AP Human Geography Unit 5
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
What four factors create climate?
Distance from Equator, Wind and Ocean currents, Proximity to large bodies of water, and topography
How does distance from the equator create climate?
It determines the length of daylight and average temperature, which affects what can grow and how much of it can be grown.
How does proximity to large bodies of water create climate?
Coastal areas have milder climates than inland areas. Coastal areas are cooled during the day and warmed at night. Coastal areas have heavier precipitation than inland.
How does topography create climate?
Coastal mountains have heavier precipitation when facing the wind and lighter when not, allows for different temperatures to grow different types of plants
Agriculture
The cultivation of plants or the raising of animals to provide goods for survival. It is used for food but other plants, such as cotton, are used for textile products.
Why do geographers study agriculture?
to understand how humans have modified the environment to sustain themselves and because observing agriculture at different scales allows geographers to find patterns and observe how sustainable our agricultural practices are
Environmental Factors that Impact Agriculture.
Climate, Elevation, Soil, and Elevation
Topography
The slop of the land affects the soil's ability to retain water, and can affect how much sun the plants get, thus affecting what plants have the ability to grow there.
Climate
Provides rain and temperature that plants need to grow. The temperature decides the growing season and what plants can survive. Wind temperatures also affect temperature, which affects crops
Elevation
The higher the elevation is, the shorter the growing season is because of the decrease in temperature. Elevation creates different cultivation opportunities.
Soil
Affects how much nutrients a plant can get depending on the amount of mineral particles.
How do Wind and Ocean currents create climate?
Affects patterns of precipitation to transfer heat away from equator and cold water towards it. Winds carry different temperatures to different regions
Climate Region
Areas that have similar climates based on their location that share a similar temperature, topography, wind currents, and precipitation
Topical Climate Region
Warm temperature, wet tropical has a lot of rain tropical monsoon has dry winters and rainy summers, tropical wet and dry is similar but less rain. Savanna Grassland, South Asia, Mid Africa, Northern SA, Southern NA
Dry Climate Region
Continental interiors and/or semi-arid regions (allows for growth of grasslands). Mid Asia, Middle East, Northern Africa, Australia, and South Africa. Plants such as rainforests may not be able to grow because of not enough water
Temperate Climate Region
Moderate temp and adequate rain. Long summers and short winters. Humid temperate is on East with cooler winters and a lot of rain. Marine West Coast climates (west coast higher latitude), cooler winters, constant rain. Mixed forests, temperate grasslands, Mediterranean shrubs, Grain, Corn, Rice
Continental Climate Region
Interior climates in the northern hemisphere with distinct seasons and cold winters with snow. Growing season is shorter because of cold winters, and because of this hardier crops such as wheat or corn are needed.
Polar Climate Region
Extremely cold: tundra has short, mild summer that can't grow anything while ice cap is rarely above freezing
Mediterranean agriculture
Growth of hardy trees (olive, fruit, nut) and shrubs (grape vines) and raising sheep and goats in areas with hot, dry summers.
What four elements make land favorable for growing crops?
Good soil, temperate climate, water, and sunlight
subsistence agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family
Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.
Bid-rent Theory
geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the Central Business District (CBD) increases.
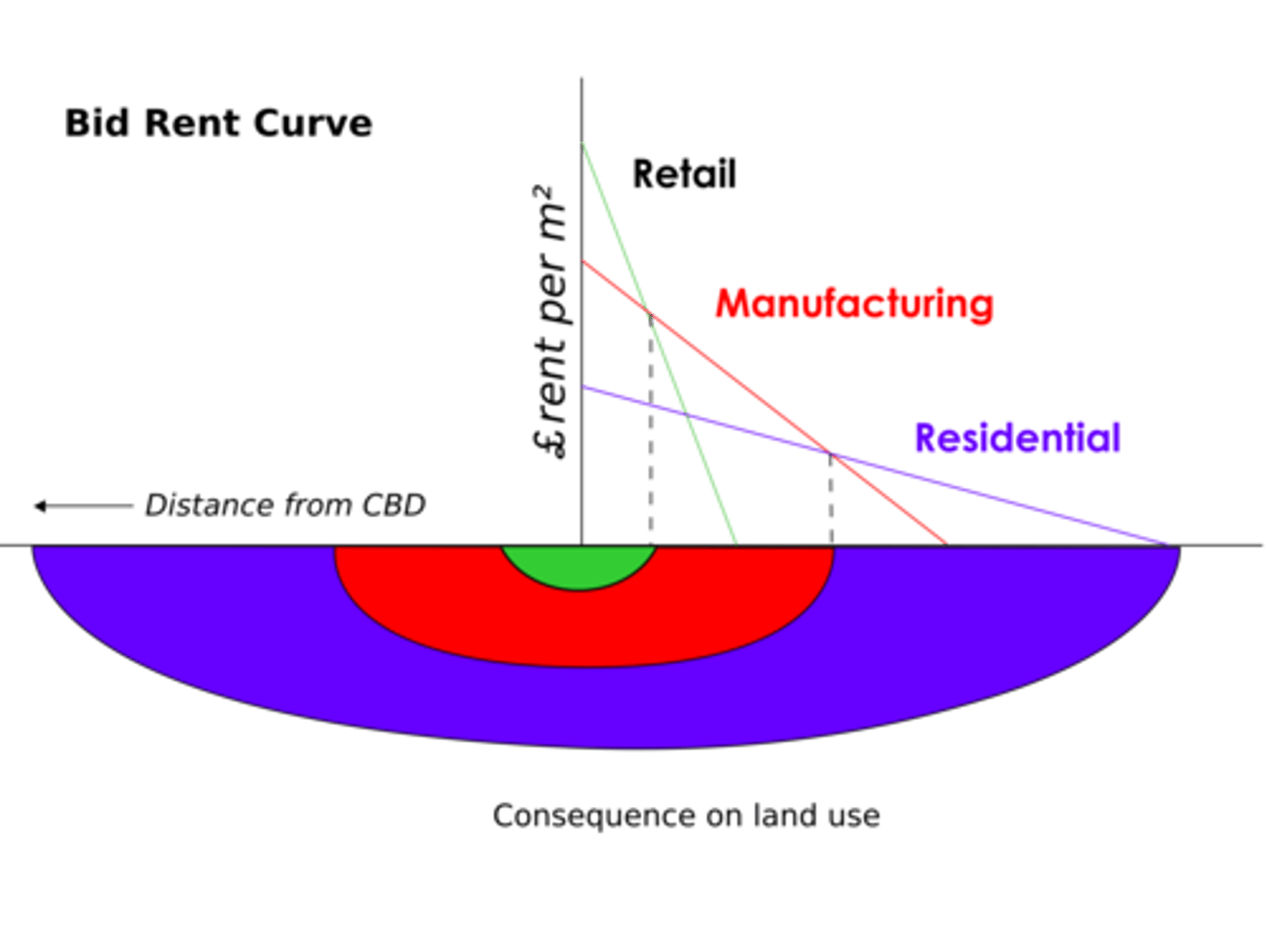
Central business district
The downtown or nucleus of a city where retail stores, offices, and cultural activities are concentrated; building densities are usually quite high; and transportation systems converge.
What does it mean to survey land?
It means to determine a property's position of points and distances and the angles between them
Metes and Bounds
A method of land description which involves identifying distances and directions and makes use of both the physical boundaries and measurements of the land.
Long-lot survey system
When a property is divided in long strips stretching back from a river or lake to provide rich soil
Township and range system
A rectangular land division scheme designed by Thomas Jefferson to disperse settlers evenly across farmlands of the U.S. interior.
Pros and Cons of Clustered Settlement
-social unity, common resources
-social friction, fields that extend too far from the settlement
Pros and Cons of a Dispersed Settlement
-promotes self-sufficiency, allows for more interaction with the natural environment
-usually not a lot of resources, reduces interactions with neighbors, little access to shared institutions, not as easy to defend residents
Pros and Cons of a Linear settlement
-follows a land feature such as a river
-the far end of fields will be distant from the homes
intensive agriculture
any agricultural system involving the application of large amounts of capital and/or labor per unit of cultivated land; may be part of either subsistence or commercial economy
Monocropping
Cultivating and rotating only one to two crops
Monoculture
raising or planting one animal or crop yearly
How are monocropping and monoculture harmful
They can deplete nutrients from the soil, but crop rotation allows for the restoration of nutrients within the soil
Plantation Farming
Large scale commercial intensive farming of one crop grown far from the market
Market Gardening
intensive farming that serves a market or urban areas where farmers are able to conveniently sell to local places. it is intensive because it takes a lot of technology to stagger a constant supply of products through the year
Mixed Crop and Livestock systems
Both crops and livestock are raised for profit, and it is intensive because it takes a lot of effort and resources to grow crops and raise animals at the same time
Extensive Agriculture
An agricultural system characterized by low inputs of labor and/or capital per unit land area.
Shifting Cultivation
The extensive farming practice of growing crops or grazing aniamls for one to two years until resources are depleted before moving on to another piece of land
Slash and Burn
Extensive practice that clears land once vegetation dries by burning it
Nomadic/herding
Extensive subsistence practice that is the movement of animals seasonally to allow for the best grazing
Ranching
A commercial extensive farming practice to raise live stock
What is the exception to the rule that raising animals is an extensive farming practice?
CAFOs (Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations)
Transhumance
The movement to cooler, higher elevations during summer and lower during the winter
Domestication
the deliberate effort to grow plants and raise animals, making plants and animals adapt to human demands and using selective breeding to develop desirable characteristics
Agricultural Hearth
the place from which agriculture, or a form of agriculture originates
What was the Fertile Crescent?
From East Mediterranean to west Türkiye through Syria and Iran and was the first hearth of domestication
Central America Agricultural Hearth
Central America: cassava, palm oil, chilies, sweet potatoes, cocoa beans, maize
Andean Highlands Agricultural Hearth
Southern North America: beans, potatoes, tomatoes
West Africa Cultural Hearth
Bambara beans, coffee, cotton, seed oil, cowpeas, millets, olives, peas, sesame, sorghum
Indus River Valley
Barley, cotton, peas, sesame
North Central China
Apples, grapefruit, grapes, lemons and limes, millets, oranges and mandarins, rice, soybeans, tea
Southeast Asia
bananas, cloves, coconuts, grapefruit, rice, sugar can, taro, tea, yams
Columbian Exchange
An exchange of goods, ideas and skills from the Old World (Europe, Asia and Africa) to the New World (North and South America) and vice versa that began in 1492 after Columbus landed in the Americas
Positive Impacts of Columbian Exchange
Brought new crops that could provide plenty of calories and meet the nutritional needs of people, introduced plants to areas that wouldn't usually be able to grow anything
Negative impacts of Columbian exchange
Replaced crops that naturally grew there, decreased biodiversity, introduced diseases
How did the 1st Agricultural revolution change people's lives
They moved from a nomadic to sedentary lifestyle
They learned to plants seeds and introduced new tools such as using oxen to pull plows and irrigation practices
Since there was enough food not as many farmers were needed and people moved to other professions
More complex societies resulted in a ruling class emerging to create laws as well as a fighting class to defend a society.
Settlements began to grow larger and become cities, and started to trade with other cities
Why did the Industrial Revolution happen in Great Britain
It has a large resource of coal and also had the ability/access to ports to get goods from around the world
What did the technologies developed during the industrial revolution do for the countries that were the first to industrialize?
Allows for more efficiency and decrease the ability/need to use hands to prep land, harvest crops, or plant crops
What was the impact of the second Agricultural revolution on labor and life
less farmers and increased food production, and also opened up jobs in factory work, more access to food
What stage of the dtm did the second Agricultural Revolution occur in?
Stage two because the societies are developing more and it is the beginning of industrialization
Where and when did the 3rd Agricultural Revolution occur
It began in the early 20th century and is continuing today and occurred in core countries, and core countries introduced the advancements to periphery countries
What two main shifts in technology occurred in the 3rd Agricultural Revolution?
The shift to electronic power and then the development of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides (genetic editing tech)
GMO
[genetically modified organism] an organism that has acquired one or more genes by artificial genes.
How did productivity increase through the use of tech?
Productivity increased because more land could be cultivated faster with machines such as tractors, electricity aided crop storage, planted more effectively, and be transported faster
Green Revolution
Starting in the US in the 1950s and 1960s. Rapid diffusion of new agricultural technology, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers.
Positive and Negative effects of 3rd Agricultural Revolution
-Saved lives, nourished millions with the amount of food that increased, made more yield
-displacement of agricultural workers, producers are vulnerable to the technology they use's company and their sales practices, increased need for water pesticides can harm helpful animals, can cause human health problems, and industrial facilities take a lot of energy and resources
Capital
the account used to summarize the owner's equity in a business
infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities (e.g., buildings, roads, and power supplies) needed for the operation of a society or enterprise.
Dual agricultural economy
An economy having two agricultural sectors that have different levels of technology and different patterns of demand
Agribusiness
The overall systems that make up the agricultural process within a commercial business
Who make up the agribusiness
food manufacturers, marketers, distributors and farmers
How do small farmers try to reach economies of scale?
They try to jointly own machinery between other small farms or join cooperatives with each other to minimize costs and share the financial burden
How has tech played a role in creating economies of scale in agriculture?
Technology has lessened the need for human labor and greatly increase its role because machinery has decreased labor costs which helps to create an economy of scale
How has tech affected the carrying capacity of land
Increase the amount of crop you can get out of the soil and almost guarantees a higher yield
How to governments play a role in what farms produce
Governments pay farmers to grow or not grow certain crops, place limits on agricultural imports and exports, and establish price supports
What trends in agriculture are threatening family farms?
People are moving away from rural areas to urban areas, and costs are rising which makes it harder for the family farms to stay in business and may convince them to sell their land
Vertical Integration
Practice where a single entity controls the entire process of a product, from the raw materials to distribution
Commodity Chains
a linked system of processes that gather resources, convert them into goods, package them for distribution, disperse them, and sell them on the market
pros and cons of tarrifs
-can cause dispute between countries and make imported goods cost more
-raise government revenue and protect domestic industries that are being threatened by foreign industries
Von Thunen Model
An agricultural model that spatially describes agricultural activity in terms of rent. Activities that require intensive cultivation and cannot be transported over great distances pay higher rent to be close to the market. Conversely, activities that are more extensive , with goods that are easy to transport, are located farther from the market where rent is less.
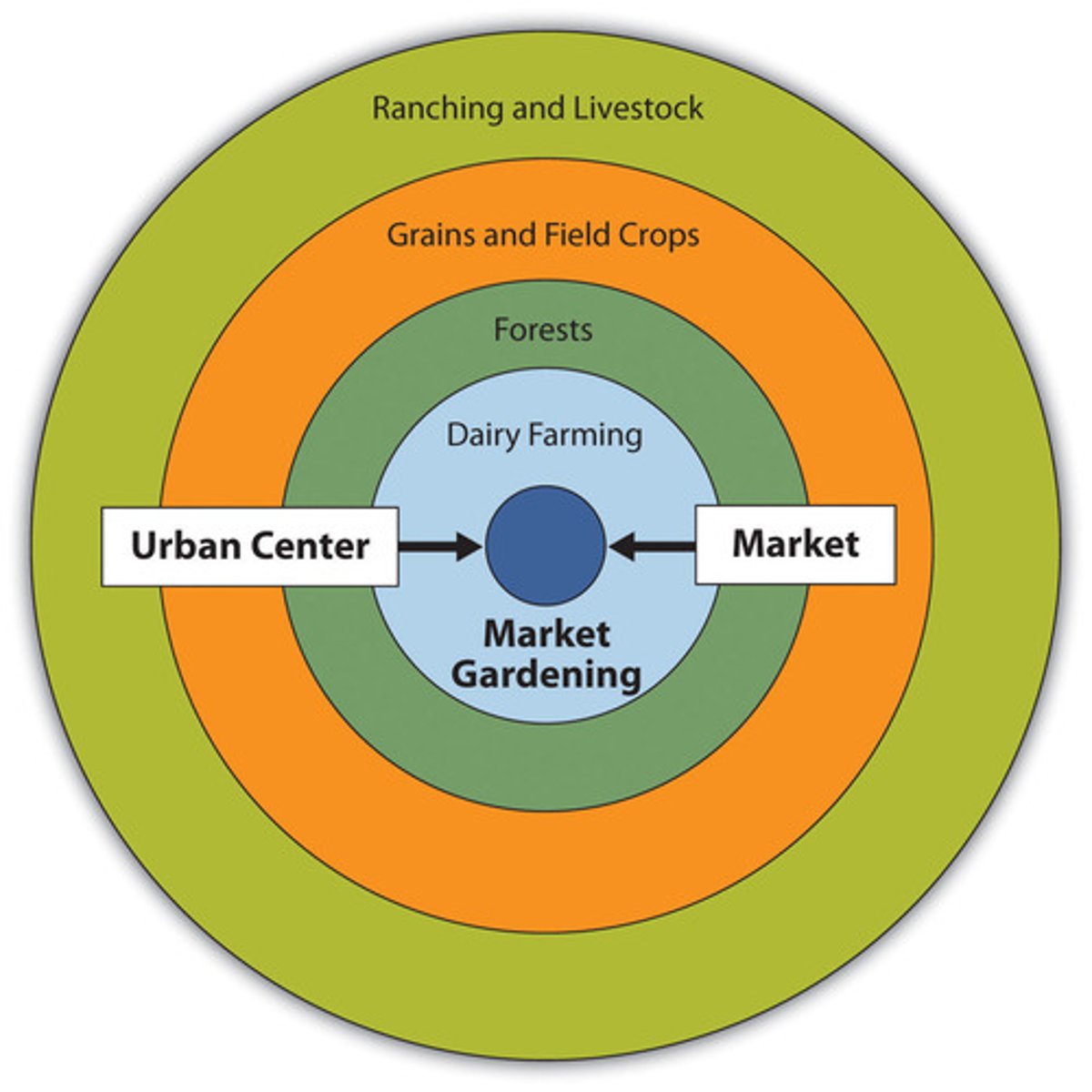
What von Thunen model assumptions that are no longer applicable in agriculture today
Markets are no longer singular within an area, there is the ability to ship products much faster than the model suggest, there is more than one mode of transportation, the land may not be isotropic, there are specialized farming practices, and the concept of selling beyond your own CBD
What political factors impact what you find on your plate every day
Political Relations, trade features and transportation methods
Why don't countries like the US just make all the food their populations need?
It may be less expensive to import goods, or a country's climate may not be suitable for certain foods
What is a cash crop?
A crop that is grown to sell for money rather than for use by the growers
Pros and Cons of cash crops
-have a lot of income tied to them as well as demand
-unhealthy for an economy to rely on one commodity because if something goes wrong or demand decreases their entire economy can collapse
Why is it mutually beneficial for core countries to help build infrastructure in periphery countries
It helps and speeds up the commodity transportation systems to increase profit for the countries by speeding up the importation and exportation processes
How have relationships between former former colonies and colonizers stayed the same?
The ex-colonies are at a disadvantage and may recieve help from their former colonizers at the cost of the continuation of unfair trade agreements
What are some recent patterns of world trade?
Different economies are emerging, trade in food has doubled, agricultural trade between periphery and semi periphery countries has increase
What is the fair trade movement?
The movement to fight unfair wages and protect farmers ability to earn a living as well as making sure the way workers are treated is fair
How has fair trade played a role in food production and consumption globally?
Fair trade is improving land management as well as helping the people who work on the farms financially. Even though the products cost more, they're still bought to support farmers and because of their quality
How does coffee production increase the interdependence between core and semi-periphery countries?
Core countries have to get the coffee from periphery/semi-periphery countries which increases the amount of dependence they have on each other because they both need each other in order to make money
What are the pros and cons of slash and burn agriculture?
It provides a nutrient rich fertilizer, but the land eventually becomes infertile and the method leads to deforestation and soil erosion.
What is terracing?
The process of carving parts of a hill or mountainside into small, level growing plots. Hilly and mountainous land becomes fertile because rain can flow down and get caught in the terraces to create fertile land with an excess of water that is able to grow crops that otherwise may not have been able to grow there
What is irrigation?
A system used to supplement rainfall by bringing water from its natural sources to farm fields through things such as canals.
Reservoir
An artificial lake created by building dams across streams and rivers to store water and aid irrigation.
Why are aquifers threatened in today's world?
If not enough water is replenished, aquifers can be greatly depleted and even completely run out
How much of the world's fresh water sources are used by the agricultural sector
60-70% of the groundwater supply is used by the agricultural sector
How can pastoral nomadism/nomadic herding cause environmental damage if done improperly?
Overgrazing causes land degradation, incur desertification, and can decrease biodiversity because the soil gets less water and less nutrients as well as all the plants can be stripped from the land during overgrazing