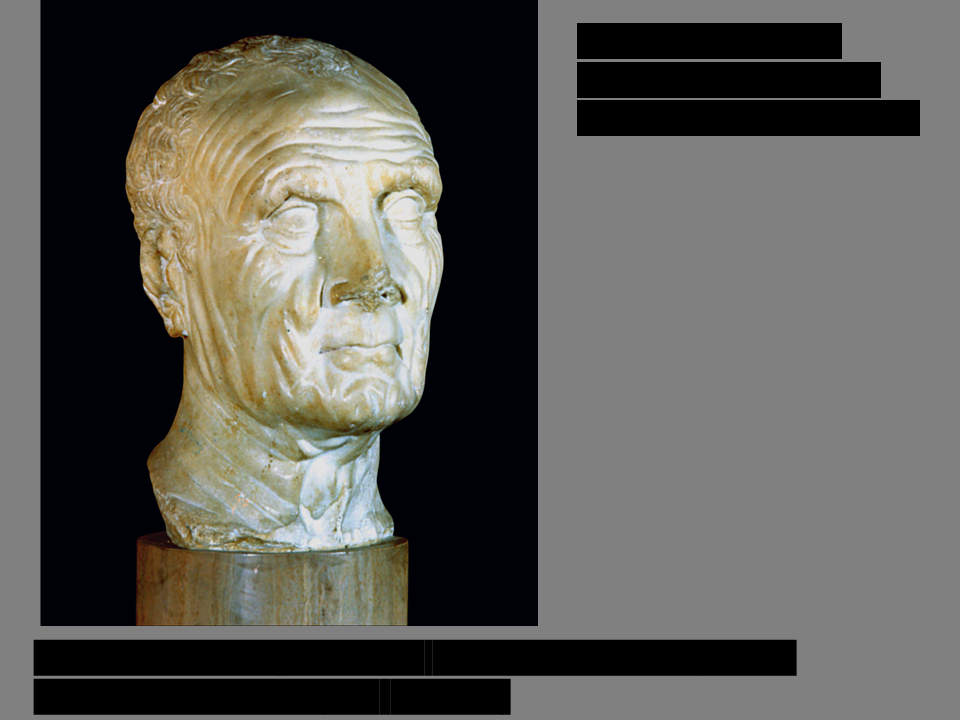

*Head of an elderly patrician*
marble, first century BCE, Roman Republican (509-27 BCE)
68
New cards

Portrait of Augustus Primaporta
10 CE
How is this a change from Veristic? How does it relate to political changes?
How is this a change from Veristic? How does it relate to political changes?
69
New cards
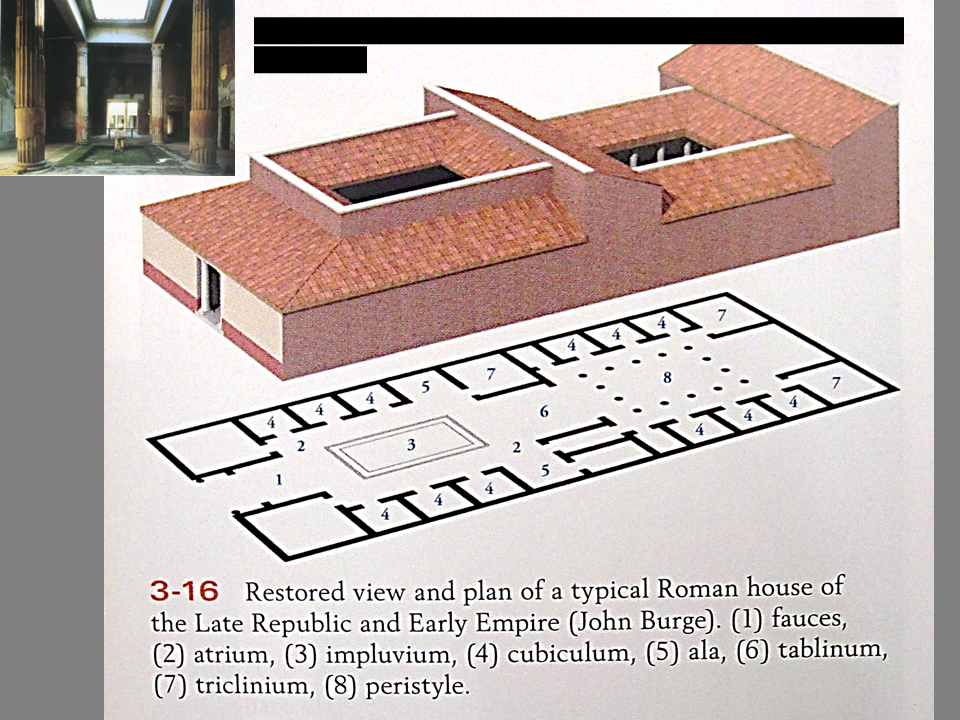
Describe the architecture & interior design of a Roman house at Pompeii
\
70
New cards
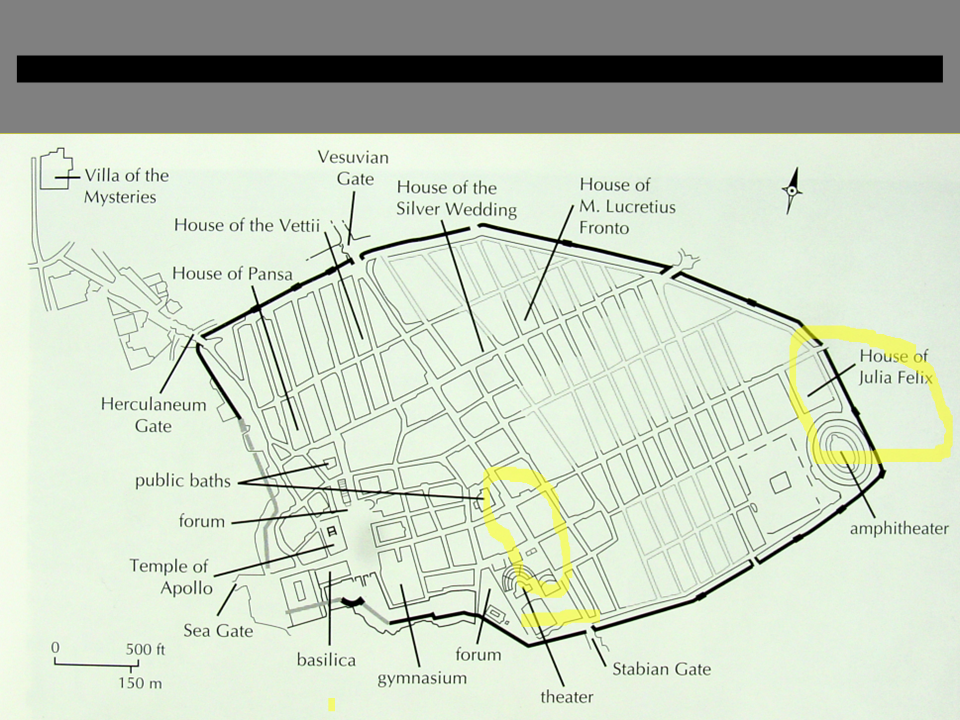
What does Pompeii tell us about Roman towns and what was in them (book & lecture)?
\
71
New cards
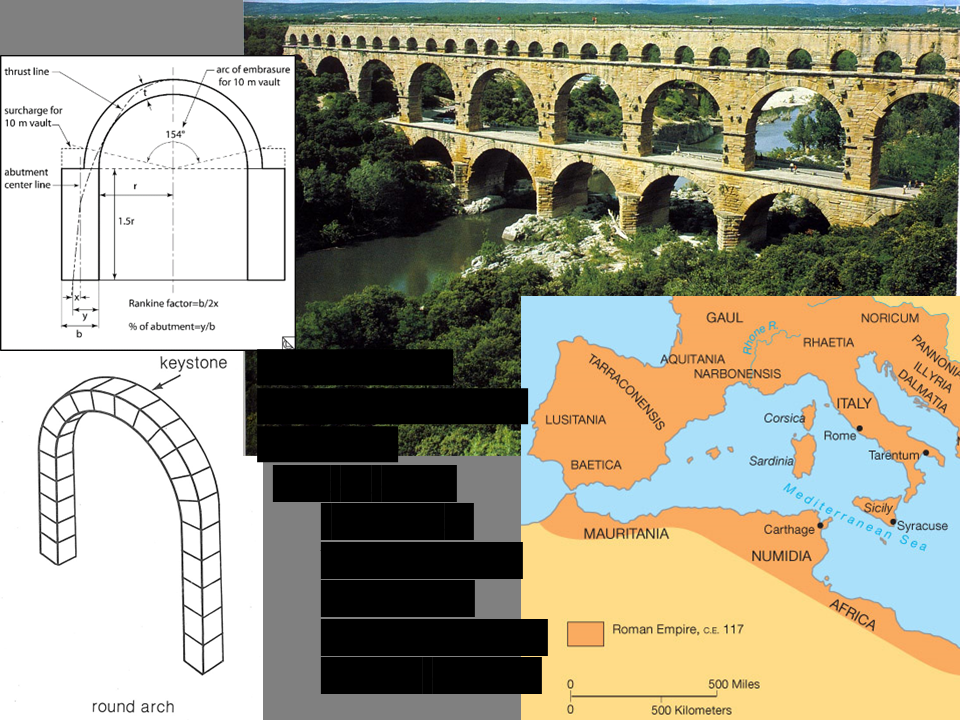
Pont-du-Gard (aquaduct),
Nimes, France, ca. 16 BCE (Roman Imperial 27 BCE-337 CE) In an arcade, where does lateral thrust go?
72
New cards

Colosseum
Rome, ca. 70-80 CE be able to write at length about this building’s purpose, materials, design, and function
73
New cards
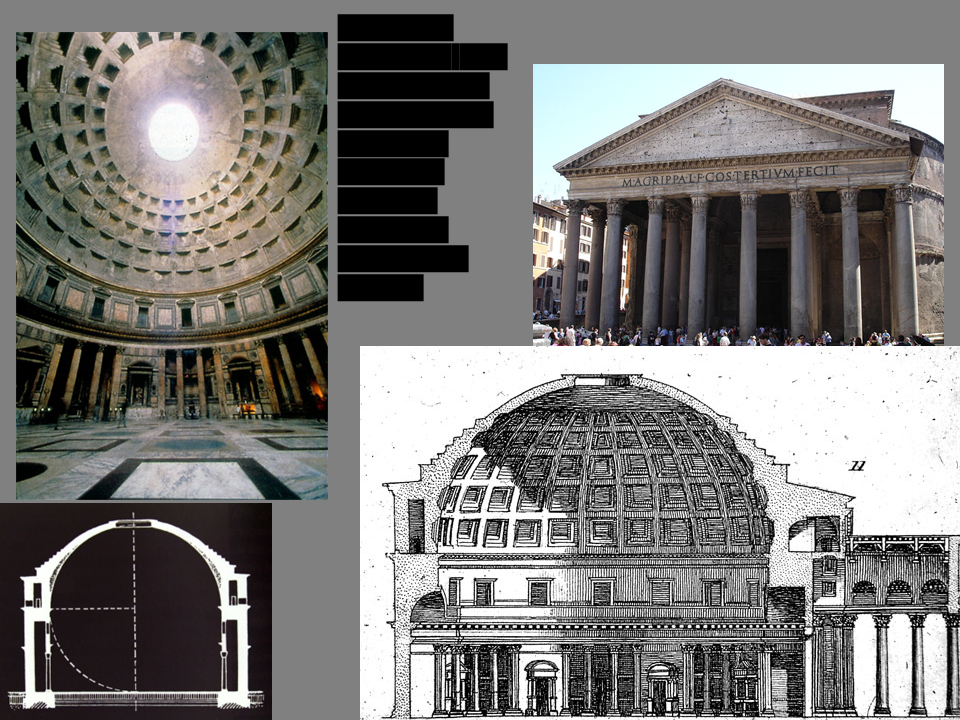
Pantheon
Rome, 118-125 CE be able to write at length about this building’s purpose, materials, design, and function
74
New cards
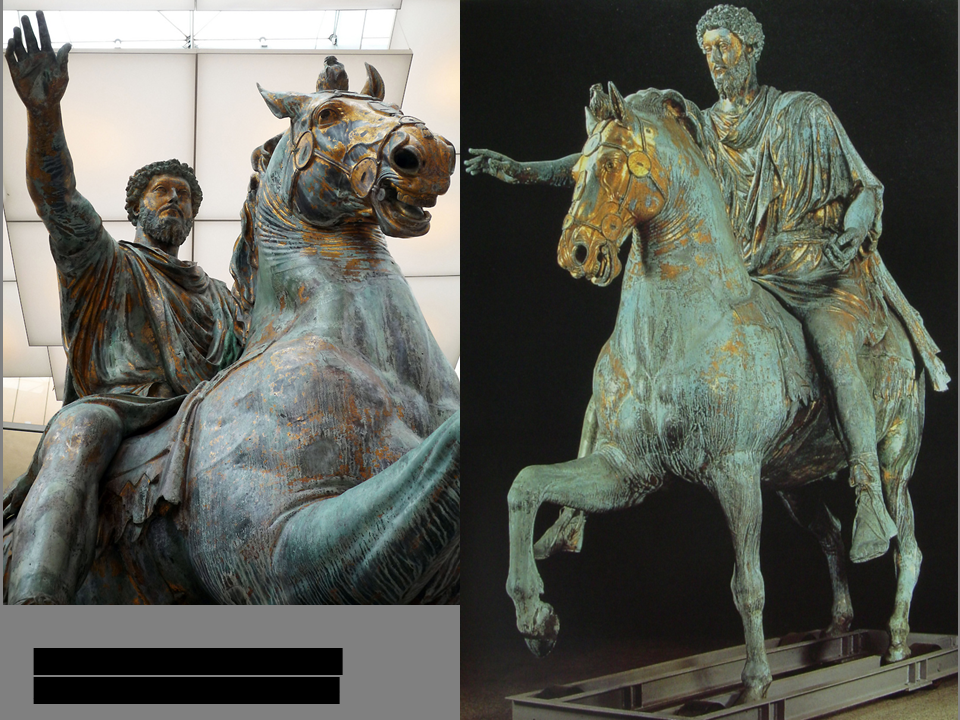

Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius
ca. 175 CE, bronze
75
New cards

Portraits of the four tetrarchs
from Constantinople, ca. 305 CE (Roman Imperial 27 BCE-337 CE), Porphyry, 4’3” What does this group portrait communicate politically and artistically?
76
New cards
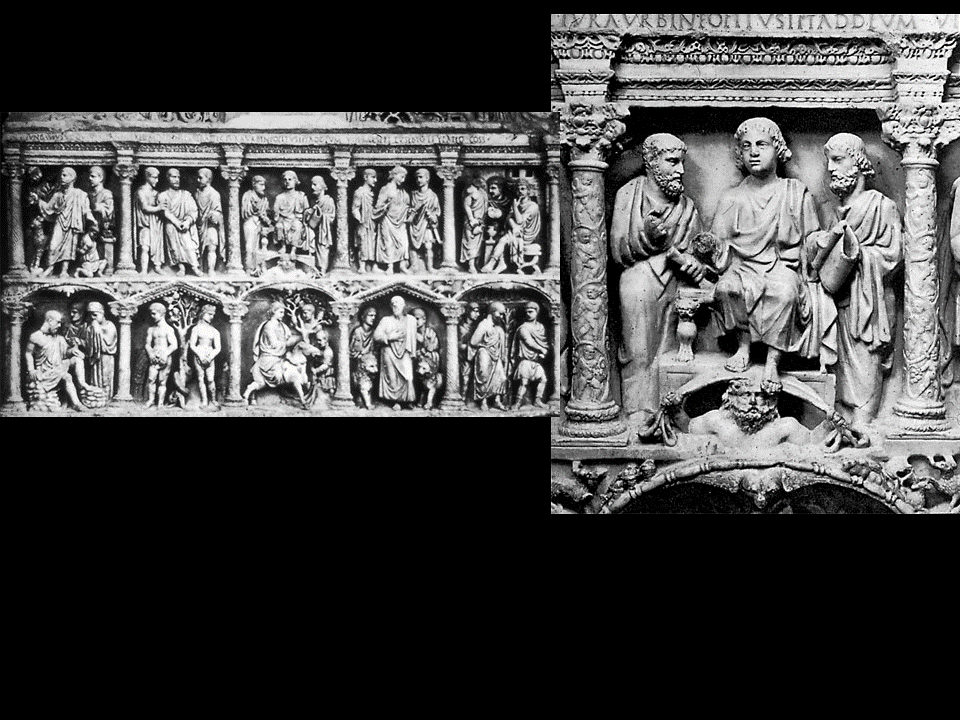

Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus
Rome, ca. 359
Detail: Hebrew scriptures,
Abraham’s sacrifice of Isaac
Detail: Hebrew scriptures,
Abraham’s sacrifice of Isaac
77
New cards
Syncretism
combining various religious elements; the appropriation (use in a different context) changes the meaning
78
New cards
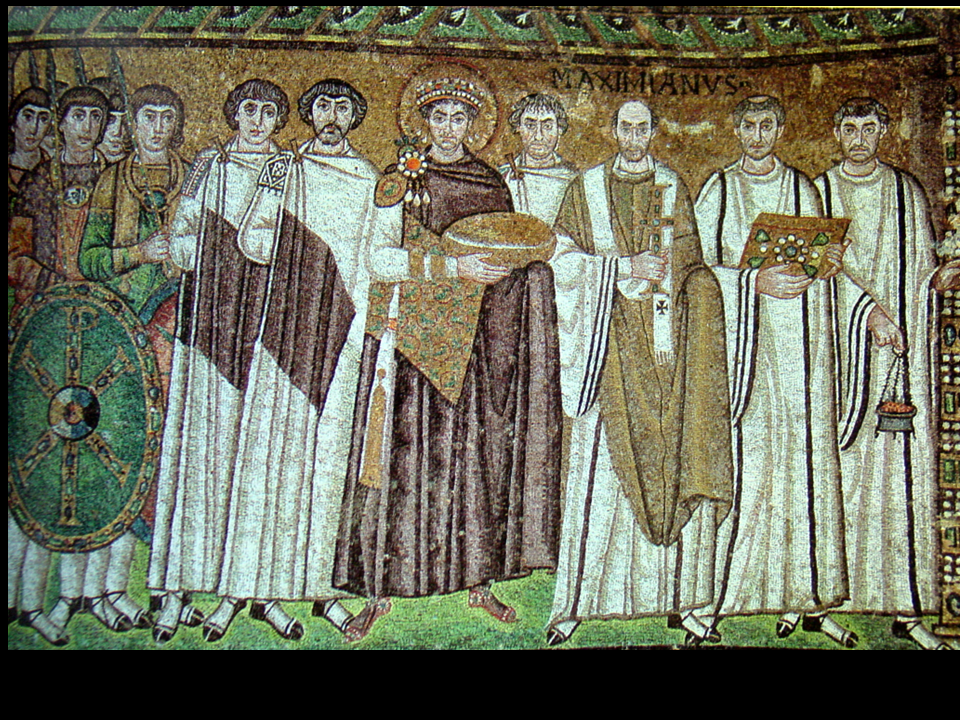

Court of Emperor Justinian of Byzantium w/ Bishop Maximianus
Ravenna, Italy, ca. 547: Mosaics from San Vitale
Court of Emperor Justinian of Byzantium w/ Bishop Maximianus
Court of Emperor Justinian of Byzantium w/ Bishop Maximianus
79
New cards
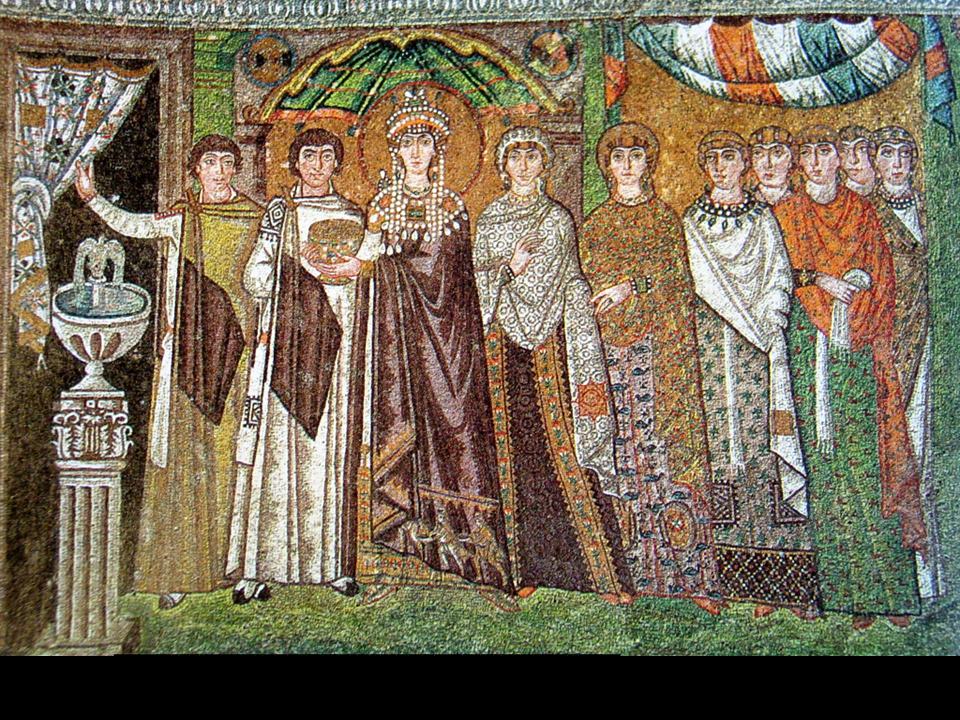

Court of Empress Theodora and her retinue
Mosaics from San Vitale, Ravenna, Italy, ca. 547:
Court of Empress Theodora and her retinue
Court of Empress Theodora and her retinue
80
New cards
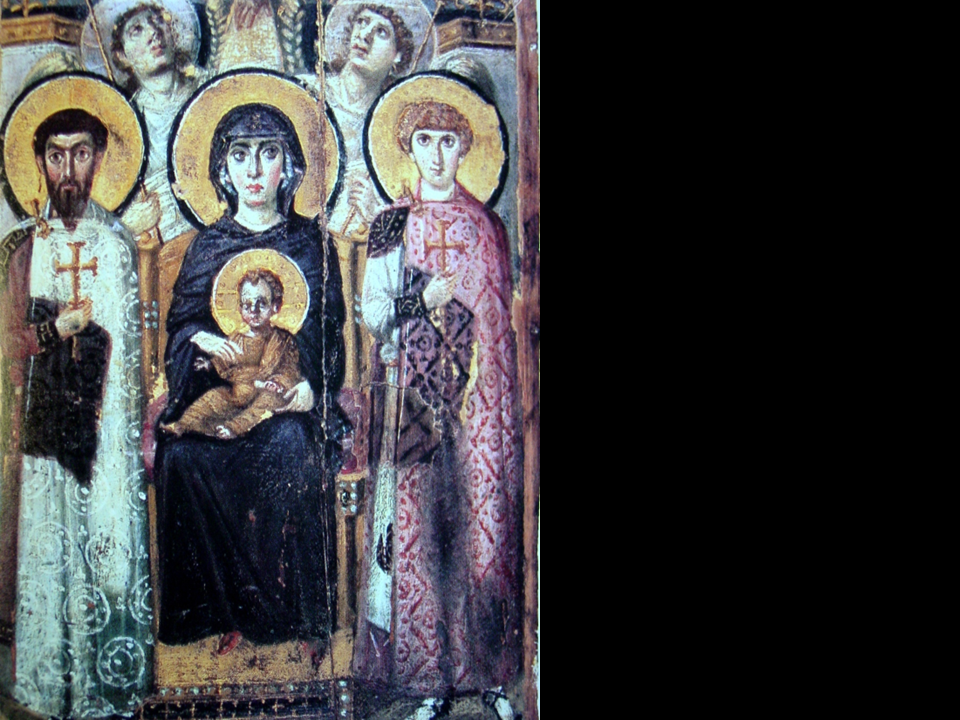

Virgin and Child Between Saints Theodore and George, icon
ca. early 7th century, encaustic on wood.
What are Christian icons, and why the Iconoclastic Controversy?
What are Christian icons, and why the Iconoclastic Controversy?
81
New cards
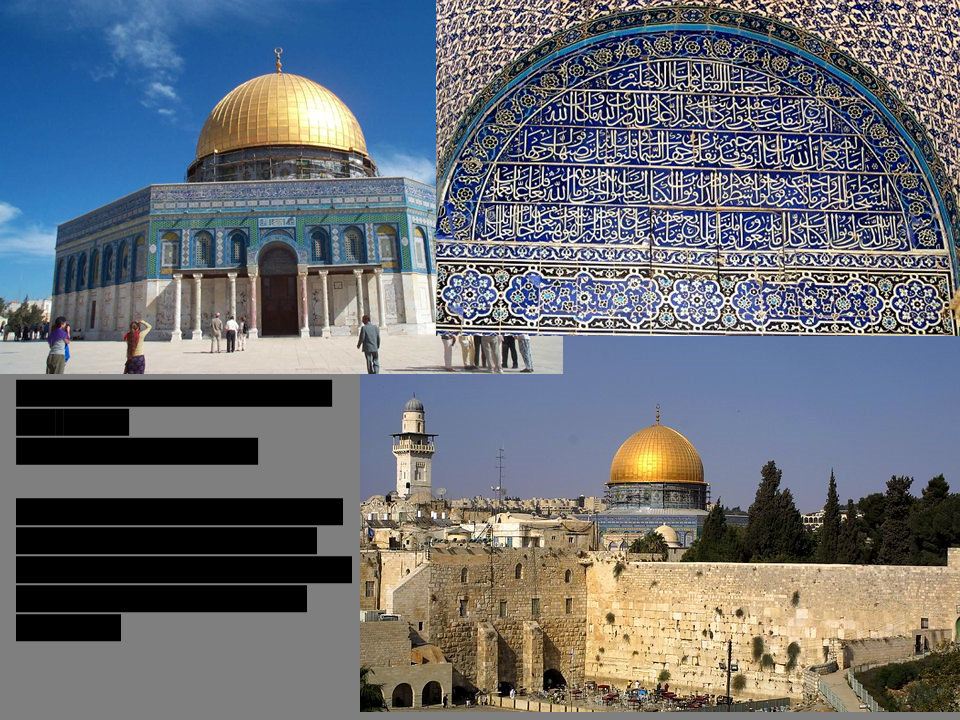
Dome of the Rock,
Jerusalem 691-2 A.D. cut ceramic tile mosaic.
Discuss the importance of this site, the type of decoration, and define a qibla, mihrab, and minbar as features of most mosques.
Discuss the importance of this site, the type of decoration, and define a qibla, mihrab, and minbar as features of most mosques.
82
New cards

Romanesque
What is a pilgrimage church and how does architectural design serve its functional requirements?
\
__Romanesque__ (11th-12th cent. mostly an architectural style)
Bernward of Hildesheim, Doors of St. Michael’s Church, Hildesheim, Germany, 1015,
Describe materials and techniques, what is portrayed, how the representation of the human figure shows a different purpose and different ideas from the Greeks we had studied. Explain the scene (detail) below
\
__Romanesque__ (11th-12th cent. mostly an architectural style)
Bernward of Hildesheim, Doors of St. Michael’s Church, Hildesheim, Germany, 1015,
Describe materials and techniques, what is portrayed, how the representation of the human figure shows a different purpose and different ideas from the Greeks we had studied. Explain the scene (detail) below
83
New cards
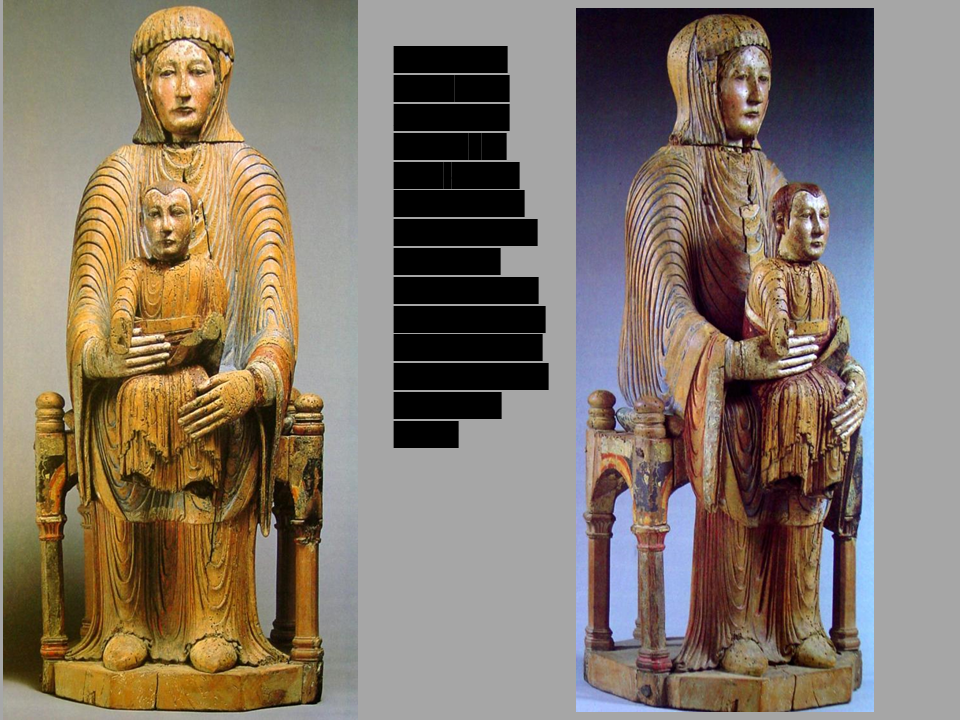

*Virgin and Child*
from Auvergne, France*,* c. 1150-1200, polychrome wood, 31” tall
What is a reliquary and why does this Romanesque sculpture look the way it does?
What is a reliquary and why does this Romanesque sculpture look the way it does?
84
New cards
treatise
a written work dealing formally and systematically with a subject.
85
New cards
sanctuaries
places of worship for specific gods ?
86
New cards
temples
places of worship for specific gods
87
New cards
colonnade
A series or row of columns, usually spanned by lintels.
88
New cards
peristyle (peripteral temple)
In classical architecture, a colonnade all around the cella and its porch(es). A peripteral colonnade consists of a single row of columns on all sides; a dipteral colonnade has a double row all around.
89
New cards
cella
The chamber at the center of an ancient temple; in a classical temple, the room (Greek, naos) in which the cult statue usually stood.
90
New cards
entasis
The convex profile (an apparent swelling) in the shaft of a column.
91
New cards
triglyph & metope
A triple projecting, grooved member of a Doric frieze that alternates with metopes.
\
The square panel between the triglyphs in a Doric frieze, often sculpted in relief.
\
The square panel between the triglyphs in a Doric frieze, often sculpted in relief.
92
New cards
frieze
The part of the entablature between the architrave and the cornice; also, any sculptured or painted band.
93
New cards
pediment
In classical architecture, the triangular space (gable) at the end of a building, formed by the ends of the sloping roof above the colonnade; also, an ornamental feature having this shape.
94
New cards
stereobate & stylobate
a solid mass of __masonry__ serving as a foundation for a wall or row of columns.
\
The uppermost course of the platform of a classical Greek temple, which supports the columns.
\
The uppermost course of the platform of a classical Greek temple, which supports the columns.
95
New cards
attached columns
self explanatory
96
New cards
stoicism
It's where the art of living converges with the creative process.
97
New cards
Geometric
(900-700 BCE)
98
New cards
Archaic
(700-480 BCE)
99
New cards
Classical
(480-400 BCE)
100
New cards
Late Classic
(400-324 BCE)