NERVOUS SYSTEM
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
1
New cards
neuron
individual nerve cell that allows neural communication
2
New cards
sensory neurons
recive and carry sensory info from external and internal enviroments to the cns
3
New cards
internuerons
in spinal chord, send messages between sensory and motor neurons
4
New cards
motor neurons
· Carry messages from cns to cells in organs muscles and glands to simulate activity
5
New cards
key rolls of ns
recive- receive sensory info from extranl and internal body part, going to brain
process- brain processes
respond- motor neurons transmit info from brain to muslces organs or glands. movment, relase of hormones, increase or decrease in funtion
process- brain processes
respond- motor neurons transmit info from brain to muslces organs or glands. movment, relase of hormones, increase or decrease in funtion
6
New cards
cns- brain and spinal cord
· Coordinates all incoming sensory info and initiates outgoing motor messages to body
· Both conscious and unconscious commands
· Both conscious and unconscious commands
7
New cards
brain
· Communicate with the body via the spinal chord and cranial nerves
· The control centre of the body
· Receive and process sensory stimuli from body
· Coordinate mental processes and behavior, regulate body activitys
· The control centre of the body
· Receive and process sensory stimuli from body
· Coordinate mental processes and behavior, regulate body activitys
8
New cards
cns- spinal chord
· Dense bundle of fibres
· Connects brain to other parts of body via pns
· Carry sensory info from the body (pns) towards brain
· Carry motor info from brain to body
· Connects brain to other parts of body via pns
· Carry sensory info from the body (pns) towards brain
· Carry motor info from brain to body
9
New cards
sensory pathways
● Sensory receptors send info to spinal cord via sensory neurons then to the brain via interneurons
10
New cards
motor pathways
● Info travels from brain to spinal cord via interneurons, then to the muscles organs and glands via motor neurons
11
New cards
pns
all parts of ns exept brain and spinal chord
· Sensory function - Carry sensory info from sensory organs to cns
· Motor function- carry motor info from cns to muscles organs and glands
· Sensory function - Carry sensory info from sensory organs to cns
· Motor function- carry motor info from cns to muscles organs and glands
12
New cards
somatic ns
sensory info from receptors to cns by sensory neurons ·
motor info from cns to muscles via motor neurons ·
All voluntary movement of skeletal muscles
· Any reception of sensory stimuli and taking to brain is by somatic nervous system
motor info from cns to muscles via motor neurons ·
All voluntary movement of skeletal muscles
· Any reception of sensory stimuli and taking to brain is by somatic nervous system
13
New cards
autonomic ns
·· Define- carry neural messages between cns and visceral muscles (smooth self regulating muscles)
· Controls all automatic internal organ function (unconscious)
· Maintain homeostasis
· Controls all automatic internal organ function (unconscious)
· Maintain homeostasis
14
New cards
sympathetic ns - division of autonomic ns
· Activates internal muscles organs and glands to prepare body for vigerous activity or deal with stressful situation
· Flight fright or freeze response
· Flight fright or freeze response
15
New cards
parasympathetic
· Maintain homeostasis
· Restore body to calm state after threat has passed
· Reverse effects of sympathetic ns
· Restore body to calm state after threat has passed
· Reverse effects of sympathetic ns
16
New cards
pupils responce
· s- dilate to let more light to enhance vision
· p- constrict
· p- constrict
17
New cards
salivery gkands responce
· s- inhibits salvation (dry mouth) as digestion is not needed to store more energy for stress situation
· p- stimulate salvation
· p- stimulate salvation
18
New cards
heart
· s- increase hr and blood pressure allow more o2 supply to muscles
· p- decrease hr and bp
· p- decrease hr and bp
19
New cards
lungs
· s- increase respiration and o2 levels to allow mor o2 to muscles to enable action
· p- slow breathing
· p- slow breathing
20
New cards
stomach
· s- slow digestion as it us not a vital survival function
· p- stimulate digestion
· p- stimulate digestion
21
New cards
liver
· s- release of glucose to provide extra energy to muscles
· p- decrease glucose
· p- decrease glucose
22
New cards
adrenal gland
· s- release adrenaline into blood to enhance body functions including hr and breathing rate
· p- not released
· p- not released
23
New cards
bladder
· s- relaxes as its not a vital body function for survavival
· p- contract and hold in urine
· p- contract and hold in urine
24
New cards
sweat glands
· s- you sweat to cool body down
· p- decrease sweating
· p- decrease sweating
25
New cards
example- recive and responding
receptor sites (name receptor site and type of info) receive incoming sensory info, via the somatic nervous system. The info is sent to the cns via sensory neurons. The info is then sent to the brain via the spinal chord, through the afferent tract (interneurons), where the brain processes the information. The brain then processes the info, and initiates a motor response, and sends motor neurons down the spinal chord via the efferent tract, then to the muscles organs and glands (effector site). This is the somatic ns or autonomic, as it is a conscious/unconsious response.
26
New cards
neuron
Nerve cells that carry messages through electro chemical processes.
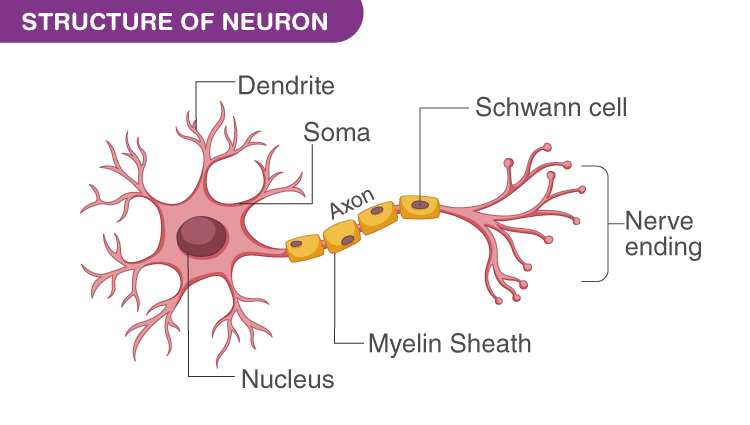
27
New cards
neurons- dentrite
· Dentrites - detect and receive neural info from other neurons
28
New cards
soma
detirmins whether the nerve will be activated, and thus send info to other neurons, contains a nucleas
29
New cards
axon
· Axon- tube extension that sends neural messages from the soma to the axon terminals
30
New cards
mylin sheath
· Myelin sheath- white fatty substance that surrounds and insulates an axon, speeds transmission of messages
31
New cards
axon terminals
· Axon terminals - Branches at end of axon that release neurochemicals into the synaps
32
New cards
process of communicating between neurons
· Info detected at dentrite, neural info travels through the soma, down the axon to the axon temrinals where neurochemicals are realieased into synaps.
Pre synaptic neuron -\> synapse -\> post synaptic neuron
Pre synaptic neuron -\> synapse -\> post synaptic neuron
33
New cards
trasnmission of info across synaps - step 1
· Step 1 - neural message reaches terminal button, synaptic vesicles that contain neurotransmitters move towards synaptic gap
34
New cards
step 2
· Step 2- neurotransmitters released into synaptic gap
35
New cards
step 3
· Step 3- neurotransmitters bind to matching receptor site of post synaptic neuron
36
New cards
step 4
· Step 4 - this binding 'unlocks' the post synaptic neuron
37
New cards
step 5
· Step 5- leftover neurons are either reabsorbed by the terminal button (reuptake), diffused (drift away) or broken down by enzymes
38
New cards
consious responce
awareness and is voluntary, and you can control it.
39
New cards
aspects
-Goal directed and purposeful, paid attention to the incoming sensory info before responding , Responses can be learn, Initiated by brain
40
New cards
unconsious responce
reaction that doesn't involve awareness, involuntary and automatic, cannot control, Don't have to pay attention to incoming sensory stimulus to respond
41
New cards
types of unconsious responces- physiological responses of autonomic nervous system
· functions controlled by autonomic ns can be classified as unconscious response, as they occur automatically without conscious control
42
New cards
types of unconsious responces- spinal reflex
· unconscious response to a sensory stimulus which is initiated by the interneurons in the spinal chord independently of the brain, when there is potential danger.
43
New cards
spinal reflex step by step
1- dangerous stimulus detected by sensory receptors
2- sensory neurons carry message along somatic ns pathways to spinal chord
3- interneurons in spinal chord relay sensory message to a motor neuron
4- motor neuron in the somatic ns carry message out from spinal chord to skeletal muscles
5- automatic involuntary unconscious response occurs in the effector muscle
6- simultaneously with step 3, message continues to brain
7- brain process stimulus after response has occurred, other consoius responses may now occur
2- sensory neurons carry message along somatic ns pathways to spinal chord
3- interneurons in spinal chord relay sensory message to a motor neuron
4- motor neuron in the somatic ns carry message out from spinal chord to skeletal muscles
5- automatic involuntary unconscious response occurs in the effector muscle
6- simultaneously with step 3, message continues to brain
7- brain process stimulus after response has occurred, other consoius responses may now occur
44
New cards
neurotransmitters produce 2 effects- excitory effect
· neuro transmitters activate post synaptic neurons to perform their functions
45
New cards
funtion
Speed up neural activity, Increase likely hood that excitatory signal is sent, Regulate basic functions
46
New cards
glucamate
· Primary excitatory neurotransmitters in the cns
making post synaptic neurons more likely to fire
memory and learning
making post synaptic neurons more likely to fire
memory and learning
47
New cards
neurotransmitters produce 2 effects- inhibitory effect
neuro transmitters prevent post synaptic neurons from firing
48
New cards
funtion
· Decrease the likelihood that an excitatory signal will be sent, Slows down neural activity, Associated with sleep, calmness and decreased aggression
49
New cards
GABA
· Primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the cns
· Makes post synaptice neurons less likely to fire
· Prevent over activation
· Calming feelings
gaba blocks neural pathways- excess leads to anxiety
· Makes post synaptice neurons less likely to fire
· Prevent over activation
· Calming feelings
gaba blocks neural pathways- excess leads to anxiety
50
New cards
GABA and glucamate
· inhibitory action of GABA and the excitatory action of glutamate work together, GABA acts like a calming agent to the excitatory activity of glutamate
51
New cards
How does the post synaptic neuron know which neurotransmitter it has received?
neuro transmitters have distinct shape, so when released it searches for matching receptor site on post neuron, if they match it binds to create desired change in neuron
52
New cards
Neuromodulation
synaptic transmission between 2 neurons is either enhanced or decreased through the action of a neuromodulator
53
New cards
neuro modulator
chemical molecule that influences multiple post synaptic neurons. released in the same way as neurotransmitters
54
New cards
what does it do
ability to talk to many post synaptic neurons, rather than just one. More efficient transmission, enhances excitatory or inhibitory effect. Eg sees gaba trying to slow and helps it out
55
New cards
how do neuromodulators work
1. Increase or decrease rate of neuro transmitter released
2. enhancing neurotransmitter excitatory or inhibitory effect
3. altering the rate at which neurotransmitters are broken down, thereby regulating the duration of neurotransmitter signals.
2. enhancing neurotransmitter excitatory or inhibitory effect
3. altering the rate at which neurotransmitters are broken down, thereby regulating the duration of neurotransmitter signals.
56
New cards
neurotransmitter vs neuro modulator - differences
Differences ·
NT affects only one or two post-synaptic neurons at once WHEREAS NM affects a group/multiple post-synaptic neurons at once ·
NT =short rapid effect, NM = long slow, l
NT directly affect the post-synaptic neuron
WHEREAS NM indirectly affects the post-synaptic neurons by enhancing the effect of the NT
NT affects only one or two post-synaptic neurons at once WHEREAS NM affects a group/multiple post-synaptic neurons at once ·
NT =short rapid effect, NM = long slow, l
NT directly affect the post-synaptic neuron
WHEREAS NM indirectly affects the post-synaptic neurons by enhancing the effect of the NT
57
New cards
neurotransmitter vs neuro modulator- similarities
Similairies
· Both are chemical messenger
· Both released from a pre-synaptic neuron
· Both bind to receptors on the post-synaptic neuron
· Both are chemical messenger
· Both released from a pre-synaptic neuron
· Both bind to receptors on the post-synaptic neuron
58
New cards
Examples of neuromodulators - Dopamine
· Voluntary motor movements, smooth coordination
· Reward based learning- when you do something and get a reward, dompamine released
· Motivation
· Reward based learning- when you do something and get a reward, dompamine released
· Motivation
59
New cards
Examples of neuromodulators - seritonin
· Mood regulation and stabilisation
· sleep
· sleep
60
New cards
synaptic plasticity
· The ability of synaptic connections to be changed over time in response to experience
61
New cards
sprouting
· The ability of dendritic spine and ax filigree appendages to develop new extensions or branches
62
New cards
rerouting
· Forming new connections between neurons to establish alternative neural pathways. Only occurs if you wish to change a skill
63
New cards
pruning
· Elimination of unused neural connections and strengthen used connections. Improves number of connected neurons which increases speed and effcency of brain function
64
New cards
long-term potentiation
· The increase likely hood of a group of neurons to fire together due to repeated stimulation.
ie As neural pathways is used more and more, signal across synaps becomes stronger
ie As neural pathways is used more and more, signal across synaps becomes stronger
65
New cards
Changes to the synapse - Functional change
· change to the process of neurotramission
eg The change in the quantity of neurotransmitter gluatamate being released
eg The change in the quantity of neurotransmitter gluatamate being released
66
New cards
Changes to the synapse - structual change
· change to the physical structure of neurons.
· number of dendritic branches on post synaptic neuron
· growth of filigree appendages on axon terminals on pre neuron due to sprouting.
· Change in number of receptor sites on post synaptic neuron.
· number of dendritic branches on post synaptic neuron
· growth of filigree appendages on axon terminals on pre neuron due to sprouting.
· Change in number of receptor sites on post synaptic neuron.
67
New cards
steo by step long term potential
1- functional change of increased neurotransmitter occurs due to continuously doing a task
2- Axon terminals on presynaptic neuron release glutamate
3- Glutamate cross synapse and binds to glutamate receptor on post synaptic neuron
4- Repeated stimulation of the neural circuit (repeating a task) results in more glutamate
5- repeated stimulation triggers structural change
6- First sprouting occurs (if changing the skill, rerouting also occurs)
7- Then this results in increased number of receptor sites on post synaptic neuron.
8- This all strengthens the connections between neurons to make them communicate more effectively
2- Axon terminals on presynaptic neuron release glutamate
3- Glutamate cross synapse and binds to glutamate receptor on post synaptic neuron
4- Repeated stimulation of the neural circuit (repeating a task) results in more glutamate
5- repeated stimulation triggers structural change
6- First sprouting occurs (if changing the skill, rerouting also occurs)
7- Then this results in increased number of receptor sites on post synaptic neuron.
8- This all strengthens the connections between neurons to make them communicate more effectively
68
New cards
long term depression
-Permanent weakening of synaptic connected as a result of low level activation
69
New cards
this leads to
· Less neuron transmitters being released
· extra dendrites and axon terminals are pruned
· extra dendrites and axon terminals are pruned
70
New cards
importance of LTD
· forget the old to be able to strengthen the new.
71
New cards
stressor
stimuli that caused stress and challenges ones abilitys to cope
72
New cards
internal vs external stressors
internal
· Comes from within individual
· Phychological and physiological processes
· Eg pain, illness, negative attitudes
external
· Comes from outside individual
· Environmental factors / activities
· Eg loud noise, relationship troubles
· Comes from within individual
· Phychological and physiological processes
· Eg pain, illness, negative attitudes
external
· Comes from outside individual
· Environmental factors / activities
· Eg loud noise, relationship troubles
73
New cards
stress
· A state of physiological or psychological arousal produced by internal or external stressors that are perceived by individual as challenging or exceeding their ability to cope.
74
New cards
acute vs chronic
· acute - high arousal level for shprt period of time
· chronic stress- ongoing worries that are long lasting
· chronic stress- ongoing worries that are long lasting
75
New cards
eustress
· positive **psychological** response to stressor
· excitement, motivation, and enthusiasm
· short term, not harmful, help achieve goal
· excitement, motivation, and enthusiasm
· short term, not harmful, help achieve goal
76
New cards
distressed
· negative psychological response to stressor
· negative psychological state such as anxiety
· can be short or long term, if it persists it impacts mental health
· negative psychological state such as anxiety
· can be short or long term, if it persists it impacts mental health
77
New cards
non specific stress response
· regardless of pos or neg stressor, body will undergo the same pysciological changes
· eg both getting ready for first date and prepping for exam you will get sweaty and flushed
· eg both getting ready for first date and prepping for exam you will get sweaty and flushed
78
New cards
acute stress and FFF
· acute stress will lead to flight or fight or freeze response (physiological reaction
· aids survival
· involuntary and automatic
· aids survival
· involuntary and automatic
79
New cards
key features of FFF
· adaptive response- gives body all necessary resources to maximise survival
· activated when confronted with a stressor
· physiological response
· controlled by autonomic ns
· activated when confronted with a stressor
· physiological response
· controlled by autonomic ns
80
New cards
FFF responce
· involuntary physical response to sudden and immediate threat eg stressor
· to minimuse harm and keep us safe
1. fight- confront and ward off threat
2. flight- escape
3. freeze- stay silent to avoid detection
· to minimuse harm and keep us safe
1. fight- confront and ward off threat
2. flight- escape
3. freeze- stay silent to avoid detection
81
New cards
physiological changes during FFF
· increase hr and bp
· blood redistributed to muscles
· increase rr
· increase glucose secretion for energy
· pupils dialate
· blood redistributed to muscles
· increase rr
· increase glucose secretion for energy
· pupils dialate
82
New cards
freeze response- how
Sympathetic ns activates, then parasympathetic also activates, When freeze stops, individuals ready to flee as body is highly engaged
83
New cards
features
· features- vocalisation stops, heart rate and blood pressure drop suddenly, keeping the body ready for action, but staying still, conserving energy for when it needs to run or fight.
· tonic immobility- the body freezes in response to threat (muscles are still by tense)
· Adaptive value of Freeze -Avoid predator detecting you, Conserve energy
· tonic immobility- the body freezes in response to threat (muscles are still by tense)
· Adaptive value of Freeze -Avoid predator detecting you, Conserve energy
84
New cards
cortisol
maintains body at high state of arousal/energise
increase blood sugar (secrete glucose) and metabolism,
supresses immune system
increase blood sugar (secrete glucose) and metabolism,
supresses immune system
85
New cards
on going stress
· If corsisol remains high for long time
· Supress immune system function
· Increase vunrability to diseas
· Coles and flu
· Mental health issues
· Supress immune system function
· Increase vunrability to diseas
· Coles and flu
· Mental health issues
86
New cards
Biological (physiological) responses to stress
· 2 widely used models for describing physiological stress response are
· Flight fight freeze
· General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
· Flight fight freeze
· General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
87
New cards
GAS
· Three stage physiological stress response produced by the body as a way of adapting and dealing with any stressor that is encountered
· Explains how body responds to chronic stress
· Explains how body responds to chronic stress
88
New cards
alarm
· Body first comes aware of stressor
· Shock phase- body acts injured, drop blood pressure, body temp and muscle tone, less effective than normal in dealing with the stressor
· Counter shock - activate sympathetic ns. Resistance to stressor increase (fight flight or freeze response is occurring). Adrenaline then cortisol is released
· Shock phase- body acts injured, drop blood pressure, body temp and muscle tone, less effective than normal in dealing with the stressor
· Counter shock - activate sympathetic ns. Resistance to stressor increase (fight flight or freeze response is occurring). Adrenaline then cortisol is released
89
New cards
resistance
· If stressor is not dealt with, state of stress continues and resistance stage is entered
· Intense arousal of alarm stage goes away, but physiological arousal remains higher than usual
· Body can cope with original stressor, but less so with additional stressors
· Cortisol continues to be released to energise the body, increase glucose in blood stream and heal any damage
· Supresses immune system
· Resistance to initial stressor has increased, decerasding resistance to other stressors
· Intense arousal of alarm stage goes away, but physiological arousal remains higher than usual
· Body can cope with original stressor, but less so with additional stressors
· Cortisol continues to be released to energise the body, increase glucose in blood stream and heal any damage
· Supresses immune system
· Resistance to initial stressor has increased, decerasding resistance to other stressors
90
New cards
exhaustion
· If stressor not dealt with and stress continuous, individual is in exhaustion
· Deplete energy stores, no longer deal with stressor
· Lead to phycological and physiological symptoms
· In extreme cases, can lead to death
· Resistance to disease is very weak as cortisol has been supressing immune system for long time
· Lead to illness, depression, anxiety
· Deplete energy stores, no longer deal with stressor
· Lead to phycological and physiological symptoms
· In extreme cases, can lead to death
· Resistance to disease is very weak as cortisol has been supressing immune system for long time
· Lead to illness, depression, anxiety
91
New cards
difference between resistance and exhuation
· Length of time delaing with stressor
· Still coping or functioning - people in restistance can be sick but still manage to go to school ect
· Severity of illness- eg cold versus the flu
· Still coping or functioning - people in restistance can be sick but still manage to go to school ect
· Severity of illness- eg cold versus the flu
92
New cards
strengths
· empirically info about physiological response to a range of stressors
· Identify physiological stress response model
widely accepted within both psychology and medicine
· Identify physiological stress response model
widely accepted within both psychology and medicine
93
New cards
limitations
· does not take into account individual differences in physiological responses to stressor
· based on research with animals - this may explain the reliance of physiological factors
· based on research with animals - this may explain the reliance of physiological factors
94
New cards
Transactional model of stress and coping
95
New cards
primary apraial- does this matter to me
1. Irrelevant - doesn't effect me, no further action
2. Benign positive- harmless or pleasant, no further action
3. Stressful- engange further
2. Benign positive- harmless or pleasant, no further action
3. Stressful- engange further
96
New cards
stress - additional appraisal
1. Harm/ loss- assessment how mauch damage has alrwady occurred
2. Threat- additional harm that may occur in the future
3. Challenge- assessment of person gain or growth that may come form situation.
2. Threat- additional harm that may occur in the future
3. Challenge- assessment of person gain or growth that may come form situation.
97
New cards
secoundary appraisal
what coping options are available and how to deal with situation. - "how am I going to deal with this"
1. Coping resources are inadequate- stress
2. Coping sources greater than demand- low stress
1. Coping resources are inadequate- stress
2. Coping sources greater than demand- low stress
98
New cards
strenths and limitations
Strengths
· Human subjects
· Personal nature of stress response
limitations
· Difficult to experiment on
· Human subjects
· Personal nature of stress response
limitations
· Difficult to experiment on
99
New cards
context specific awarness
appropriate match between coping strategy , the stressor and the situation.
Coping strategy appropriate for unique demands of stressor
Coping strategy appropriate for unique demands of stressor
100
New cards
coping flexability
adjust coping strategies according to the demands of different stressful situations. (recognise when a strategy isn't working and change it)