AP World Vocab and Dynasty Location Warnke Review.
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Chinese dynasty (960 - 1279 CE) that could be considered their "golden age" when China saw many important inventions. There was a magnetic compass; had a navy; traded with India and Persia; paper money, gun powder
Song Dynasty
A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society in the present world and stresses a moral code of conduct.
Confucianism
In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors.
Filial Piety
The Confucian response to Buddhism by taking Confucian and Buddhist beliefs and combining them into this. However, it is still very much Confucian in belief.
Neo-Confucianism
the oldest of the two major branches of Buddhism. Practiced mainly in Sri Lanka, Thailand, Burma, and Cambodia, its beliefs are relatively conservative, holding close to the original teachings of the Buddha
Theravada Buddhism
"Great Vehicle" branch of Buddhism followed in China, Japan, and Central Asia. The focus is on reverence for Buddha and for Bodhisattva, enlightened persons who have postponed Nirvana to help others attain enlightenment. It was a more "user friendly" Buddhism that developed as Buddhism spread into East and Southeast Asia.
Mahayana Buddhism
a Buddhist doctrine that includes elements from India that are not Buddhist and elements of preexisting shamanism, a tradition of Buddhism that teaches that people can use special techniques to harness spiritual energy and can achieve nirvana in a single lifetime
Tibetan Buddhism
Quick-maturing rice that can allow two harvests in one growing season; led to increased populations in Song Dynasty China. Originally introduced into Vietnam from India, it was later sent to China as a tribute gift by the Champa state (as part of the tributary system.)
Champa Rice
The 1,100-mile (1,700-kilometer) waterway in China linking the Yellow and the Yangzi Rivers. It was begun in the Han period and completed during the Sui Dynasty.
Grand Canal
Chinese credit instrument that provided credit vouchers to merchants to be redeemed at the end of the voyage; reduced danger of robbery; early form of currency
Flying Money
Turkic empire ruled by sultans in Persia and modern-day Iraq (11th and 12th centuries); Established Turks as major ethnic group carrying Islam across Eurasia, along with Arabs and Persians; Demonstrated weakness of Abbasid caliphate in its later years; sultans held real power in the empire; Helped to spread the influence of Islam throughout the region
Seljuk Empire
The first Islamic government established within India from 1206-1520. Controlled a small area of northern India and was centered in Delhi.
Delhi Sultanate
(750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. Had a bureaucracy that any Muslim could be a part of.
Abbasid Caliphate
Large Islamic-based Library and learning center. Focus of conversion of Greek and Roman classics and Indian learning into Arabic. Preserved knowledge.
House of Wisdom in Baghdad
An immensely popular development in Hinduism, advocating intense devotion toward a particular deity.
Bhakti Movement
An Islamic mystical tradition that desired a personal union with God--divine love through intuition rather than through rational deduction and study of the Shari'a. Followed an ascetic routine (denial of physical desire to gain a spiritual goal), dedicating themselves to fasting, prayer, meditation on the Qur'an, and the avoidance of sin.
Sufism
A political system in which nobles are granted the use of lands that legally belong to their king, in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land
Feudalism
a person under the protection of a feudal lord to whom he or she owes allegiance
Vassal
an agricultural laborer bound under the feudal system to work on their lord's estate.
Serf
Economic system during the Middle Ages that revolved around self-sufficient farming estates where lords and peasants shared the land; the economic side of feudalism
Manorialism
Classical culture in Southern Mexico and Central America; contemporary with Teotihuacan; extended over broad region; featured monumental architecture, written language, calendar system, mathematical system
Maya city-states
government or the holding of power by people selected on the basis of their ability; used in China via the Civil Service Exam
Meritocracy
The unification or blending of opposing people, ideas, or practices, frequently in the realm of religion. For example, when Christianity or Buddhism was adopted by people in a new land, they often incorporate it into their existing culture and traditions.
Syncretism
economic system in Inca society where people paid taxes with their labor and what they produced; men and women were expected to contribute this labor to the state yearly
Mita System
Floating gardens constructed along lake shores by the Mexica/Aztecs to increase agricultural yields.
Chinampas
A rotational system for agriculture in which one field grows grain, one grows legumes, and one lies fallow. Restores nutrients to the soil to improve crop yields. It gradually replaced two-field system in medieval Europe.
three-field system
A series of holy wars from 1096-1270 AD undertaken by European Christians to free the Holy Land from Muslim rule; ultimately spread culture and increased trade but were not successful
Crusades
"rebirth"; following the Middle Ages, a movement that centered on the revival of interest in the classical learning of Greece and Rome; began in Florence, Italy and spread throughout Europe
Renaissance
in 1054, divided medieval Christianity into (Greek) and Western (Latin) branches, which later became known as the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church. Relations between East and West had long been embittered by political and ecclesiastical differences and theological disputes.
Great Schism
Any labor system that involves force (slavery, chattel slavery, serfdom, and indentured labor)
coercive labor
land granted by a lord to a vassal in exchange for loyalty and service
Fief
large flat-bottom sailing ship produced in the Tang and Song Empires, specially designed for long-distance commercial travel and participation in the tribute system
junk ship
a central Asian city where the western and the eastern Silk Roads met; one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with modern day Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, and Tajikistan.
Kashgar
During the rule of Timur Lane was the most influential capital city, a wealthy trading center known for decorated mosques and tombs; a key trading city along the Silk Roads
Samarkand
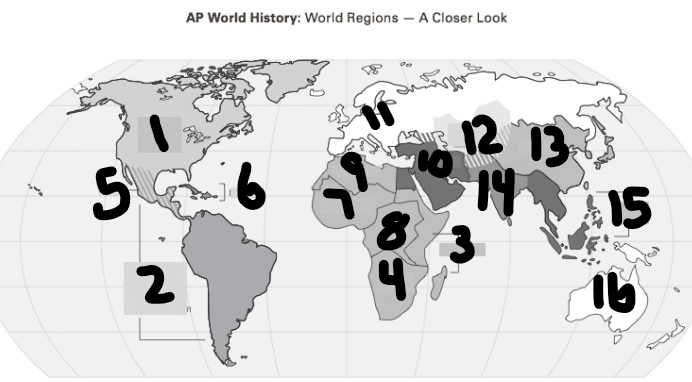
What is #1?
North America
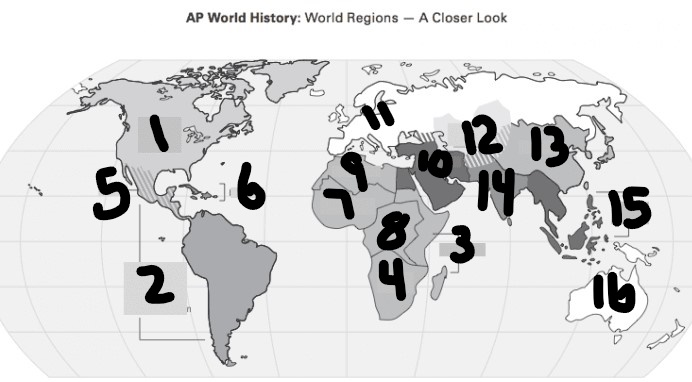
What is Number 2
Latin America
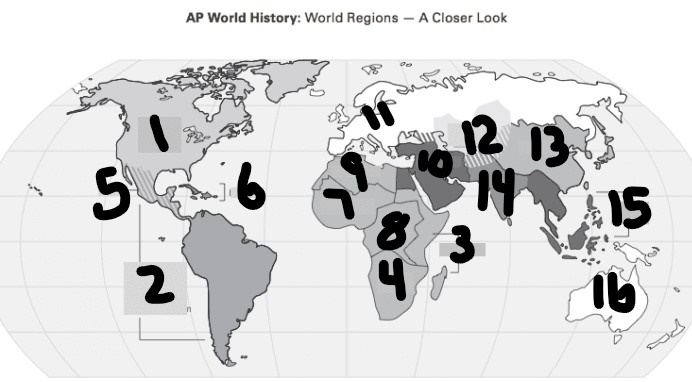
What is Number 3
East Africa
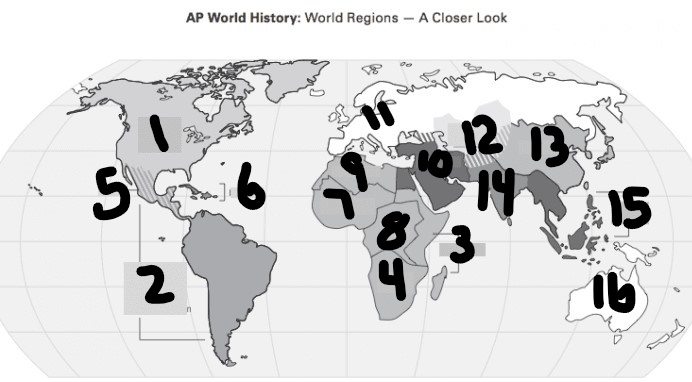
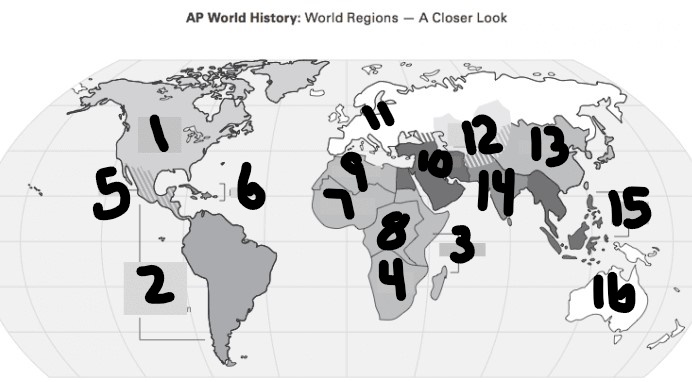
What is Number 4
Southern Africa
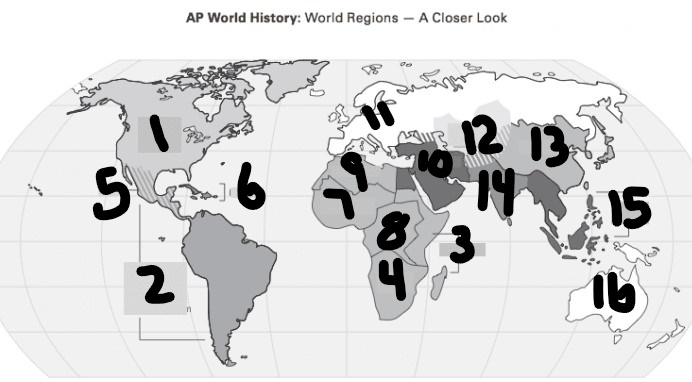
What is Number 5
Meso-america
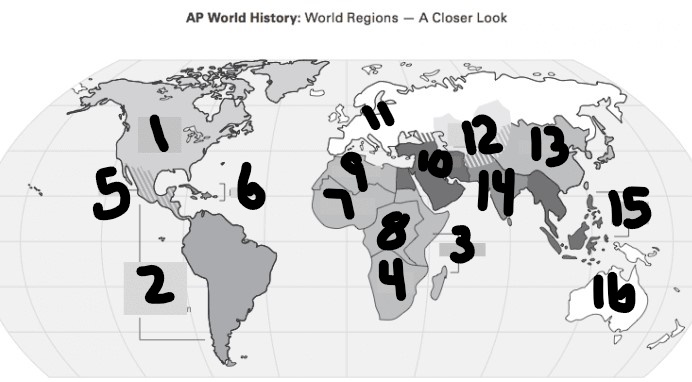
What is Number 6
Carribean
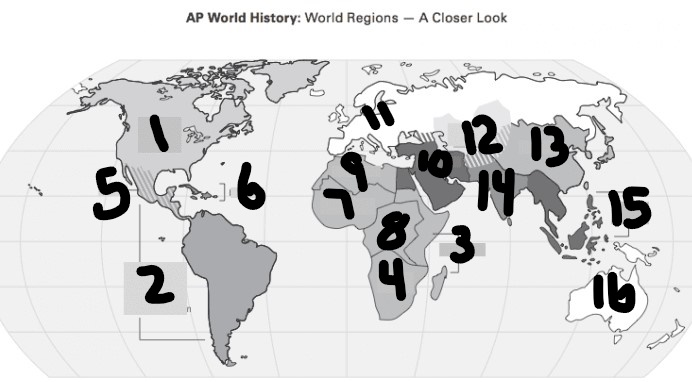
What is number 7
West Africa
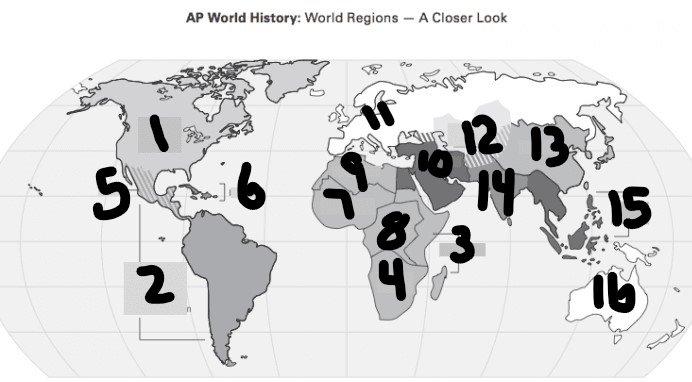
Number 8 Region
Centeral Africa
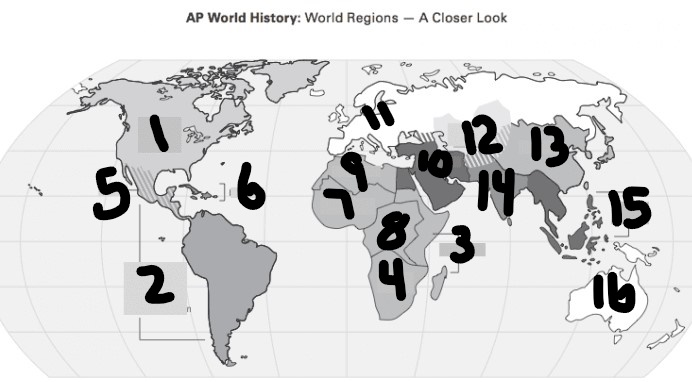
9
North Africa
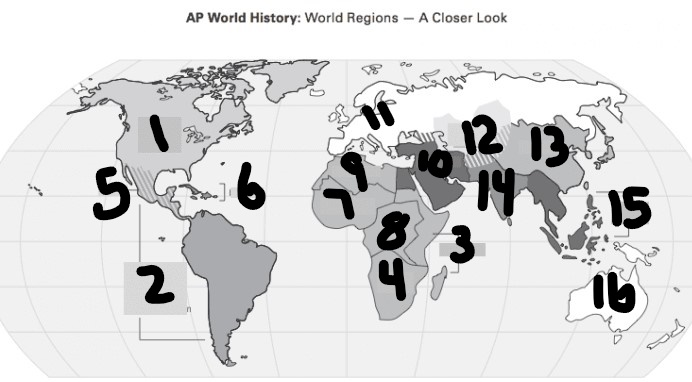
10
Middle East
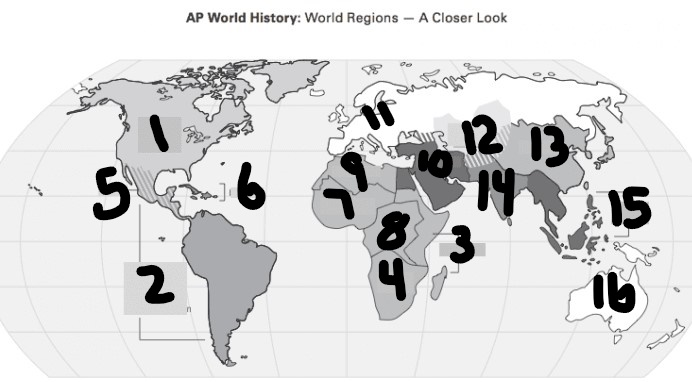
11
Europe
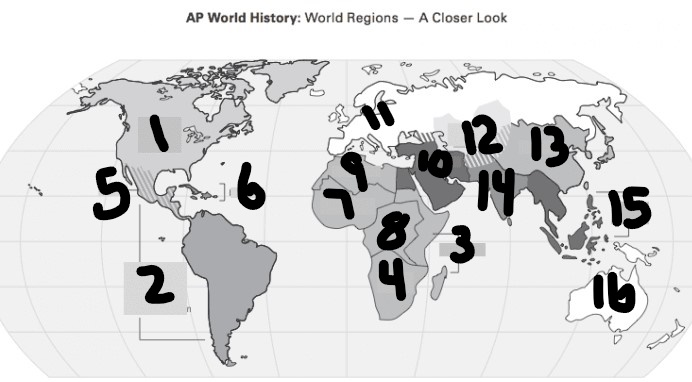
12
Central Asia
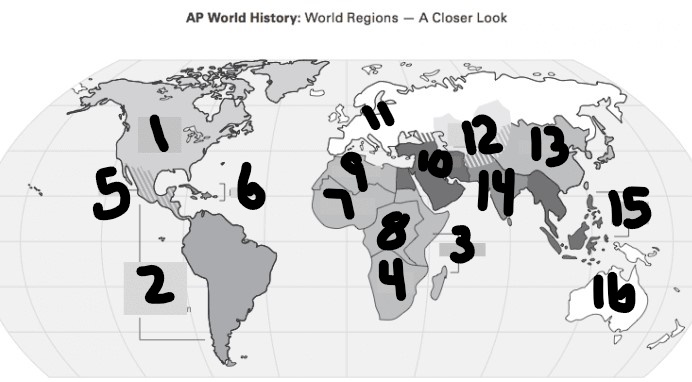
13
East Asia
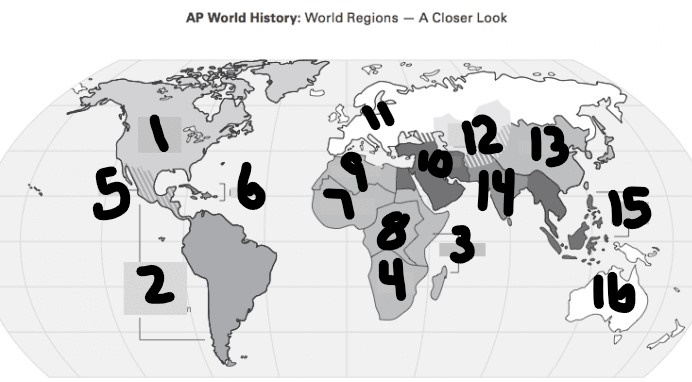
14
South Asia
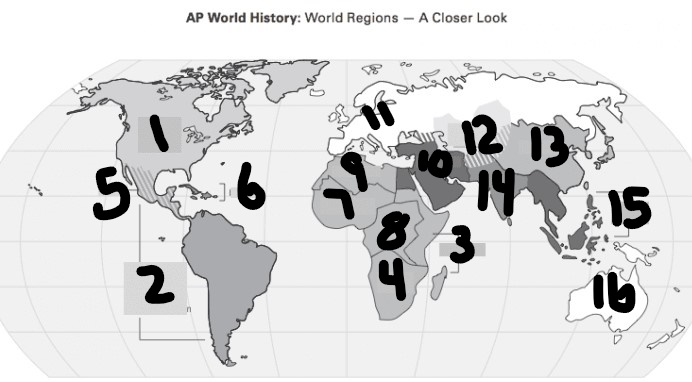
15
Southeast Asia
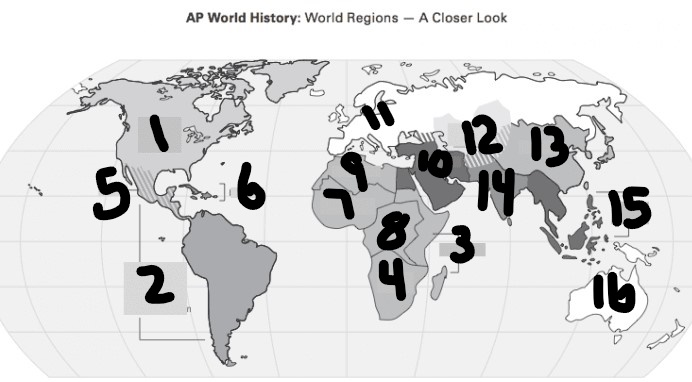
16
Oceania
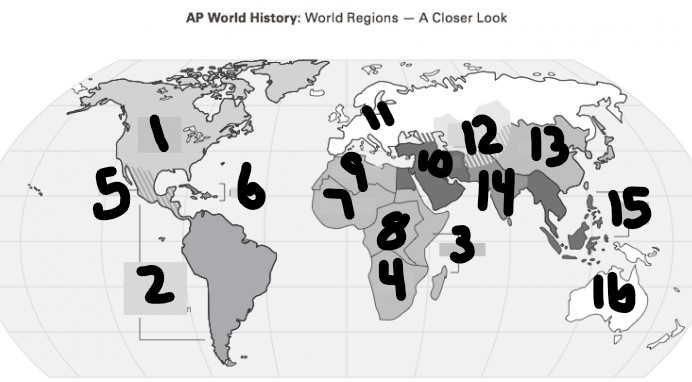
Where were the byzantine located
11,10,9( Europe, Middle East, North Africa)
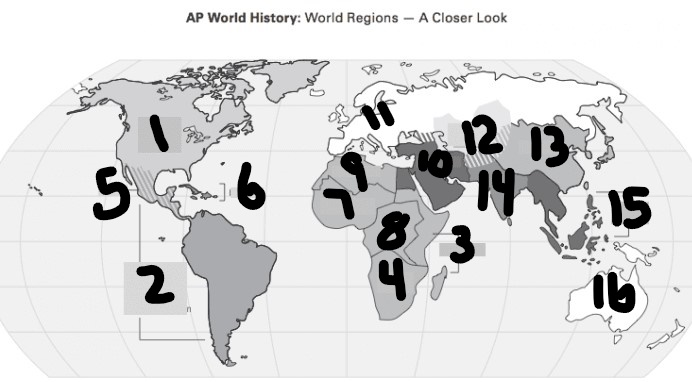
Incan Empire?
6(Latin America)
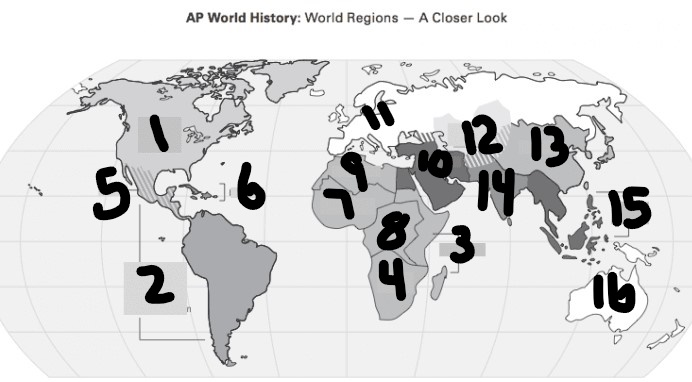
Where was the islamic calihpates located
14(South Asia)
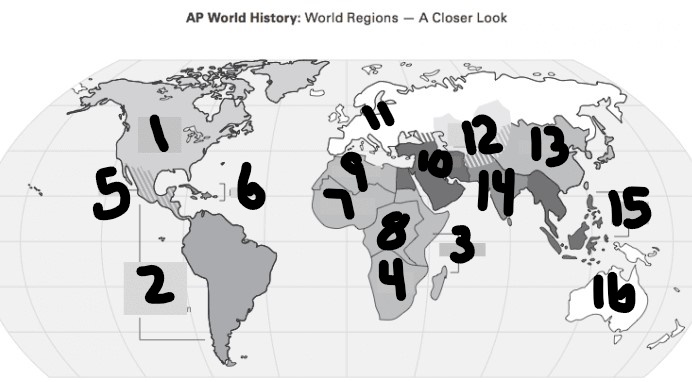
Where were the italian city states located?
11 (Europe)
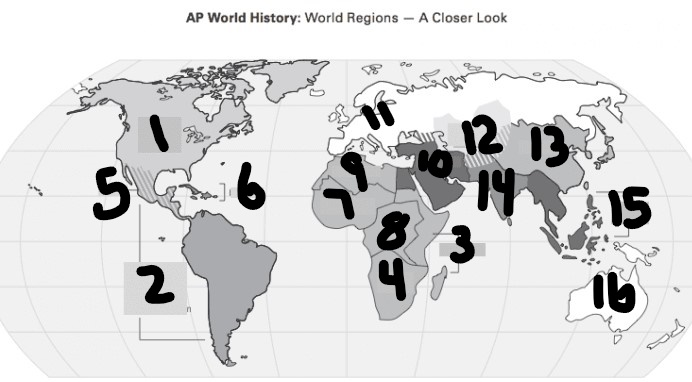
Japan
13(East Asia)
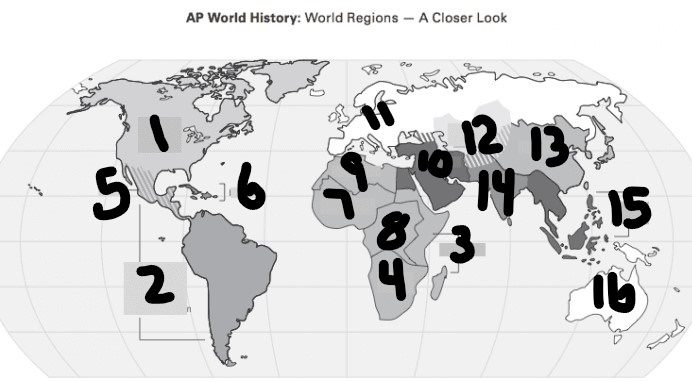
Mongolian Empire
12 and 13 (Centeral and East Asia)
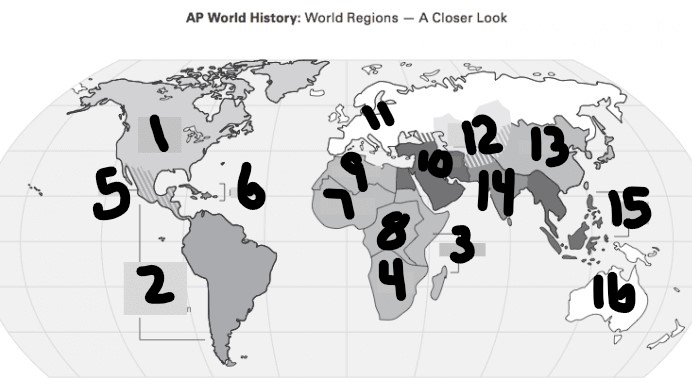
Where is Polynisia Located
16(Ocenia)
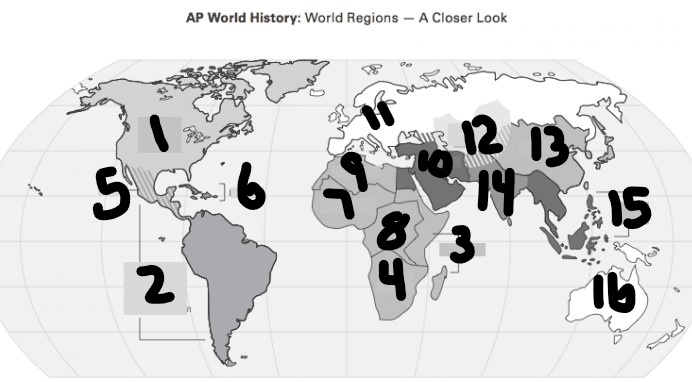
Swhali City States are in?
3(East Africa)
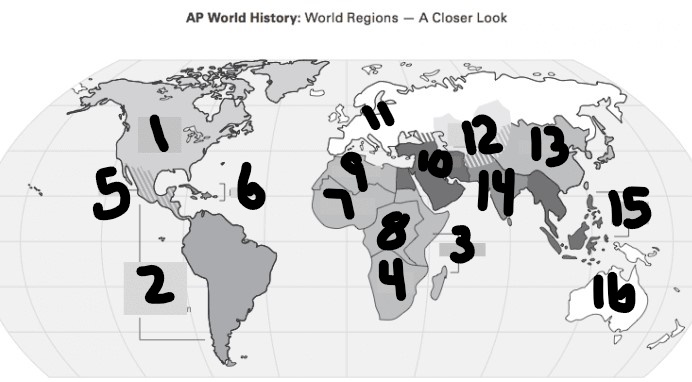
Where is Song/Tong/Sui Dynasty Located?
1(East Asia)
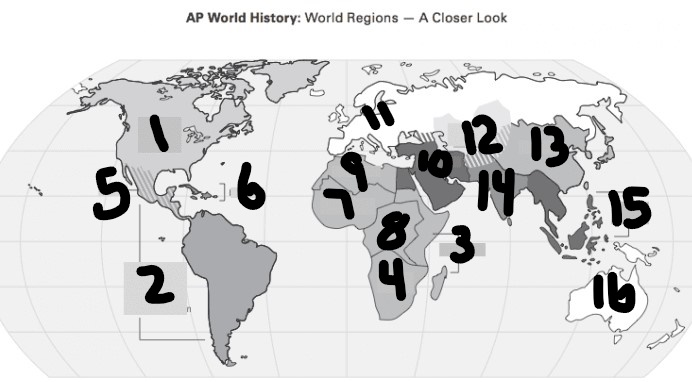
Where were the toltecs located
5(Meso-America)