Bio 111 Cumulative Part Final
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
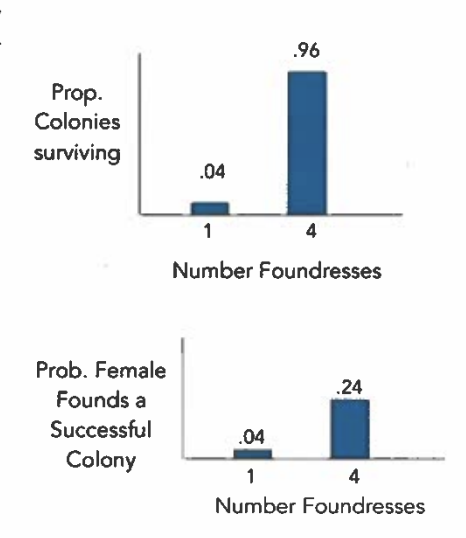
The following data are an example of how ecological constraints can favor cooperation. Note that the foundresses are not related. Explain both graphs and how they show why cooperation among unrelated individuals is better than establishing a colony alone.
The top graph shows that the probability of colony survival is much higher (0.96) if 4 females (=foundresses) cooperate to build a nest than if a female (1 foundress) starts a nest alone (0.04). The bottom graph indicates the probability of colony survival after the four original foundresses fight over .96 possession of the nest and only one inherits it. Selection favors cooperation in this case because the chance of having a successful colony for one female is still much greater in a nest that started with 4 foundresses (0.24) than if a female tries to start a nest alone (0.04). The upshot is that it 1 4 is better to cooperate, even with non-relatives, when the nest is established and have a one in four chance of being the queen of the nest than start a nest alone.
What are two short term disadvantages of recombination, or sex?
I. Recombination breaks up adaptive combinations of genes
2. Sex reduces the rate at which females pass genes on to their offspring
3. Dividing offspring into separate genders greatly reduces the overall reproductive rate
How does inbreeding change the frequency of homozygotes and heterozygotes in the following generation?
Frequency of homozygotes increases and frequency of heterozygotes decreases
Compare and Contrast: Founder event and allopatric speciation
Founder events occur when one ora very fewindividuals from a much larger population begin a new population.
Allopatric speciation refers to species formation due to the separation of populations by a natural barrier such as formation of a mountain or canyon, glaciation etc.
Founder events result in the loss of genetic diversity because of the small number of individuals involved but genetic diversity is not necessarily lost when speciation occurs allopatrically. Founder events also do not invariably lead to species formation, while speciation by alloparty does by definition.
Compare and Contrast: Correlation and causation
Correlation occurs when two variables are related, either positively or negatively or not at all.
Causation is when one variable causes another. Correlations show variables are changing predictably but not necessarily because of cause and effect.
Cause and effect is often demonstrated by experimentation- correlations are observed patterns but can also be demonstrated by experiments
Compare and Contrast: Common garden experiment and cross fostering experiment
Common garden experiments are used most often on plants (but not always) that can be grown in the same location so that all individuals experience identical environments.
Cross fostering experiments involve translocating offspring to be raised by parents with different phenotypes. This randomizes the environment contribution to the phenotype.
Both experiments are used to estimate the heritability component of traits. In both experiments the variation amongindividuals will represent the heritable component of a trait.
Explain how the composition of individuals in populations change over generations under natural selection and under artificial selection.
In natural selection, the proportion of individuals with favorable traits in the last generation will increase the following generation and the proportion of individuals with poorly adapted traits will decrease. Changes in the population under artificial selection will be completely represented by individuals the humans preferred.
Explain what causes populations to change under natural selection and artificial selection.
Changes in populations due to natural selection are because individuals with favorable traits have more offspring than others. Humans that select traits they prefer are what cause populations change under artificial selection.
Why is the biological species concept (BSC) not applicable to asexually reproducing organisms?
The BSC defines species as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Organisms that reproduce asexually do not interbreed.
What is a nonsense mutation and what is a consequence to a protein if it occurs in a coding gene?
Nonsense mutations result in a stop codon. If this occurs in a protein coding gene, it will make the gene nonfunctional or a pseudogene.
What is Lyell’s theory of uniformitarianism and why was it critically important to Darwin as he formulated of the theory of evoLution by natural selection?
Darwin realized that natural selection was a very slow process and if he was right, that it generated all life on earth, this would take a very long time. Uniformitarianism proposed that given enough time everyday process such as erosion, the tides, etc. could explain formation of massive river deltas, canyons and otherfeatures. The implications of this simple idea were that the earth was far older than people realized in the 1700’s. Darwin argued that the earth was old enough for natural selection to explain all of life. NOTE: Darwin did not come to the conclusion that slow geological processes were mirrored by natural selection: natural selection had to have a very long time to generate all the diversity of life on earth.
If a dominant allele of one gene, A, is necessary for hearing in hamsters, and the dominant allele of another unlinked gene, B, results in deafness regardless of the genotype of other genes, what is the probability that a pairing of AaBb xAabb individuals will result in a deaf offspring?
5/8 will be deaf
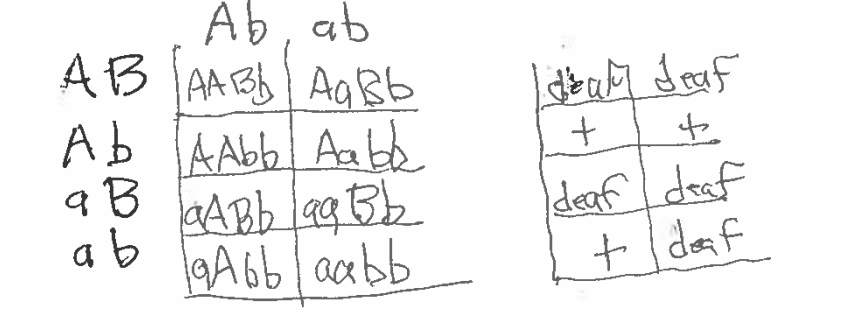
Redraw the graph below it ectoparasites were attracted to heat and nicotine had no effect
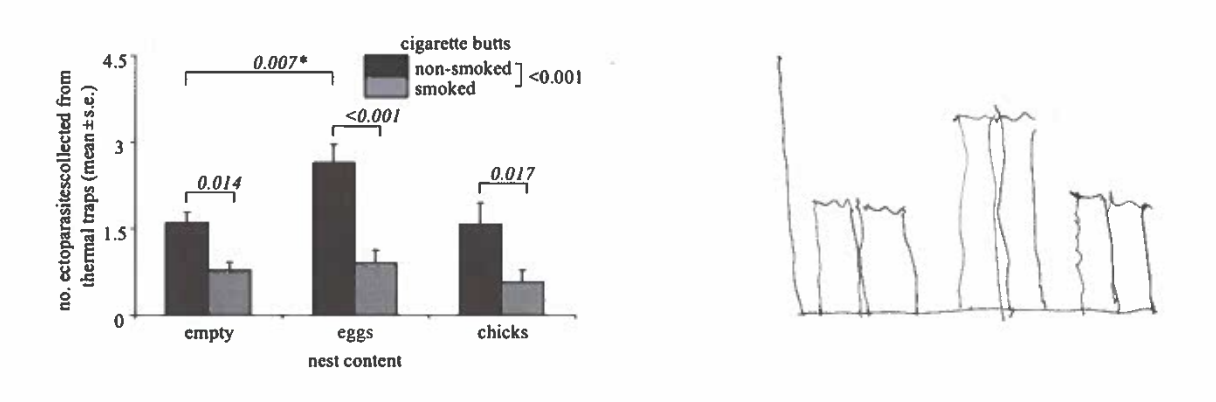
In the human pedigree below mates are squares, females are circles, and the disease phenotype is black. The trait is qualitative.
a. Is the trait recessive or dominant?
b. circle the one individual that must be a carrier.
c. is the gene on an autosomal chromosome or a sec chromosome?
a. recessive
b. image
c. sex chromosome
If DNA polymerases were perfect, such that they never introduced an incorrect base, would mutations still occur?
Yes, mutations from high energy radiation, other mutaqens, etc. would be possible
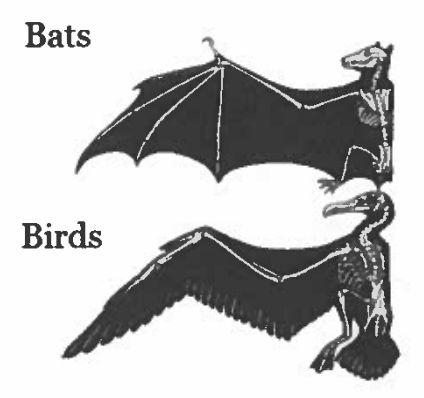
Define homology and explain howthe figure below iLlustrates the concept.
Homology is similarity due to common descent. In other words, similar structures occur in different species because they were inherited from a common ancestor The bones that support the wing in both the bat and bird are found in all the ancestors of birds and bats to their common ancestor
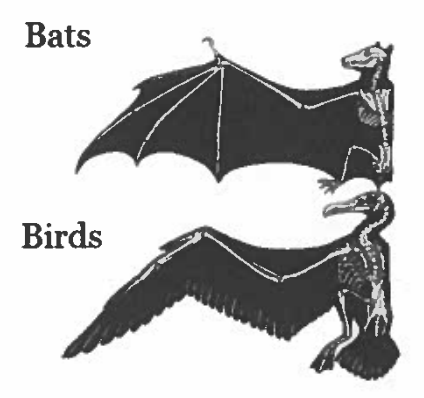
Define convergent evolution and explain how the figure above illustrates the concept.
Convergent evolution refers to similar structures in unrelated organisms that have evolved to solve a common environmental problem, not similarity due to common descent. The wings of birds and bats are convergent because we know that many ancestors of these two groups do not hove wings.
Carefully explain the following statement, “Natural selection acts on individuals, but its’ consequences are within populations”
If individuals differ in phenotypes, natural selection will discriminate among those with traits that are well-suited to the environment and those that are poorly-suited. Individuals that are well-suited to current environmental conditions will have more offspring or greater fertility than those that are poorly-suited to current conditions. This differential reproductive success has the consequence of changing the population in the next generation to be composed of a greater proportion of individuals with the well-adapted trait.
Use sexual selection theory to explain why reinforcement mechanisms are stronger among females than among males?
Females of most sexual species invest far more time and energy into their offspring than males. Because of the greater investment, the cost of making a poor choice (about the species or quality of a same-species mate) is males greater. Male fitness, of most species, is more closely tied to the number of mates they obtain, so the cost of making a bad choice is less than it is for females. Reinforcement reflects this difference in the cost of making a bad choice in females and males. Selection will favor females that avoid the cost of making hybrids or any type of unfit offspring. Males that make similar mistakes will have their fitness reduced but selection will not be as strong
Compare and Contrast: Homology and synapomorphy
Homology is similarity of structures or sequences, etc. due to inheritance from a common ancestor
Synapomorphy is a shared, derived characteristic used to define groups.
Homology is a hypothesis about characters or traits and synapomophies are the evidence used to define groups that are monophyletic.
Compare and Contrast: Organelle and endosymbiont
Recognition of on organelle have apparatus for proteins encoded in the host nucleus to be imported into the organelle.
Endosymbionts live in the host cell and may have reduced genomes.
Both organelles and endosymbionts reproduce independently of the host cell and often have reduced genomes although endosymbionts lock specialized import apparatus to import proteinsfrom the host nucleus and organelles hove these specializations.
Compare and Contrast: Gram negative and gram positive bacteria
Gram negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer that does not stain darkly.
Gram positive bacteria hove a thicker peptidoglycan layer that picks up stain readily.
These types of bacteria are classified as different groups and differ in their pathogenesis- gram negative being associated with sepsis ond other ailments.
Compare and Contrast: Mesoglea and Coelom
Mesoglea is on acellular productfound in the interior of the body wall of sponges (Porifera) and Ctenophora.
Coelom is a body cavity without an opening in certain animal groups.
Both increase the girth of organisms but do not require any metabolic effort- mesoglea is secreted but the coelom is an open, fluid-filled cavity.
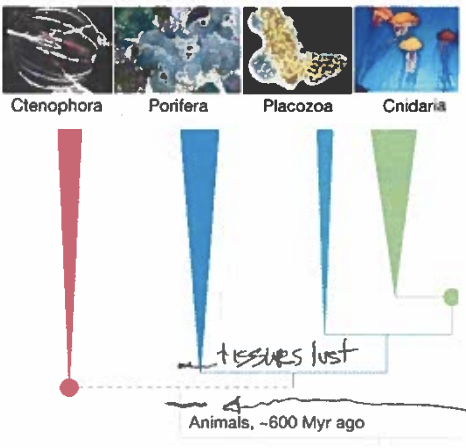
a. Tissues are found in which of the phyla shown in the phylogeny below?
b. Mark and label on the phylogenetic tree below where tissues originated, assuming parsimony.
c. Mark and label on the phylogenetic tree below where tissues were lost, assuming parsimony.
a. Ctenophora, Placazoa, Cnidaria
b. image
c. image

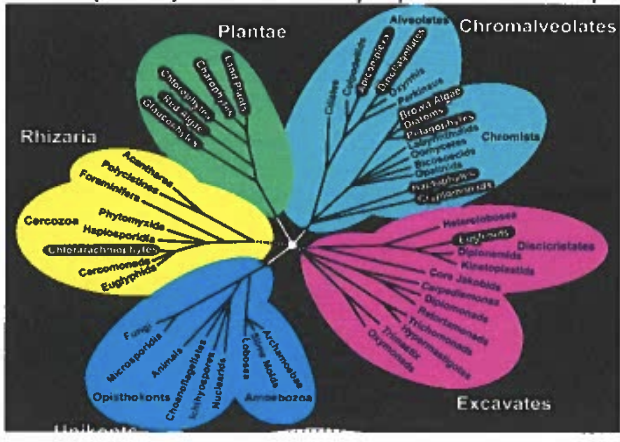
Sequence data from plastid genomes strongly suggest plastids originated once about 1.5 billion years ago. The groups scattered across the phylogeny in black (white font) are photosynthetic. Carefully explain how this very different pattern arose if plastids evolved once.
The pattern reflects a history of multiple cases of endosymbiosis, Heterotrophs that ingest a photosynthetic autotroph can use the sugars produced by photosynthesis and the waste products of respiration are used by the autotroph. The advantage of these endosymbiotic events must be great given the number of times they hove independently occurred.
Where do humans acquire their gut microbiome?
The environment
Why does subduction not occur when continental plates collide?
Continental plates are on the same horizon of the earth and buckle up forming mountains when they collide instead of one plate diving underneath another plate as occurs when oceanic plates collide with continental plates.
Explain the process that powers tectonic plate movement
It is the movement of the hot, semi-liquid molten core of the earth.
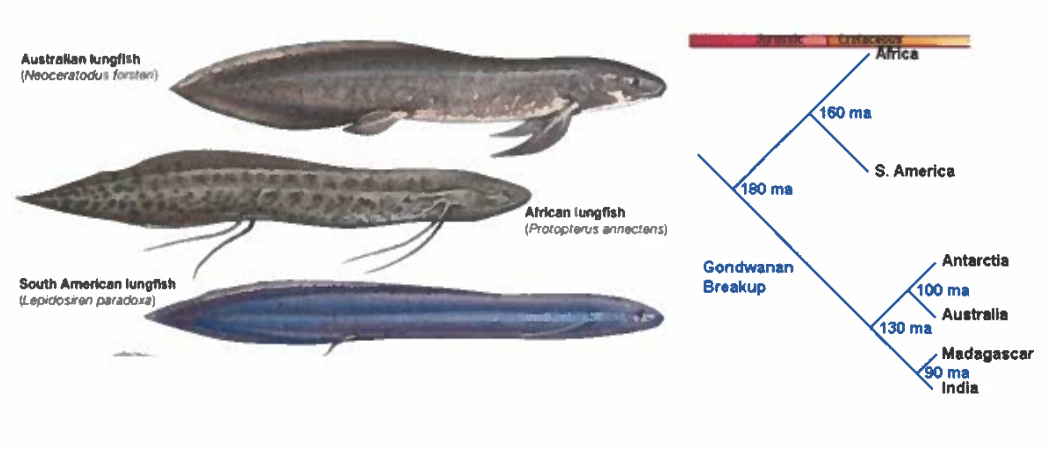
Lungfish are freshwater fish that only occur in Australia, South America, and Africa. What is the minimum age (=ma) for the origin of this group based on the information shown below?
180 million years
Why was the discovery of a ribozyme critically important evidence in favor of the RNA World hypothesis?
The first molecule had to be able to fulfill a number offunctions including the ability to catalyze other reactions. Because RNA is a single strand it can change shape and act as an enzyme which DNA cannot because it is an inflexible double strand. The term ribozyme refers to RNA-based enzymes.
What are two arguments suggesting the protocell membrane could not have been a phospholipid bilayer?
The phospholipid bilayer has hydrophobic layer and hydrophilic layer that molecules cannot cross without speciolized pores and the use of ATP’s. As such, there would be no way for molecules to get into or be removed from the first cell if it was surrounded by membrane of phospholipids- it (=the phospholipid membrane) must have evolved after the protocell.
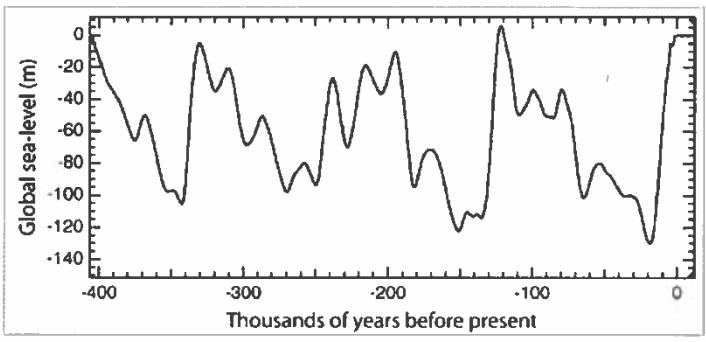
What accounts for the long-term changes in sea level shown below?
Changes in the ocean levels reflects how much water is locked up in ice and the poles and in glaciers
Assume that you find a fossil tooth of an extinct horse and are interested in estimating how long ago it roamed the earth. If the half-life of the isotope you measure is 20,000 years and you find only 12.5% of the isotope remains in your sample, approximately how old is your specimen?
The horse must have died about 3 (half-lives) * 20,000 years ago
Discuss two lines of evidence that support the recognition of a new geological era called the Anthropocene.
Chemical markers from the increase in plastic production, nitrogen production and other man-made products.
Greater rate of species extinction
Explain why polymorphic genes are more likely to be neutral than deleterious genes?
Genes that are deleterious or lethal will be quickly eliminated from the population, or fixed at zero, and genes that are advantageous will spread through the population until it is present in al/individuals, or fixed at one. Neutral genes do not have a phenotype so theirfrequency is governed solely by genetic drift and therefore more likely to be the polymorphic genes found in a study.
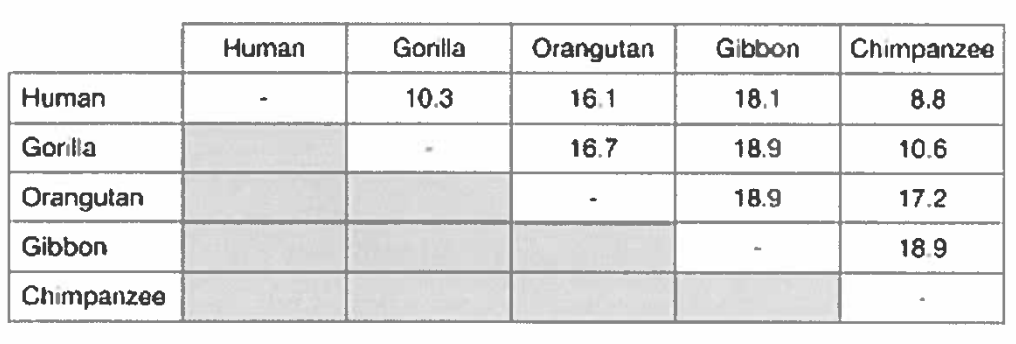
The data below represents percent difference of mitochondrial sequences for 5 primates. Do these data allow you to conclude what the closest relative to humans might be? (Carefully explain your reasoning)
The data suggest that chimps and humans are most closely related because the difference in mitochondrial sequence between these two groups is least. A caveat is that this assumes that mutation rates are similarfor all these groups, which may not be true.
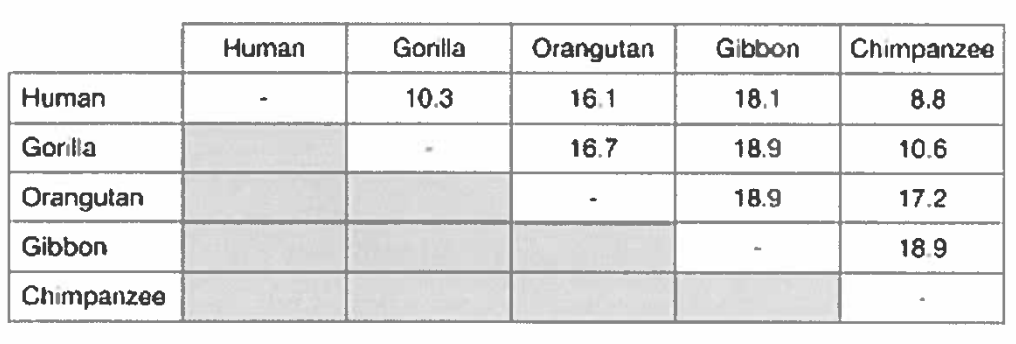
Do the data above provide enough information to estimate how long-ago humans diverged from its closest relative? (Carefully explain your reasoning)
No, to estimate how long-ago species diverged requires percent difference of proteins or sequences (which are shown above) and a calibration point to estimate rate. Calibration points can be from fossils, biogeographic events, etc.
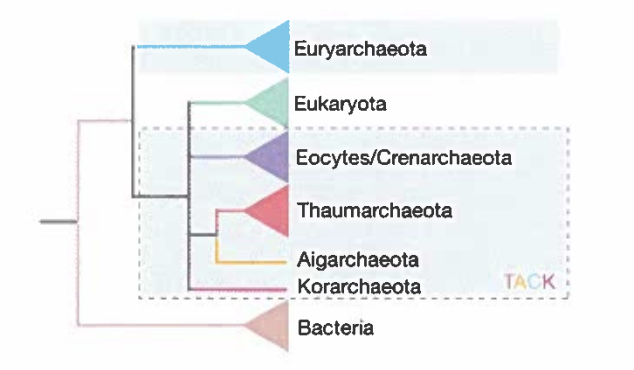
a. How many Domains, as traditionally defined, are represented in the graph below?
b. Why do Eukaryotes make Archaea paraphyletic?
c. If the phylogeny above is right, how many Domains will there be in the future if only monophyletic Domains are recognized? Name them.
a. 3-Bacteria, Archaea, Eukaryotes
b. Monophyletic groups include the ancestor and all of the descendants, Paraphyletic groups include the ancestor and some but NOT all descendants. If Eukaryota is not considered an Archaea then the common ancestor of Archaea does not include all of its descendants.
c. Archaea and Bacteria
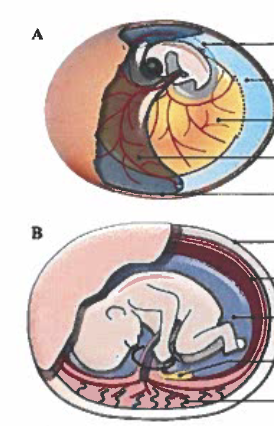
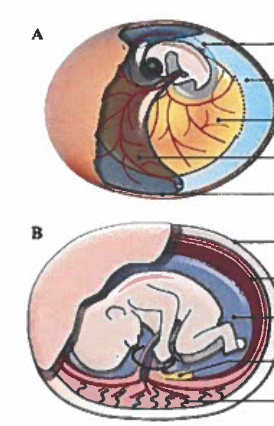
Label the amniotic sac and the chorion on the figures below
Why is there no Thermoneutral zone for poikilothermic animals? (Include in your
answer what the thermoneutral zone is)
The thermoneutral zone is a temperature range around the preferred body temperature of an organism that can be maintained without any variation in metabolic output/expenditure. Organisms that regulate body temperoture, instead of conforming to the temperature of the ambient environment, expend energy
to cool off or warm up when it is too hot or too cold, respectively. Poikilothermic organisms do not expend energy to maintain their body temperature but can use various behavioral adaptations to thermoregulate. For these organisms, any change in temperature will change how they use energy. Poikilotherms do not have a preferred temperature range but not a thermoneutral zone.
What evidence supports the phylogenetic relationship between land plants and the
various groups of aquatic green algae?
They all use/have the same photosynthetic pigments
In the circulatory system,
a) list two mechanisms that generate high blood pressure through the arteries and arterioles
b) Why is blood pressure low from the venules, veins to the heart?
a) muscles of the heart and smooth muscle surrounding the arterioles
b) there are no muscles to generate pressure lining the vessels in the part of the circulatory system involved in returning the blood to the heart.
Which is likely to require more food over a given time period, a group of 60 skates,
each weighing 1 kilogram, or a pair of 30-kilogram sharks? Skates and sharks belong to the same group of animals, the cartilaginous fishes. Carefully explain your reasoning.
There is far more heat lost in 60 skates that each weigh 1 kg than from 2 skates that weigh 30 kg simply because of differences in the surface area to volume ratios. Therefore, the 60kg of biomass in 60kg skates will require more food than the 60kg of biomass in 2 30kg skates
What are two paedomorphic traits in Homo sapiens?
Learning into adulthood, late arrival of teeth, flat face
Reinhold Messner is one of two people known to reach the peak of Mount Everest
(elevation 8,848 meters) while breathing atmospheric air. Although in superb physical condition he required an entire hour to climb the final 100 meters. That is, during the last hour of climbing he covered only 1.7 meters per minute.
a) What is the percentage of oxygen in the air at the top of Mt. Everest?
b) What is the percent of the oxygen in the air at sea level?
c) Explain why basal metabolic rate changes with altitude?
a) 21%
b) 21%
c) Because the pressure of air is greater at sea level, inhalation of the lungs brings in more oxygen per
inhalation event than inhalation does at higher elevations. (In terms of partial pressure-the total partial pressure decreases at high altitudes which decreases the partial pressure of oxygen resulting in less overall oxygen molecules in the air). At high elevations the pressure of air is less, the amount of oxygen per breath is less, so metabolic demands (or basal metabolic rate) must be reduced.
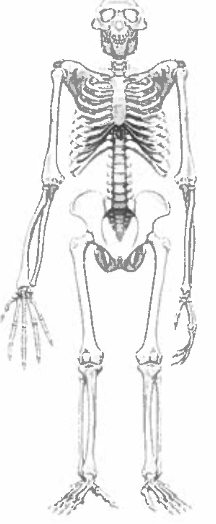
The figure below is a reconstruction of the complete skeleton of Ardi (Ardipithecus
ramidus).
a) What are two features of the skeleton visible on the figure that suggest Ardi was bipedal?
b) What is one feature of the skeleton visible on the figure suggesting Ardi was arboreal?
a) Broadened pelvis and the greater angle of the femur in relation to the pelvis (ball joint positioned perpendicular to pelvis instead of straight down).
b) Grasping toes, instead of flat as in Homo sapiens, with an opposable “thumb” on the foot
The largest group of metazoans (in terms of number of species) are in what phylum?
insects, arthropods, ecdysozoa
What pattern of early cleavage foes the blastula undergo?
spiral
All cells in the embryo are totipotent up to what stage?
before the 8 cell stage
How does the behavior of stomata differ over the day between plants that use
CAM photosynthesis and plants that use C3 photosynthesis?
Stomata in CAM plants open only at night. Stomata in C3 plants open in the day o day and night.
what group of mammals is not viviaparous
monotremes — echidnas and duck-billed platypus
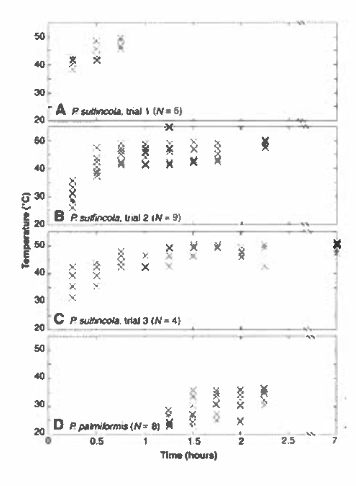
The data below are of two species of worms that live near hot hydrothermal
vents deep in the ocean. Worms were placed in a tank with a temperature gradient and given time to find their preferred temperature. What species do you predict occurs closest to the vent? Explain your answer
The graph shows time on the x-axis and temperature on they-
axis. Each xis an individual. In all 3 trials of P suljinicolo,
individuals eventually settle at temperatures between 40 and 50
degrees, and in P palm qormis individuals settle at 30-40 degrees.
This suggests P sulJiriicola prefers higher temperatures and will
be closer to the scorching hydrothermal vent than P polmiformis.
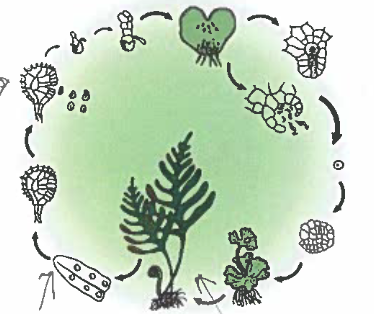
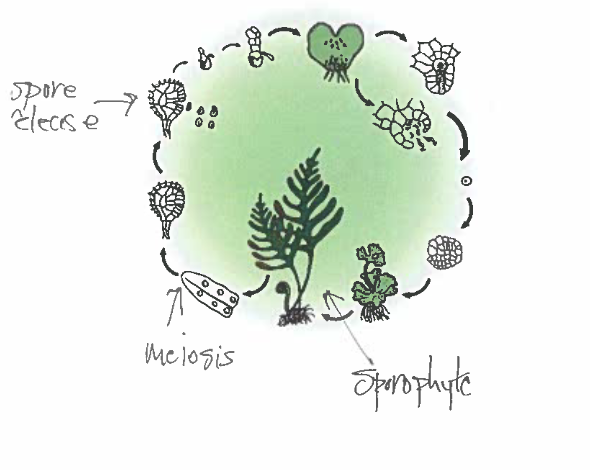
on the figure below, label the following
a) sporophyte
b) where meiosis occurs
c) spore release
Compare & Contrast: Endosperm and germ tissue
Endosperm is triplold tissue inside of a seed that is the nutritive source for the embryo.
Germ tissue inside a seed is the embryo.
The two differ in their ploidy (3N for endosperm, 2N for the germ tissue) and their fate (endosperm consumed by the germ line and a new individual for the germ tissue)
Compare & Contrast: Neotony and heterochrony
Neotony is the retention of juvenile traits in the adult stage
Heterochrony refers to developmental changes in the timing of genes that result in changes in shape and form.
Neotony is one kind of heterochrony that refers to delayed timing of juvenile traits but heterochrony refers to timing of ony and al/structures.
Compare & Contrast: Notochord and Vertebrae
Vertebrae are cartilaginous or bony structures that protect the dorsal nerve chord in some Chordates.
Notochord is rod that provides support for the body in Chordates that is located dorsal to the dorsal nerve chord.
The Notochord is a synapomorphy of Chordata that evolved before the evolution of the vertebrae that is not involved in protecting the nerve chord.
Compare & Contrast: Arbuscular fungi and lichens
Arbuscular fungi are associated with the roots of plants. The form a special structure, called an arbuscle, that forms in contact with the cell membrane of the plant inside the plant cells wall. Most mycorrhizal fungi are arbuscular.
Lichens are symbiotic relationships wherein algae (and sometimes cyanobacteria)
live inside the thallus of a fungus. Lichens are a collection of unrelated organisms.
The terms below relate to the immune response of plants and animals. For each
term indicate (= write next to the term) what GENERAL category of immunity the term falls under. Some terms will fall into more than one GENERAL category
a) milk allergy
b) phagocytes
c) memory cells
d) encapsulations
e) agglutination
f) tannins
a) adaptive, humoral
b) innate, cellular
c) adaptive, humoral
d) cellular, humoral
e) adaptive, humoral
f) constitutive