Physiology
1/179
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
System Integration is dependent on
effective communication between components
positive/ negative feedbacks
complex and multifactorial loops and branches
Emergent Properties
sum of body systems of an organism that interact and integrate
integration occurs through 2 processes
hormonal signaling
nervous signaling
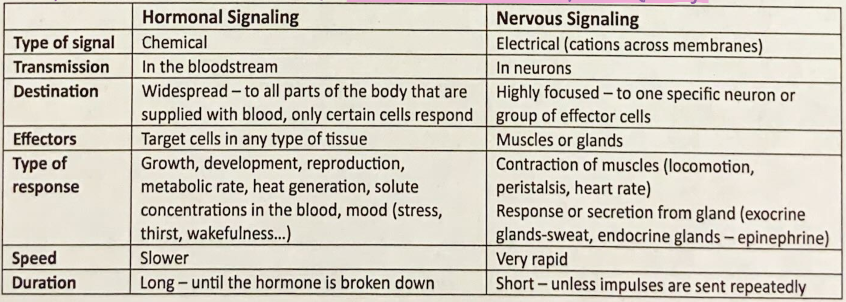
Nervous signaling is
executed by neurons and done through the transmission of impulses in the nervous system
Hormonal signaling is
executed by the endocrine system and is composed of glands that release hormones
Difference between hormonal and nervous signaling
Describe the integration of epinephrine

The brain is made up of
Cranial Nerves: 12 paired nerves connecting to parts of the body to the brain through brain stem.
What does the brain do
receive info from sensory receptors in specialized sense organs and receptor cells
processes info, stores some and sends instructions to parts of the body
cerebellum controls
skeletal muscle contractions and balance
timing of contracts
coordination of movements and maintains posture
memory based activities
Spinal cord is made up of
31 pairs of spinal nerves that branch off left & right between the vertebrae each to different part of body.
Central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord located inside vertebral column
Spinal cord has 2 main tissues called
white matter and grey matter
White matter contains
myelinated axon and nerve fibers that send signals from sensory receptors to brain and from brain to organs
Grey matter contains
cell bodies of motor neurons and interneurons with synapses between these neurons
Synapses in grey matter are used for
processing info and for decision making
is the spinal cord an integrating center
Yes
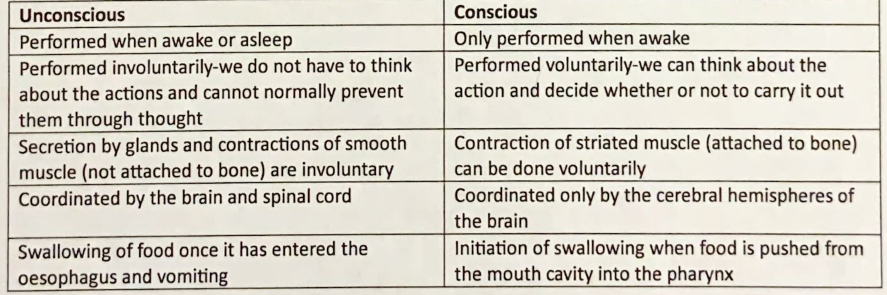
The spinal cord coordinates
unconscious processes and reflexes
Difference between conscious and unconscious processes
What receptors are involved with conscious response
photo
Leucocyte
type of white blood cell
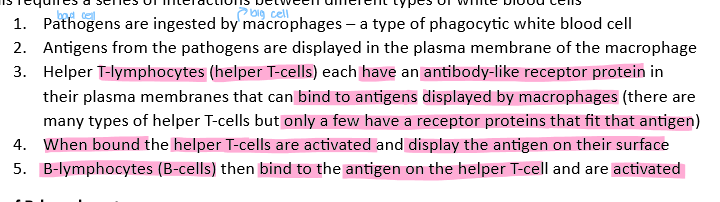
What is a phagocytes main function
first line of defense once a microorganism breaks the physical barriers of the skin and mucous
Amoeboid movement
when phagocytes squeeze through pores in the walls of capillaries and move to the site of infection
what do phagocytes do
engulf pathogens by endocytosis and digest them using enzymes from lysosomes
Where do phagocytes get digestive enzymes
lysosomes
what happens to infected wounds
attract large number of phagocytes resulting the formation of white liquid called pus
What is a phagocyte
a type of leucocyte
what is a lymphocyte
type of leucocyte
where are lymphocytes found
in the lymph system and contained in the lymph nodes
What do lymphocytes do
produce a specific antibody that destroys a specific pathogen
what is an antibody
a large protein
what is the role of the lymphocytes when a pathogen is present
lymphocytes produce antibodies that work together to produce large clones of cells that produce more antibodies; controls the pathogen and clear infection.
What is an antigen
Glycoproteins and large polysaccharides located on the surface of the pathogen.
what is the role of antigen
help lymphocytes distinguish between “self cells” and “non self cells” by recognizing differences between their molecules and body cells.
what is the immune systems response to antigens
production of specific antibodies by lymphocytes that bind to the antigen
how do antigens bind to antibodies
match specific shapes and chemical properties which does not change unlike enzyme substrate connections
What are the steps required for the interactions between different types of white blood cells
what does immunity depend on
presence of b cells capable of producing an effective antibody
what happens when b lymphocytes are activated
due to the low number b-lymphocytes undergo mitosis to form clones which grow and develop an ER with many ribosomes and a large Golgi apparatus
what does the large golgi apparatus and ribosome allow in b lymphocytes
rapid production of antibodies by protein synthesis
plasma B-cells are
cells that have grown and differentiated for antibody production
what is immunity
ability to eliminate an infectious disease from the body
what do antibodies do
provide immunity to a disease
how long do antibodies provide immunity for
few weeks/ months after being secreted by plasma b cells
what secretes antibodies
plasma b cells
what happens to the plasma b cells that secrete antibodies
gradually lost after an infection is cleared
why are plasma b cells slowly lost after an infection is cleared
the antigens associated with the infection are no longer present
how are b cells in a clone produced
mitosis
what do cloned b cells become
plasma b cells
how long do cloned b cells survive
not long after fufilling role of rapid antibody production
What cells remain after the infection
memory b cells
what are memory b cells
small number of cloned cells that don’t immediately secrete antibodies
what do memory b cells do
remain inactive unless the same pathogen infects the body in which they are activated and respond rapidly
immunity to an infectious disease is due having what 2 factors
antibodies against the pathogen
memory cells that allow rapid production of antibody
what is an antibiotic
chemical that inhibits metabolism of microorganisms (prokaryotes)
are antibiotics effective on viruses/non-living pathogens?
no because they lack metabolism and rely on host cells for metabolic pathways like transcription and protein synthesis (drugs cannot target these processes as it would damage the host cell)
antibiotic resistance can be prevented by
exclusion as animal growth stimulants, proper hygiene in hospitals, developing new classes of antibiotics, using only for serious bacterial infections
what is zoonosis
disease transmitted from human to animal (rabies)
how does HIV spread
blood or body fluids (sex without condom, hypodermic needles, transfusion of infected blood)
what does HIV do to the immune system
HIV destroys helper T-cells which reduces antibody production; if the immune system is so ineffective, opportunistic infections arrive and lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
what type of virus is HIV
retrovirus; uses reverse transcriptase to produce DNA copies of its genes from RNA
How does immunization occur
vaccine triggers immunity
what do vaccines contain
antigen that allow a pathogen to be recognized by the immune system
OR
nucleic acid from which antigens can be made
What do antigens from a vaccine do
Stimulate
primary immune response by activation of t-lymphocytes and b-lymphocytes
production of plasma cells, thus specific antibodies.
what happens when memory cells are produced
long lasting immunity
what happens in the vaccine triggers memory cells
pathogenic microorganism destroyed by secondary immune response if it enters body
How is heard immunity achieved
when significant proportion of population already contracted a disease or been vaccinated
what is the result of herd immunity
spread of virus or pathogen is impeded as it always encounters people who are already immune.
what happens when herd immunity is reached
new outbreak of disease will decline and disappear
What is cell proliferation
rapid increase in # of cells - division happens faster than cell death
The role of mitosis in cell proliferation
ensures continuity of the genome
what are nerves
sheathed bundle of sensory + motor neurons
outline the reflex arc
receptor cells detect stimulus, sensory neurons carry to CNS interneurons, motor neurons receive via synapses, effector cells
dendrites vs axon
dendrites are short, branched nerve fibres while axons are long singular fibres
what are nerve impulses
electrical signals caused by movement of Na+/K+ ions
resting potential of neuron
-70mV
is the Na/K pump in a neuron’s membrane balanced?
active transport of 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in
action potential of neuron
+30 mV
what are myelinated fibres?
neurons with Schwann cell coat where impulses jump between nodes of Ranvier; less ATP
how does action potential function?
depolarization as Na+ enters then repolarization as K+ exits
outline depolarization (HL) as voltage changes
voltage-gated Na channels open for Na+ to enter, causing positive feedback to make potential +30mV in all areas (self-propagating)
outline repolarization (HL) as voltage changes
voltage-gated K channels subsequently open, K+ diffuses out until potential is -70mV, Na/K pump re-establishes gradients
what is myelin
layers of phospholipid membrane deposited around nerve fibres
what is a synapse
junction between two cells in nervous system
where are synapses
between sensory receptor cells and neurons, neurons, and neurons and effectors (muscles/glands)
can action potential be sent when resting potential is not restored
no
what is synaptic transmission
release of neurotransmitters carrying signals across fluid gap
how are neurotransmitters released from their vesicles
depolarization of presynaptic neuron causes Ca+ to diffuse into membrane and move vesicles to membrane for exocytosis
what do neurotransmitters do in the cleft
diffuse quickly towards receptors on postsynaptic neuron
what happens when neurotransmitters bind to receptors
ion channels open and Na+ diffuses down gradient into post neuron; changes potential
what is an excitatory postsynaptic potential
increased potential; triggers action potential which propagates away from synapse if strong
what is acetylcholine
neurotransmitter
what is acetylcholinesterase
enzyme in cleft that separates acetate and choline
what happens to acetylcholine after transmission
broken down and choline reabsorbs into pre neuron to combine with acetyl group
what are G-Protein-coupled receptors
group of transmembrane receptors; conveys signals to G proteins
what does guanosine diphosphate (GDP) do
binds to secondary G protein in membrane; deactivates
what happens when a ligand binds to receptor
changes receptor shape and GDP detaches for GTP to replace it
what happens when GTP binds to G protein
activates G protein which then disassociates from receptor
what does the G protein do
once dissociated, it triggers cell response to signal
Define Circadian rhythms
rhythms in behaviour that fit the 24 hour cycle.
Controlled by an internal system