UW-Madison - Psych 403 - Vocab 10/11 thru 11/8
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/309
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
310 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomical aspects of the brain
Researchers examine the functions of different parts of the brain and try to determine the physical location and timing of various brain processes
2
New cards
Biochemistry aspects of the brain
Researchers examine the effects of 2 fundamental groups of chemicals: neurotransmitters and hormones
3
New cards
Interneurons
Central nervous system neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs (biggest bundle is in the brain)
4
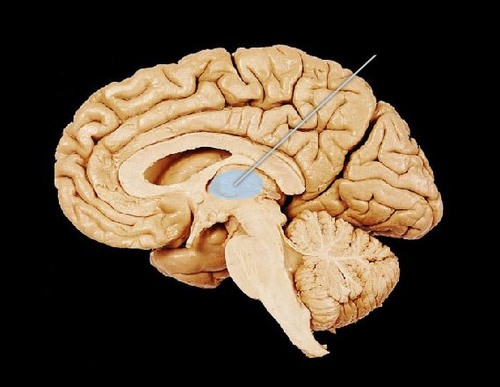
New cards
Thalamus
The brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; regulates homeostatic systems (thirst, hunger, temperature); secretes several hormones (including dopamine)
5
New cards
Hormones
Chemicals produced by your glands that regulate the activities of different body cells (main function is to act throughout the body, stimulating the activity of neurons in many locations in the brain and body at the same time)
6
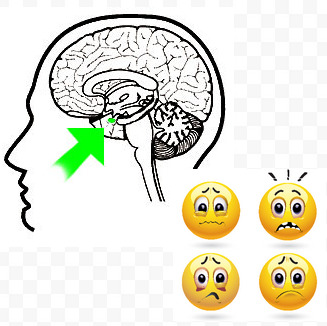
New cards
Amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression
7
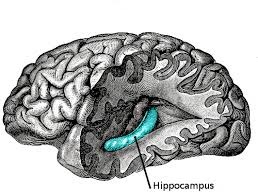
New cards
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage
8
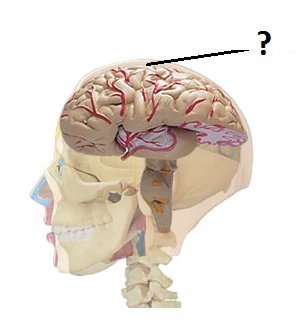
New cards
Cortex
Outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input
9
New cards
Neocortex
The outermost part of the cerebral cortex (making up 80 percent of the cortex in the human brain)
10
New cards
Frontal cortex
Brain region in which most conscious thinking takes place
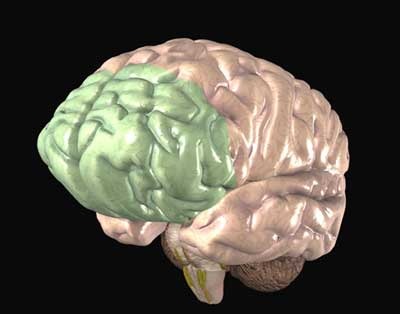
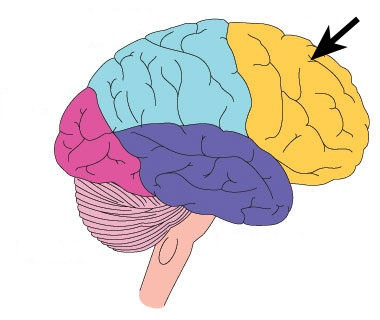
11
New cards
Frontal lobes
Associated with cognitive functioning such as planning, foresight, and understanding; crucial for cognition, planning ahead, anticipating consequences, aspects of emotional experience (empathy, moral reasoning)
12
New cards
Study of brain damage, experiments using brain stimulation, brain imaging
What are the 3 main methods researchers use for learning about how the brain works?
13
New cards
Lesioning
Destroying a piece of the brain
14
New cards
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
Uses rapidly changing magnetic fields to temporarily knock out areas of brain activity
15
New cards
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)
A neuroscience technique that passes mild electrical current directly through a brain area by placing small electrodes on the skull (researchers have found that the right frontal lobe, but not the left, is important for making morally relevant decisions)
16
New cards
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Recording the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes on the scalp
17
New cards
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Technique that measures brain activity by detecting tiny magnetic fields generated by the brain
18
New cards
Tomographs
Very thin slices of the brain
19
New cards
Computed tomography (CT)
A scanning technique using multiple X-rays to construct three-dimensional images
20
New cards
Positronemission tomography (PET)
Tracks the uptake of radioactively labeled glucose to reveal areas of metabolic activity in the brain
21
New cards
Functional magnetic resonance imagine (fMRI)
Uses a powerful magnet to help to detect blood flow in the brain
22
New cards
Blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) signal
The signal typically measured in fMRI that results from changes in the ratio of oxygenated hemoglobin to deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood (calculated as a difference in levels of brain activity between experimental conditions or different individuals)
23
New cards
Perfusion imaging
Used in conjunction with diffusion imaging, relies on fast scanning techniques to visualize the transit time of blood through a specific area (more precise measures than BOLD signals)
24
New cards
Characteristics of the amygdala
Aggression, anger, fear, social attraction, sexual responsiveness; (highly active in shy people when they are shown pictures of people they don't know; people with anxiety disorders tend to have an active amygdala at all times, even at rest) links perceptions and thoughts with emotional meaning; role in assessing whether a stimulus is threatening or rewarding
25
New cards
Frontal lobes and neocortex characteristics
Important for higher cognitive functions such as speech, planning, and interpreting the world
26
New cards
When is the left frontal lobe more active?
When a person wants to approach something pleasant
27
New cards
What is the right frontal lobe associated with?
Wanting to approach something pleasant
28
New cards
What is the left frontal lobe capable of?
Promote good feelings and dampen bad ones
29
New cards
What is an especially active left brain associated with?
Emotional stability
30
New cards
What is an especially active right brain associated with?
Neuroticism
31
New cards
Somatic marker hypothesis
Neurologist Antonio Damasio's idea that the bodily (somatic), emotional component of thought is a necessary part of problem solving and decision making
32
New cards
Capers syndrome
Believe family members/friends are imposters due to lack of emotional connection
33
New cards
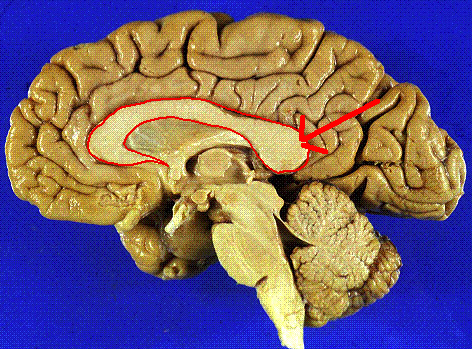
Cingulate
Cognitive control, error detection, conflict monitoring
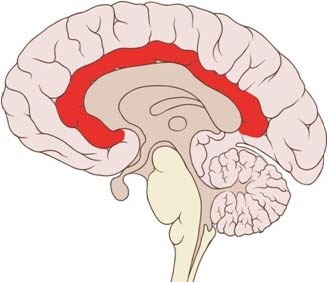
34
New cards
Corpus collosum
The large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
35
New cards
Posterior cingulate
Important for processing information about time and space and in reacting rapidly to threatening situations
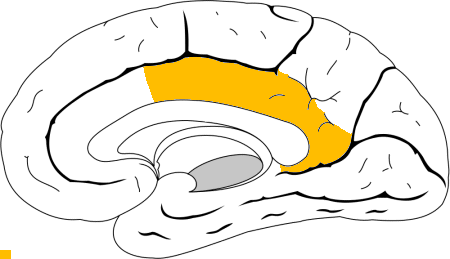
36
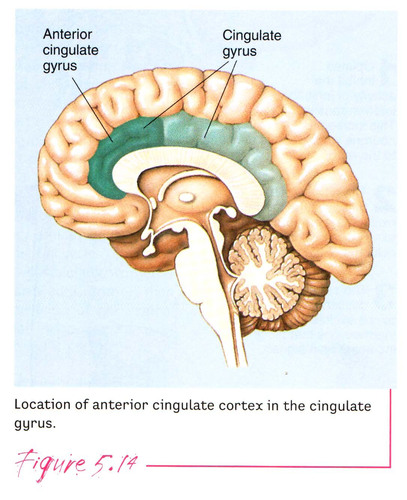
New cards
Anterior cingulate
Important for the experience of normal emotion and self-control (projects inhibitory circuits into the amygdala)
37
New cards
What may be a result when the anterior cingulate is chronically overactive?
Neuroticism
38
New cards
Prefrontal leucotomy (Moniz)
Small areas of white matter behind each of the frontal lobes were deliberately damaged
39
New cards
Psychosurgery
Surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue specifically for altering personality, emotions, or behavior
40
New cards
Prefrontal lobotomy
Psychosurgery in which the connections of the prefrontal lobes of the brain to the rear portions are severed
41
New cards
Persistence
The ability to complete a task in the face of obstacles and in the absence of immediate reward
42
New cards
C-system
Involved in effortful, reflective thinking about the self and others (lateral prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, medial temporal lobe, posterior parietal cortex)
43
New cards
X-system
Involved in effortless, reflexive social thought (ventromedial prefrontal cortex, amygdala, lateral temporal cortex)
44
New cards
Neurotransmitters, hormones
2 important chemicals for behavior
45
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that allow one neuron to affect, or communicate with, another
46
New cards
Chemicals make them up, enzymes break them down
What make up and break down neurotransmitters?
47
New cards
Personality
What are levels of neurotransmitters related to?
48
New cards
Synapse
Space between two neurons across which impulses are carried by neurotransmitters
49
New cards
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord
50
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord
51
New cards
Endorphins
Natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure (operate by blocking transmission of pain messages to the brain)
52
New cards
Monoamine oxide (MAO)
Enzyme that regulates breakdown of neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin (low level of MAO allows these to build up; associated with sensation seeking, extraversion, and criminal behavior)
53
New cards
Dopmaine
Neurotransmitter that impacts our arousal and mood states, thought processes, and physical movement (motivation to action, reward responses)
54
New cards
Dopaminergic systems
Systems affected by dopamine; foundation of plasticity (a general tendency to explore and engage with possibilities)
55
New cards
Nucleus accumbens
A subcortical structure that participates in reward and addiction (in the basal ganglia)
56
New cards
Behavioral activation system (go system)
Produces and reinforces the motivation to seek rewards
57
New cards
Serotonin
Important role in the regulation of emotion and motivation
58
New cards
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
Raise serotonin levels in the nervous system (better classified as "antineurotics" than antidepressants; helps people organize behavior and get work done; get along with others, even annoying ones; avoid mood swings/overreactions; stabilize information processing in the brain and slow things down)
59
New cards
Hypothalamus, gonads, adrenal cortex
What structures release hormones?
60
New cards
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Neurotransmitter in the brain and hormone that is related by the adrenal gland as part of the body's response to stress
61
New cards
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter in the brain associated with responses to stress
62
New cards
Heart speeds up, digestion stops, muscles tense (fight or flight)
What happens when epinephrine/norepinephrine are released into the bloodstream?
63
New cards
Oxytocin
A hormone that is important for mothers in bonding to newborns; emotional attachment and calming; relaxation and reduction of fear ("love hormone")
64
New cards
Testosterone
Male sex hormone, related to aggressive behavior
65
New cards
Cars, sports, victory
What activities can increase testosterone levels?
66
New cards
Violent crime, sexual interest, desire
How does testosterone affect behavior in women?
67
New cards
Anabolic steroids
Synthetic testosterone
68
New cards
Cortisol
Factor of the flight-or-flight response; collective term for glucocorticoid hormones which are released into the bloodstream by the adrenal cortex (people with severe stress, anxiety/depression have chronically high levels of it)
69
New cards
Physiognomic belief
Generic (folk) beliefs that aspects of personality can be inferred from the face
70
New cards
Behavioral genetics
Addresses how traits are passed from parent to child and shared by biological relatives (in traits that differ among individuals) (influence of genes on broad behavior patterns)
71
New cards
Evolutionary psychology
Addresses how patterns of behavior that characterize all humans may have originated in the way these characteristics promoted survival during the early history of the species
72
New cards
Eugenics
The belief that humanity could (and should) be improved through selective breeding
73
New cards
An individual's genes and the environment
Personality is the result of a complex interaction between...
74
New cards
Phenotypes
Observable traits
75
New cards
Genotypes
Genetic makeup of an organism
76
New cards
Monozygotic
Identical twins
77
New cards
Dizygotic
Fraternal twins
78
New cards
Heritability coefficient
Degree to which variance of the trait in the populations can be attributed to variance in genes
79
New cards
(rMZ - rDZ) x 2
Heritability quotient
80
New cards
Allele
Particular variant/form of a gene; most genes have 2 or more alleles
81
New cards
DRD4
Gene that affects development of dopamine receptors (different forms associated with attention-seeking) (associated with risk for ADHD)
82
New cards
40%
Average heritability (twin studies)
83
New cards
20%
Heritability from non-twin studies
84
New cards
Genome-wide association (GWA)
Data concerning hundreds of thousands of genes and patterns of genes in thousands of people are compiled into a computer with information about these peoples' personalities
85
New cards
Difficult and expensive, large numbers of people need to be examined to provide sufficient data; in many analyses performed, results may be merely due to chance
Characteristics of GWAs
86
New cards
Epigenetics
Nongenetic influences on a gene's expression, such as stress, nutrition, etc. (experience, especially in early life, can influence how or whether a gene is expressed during development)
87
New cards
Aggression
Can help a person protect territory, property and mates, and also lead to dominance int he social group and higher status; can also lead to fighting, murder, and war
88
New cards
Altruism
A tendency to aid and protect other people; might help ensure the survival of one's own genes into succeeding generations, an outcome called inclusive fitness
89
New cards
Inclusive fitness
Adaptive benefit of transmitting genes rather than focusing on individual survival
90
New cards
Self-esteem
Evolved to monitor the degree to which a person is accepted by others (sociometer theory)
91
New cards
Sociometer theory
The theory that self-esteem is a gauge that monitors our social interactions and sends us signals as to whether our behavior is acceptable to others
92
New cards
Survival value
Why might have depression evolved?
93
New cards
Pain, crying, seeking social support
What is depression following a social loss characterized by?
94
New cards
Fatigue, pessimism, shame, guilt
What is depression following failure characterized by?
95
New cards
Signal something has gone wrong and must be fixed; risk to chances of reproduction
How are pain and emotional pain beneficial to survival?
96
New cards
Fast life history
Species that live in dangerous circumstances and typically die young

97
New cards
Slow life history
Long-lived species that have a chance for extended protection and nurturing of their offspring

98
New cards
methodology, reproductive instinct, conservative bias, human flexibility, biological determinism or social structure
5 stress tests for evolutionary psychology
99
New cards
Methodology of evolutionary theorizing
Degree to which people are consciously aware of following evolutionary strategies to promote survival and reproduction
100
New cards
Biological reductionism
Everything about the mind can be reduced to biology