BIOL301 Final Review [Part 1]
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UofSC Dr. Knott's BIOL301 final exam prep part 1.
Last updated 3:49 AM on 4/12/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Water's polar nature __________________________.
makes it a good solvent
2
New cards
The low density of ice _____________________________.
allows aquatic plants to survive in the winter
3
New cards
A liquid with low pH would have a ____ H+ concentration and would be called ____.
word bank: low, high, similar, acidic, basic, alkaline
word bank: low, high, similar, acidic, basic, alkaline
high; acidic
4
New cards
Fish obtain oxygen from the water through their gills using ______ ______.
countercurrent circulation
5
New cards
The temperature that water reaches its maximum density is ____.
(the number not the word)
(the number not the word)
4°C
6
New cards
The rate of biological processes increases two to four times for each ____ increase in temperature.
10°C
7
New cards
Anaerobic conditions __________________________________.
are more common in deep water than in the shallows
8
New cards
The primary cause of coral bleaching is ________________.
increased water temperature
9
New cards
Match the structural adaptations to the benefit it provides.
Questions:
Prevent loss of leaf tissue: _________
Produce a boundary layer of still air: __________
Able to take up water after brief rainfall events: __________
Protect plants from slow water loss: ______________
Word bank:
Resin, shallow roots, small leaves with a high density of veins, flowers, long roots, spines and hairs
Questions:
Prevent loss of leaf tissue: _________
Produce a boundary layer of still air: __________
Able to take up water after brief rainfall events: __________
Protect plants from slow water loss: ______________
Word bank:
Resin, shallow roots, small leaves with a high density of veins, flowers, long roots, spines and hairs
Prevent loss of leaf tissue: small leaves with a high density of veins
Produce a boundary layer of still air: spines and hairs
Able to take up water after brief rainfall events: shallow roots
Protect plants from slow water loss: resin
Produce a boundary layer of still air: spines and hairs
Able to take up water after brief rainfall events: shallow roots
Protect plants from slow water loss: resin
10
New cards
Aquatic organisms have developed streamlined shapes to adapt to the ________________.
viscosity of water
11
New cards
Availability of soil nutrients varies with ______________.
the presence of other ions, pH, and soil temperature.
12
New cards
Which is NOT an adaptation to low-oxygen aquatic environments?
A. breathing air
B. symbiotic relationship with algae
C. increased hemoglobin
D. increased metabolic activity
A. breathing air
B. symbiotic relationship with algae
C. increased hemoglobin
D. increased metabolic activity
increased metabolic activity
13
New cards
Which is NOT a true statement?
A. All ectotherms are poikilotherms
B. Ectotherms tend to have lower metabolic rates than endotherms
C. Ectotherms are able to alter their body temperature
D. Ectotherms have body temperatures that are determined largely by their external environment
A. All ectotherms are poikilotherms
B. Ectotherms tend to have lower metabolic rates than endotherms
C. Ectotherms are able to alter their body temperature
D. Ectotherms have body temperatures that are determined largely by their external environment
All ectotherms are poikilotherms
14
New cards
Which is NOT an adaptation that exploits the density of water?
A. high percentages of fat
B. long, filamentous appendages
C. droplets of oil on algae
D. a gas-filled swim bladder
A. high percentages of fat
B. long, filamentous appendages
C. droplets of oil on algae
D. a gas-filled swim bladder
long, filamentous appendages
15
New cards
Which photosynthesis method is best suited to warm, dry environments?
I. C3 fixation
II. C4 fixation
III. CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism)
I. C3 fixation
II. C4 fixation
III. CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism)
II and III only
16
New cards
Why are both carbon dioxide and oxygen limited in aquatic environments?
They are not very soluble in water
17
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a part of the carbon equilibrium in water?
A. ammonia
B. carbonic acid
C. hydrogen ions
D. bicarbonate
A. ammonia
B. carbonic acid
C. hydrogen ions
D. bicarbonate
ammonia
18
New cards
Which does NOT limit the ability of aquatic plants to photosynthesize?
high levels of carbonic acid
19
New cards
Spotted salamanders lay eggs in gelatinous masses on twigs partially submerged in small ponds or vernal pools. Associated with the eggs, scientists have found a species of alga living in a mutualistic relationship with the developing eggs. What benefit does the salamander receive from this relationship?
The salamander embryos receive an increased oxygen supply
20
New cards
[T/F] Adding dissolved compounds such as salt to water increases the boiling point and increases the freezing point.
False
21
New cards
A fish that has tissue solute concentrations that are higher than surrounding water...
is trying not to drink the environmental water in an attempt to maintain internal water concentrations AND is hyperosmotic
22
New cards
Photosynthesis occurs in two steps, known as ____ and the _____.
light reactions and the calvin cycle
23
New cards
A smallmouth bass swimming in colder water of a springtime lake would likely expend _____ energy than when swimming in warmer water of the same lake during the summer (all things being equal).
more
24
New cards
A plant with a high number of stomata _________.
has a high rate of transpiration
25
New cards
Photosynthesis primarily allows plants to produce ______.
glucose
26
New cards
Many types of traits are plastic, such as.....
development, growth, behavior, and reproduction.
27
New cards
When the protist Euplotes detects predators, it grows "wings" and other projections to discourage predators. However, developing the projections and wings slows down growth. This is an example of:
I. phenotypic trade-offs
II. phenotypic plasticity
III. inbreeding depression
I. phenotypic trade-offs
II. phenotypic plasticity
III. inbreeding depression
I and II only
28
New cards
If a goldfish is acclimated at 25°C, at which temperature would we expect the fish to swim fastest?
A. equally fast at all temperatures
B. 40°C
C. 25°C
D. 5°C
A. equally fast at all temperatures
B. 40°C
C. 25°C
D. 5°C
25°C
29
New cards
Match the dormancy type to its definition and/or example.
Question:
Chipmunks: __________.
A shutting down of metabolic processes during the summer in response to hot or dry conditions: __________.
Crocodiles: ___________.
West indian hummingbird: _____________.
A complete physiological shutdown: ___________.
A brief period of dormancy in which individuals reduce activity: _____________.
Word bank:
torpor, hibernation, diapause, aestivation, osmoregulation, metaslow
Question:
Chipmunks: __________.
A shutting down of metabolic processes during the summer in response to hot or dry conditions: __________.
Crocodiles: ___________.
West indian hummingbird: _____________.
A complete physiological shutdown: ___________.
A brief period of dormancy in which individuals reduce activity: _____________.
Word bank:
torpor, hibernation, diapause, aestivation, osmoregulation, metaslow
Chipmunks: hibernation
A shutting down of metabolic processes during the summer in response to hot or dry conditions: aestivation
Crocodiles: aestivation
West indian hummingbird: torpor
A complete physiological shutdown: diapause
A brief period of dormancy in which individuals reduce activity: torpor
A shutting down of metabolic processes during the summer in response to hot or dry conditions: aestivation
Crocodiles: aestivation
West indian hummingbird: torpor
A complete physiological shutdown: diapause
A brief period of dormancy in which individuals reduce activity: torpor
30
New cards
[T/F] Some foragers consume a singular food type as a diet mixing foraging response because of one type of food will provide all of the necessary nutrients.
False
31
New cards
Since resources vary in ____ and _____, no single foraging strategy can maximize an animal's fitness.
space and time
32
New cards
[T/F] Slow environmental fluctuations favor slow phenotypic responses, whereas rapid fluctuations favor rapid phenotypic responses.
True
33
New cards
A scientist is studying bird that forages for worms and takes them back to its nest. If the relation between search time and the number of prey caught remains constant but the scientist moved the food closer, what change in the bird's behavior would central place foraging predict?
Fewer worms would be brought back per trip.
34
New cards
What is the risk to a species of inbreeding depression?
an increased likelihood of deleterious genes being inherited from both egg and sperm
35
New cards
Which statement about predator and prey phenotypic plasticity is accurate?
I. Prey can change morphology to avoid predators
II. Predators can change morphology to capture prey
III. Both predators and prey can exhibit phenotypic trade-offs
I. Prey can change morphology to avoid predators
II. Predators can change morphology to capture prey
III. Both predators and prey can exhibit phenotypic trade-offs
I, II, and III
36
New cards
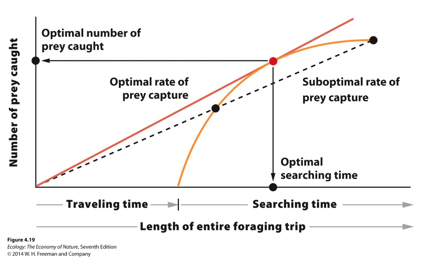
Based on the central-place foraging theory and the figure, identify the optimal number of prey for a forager to catch. In the figure, the straight orange line indicates the optimal rate of prey capture.
8 prey
37
New cards
When humans move from low elevations to high elevations, it typically takes one or more weeks for their bodies to improve their ability to carry oxygen. This is an example of ______________.
acclimation
38
New cards
Different species of birds found feeding in different parts of the same forest canopy at the same time may be an example of _______ _______.
microhabitat differences
39
New cards
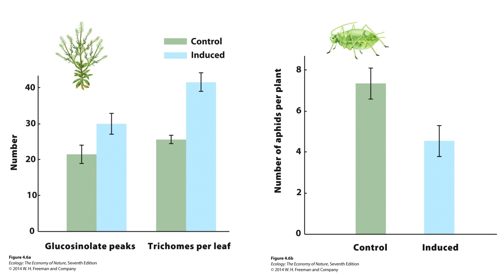
Consider the figure, which shows how Virginia pepperweed responds to herbivores. Which of the following conclusions can we make solely using the data shown?
I. Plants increased glucosinolate production when aphids were present.
II. Plants with more glucosinate and trichomes had fewer aphids.
III. Producing glucosinate and trichomes reduced plant fitness when aphids were absent.
I. Plants increased glucosinolate production when aphids were present.
II. Plants with more glucosinate and trichomes had fewer aphids.
III. Producing glucosinate and trichomes reduced plant fitness when aphids were absent.
I and II only
40
New cards
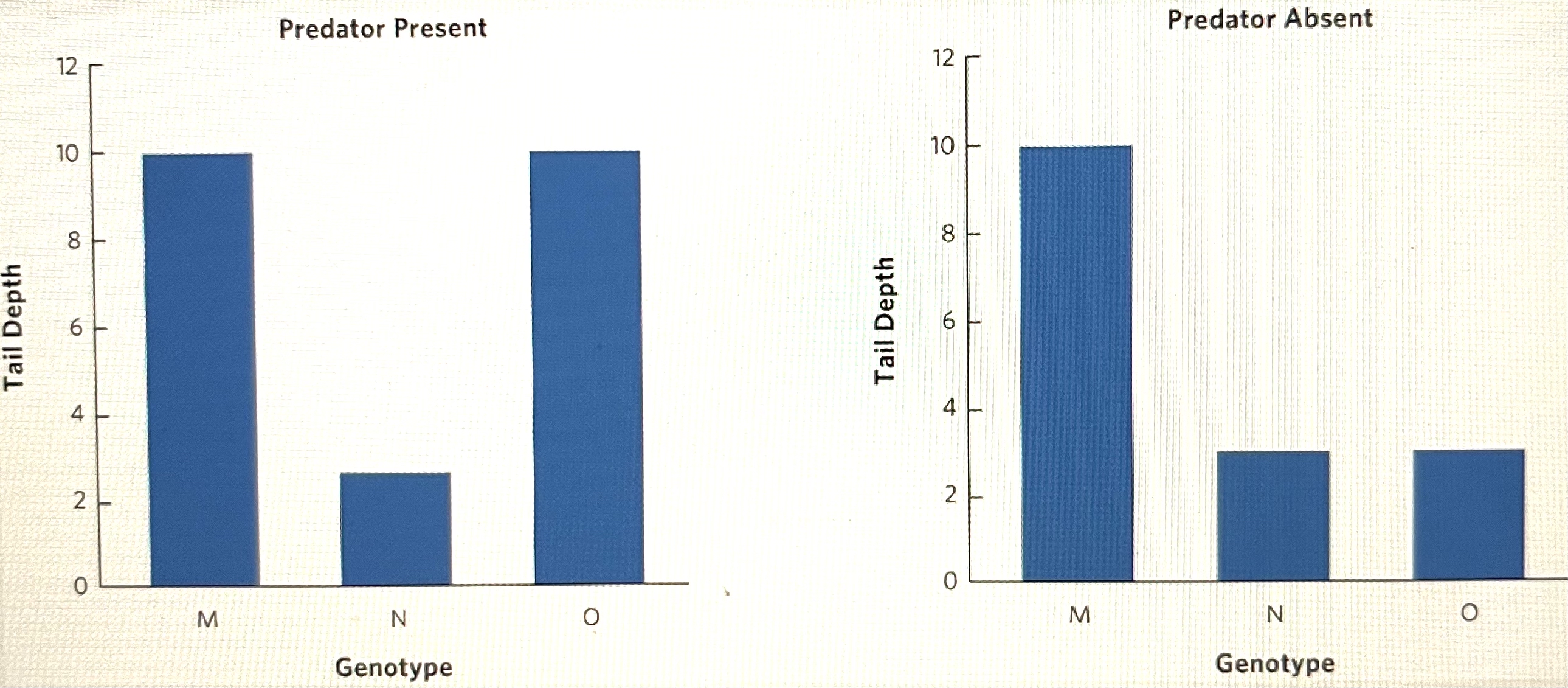
This figure shows the tail shape developed by three tadpole genotypes (M, N, and O) when raised in an environment with an environment with predators and an environment without predators. In the presence of predators, tadpoles with large tails have high fitness and tadpoles with small tails have low fitness. When predators are not present, tadpoles with large tails have low fitness and tadpoles with small tails have high fitness.
Which genotype(s) exhibit(s) phenotypic plasticity in response to predators?
Which genotype(s) exhibit(s) phenotypic plasticity in response to predators?
O only
41
New cards
Consider a mouse that can forage in one of two fields. The south field has three times more seeds than the north field. However, an owl (a predator that eats mice) lives at the south field. The mouse forages in the north field despite the fact that it contains less food. This is an example of:
risk-sensitive foraging
42
New cards
The average annual rainfall measured in a desert over 10 years is which type of variation?
climate
43
New cards
In response to a specific type of environmental variation, the Burmese python can drastically increase the size of its heart and length of its intestines in fewer than 2 days. What environmental variation causes this drastic change?
variation in availability of food
44
New cards
A predator should always eat the prey species that provides the highest amount of energy gained per unit time... this is for the ____ response to food variation in space and time.
optimal
full name: optimal diet composition
full name: optimal diet composition
45
New cards
[T/F] energy benefit of a resource item / handling time = amount of energy gained per unit time
true
46
New cards
Changes in ____ and _____ are often relatively slow phenotypic responses.
morphology; life history
47
New cards
Which of the following are phenotypic plastic responses of plants to reduced water availability?
I. Develop trichomes and produce more glucosinolate
II. Close stomata in leaves
III. Increase the root/shoot ratio
I. Develop trichomes and produce more glucosinolate
II. Close stomata in leaves
III. Increase the root/shoot ratio
II and III only
48
New cards
Which of the following is an example of weather?
A single location received 10 cm of snow on January 1, 2011, but no snow on January 2, 2011.
49
New cards
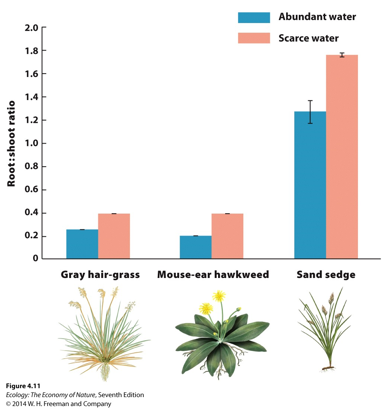
The figure shows plant growth responses to variation in availability of water. If this is an example of adaptive phenotypic plasticity, how would we expect the root-to-shoot ratio be related to fitness?
When water is scarce, plants with high root-to-shoot ratios have higher fitness.
50
New cards
The ocean zone with the highest productivity is the _______.
neritic zone
51
New cards
Which of the following is the most likely reason a soil would not have an O horizon?
The soil is in a desert
52
New cards
Many factors create ocean currents. Some factors are....
unequal heating, salinity, coriolis effects, and wind directions
53
New cards
Oceans and lakes cover a ____ percentage in the Northern Hemisphere compared to the Southern Hemisphere. Therefore, ____ rain falls in the Northern Hemisphere.
lower; less
54
New cards
In which lake zone would photosynthesis not occur?
profundal zones
55
New cards
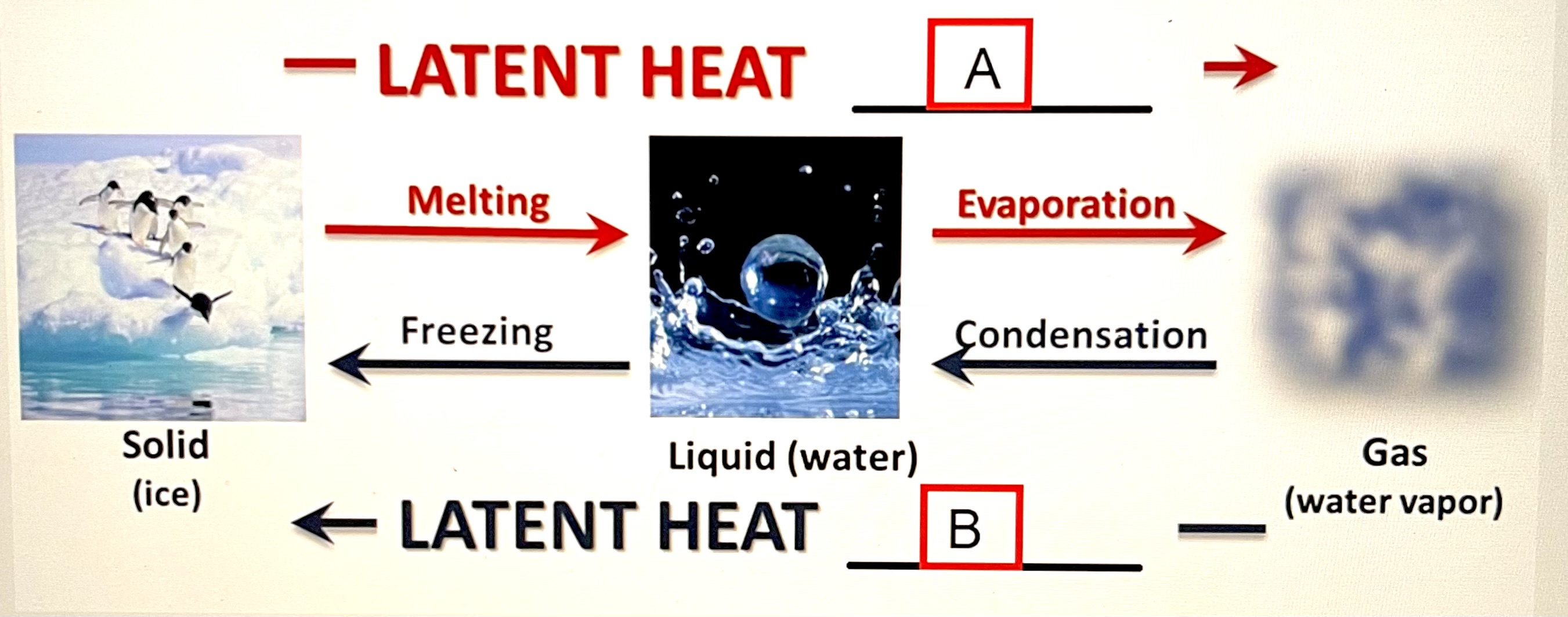
Based on the image below, identify the latent heat movement. A is representative of _____ and B is representative of _____.
absorbed; released
56
New cards
The energy of incident solar radiation reaching the surface of Earth declines towards the poles from its maximum in equatorial regions. Which of these is NOT a reason for this?
a. The tilt of the Earth increases the reflection of solar radiation
b. A given amount of solar radiation is spread over a larger area at higher latitudes
c. Solar radiation travels a longer path through Earth's atmosphere at higher latitudes
d. The rays of the Sun strike Earth at right angles over the equator as compared to oblique angles at the poles
a. The tilt of the Earth increases the reflection of solar radiation
b. A given amount of solar radiation is spread over a larger area at higher latitudes
c. Solar radiation travels a longer path through Earth's atmosphere at higher latitudes
d. The rays of the Sun strike Earth at right angles over the equator as compared to oblique angles at the poles
The tilt of the Earth increases the reflection of solar radiation
57
New cards
A symbiotic relationship with algae is central to _______ ______.
coral reefs
58
New cards
What kind of oceanic circulation would you predict for the western costs of continents?
cold currents moving from the poles toward the equator
59
New cards
As a river flows down stream, it generally:
has more nutrients.
60
New cards
Which of the following does NOT drive ocean currents?
a. the Coriolis effect
b. topography of the ocean basins
c. temperature differences
d. continental water sources
e. differences in salinity
a. the Coriolis effect
b. topography of the ocean basins
c. temperature differences
d. continental water sources
e. differences in salinity
continental water sources
61
New cards
Thermohaline circulation is driven by:
sinking polar water with high salinity
62
New cards
The aphotic zone is a feature in:
the open ocean
63
New cards
In which aquatic environment are organisms most likely to produce bioluminescence?
aphotic zones
64
New cards
Manure from a farming operation that enters into a stream would be considered:
allochthonous
65
New cards
Albedo is the fraction of solar energy reflected by an object. Forests have ____ albedo and snow has _____ albedo.
low; high
66
New cards
An important characteristic of streams is:
high allochthonous inputs.
67
New cards
What is a unique characteristic of estuaries?
the mixing of fresh and salt water
68
New cards
Which of the following is used to distinguish aquatic biomes?
I. salinity
II. depth
III. flow
I. salinity
II. depth
III. flow
I, II, and III
69
New cards
What is NOT a reason why cold regions with high rainfall are rare?
a. water does not evaporate at high temperatures
b. water does not evaporate at low temperatures
c. cold atmosphere holds a lot of water vapor
d. cold atmosphere holds a little water vapor
a. water does not evaporate at high temperatures
b. water does not evaporate at low temperatures
c. cold atmosphere holds a lot of water vapor
d. cold atmosphere holds a little water vapor
Water does not evaporate at high temperatures.
Cold atmosphere holds a lot of water vapor.
Cold atmosphere holds a lot of water vapor.
70
New cards
Compared to coastal regions, the interior of a continent usually has _____ precipitation and ______ variation in climate.
less; more
71
New cards
Lakes are generally divided into zones, each of which has unique physical and biological attributes. In which zone would you expect to find rooted vegetation?
littoral
72
New cards
Which combination of factors causes the fastest nutrient cycling in a biome?
high precipitation and high temperatures
73
New cards
In areas with significant leaching, which soil horizon would be largest?
E
74
New cards
Plant growth and it's growing season can be constrained by ____ and _____.
temperature; precipitation
75
New cards
Consider three populations of plant species, each of which is isolated from other populations of the same species. Population X has had approximately 100 individuals in each generation for the past 200 generations. Population Y has had approximately 10,000 individuals in each generation for the past 200 generations. Population Z has had approximately 1 million individuals in each generation for the past 200 generations. If the environment changed and a new environmental condition exerted the exact same strength of directional selection on all three populations, which population would we expect to evolve most rapidly?
Population Z
76
New cards
Which of the following is/are correct?
I. Sympatric speciation occurs without geographic barriers
II. Sympatric speciation can occur through polyploidy
III. Sympatric speciation is less common than allopatric speciation
I. Sympatric speciation occurs without geographic barriers
II. Sympatric speciation can occur through polyploidy
III. Sympatric speciation is less common than allopatric speciation
I, II, and III
77
New cards
Consider a situation in which overharvesting causes the number of fish in a population to become drastically smaller, which causes genetic variation in that fish to decrease over a few generations. This is an example of:
bottleneck effect
78
New cards
Consider a gene that affects fur color in mice. This gene has two alleles, A and a. If AA mice have white fur, Aa mice have gray fur, and aa mice have black fur, how would we describe the effect of these alleles?
A and a are codominant
79
New cards
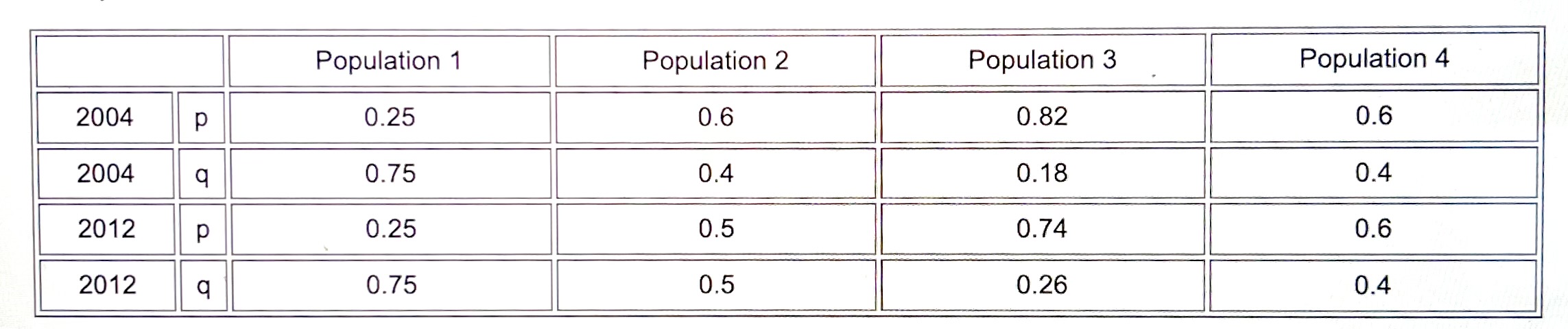
Here is a table of 4 populations of dragons with the allele frequencies that relate to breathing fire over 10 years. Which of the populations evolved? You may choose more than one answer if necessary.
Population 2; Population 3
80
New cards
Match the word with its definition.
________: allele whose phenotypic effect is NOT typically observed in a heterozygote.
________: the observable physical and physiological traits of an organism that are determined by its genetic makeup.
________: any of the alternative versions of a gene that may produce distinguishing phenotypic effects.
________: having two identical alleles for a given gene (example genotype: AA or aa)
________: a cellular structure carrying genetic material that consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins
________: a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence of DNA
word bank:
gene, heterozygous, chromosome, homozygous, dominant, phenotype, recessive, allele
________: allele whose phenotypic effect is NOT typically observed in a heterozygote.
________: the observable physical and physiological traits of an organism that are determined by its genetic makeup.
________: any of the alternative versions of a gene that may produce distinguishing phenotypic effects.
________: having two identical alleles for a given gene (example genotype: AA or aa)
________: a cellular structure carrying genetic material that consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins
________: a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence of DNA
word bank:
gene, heterozygous, chromosome, homozygous, dominant, phenotype, recessive, allele
recessive : allele whose phenotypic effect is NOT typically observed in a heterozygote.
phenotype : the observable physical and physiological traits of an organism that are determined by its genetic makeup.
allele : any of the alternative versions of a gene that may produce distinguishing phenotypic effects.
homozygous : having two identical alleles for a given gene (example genotype: AA or aa)
chromosome : a cellular structure carrying genetic material that consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins
gene : a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence of DNA
phenotype : the observable physical and physiological traits of an organism that are determined by its genetic makeup.
allele : any of the alternative versions of a gene that may produce distinguishing phenotypic effects.
homozygous : having two identical alleles for a given gene (example genotype: AA or aa)
chromosome : a cellular structure carrying genetic material that consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins
gene : a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence of DNA
81
New cards
Which is a prediction of the hypothesis that predation caused industrial melanism?
Birds more frequently capture dark moths on light trees than those on dark trees
82
New cards
Since I am so interested in populations of lizards, I kept track of the number of homozygous recessive lizards over a period of several years within a population of 100 lizards. Use the following equations and assume that the populations I researched were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium to figure out allele frequencies and the number of individuals below.
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 ------------------------ p + q = 1
I found that 16 lizards out of the 100 in the year 2004 had the ability to breathe underwater (genotype ff).
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2004?
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2004?
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2004?
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2004?
I found that 64 lizards out of the 100 in the year 2012 had the ability to breathe underwater (genotype ff).
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2012?
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2012?
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2012?
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2012?
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 ------------------------ p + q = 1
I found that 16 lizards out of the 100 in the year 2004 had the ability to breathe underwater (genotype ff).
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2004?
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2004?
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2004?
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2004?
I found that 64 lizards out of the 100 in the year 2012 had the ability to breathe underwater (genotype ff).
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2012?
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2012?
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2012?
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2012?
I found that 16 lizards out of the 100 in the year 2004 had the ability to breathe underwater (genotype ff).
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2004? ----> 0.6
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2004? ----> 0.4
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2004? ----> 36
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2004? ----> 48
I found that 64 lizards out of the 100 in the year 2012 had the ability to breathe underwater (genotype ff).
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2012? ----> 0.2
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2012? ----> 0.8
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2012? ----> 4
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2012? ----> 32
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2004? ----> 0.6
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2004? ----> 0.4
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2004? ----> 36
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2004? ----> 48
I found that 64 lizards out of the 100 in the year 2012 had the ability to breathe underwater (genotype ff).
- What was the frequency of the dominant allele (p) in 2012? ----> 0.2
- What was the frequency of the recessive allele (q) in 2012? ----> 0.8
- What is the expected number of homozygous dominant individuals in 2012? ----> 4
- What was the expected number of heterozygous dominant individuals in 2012? ----> 32
83
New cards
The drastic phenotypic differences between large dogs, such as bloodhounds, and small dogs, such as chihuahuas, are a result of:
artificial selection
84
New cards
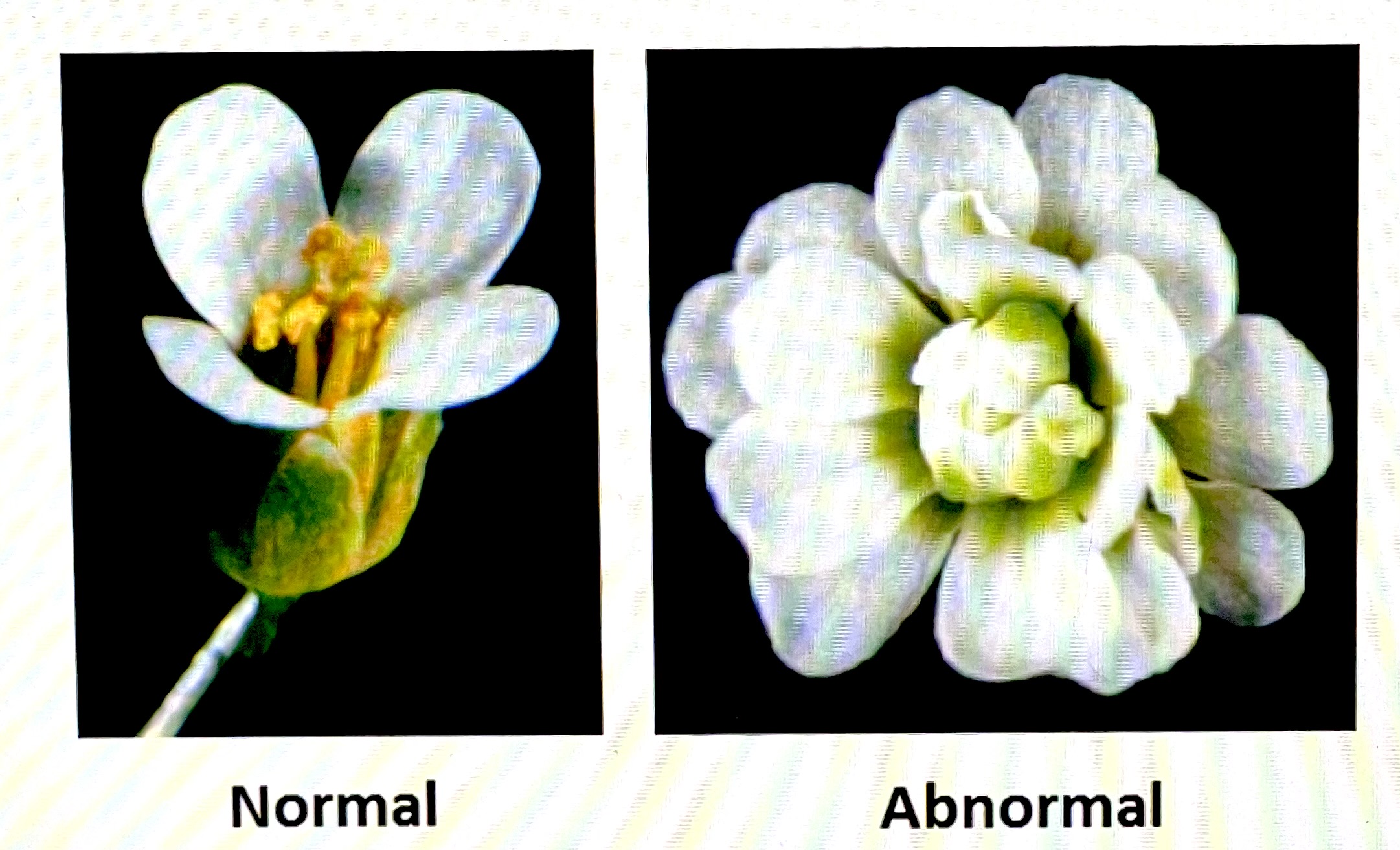

Shown below are pictures of Arabidopsis spp. which typically has four flowers as in the picture on the left. the picture on the right represents a flower from an organism where a change occurred in the nucleotide sequence of the sex cells of its parents. This example represents the mechanism of evolution called:
mutation
85
New cards
Body size is a heritable trait in the amphipod, an aquatic crustacean. Fish preferentially consume large amphipods, leaving primarily small amphipods to breed. Based on these observations, how would we expect evolution to affect ponds with and without fish?
ponds with fish should have smaller amphipods
86
New cards
What process creates new alleles in a population?
mutation
87
New cards
Stickleback fish exhibit variation in a morphological trait known as gill rakers. Fish with long gill rakers are very good at eating plankton, and fish with short gill rakers are good at eating deep-water invertebrates. However, fish with intermediate-length gill rakers are poor at eating either type of food. Fish that are better at consuming food have higher survival and reproduction rates than poorer consumers. Based on this information, what type of selection is likely acting on stickleback gill raker length?
disruptive selection
88
New cards
Amy has a population of 500 rats.
- 245 of her rats are auburn while 255 are black.
- Being auburn is a homozygous recessive trait (aa).
- If this population is currently in H-W equilibrium,
1. The value of p is:
2. The value of q is:
3. How many rats are homozygous dominant?
4. How many rats are heterozygous?
p + q = 1 ------------- p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
- 245 of her rats are auburn while 255 are black.
- Being auburn is a homozygous recessive trait (aa).
- If this population is currently in H-W equilibrium,
1. The value of p is:
2. The value of q is:
3. How many rats are homozygous dominant?
4. How many rats are heterozygous?
p + q = 1 ------------- p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
1. The value of p is: 0.3
2. The value of q is: 0.7
3. 45 rats are homozygous dominant
4. 210 rats are heterozygous
2. The value of q is: 0.7
3. 45 rats are homozygous dominant
4. 210 rats are heterozygous
89
New cards
If a population of butterflies is under strong natural selection favoring large wings but there is no genetic variation for wing size, what do we expect to occur in the next population?
There will be no evolutionary change in wing size.
90
New cards
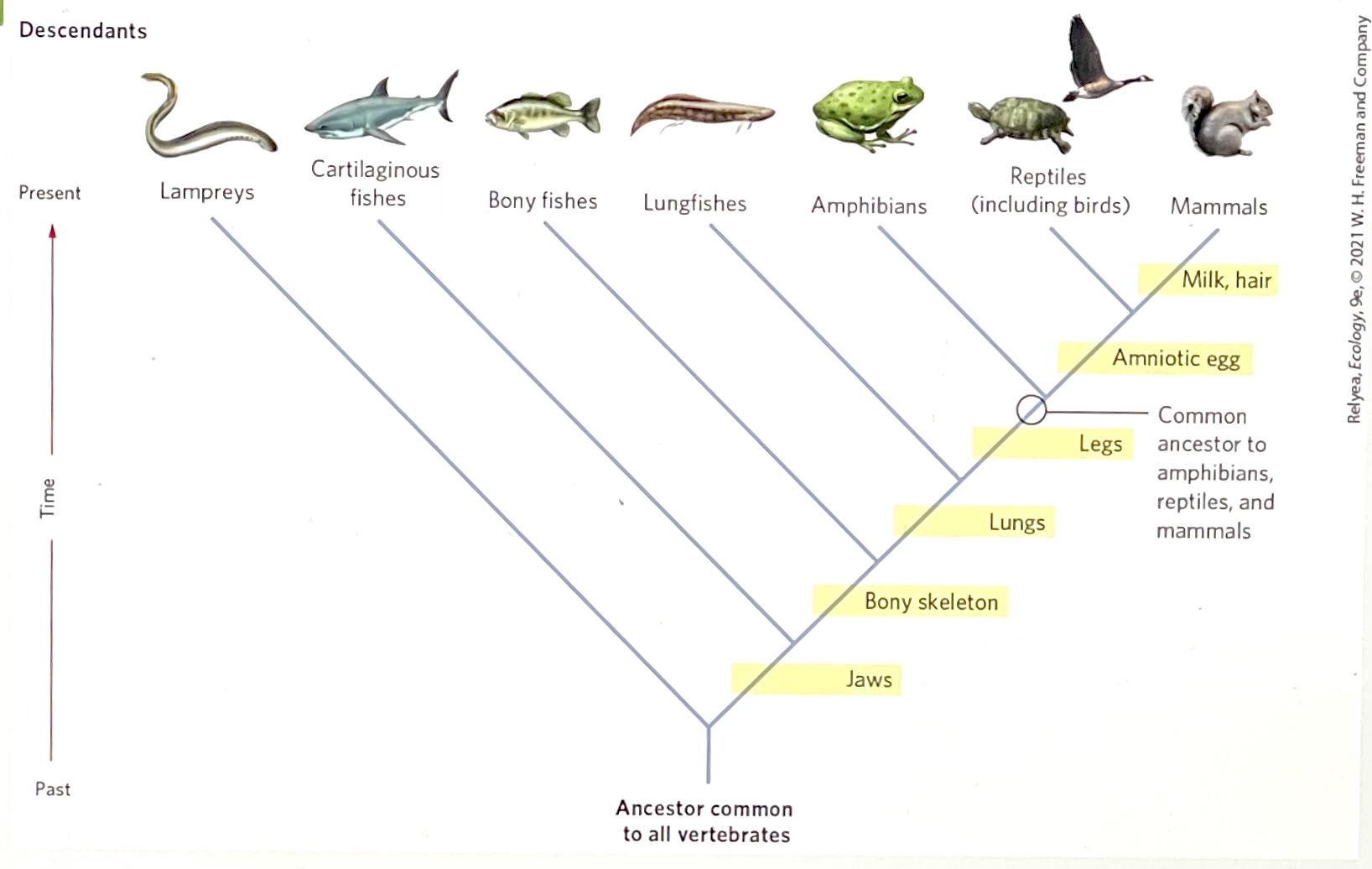
Based on the phylogeny in the figure, which group is most closely related to the reptiles?
mammals
91
New cards
Consider three populations of plant species, each of which is isolated from other populations of the same species. Population X has had approximately 100 individuals in each generation for the past 200 generations. Population Y has had approximately 10,000 individuals in each generation for the past 200 generations. Population Z has had approximately 1 million individuals in each generation for the past 200 generations. If genetic drift is the only evolutionary process acting on these populations, how can we expect the amount of genetic variation to differ among these populations?
X will have the lowest variation, Y will have intermediate variation, and Z will have the highest variation.
92
New cards
Which is/are correct about the founder effect?
I. Founder effect occurs when individuals are transplanted to a new location.
II. Founder effect produces new alleles.
III. Founder effect may see further reduction in genetic variation.
I. Founder effect occurs when individuals are transplanted to a new location.
II. Founder effect produces new alleles.
III. Founder effect may see further reduction in genetic variation.
I and III
93
New cards
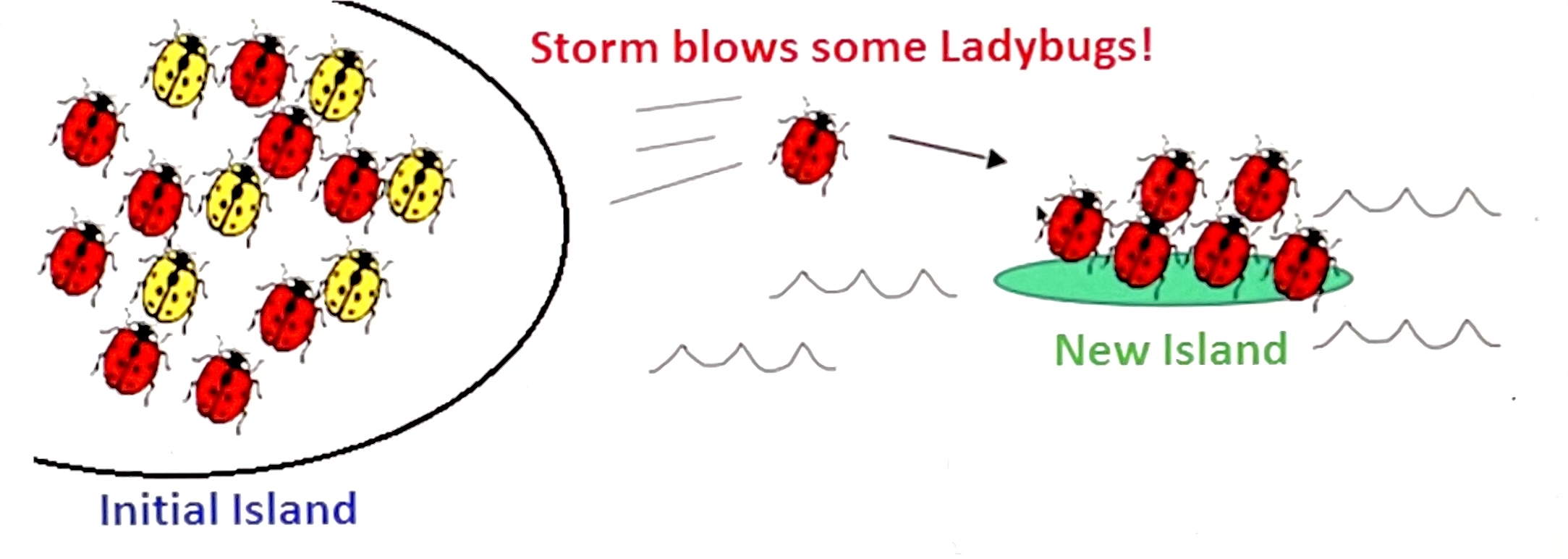
Shown here is a picture of an island with a species of ladybug that comes in two colors, yellow and red. The ladybugs are not strong enough to fly to the new island but there is a large storm that blows several ladybugs onto the new island. The ladybugs on this new island are all red while the ladybugs in the initial population still contain some of the yellow colored ladybugs. The mechanism of evolution for this chance change in allele frequency is called:
genetic drift
94
New cards
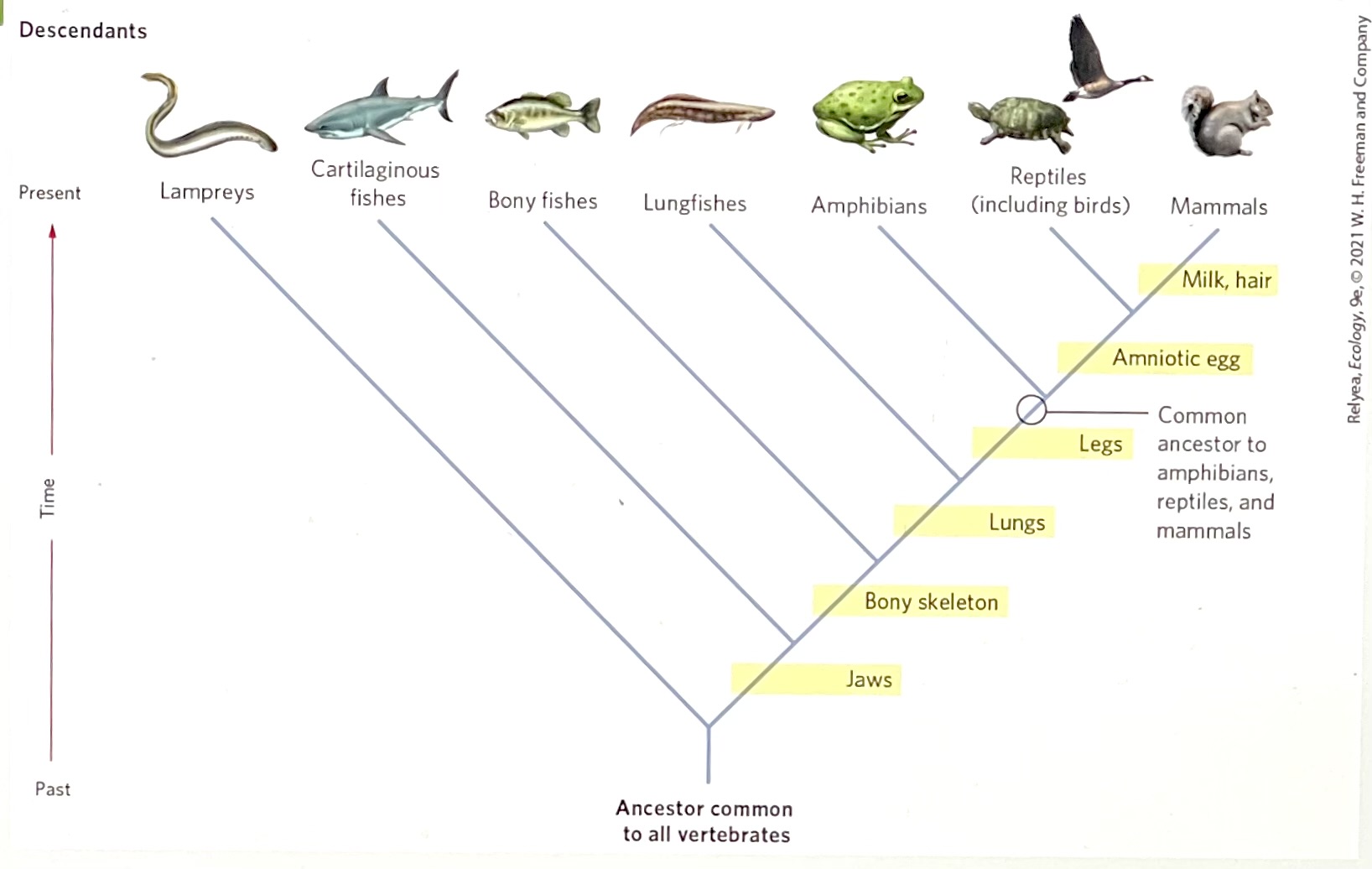
Based on phylogeny in the figure, which traits are shared by bony fishes and amphibians?
jaws and bony skeleton
95
New cards
Which of the following types of allele would we expect to have the lowest frequency in a population?
harmful dominant allele
96
New cards
Select the requirements for evolution by natural selection.
1. The parents in a population overproduce offspring so that some will not survive.
2. Those individuals with traits that make them fitter will be the ones to survive while the least fit die off.
3. Causes of phenomena are purposeful and immutable
4. The individuals in a population display a variation in traits such as color, behavior, size, and shape due to genetic variation.
5. Some of the traits are passed down from parents to descendants and are heritable.
1. The parents in a population overproduce offspring so that some will not survive.
2. Those individuals with traits that make them fitter will be the ones to survive while the least fit die off.
3. Causes of phenomena are purposeful and immutable
4. The individuals in a population display a variation in traits such as color, behavior, size, and shape due to genetic variation.
5. Some of the traits are passed down from parents to descendants and are heritable.
1. The parents in a population overproduce offspring so that some will not survive.
2. Those individuals with traits that make them fitter will be the ones to survive while the least fit die off.
4. The individuals in a population display a variation in traits such as color, behavior, size, and shape due to genetic variation.
5. Some of the traits are passed down from parents to descendants and are heritable.
2. Those individuals with traits that make them fitter will be the ones to survive while the least fit die off.
4. The individuals in a population display a variation in traits such as color, behavior, size, and shape due to genetic variation.
5. Some of the traits are passed down from parents to descendants and are heritable.
97
New cards
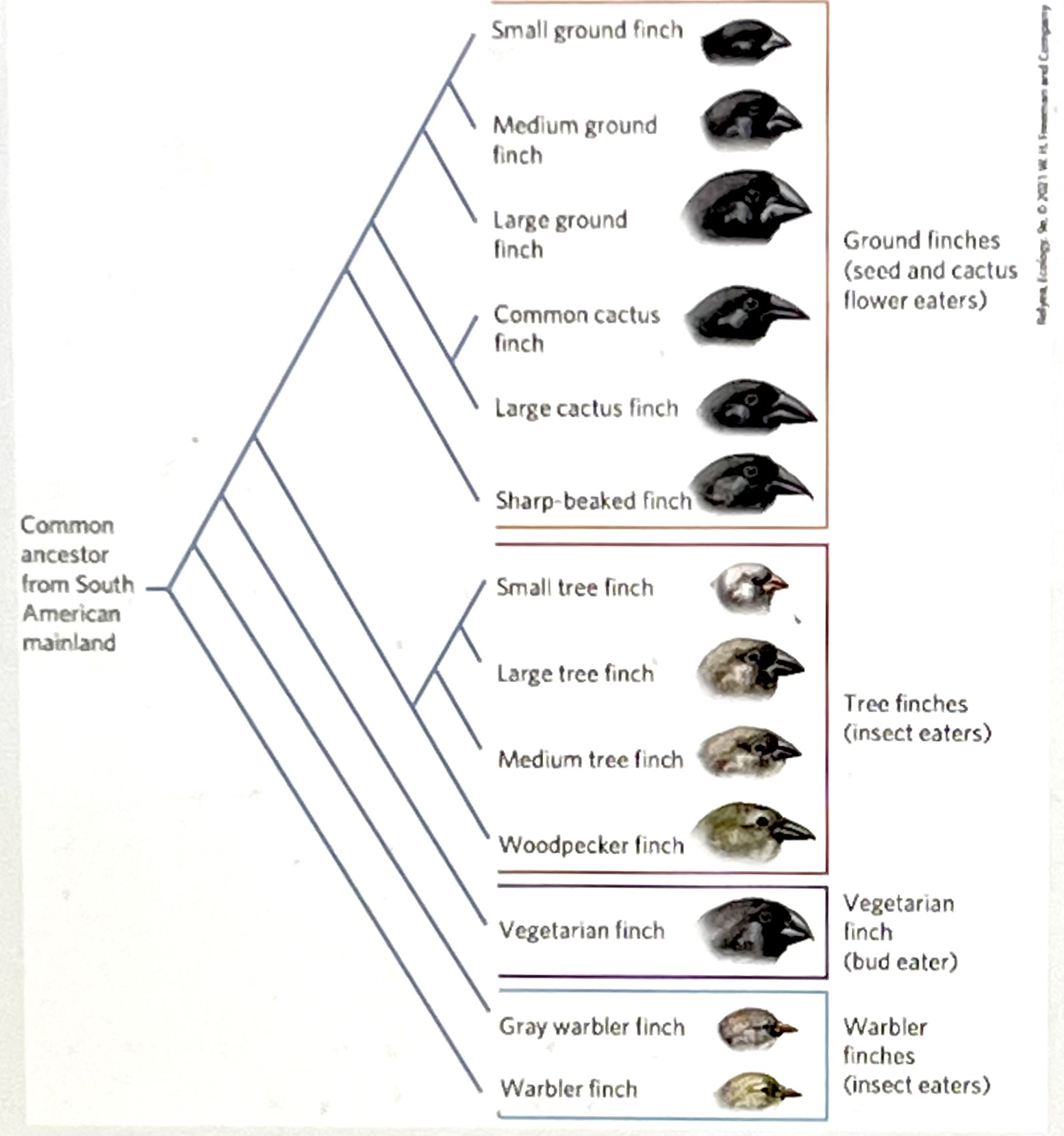
Based on the phylogeny of the Galapagos finches, which statement is correct?
a. The ground finches and the tree finches have no common ancestor
b. The ancestor of the small tree finch and large tree finch probably ate insects.
c. The ancestor of the large cactus finch and common cactus finch likely ate insects.
d. The small tree finch is most closely related to the sharp-beaked finch.
a. The ground finches and the tree finches have no common ancestor
b. The ancestor of the small tree finch and large tree finch probably ate insects.
c. The ancestor of the large cactus finch and common cactus finch likely ate insects.
d. The small tree finch is most closely related to the sharp-beaked finch.
The ancestor of the small tree finch and large tree finch probably ate insects.
98
New cards
When a parental generation undergoes stabilizing selection, how will the distribution of phenotypes in the population change between the parental generation and their progeny?
Mean phenotype stays the same, but variability decreases.
99
New cards
Evolution by artificial selection is similar to evolution by natural selection because:
I. both require traits to be heritable.
II. both incorporate founder effects.
III. both favor certain traits over others.
I. both require traits to be heritable.
II. both incorporate founder effects.
III. both favor certain traits over others.
I and III only.
100
New cards
Fig wasp populations contain a high proportion of females to males because of local male competition. This occurs because:
a large number of females can mate with a single male