Understanding Groundwater: Importance and Protection
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Groundwater
All water which is below the surface of the ground and within the permanently saturated zone.
Groundwater body
A distinct volume of groundwater within an aquifer.
Hydrogeology
The nature, distribution and movement of groundwater in soils and rocks, including in aquifers.
Meteoric water
Precipitation that falls on the Earth's surface, in a form of rainfall or snow, infiltrates through the soil and percolates downward.
Connate waters
Water trapped in marine sediments at the time of their deposition; cannot be a source of exploitable groundwater because it is saline.
Fossil water
Underground water reservoirs that have been geologically sealed.
Juvenile Water
Magmatic water found in the cracks or crevices of rocks due to condensation of steam emanating from hot molten masses; associated with hot springs and geysers.
Irrigation
A use of groundwater for agricultural purposes.
Public Supply
A use of groundwater for providing drinking water to the public.
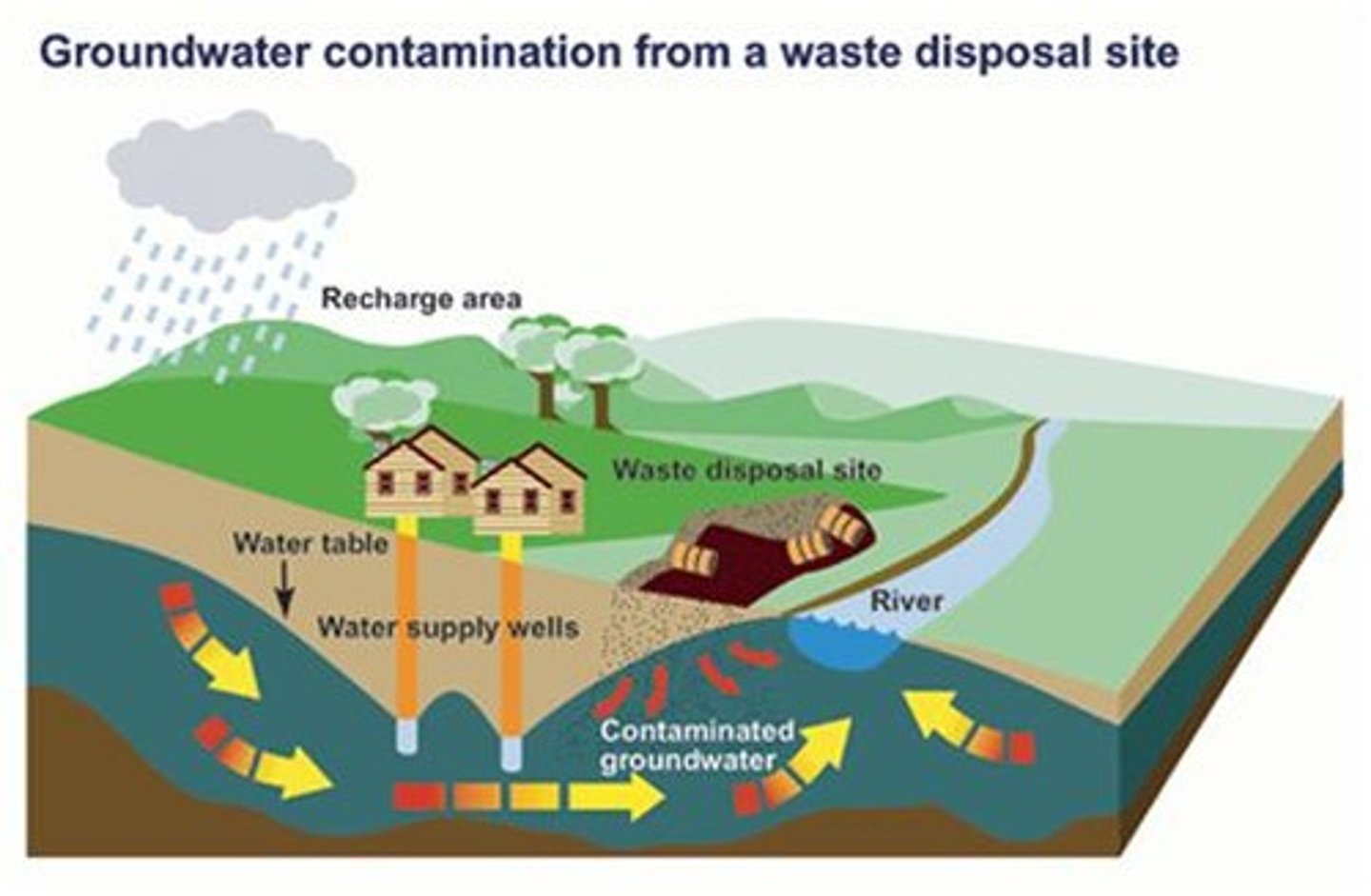
Groundwater contamination
Occurs when man-made products such as gasoline, oil, road salts and chemicals get into the groundwater and cause it to become unsafe and unfit for human use.
Lowering of the Water Table
Excessive pumping can lower the groundwater table, causing wells to no longer be able to reach groundwater.
Increased Costs
As the water table lowers, the water must be pumped farther to reach the surface, using more energy.
Reduced Surface Water Supplies
When groundwater is overused, the lakes, streams, and rivers connected to groundwater can also have their supply diminished.
Land Subsidence
Occurs when there is a loss of support below ground.
Water Quality Concerns
Excessive pumping in coastal areas can cause saltwater to move inland and upward, resulting in saltwater contamination of the water supply.
General Importance of Groundwater
Provides drinking water for more than 90% of the rural population in the US and is used for irrigation processes; 99% of all the freshwater in the world.
Structural Stability
Impacts of groundwater on buildings and foundation systems.
Capillary Rise
The upward movement of water through soil due to capillary action.
Flooding
Reduction of strength of soil due to excess water.
Sinkhole formation
A phenomenon where the ground collapses due to the dissolution of limestone or other soluble rocks, often linked to groundwater depletion.

Slope Instability
Groundwater can affect the stability of slopes, leading to landslides.
Ways to Protect Groundwater
Strategies include going native, reducing chemical use, managing waste, fixing leaks, and using water wisely.