Indirect Tax
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Why would a government implement an indirect tax
Raise gov revenue
Reduce consumption of demerit goods
Define direct taxes
Taxes on income which cannot be transferred to anyone else
e.g: Income, Corporation tax and national insurance
Define indirect taxes
Extra taxes on goods and services - can be transferred to consumers by increasing price of goods - best applied on elastic goods as they cannot pass on costs
What are the types of indirect taxes
Ad Valorem - Tax is a percentage of price
Specific - Tax on each product sold
Show the effect of a specific tax being implemented on a diagram
Supply shifts inwards - wherever on the supply curve there will always be the same distance apart from the new supply curve as each product is taxed the same no matter the price
Show the effect of an ad-valorem tax being implemented
Supply does not shift but increases in steepness. This is because as price increases the tax increases as well and so it adds even more to the firms costs causing them to cut back further on supply

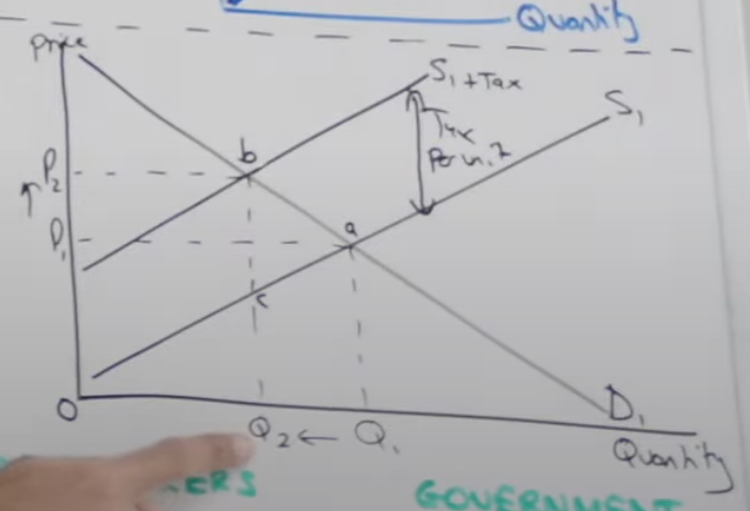
Identify the tax per unit
Identify tax revenue
What is the consumer burden
What is the producer burden
Producer Revenue
P(b) - P(c ) = Tax per unit
C, B, Q2 square though
Top bit of tax revenue
Bottom bit of tax revenue
C, Q2, 0 square though
Draw an indirect tax implementation on a negative production externality

Draw indirect tax implementation on a negative consumption externality
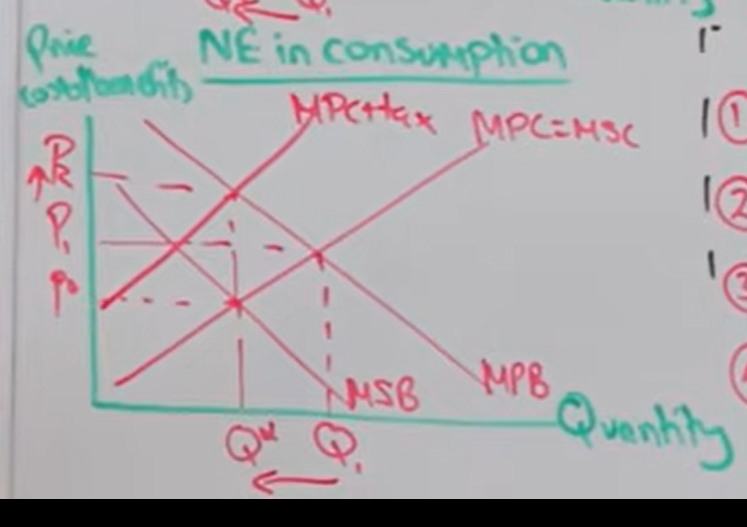
What does it mean to ‘Internalise’ an externality
Usually an externality is unaccounted for by producer and consumer however when a tax is implemented the price increases and accounts for the negative externality (Internalised)
Analyse the effect that indirect tax has on correcting market failure
Indirect tax is implemented
This increases a firms costs of production
So price increases which mean negative externality is internalised
This solves overconsumption / production
Promotes allocative efficiency and increases gov revenue
Problems with implementing an indirect tax on a negative externality
Price increase may result in black markets forming
Imperfect information -Tax may be set too high/ low
Indirect tax is regressive = worse inequality
If price is inelastic all extra costs will be passed onto the consumer
What is a hypothecated tax
A tax which has a stated purpose for the collected revenue