Chapter 10: Market Research and Information Systems
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
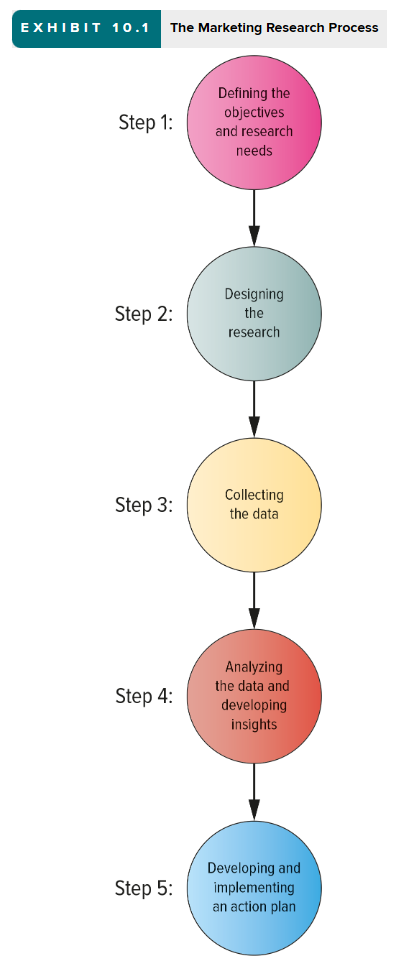
5 Steps of the Marketing Research Process
Defining the objectives and research needs
Designing the research
Collecting the data
Analyzing the data and developing insights
Developing and implementing an action plan
active analytics tools
AI algorithms that are used to analyze input gathered by the Internet of Things
big data
Data sets that are too large and complex to analyze with conventional data management and data mining software
churn (or churn rate)
The number of consumers who stop using a product or service divided by the average number of consumers of that product or service
customer lifetime value (CLV)
The expected financial contribution from a particular customer to the firm’s profits over the course of their entire relationship
data
Raw numbers or facts
data mining
Statistical tools used to uncover previously unknown patterns or relationships among variables stored in the big databases
data warehouses
A large computer file containing data including sales transactions, CRM systems, websites, social media, blogs, locational devices, wearables, etc.
descriptive analytics tools
Methods that help firms organize, tabulate, and depict their available data, usually in easy-to-understand reports, tables, and charts
experimental research
A type of conclusive and quantitative research that systematically manipulates one or more variables to determine which variables have a causal effect on another variable
focus group interview
A research technique in which a small group of 8-12 people come together for an intensive discussion about a particular topic, with the conversation guided by a trained moderator using an unstructured method of inquiry
in-depth interview
An exploratory research technique in which trained researchers ask questions, listen to and record the answers and then pose additional questions to clarify or expand on a particular issue
information
Organized, analyzed, interpreted data that offer value to marketers
marketing analytics
Techniques that use advanced technologies and models to gather data so that markets can improve their decision making, optimize their returns, and make appropriate customer-related decisions
marketing research
A set of techniques and principles for systematically collecting, recording, analyzing, and interpreting data that can aid decision makers involved in marketing goods, services, or ideas
observation
An exploratory research method that entails examining purchase and consumption behaviors through personal or video camera scrutiny
panel data
Contains information collected from a group of consumers
predictive analysis tools
Methods that rely on historically available data to forecast the future
prescriptive analysis tools
Analyses that use simulations, which ask a series of what-if type questions, and optimization techniques, which find the most effective or best result, to help firms better understand what they should do
primary data
Data collected to address specific research needs
qualitative research
Informal research methods, including observation, following social media sites, in-depth interviews, and focus groups
quantitative research
Structured responses that can be statistically tested to confirm insights and hypotheses generated via qualitative research or secondary data
questionnaire
A form that features a set of questions designed to gather information from respondents and thereby accomplish the researchers’ objectives; question can be unstructured or structured
sample
A group of customers who represent the customers of interest in a research study
scanner data
A type of syndicated external secondary data used in quantitative research that is obtained from scanner readings of UPC codes at checkout corners
secondary data
Pieces of information that have already been collected from other sources and are usually readily available
structured questions
Closed-ended questions for which a discrete set of response alternatives, or specific answers, is provided for respondents to evaluate
survey
A systematic means of collecting information from people that generally uses a questionnaire
syndicated data
Data available for a fee from commercial research firms such as IRI, NDP Group, and Nielsen
unstructured questions
Open-ended questions that allow respondents to answer in their own words
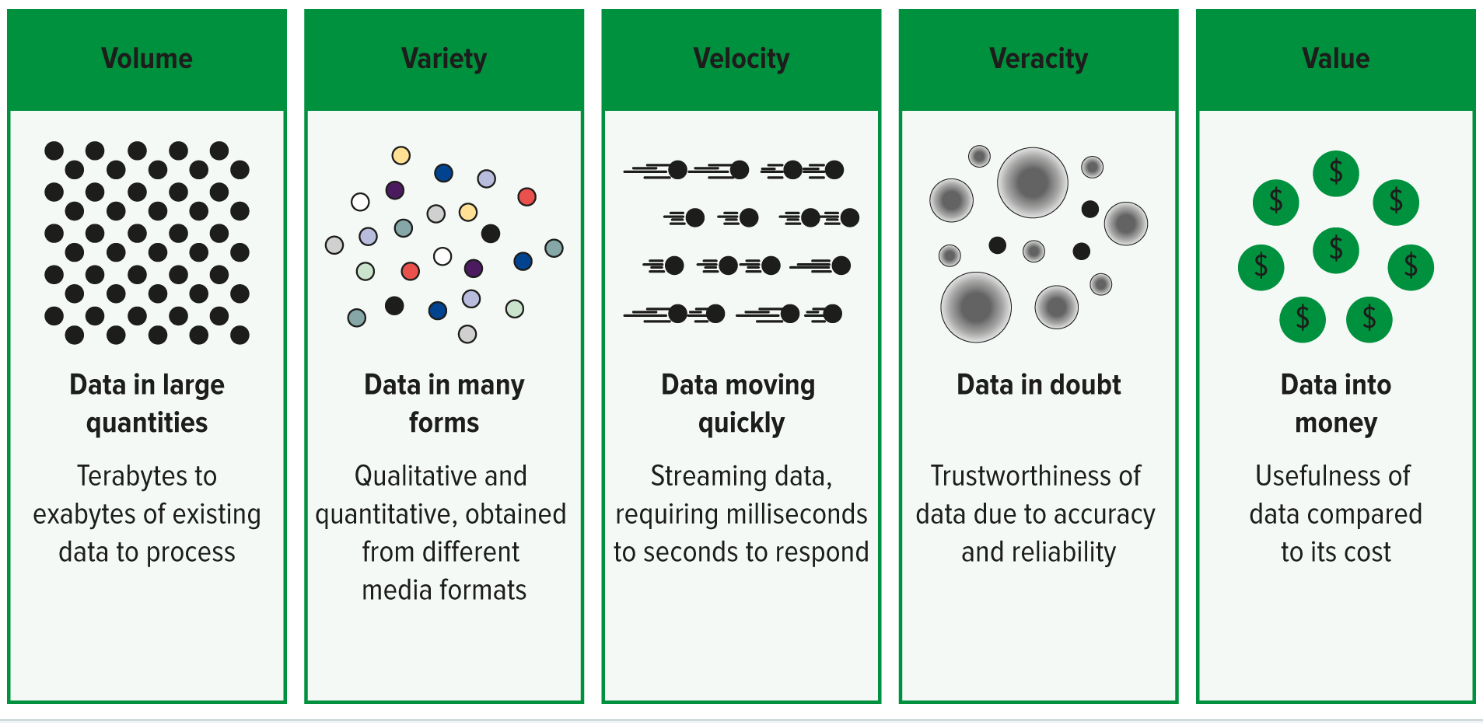
value (of big data)
The more valuable the data are to users, the better they are
variety (of big data)
Inherent quality of big data that infers that big data contain both numeric and textual data and are obtained from different media formats
velocity (of big data)
Inherent quality of big data that infers that data are collected and can be analyzed and accessed quickly
veracity (of big data)
Inherent aspect of big data that infers that big data users must evaluate the accuracy and reliability of the collected data
volume (of big data)
Inherent quality of big data that infers that big data contain a large amount of data
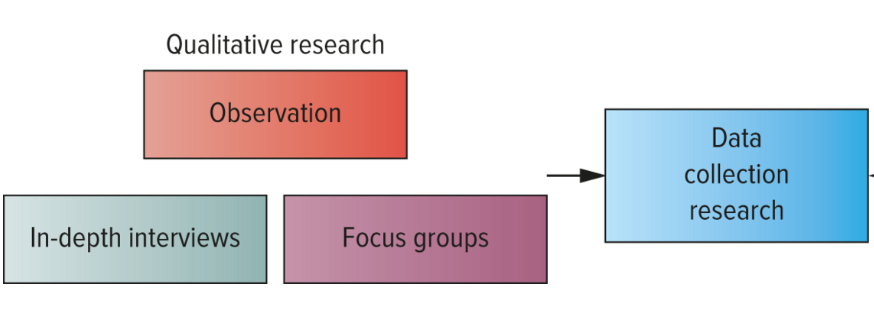
Types of Qualitative research
Observation
In-depth interviews
Focus groups
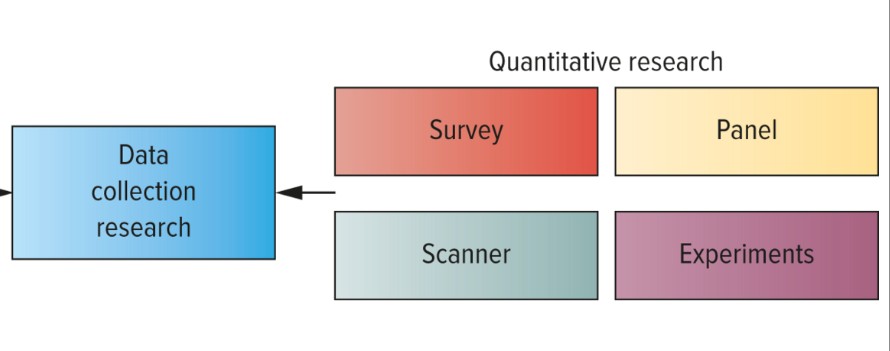
Types of Quantitative research
Survey
Panel
Scanner
Experiments
Advantages of Primary Research
Specific to the immediate data needs and topic at hand
Offers behavioral insights generally not available from secondary research
Disadvantages of Primary Research
Costly
Time-consuming
Requires more sophisticated training and experience to design study and collect data
Advantages of Secondary Research
Saves time in collecting data because it is readily available
Free or inexpensive (besides syndicated data)D
Disadvantages of Secondary Research
May not be precisely relevant to information needs
Information may not be timely
Sources may be unoriginal and not useful
Data collection methods used may be inappropriate
Data sources may be biased
The 5 Vs of Big Data
Volume
Variety
Velocity
Veracity
Value