! BIOL 1410 Urinary system
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LECTURE 16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the 4 structures of the urinary system (and how many there are of each)?
2 kidneys, 2 ureters, 1 urinary bladder, 1 urethra
What 4 things does the urinary system regulate?
Blood volume, blood pressure, pH, ion concentrations
What are some examples of wastes the urinary system eliminates?
E.g. urea, uric acid, hormones, drugs
What does retroperitoneal mean?
Refers to a structure situated behind the peritoneum
What is the peritoneum?
Serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity + most of the abdominal organs
Which kidney is placed lower than the other (right/left)?
Right (lower than left)
What are the 3 layers (outer → inner) of CT of the kidneys?
Fibrous capsule, perirenal fat capsule, renal fascia
What is the renal hilus (hilum)?
Medial indentation of the kidneys, entry point of renal artery/vein, ureter, nerves
Which is superior/inferior in the renal hilus; renal artery + renal vein
Renal artery (superior), renal vein (inferior)
What are the 2 main components of the internal anatomy of kidneys?
Renal cortex, renal medulla
Of the two components of the internal anatomy of kidneys, which is superficial?
Renal cortex
What is contained in the renal cortex?
Contains parts of nephrons, afferent/efferent arterioles, glomeruli
What are glomeruli?
Tiny, specialized blood vessels in kidneys, primary filters for bloodstream
Differentiate between afferent and efferent arterioles, small blood vessels in the kidneys
Afferent (larger, carries blood to site of filtration), efferent (smaller, carries blood away from site of filtration)
What 2 things are contained in the renal medulla?
Renal pyramids, renal columns
What is the apex (tip) of the renal pyramid called?
Renal papilla
What is contained in the renal pyramids of the renal medulla?
Parts of nephrons
What are renal columns of the renal medulla?
Projection of cortex
What do the renal columns separate?
Pyramids
What is contained in the renal columns of the renal medulla?
Blood vessels
What is a nephron?
Microscopic functional filtering unit of the kidneys to produce urine
What are the 2 components of a nephron?
Renal corpuscle, renal tubules
Where is the renal corpuscle of a nephron located?
In cortex (outer layer)
What is the renal corpuscle the site of (and first step of)?
Blood filtration (aka first step in urine formation)
What are the 4 parts of the renal corpuscle?
Glomerulus, afferent arteriole, efferent arteriole, Glomerular (Bowman’s) Capsule
What component of the renal corpuscle is the capillary bed?
Glomerulus
What major/subtype tissue is the glomerulus composed of?
Simple squamous epithelium
Glomerulus’ contain fenestrations between cells. What is meant by this?
Fenestrations are small pores within the cytoplasm of certain cells to facilities efficient exchange, crucial for the kidneys’ filtration function
The afferent arteriole enters the glomerulus, carrying blood from the ______ ________ to the _______.
“renal artery,” “kidney”
The efferent arteriole exits the glomerulus, draining into what 2 structures?
Peritubular + vasa recta
What structures surrounds the glomerulus?
Glomerular (Bowman’s) Capsule
What does the Glomerular (Bowman’s) Capsule collect from the glomerulus?
Filtrate
There are 2 layers of the Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule. What is the major/subtype tissue of the outer layer?
Simple squamous epithelium
There are 2 layers of the Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule. What cell is contained in the inner layer, and where are they found?
Podocytes; wrapped around glomerular capillaries
The filtration membrane of the renal corpuscle consists of what 3 things?
Glomerular endothelium (capillaries), basement membrane, podocytes
Glomerular endothelium of the filtration membrane within the renal corpuscle are simple squamous epithelium with pores. These pores are called (review)?
Fenestrations
Podocytes are projections that form?
Network of filtration slits
What are the 4 parts of renal tubules (second component of a nephron)?
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT), nephron loop, Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT), collecting ducts
What does the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) receive (and from where)?
Receives filtrate from glomerular capsule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) is composed of what subtype of epithelium and _________
Simple cuboidal epithelium, “microvilli”
What does the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) take and give to filtrate?
Reabsorbs useful substances from filtrate, secretes waste into filtrate
The Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) is found in what region?
In cortex
The nephron loop is found in what region?
In medulla
Is the descending or ascending limb of the nephron limb thin/thick?
Descending (thin), ascending (thick)
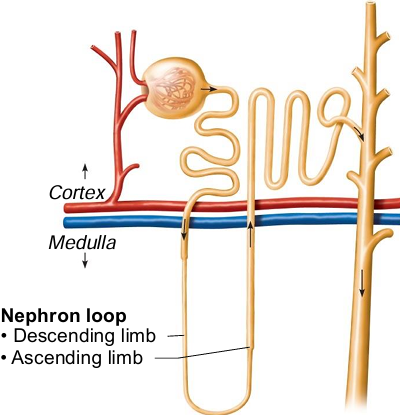
The one of the limbs of the nephron loop is highly water permeable, while the other is water impermeable. Which is which?
Descending (water permeable), ascending (water impermeable)
The descending and ascending limbs are both epithelium, but are of different subtypes. State each.
Descending (simple squamous), ascending (simple cuboidal)
pg. 69
ss