4.2 Monopoly
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Monopoly
A market where there is only one firm in operation. They have some influence over price by choosing a combination of price and output which maximises profits. Supernormal profits are earned in the short and long run.
Dynamic efficiency
Takes into account innovation and technical progress on productive and allocative efficiency in the long run
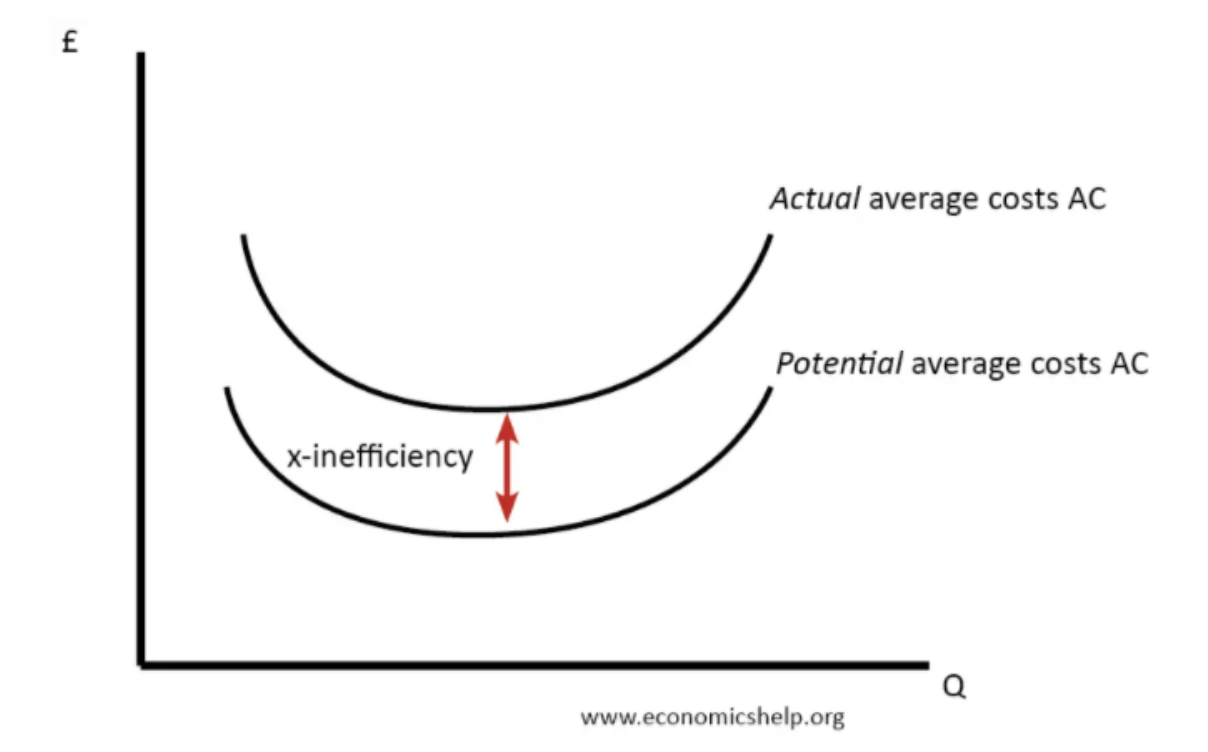
X-inefficiency
Occurs when a firm is not operating at minimum cost, possibly due to organisational slack
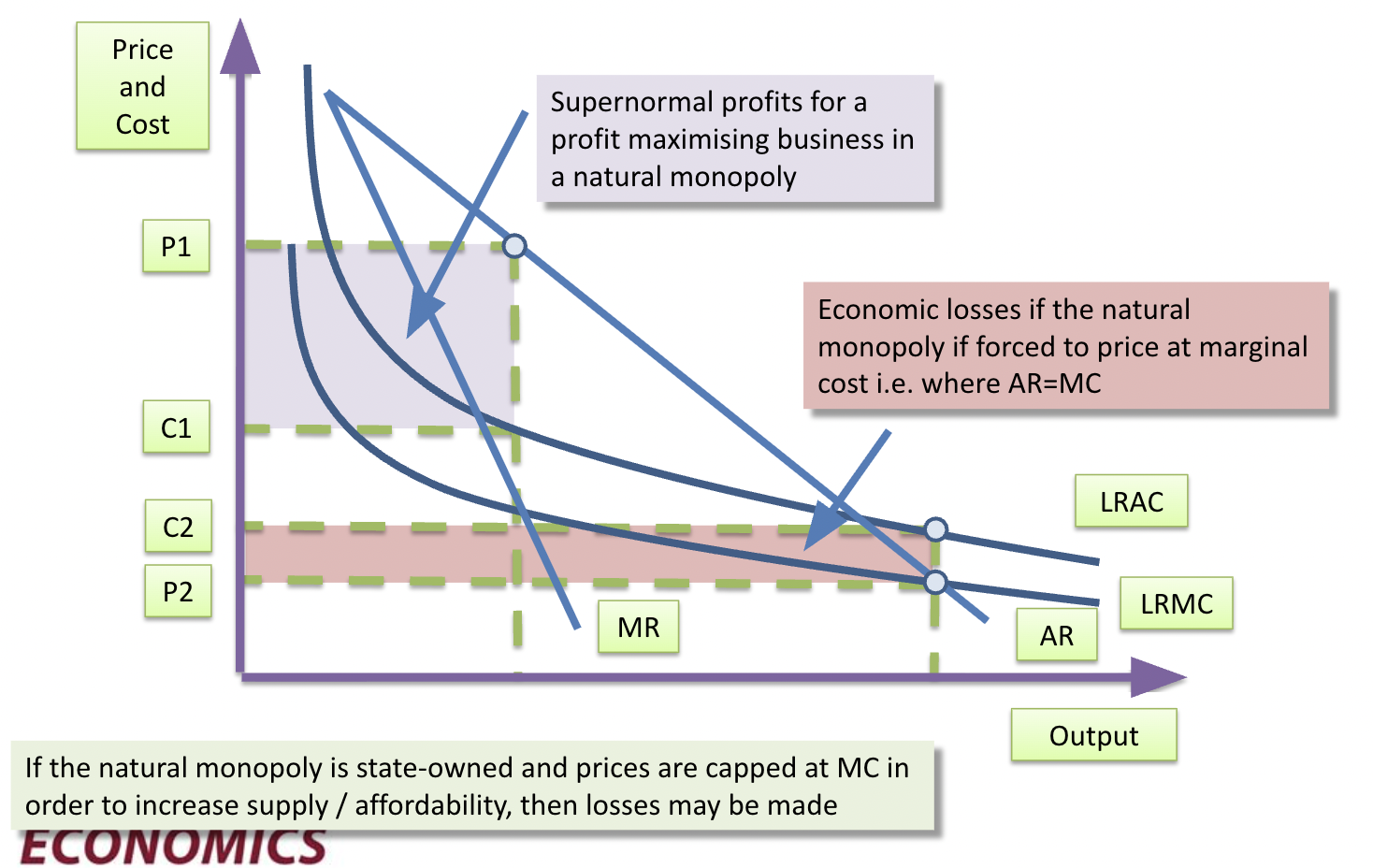
Natural monopoly
Arises in an industry in which there are such substantial economies of scale that only one firm is viable
Characteristics of Monopolies
-A monopoly has price-setting or price-making power (price-maker)
-Barriers to entry exist – help to maintain supernormal. (monopoly) profits in the long run
-Imperfect information is assumed
-Profit maximisation is assumed but the actual conduct of firms with market power is often different
-Often firms with market power do not profit maximise as one of their aims is to maintain their market share
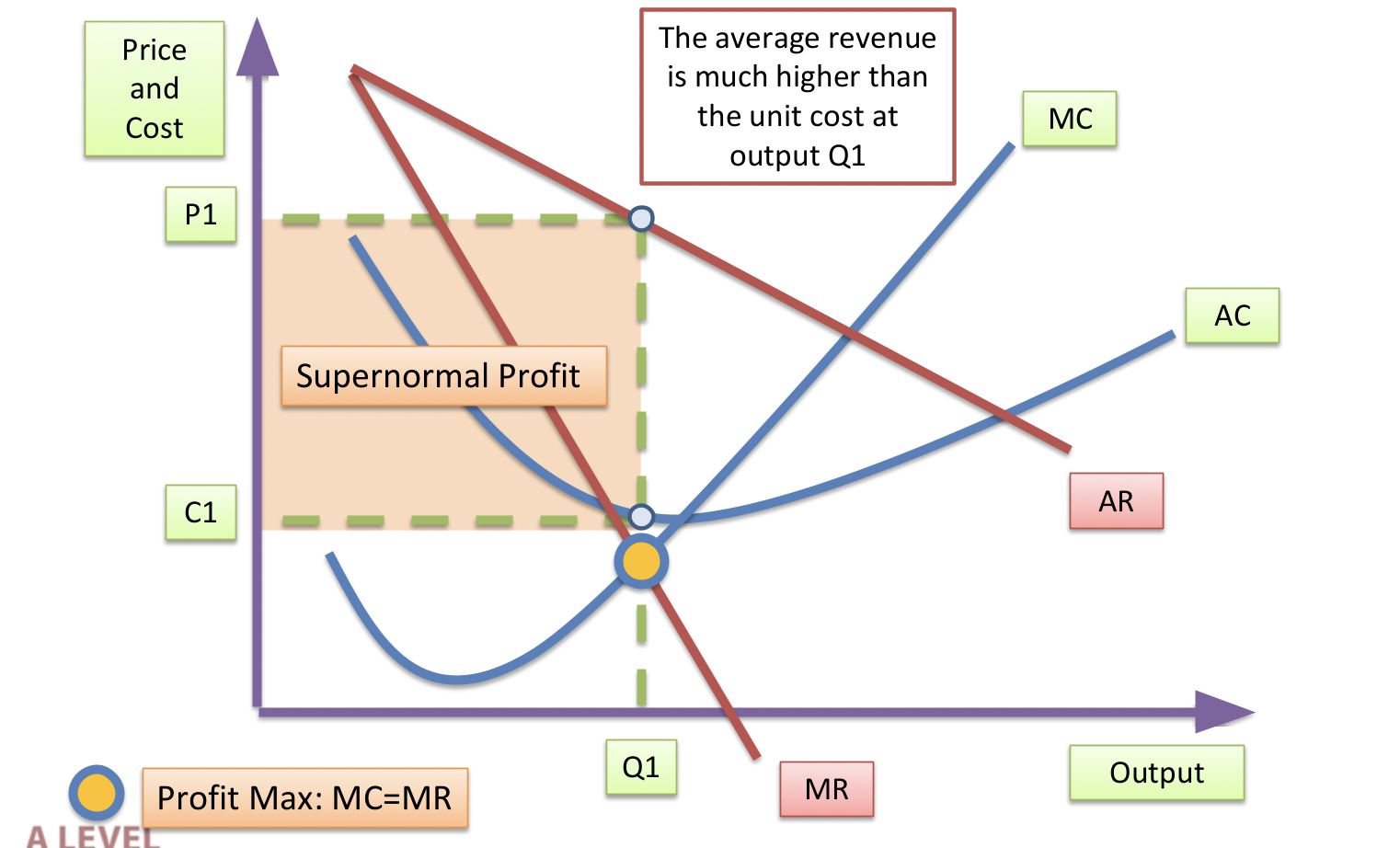
Monopoly curve
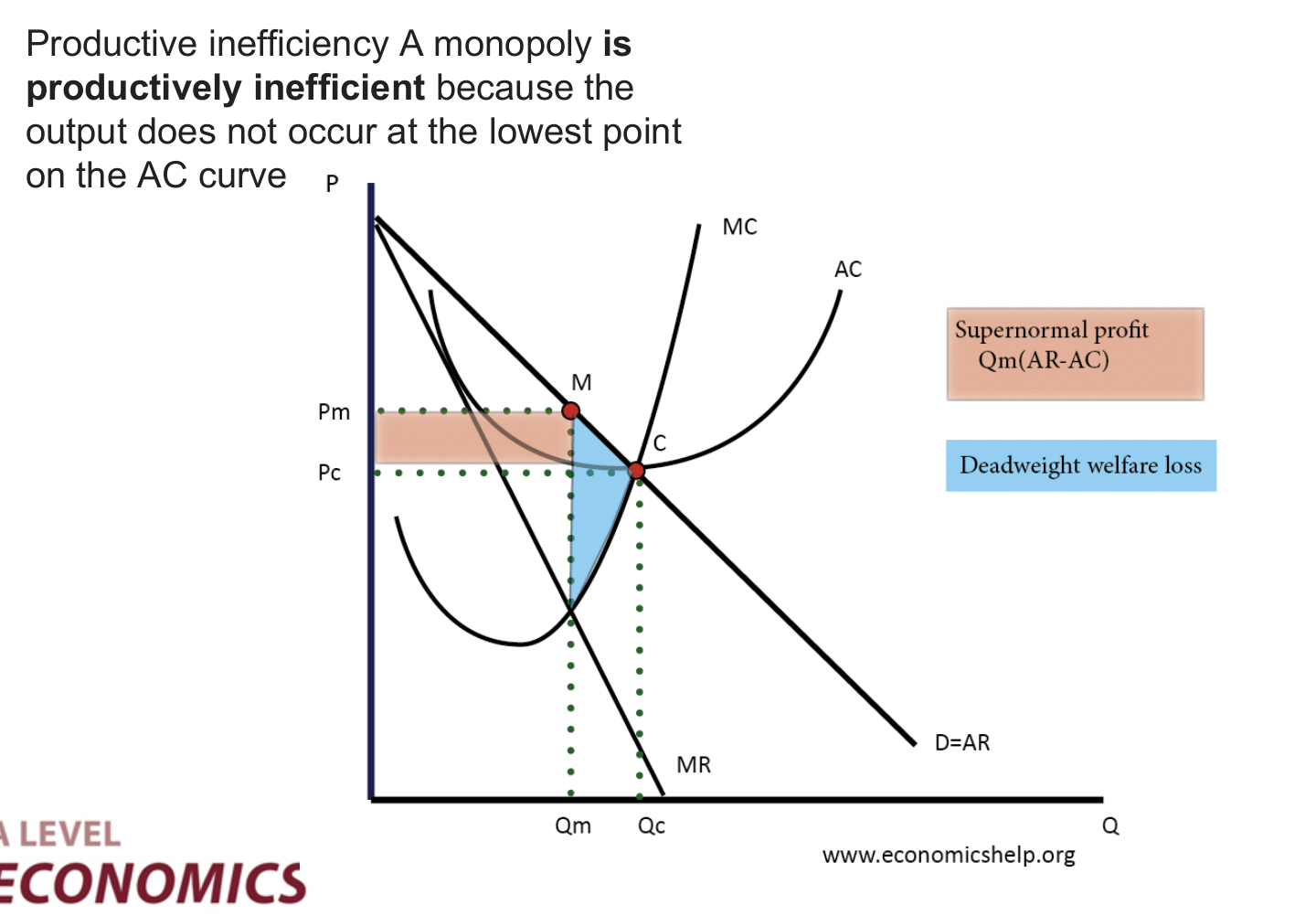
Productive inefficiency
A monopoly is productively inefficient because the output does not occur at the lowest point on the AC curve
Key Factors affecting Profitability
-Growth of demand and the average price that sellers can achieve
-Scale of installed customer base – much cheaper to sell to an existing active customer than the marketing cost of selling to new buyers
-Changes in business operating costs e.g. wages, prices of essential raw materials and components
-Changes in the efficiency of factor resources – e.g. improvements in labour productivity lead to lower unit costs and therefore higher profits for a given selling price
-The effects of economies of scale to lower unit costs in the long run and therefore increase profitability
-Impact of intervention in markets by the government that can affect profitability e.g. a minimum carbon price, the congestion charge
-The cost of meeting government regulations such as EU legislation
-Impact of government subsidies / tax relief / investment allowances
-Strategic behaviour by other firms in the market e.g. short-term price wars might lead to a cut in profits
-Effects of changes in exchange rates affecting the profitability of exporting and the relative prices of imports
How do monopolies arise?
Barriers to entry
- The government may pass legislation that grants sole rights to produce a good or service to one firm, to reduce unnecessary waste.
-Ownership of patent of copyright. No other firms can produce the good until the patent expires.
-A firm may have complete control over the essential raw materials.
-In some industries the minimum size of a firm required to operate efficiently is so large that these is no room for competitors.
-A firm may gain monopoly power by merging with or taking over a rival company thus eliminating competition.
-Firms may enter into trade agreements with similar companies and divide up the market, thus ensuring no competition exists (Illegal monopolies)
Advantages of monopolies
-Profits used to fund investment & research
-Natural monopoly – economies of scale
-Domestic monopoly faces global competition
-Price discrimination may help some consumers
-Little need for monopoly firms to advertise, therefore keeping costs down and maybe prices
-The Government will not exploit consumers with high prices. It will even continue to provide necessary service when the firm is making a loss
-As there is no competition, employees have greater security and better conditions of employment
Interventions for monopolies
-Tax on monopoly profits: A one-off windfall tax on supernormal profits from monopoly power - however risk of tax avoidance / loss of capital investment spending
-Liberalisation of markets: Break up monopolies, allowing smaller businesses to enter and increased contestability - however smaller businesses may struggle to scale up and compete
-Introduce price capping policies: Encourages cost efficiency and increases consumer surplus - however Monopolists may find revenues in other ways
-Nationalisation: Take some monopoly utilities back into public ownership - however possible loss of productive efficiency
Natural monopoly curve
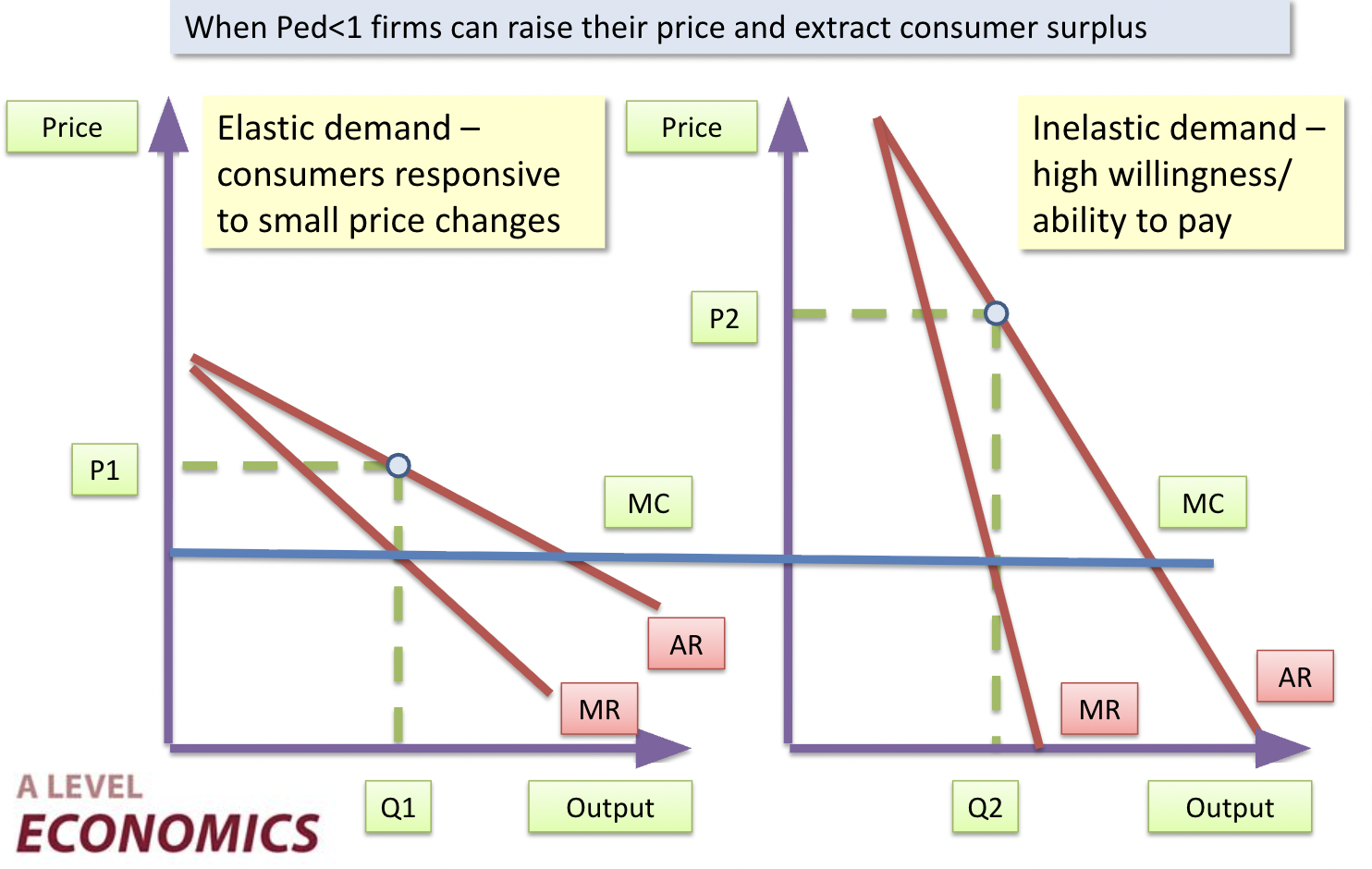
Price discrimination
A business charging different consumers different prices for the same product
Conditions for Price Discrimination
-Firms must have sufficient price setting power
-Identifying different market segments (groups of consumers with different price elasticities of demand)
-Ability to separate different groups (sufficient market intelligence on purchasing behaviour of consumers)
-Ability to prevent re-sale (arbitrage)
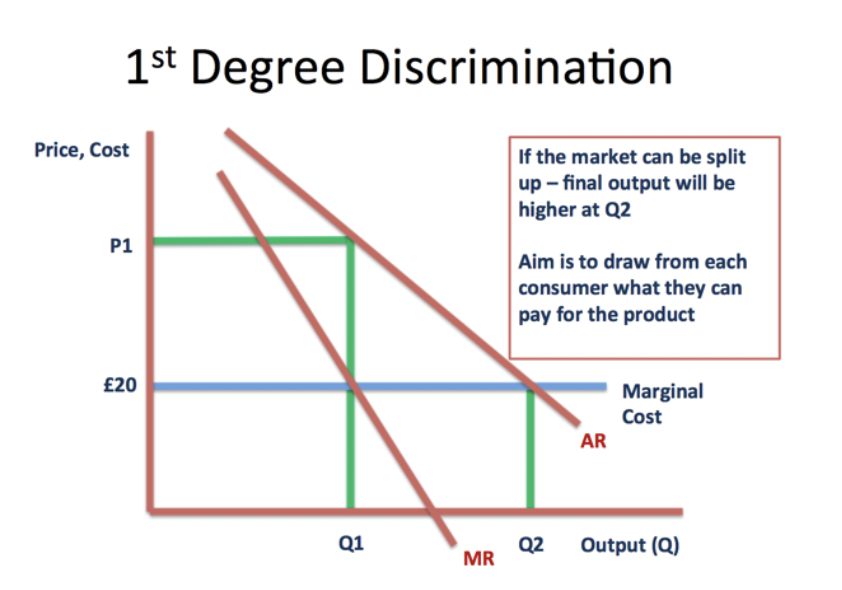
1st degree price discrimination
Charging different prices for each individual unit purchased (people pay based on their own willingness)
2nd degree price discrimination
Prices varying by quantity sold e.g. bulk purchase discounts
Prices varying by time of purchase e.g. peak-time prices
3rd degree price discrimination
Charging different prices to groups of consumers segmented by price elasticity of demand, income, age, sex