Brain and Behavior midterm 2: Chapter 4-7
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy of the Nervous System, Sensory Systems, Sensorimotor Systems, Motor Systems, Brain Damage/Disorders, & Learning and Memory
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
1
New cards
Planes of brain orientation
Horizontal plane
Sagittal plane
Coronal plane
Sagittal plane
Coronal plane
2
New cards
Horizontal plane
Parallel to floor
3
New cards
Sagittal plane
Splits down middle, left and right
4
New cards
Coronal plane
Dividends front back back Posterior and anterior
5
New cards
Medial or proximal
towards the middle
6
New cards
Lateral or distal
going towards the side
7
New cards
Ipsilateral
Same side
8
New cards
Contralateral
opposite side
9
New cards
Superior
Above
10
New cards
Inferior
Below
11
New cards
Anterior or rostral
near the head
12
New cards
Posterior or caudal
near the feet
13
New cards
Dorsal
Towards the back
14
New cards
Ventral
Towards the belly or front
15
New cards
Afferent
Neurons carry information into a region of interest
16
New cards
Efferent
Neurons carry information away from region of interest
17
New cards
Nervous systems:
The central nervous system
The peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system
18
New cards
Central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord
19
New cards
The peripheral nervous system
all other parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord
\
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
\
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
20
New cards
Somatic nervous system
* Nerves that connect the brain and major muscles and sensory systems of the body
* Voluntary
* Voluntary
21
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
* Nerves that connect to the viscera (internal organs)
* Automatic
\
* Sympathetic nervous system
* Parasympathetic nervous system
* Automatic
\
* Sympathetic nervous system
* Parasympathetic nervous system
22
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
* Axons that innervate the sympathetic ganglia
* Small clusters of neurons
* “Fight or flight”
* Sweat, jump, digestion stops, heart rate, blood pressure, pupils
* Small clusters of neurons
* “Fight or flight”
* Sweat, jump, digestion stops, heart rate, blood pressure, pupils
23
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system
* Helps body relax and recuperate
* “Rest and digest”
* Calms down body
* Farther from CNS, closer to organs
* “Rest and digest”
* Calms down body
* Farther from CNS, closer to organs
24
New cards
Bundles of axons names:
CNS - Tracts
PNS - Nerves
PNS - Nerves
25
New cards
Groups of cell bodies
CNS - Nuclei
PNS - Ganglion, Ganglia (plural)
PNS - Ganglion, Ganglia (plural)
26
New cards
Myelin made by:
CNS - Oligodendrocytes
PNS - Schwann cells
PNS - Schwann cells
27
New cards
Motor nerves
Transmit information from the spinal cord and brain to muscles and glands
28
New cards
Sensory nerves
Convey information from the cell body to the central nervous system
29
New cards
Nerves of the somatic nervous system
* Cranial nerves
* Spinal nerves
* Spinal nerves
30
New cards
Cranial nerves
* Coming from head and neck going to visceral organs
* 12 pairs - one right and one left side
* Sensory, motor, or both
* Information from touch receptors in the head enters the CNS through the cranial nerves
* Vagus also has parasympathetic
* Diaphragm
* Misfire is vagus nerve
* Hiccups (literally)
* 12 pairs - one right and one left side
* Sensory, motor, or both
* Information from touch receptors in the head enters the CNS through the cranial nerves
* Vagus also has parasympathetic
* Diaphragm
* Misfire is vagus nerve
* Hiccups (literally)
31
New cards
Spinal nerves
31 pairs - named after the vertebrae
* Cervical
* Thoracic
* Lumbar Lower back 5 segments
* Sacral Pelvic 5 segments
* Coccygeal Bottom 1 segment
\
SAD = sensory afferent dorsal
* Types of info coming to and from spinal cordy
\
* Depends on where touched
* Information from receptors below the head enters the spinal cord and travel through the 31 spinal nerves to the brain
* Cervical
* Thoracic
* Lumbar Lower back 5 segments
* Sacral Pelvic 5 segments
* Coccygeal Bottom 1 segment
\
SAD = sensory afferent dorsal
* Types of info coming to and from spinal cordy
\
* Depends on where touched
* Information from receptors below the head enters the spinal cord and travel through the 31 spinal nerves to the brain
32
New cards
Cervical
* Neck
* 8 segments
* 8 segments
33
New cards
Thoracic
* Trunk
* 12 segments
* 12 segments
34
New cards
Lumbar
* Lower back
* 5 segments
* 5 segments
35
New cards
Sacral
* Pelvic
* 5 segments
* 5 segments
36
New cards
Coccygeal
* Bottom
* 1 segment
* 1 segment
37
New cards
cauda equina
* “horse's tail”
* extension of spinal nerves beyond end of spinal cord
\
* Epidurals are below the spinal cord
* extension of spinal nerves beyond end of spinal cord
\
* Epidurals are below the spinal cord
38
New cards
dermatomes
* Areas of the body innervated by a specific spinal nerve
* Different areas of the periphery that are innovative by a different spinal nerve
* At all levels, inputs are organized into dermatomes, strips of skin each innervated by a particular spinal nerve
* Essentially is a receptive field
* Different areas of the periphery that are innovative by a different spinal nerve
* At all levels, inputs are organized into dermatomes, strips of skin each innervated by a particular spinal nerve
* Essentially is a receptive field
39
New cards
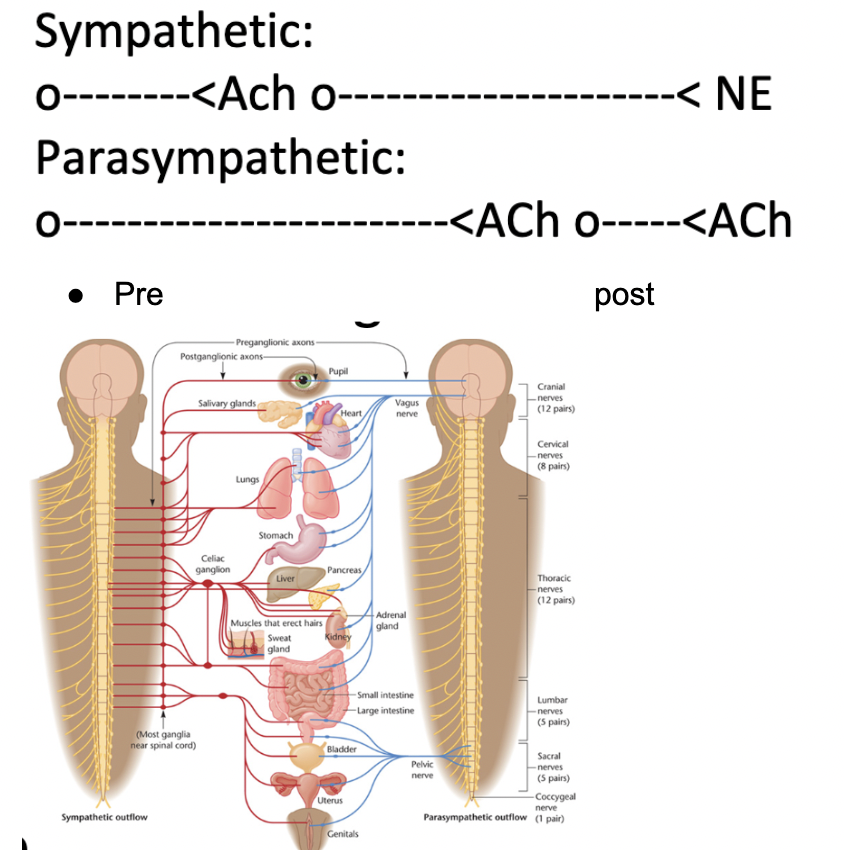
Different effects on organs due to different neurotransmitters released by postganglionic neurons
* All preganglionic neurons release ACh.
* Sympathetic postganglionic neurons release epinephrine (= adrenaline)
* Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons release ACh
* Sympathetic postganglionic neurons release epinephrine (= adrenaline)
* Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons release ACh
40
New cards
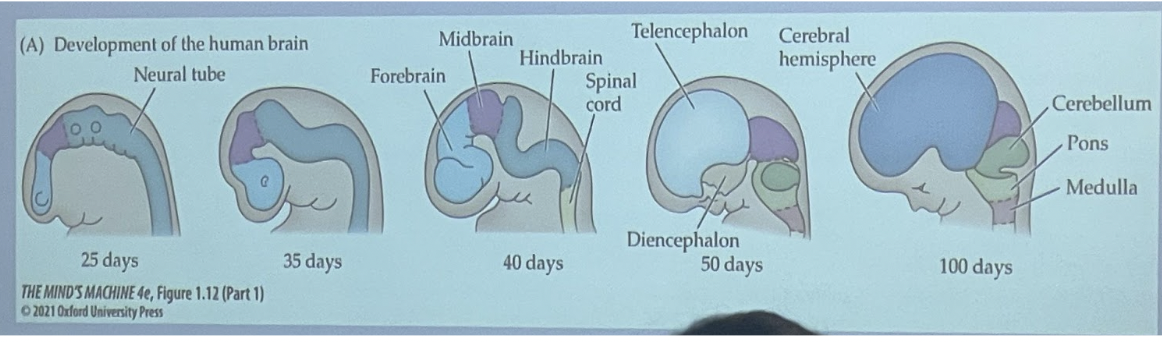
Embryonic development of brain and spinal cord
* Neural tube
* Then subdivides
* Front, forbrain
* Middle midbrain
* Hindbrain
* he hindbrain develops into the cerebellum, pons, and medulla.
* Brainstem refers to the midbrain, pons, and medulla combined
* Then subdivides
* Front, forbrain
* Middle midbrain
* Hindbrain
* he hindbrain develops into the cerebellum, pons, and medulla.
* Brainstem refers to the midbrain, pons, and medulla combined
41
New cards
Protection of the nervous system:
* Chemical protection
* Physical protection
* Meninges
* Physical protection
* Meninges
42
New cards
Chemical protection
* Blood brain barrier
* Tightly packed blood vessel cells and astrocytes
* Tightly packed blood vessel cells and astrocytes
43
New cards
Physical protection
* Skull and vertebral column(spine)
* Meninges
* Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
* Meninges
* Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
44
New cards
Meninges
* Dura mater
* Arachnoid membrane
* Subarachnoid space
* Pia mater
\
* Meningitis - acute infection of the meninges
* Meningiomas - tumors formed in meninges
* Arachnoid membrane
* Subarachnoid space
* Pia mater
\
* Meningitis - acute infection of the meninges
* Meningiomas - tumors formed in meninges
45
New cards
Dura mater
* outer layer
* “Tough mother”
* “Tough mother”
46
New cards
Arachnoid membrane
* middle layer
* Spider weblike membrane
* Below dura mater
* Spider weblike membrane
* Below dura mater
47
New cards
Subarachnoid space
* below the arachnoid membrane
* Containing many blood vessels and cerebrospinal fluid
* Looks like spider web
* Containing many blood vessels and cerebrospinal fluid
* Looks like spider web
48
New cards
Pia mater
* “Pious mother”
* Layer closest to brain and spinal cord
* Layer closest to brain and spinal cord
49
New cards
**Ventricular system**
* **Ensuring the brain doesn’t “dry out”**
* Chambers filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
* **Lateral ventricle**
* In each hemisphere
* Extends to all four lobes and lined with **choroid plexus**
* CSF flows into the **third ventricle** at the midline, through the **cerebral aqueduct**, and into the **fourth ventricle** where it exits to circulate over the brain and via the **central canal** of the spinal cord
* Chambers filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
* **Lateral ventricle**
* In each hemisphere
* Extends to all four lobes and lined with **choroid plexus**
* CSF flows into the **third ventricle** at the midline, through the **cerebral aqueduct**, and into the **fourth ventricle** where it exits to circulate over the brain and via the **central canal** of the spinal cord
50
New cards
Too much cerebrospinal fluid
* Absorbed into sinuses (large, blood filled spaces)
* Run through dura and drain into jugular veins of neck
* **Hydrocephalus**
* (water head)
* Expansion of ventricles
* Ex: due to blockage by tumor, etc
* Need to drain
* Run through dura and drain into jugular veins of neck
* **Hydrocephalus**
* (water head)
* Expansion of ventricles
* Ex: due to blockage by tumor, etc
* Need to drain
51
New cards
Glymphatic System
* Glial cells (picking up junk) take info and take it to blood vessels to CSF
* Clear the gunk out
* More active while a person is sleeping
* Deep sleep
* If can't sleep: excess debris
* Problems with glymphatic system can relate to alzheimer’s disease
* Build up
* Clear the gunk out
* More active while a person is sleeping
* Deep sleep
* If can't sleep: excess debris
* Problems with glymphatic system can relate to alzheimer’s disease
* Build up
52
New cards
Cerebral blood flow and stroke
* Brain depends on a an ample supply of oxygenated blood from the **cerebral arteries**
* Need good supply!!
* Stroke: rupture, break, or blockage of blood vessels to prevent significant oxygen supply
* Types of stroke: (completely opposite)
* Ischemic
* Hemorrhagic
* Need good supply!!
* Stroke: rupture, break, or blockage of blood vessels to prevent significant oxygen supply
* Types of stroke: (completely opposite)
* Ischemic
* Hemorrhagic
53
New cards
Ischemic
* Blood flow restricted by clot or other obstruction
* Treat by breaking the clot up
* Treat by breaking the clot up
54
New cards
Hemorrhagic
* Artery ruptures causing blood to leak within the brain
* Only way to stop is naturally or to cauterize it
* Only way to stop is naturally or to cauterize it
55
New cards
Warning signs of stroke:
* Sudden numbness or weakness
* Altered vision
* Dizziness
* Severe headache
* Confusion or difficulty speaking
* Altered vision
* Dizziness
* Severe headache
* Confusion or difficulty speaking
56
New cards
Cerebral cortex
* Covering over the brain
* Outermost layer of the brain
* NOT FLAT FOR HUMAN
* Has ridges/bulges
* Gyri
* Sulci
* Grey = cell bodies
* White = axons
* Split into two:
* **Cerebral hemispheres** divided by the **longitudinal fissure**
* Longitudinal fissure - large sulcus
* Outermost layer of the brain
* NOT FLAT FOR HUMAN
* Has ridges/bulges
* Gyri
* Sulci
* Grey = cell bodies
* White = axons
* Split into two:
* **Cerebral hemispheres** divided by the **longitudinal fissure**
* Longitudinal fissure - large sulcus
57
New cards
Gyri
Ridges or raised portions (mountains)
58
New cards
Sulci
Furrows (valleys)
59
New cards
Four cerebral hemispheres
* Frontal lobe
* Parietal lobe
* Occipital lobe
* Temporal lobe
* Parietal lobe
* Occipital lobe
* Temporal lobe
60
New cards
Frontal lobe
* most anterior region
* Prefrontal cortex - planning, attention much of frontal cortex devoted to motor control
* Prefrontal cortex - planning, attention much of frontal cortex devoted to motor control
61
New cards
Parietal lobe
* Lies between the frontal and occipital lobes; somatosensory functions
62
New cards
Occipital lobe
* Posterior region, visual processing
63
New cards
Temporal lobe
* Lateral region, auditory processing
64
New cards
Lateral (sylvian) fissure
* boundary of the temporal lobe
65
New cards
Longitudinal fissure
* Splits the left and right hemisphere
66
New cards
Central sulcus
* Divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
67
New cards
Corpus callosum
* a bundle of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres
68
New cards
Postcentral gyrus
* a strip of parietal cortex posterior to the central sulcus
* primary somatosensory cortex
* In sensory cortex
* primary somatosensory cortex
* In sensory cortex
69
New cards
Precentral gyrus
* posterior gyrus of **frontal lobe**
* primary motor cortex
* In motor cortex
* primary motor cortex
* In motor cortex
70
New cards
Forebrain/cerebral hemispheres
* Basal ganglia
* Limbic system
* Thalamus
* Limbic system
* Thalamus
71
New cards
Basal ganglia
* Two major functions: motor system and cognitive process
* Consists of: caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
* (Caudate + putamen = Striatum)
* Nigrostriatal pathway
* Consists of: caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
* (Caudate + putamen = Striatum)
* Nigrostriatal pathway
72
New cards
Limbic system
* Groups of structure
* Structures important for emotion and learning
* Form a border around the brainstem
* Consists of:
* Amygdala
* Hippocampus(aka seahorse) and fornix(connected fibers)
* Cingulate gyrus
* Olfactory bulb
* Hypothalamus
* Structures important for emotion and learning
* Form a border around the brainstem
* Consists of:
* Amygdala
* Hippocampus(aka seahorse) and fornix(connected fibers)
* Cingulate gyrus
* Olfactory bulb
* Hypothalamus
73
New cards
Amygdala
* emotion regulation and perception of odor, fear
74
New cards
Hippocampus(aka seahorse) and fornix(connected fibers)
* learning and memory, emotion is tied to memory
75
New cards
Cingulate gyrus
* attention
* processing emotions and behavior regulation
* processing emotions and behavior regulation
76
New cards
Olfactory bulb
* sense of smell
77
New cards
Hypothalamus
* contains nuclei with many functions; also controls pituitary
* many nuclei
* below thalamus
* motivated behaviors (feeding, drinking, temp regulation, rhythms, sex behavior, sleep)
* connections with limbic system
* input to pituitary gland
* many nuclei
* below thalamus
* motivated behaviors (feeding, drinking, temp regulation, rhythms, sex behavior, sleep)
* connections with limbic system
* input to pituitary gland
78
New cards
Thalamus
* Single structure
* Cluster of nuclei that relay sensory information
* Ex: train station → stuff coming in and stuff going out
* Lateral geniculate nucleus – visual
* Medial geniculate nucleus – auditory
* Optic nerve into the thalamus and optic tract brings it out
* Cluster of nuclei that relay sensory information
* Ex: train station → stuff coming in and stuff going out
* Lateral geniculate nucleus – visual
* Medial geniculate nucleus – auditory
* Optic nerve into the thalamus and optic tract brings it out
79
New cards
Midbrain
* the “house”
\
* Tectum(roof)
* Tegmentum (basement)
\
* Tectum(roof)
* Tegmentum (basement)
80
New cards
Tectum(roof)
* includes sensory areas:
* Superior colliculi - visual processing
* Inferior colliculi - auditory processing
* Colliculi - “little hills” - feel little bumps
* Superior colliculi - visual processing
* Inferior colliculi - auditory processing
* Colliculi - “little hills” - feel little bumps
81
New cards
Tegmentum (basement)
* Substantia nigra - connects to basal ganglia, motor system
* Nigrostriatal tract - degenerates in Perkinson’s Disease
* Red Nucleus - sensorimotor integration (somewhat middle)
* Periaqueductal gray - around the cerebral aqueduct, pain perception, site of opiate receptors
* Nigrostriatal tract - degenerates in Perkinson’s Disease
* Red Nucleus - sensorimotor integration (somewhat middle)
* Periaqueductal gray - around the cerebral aqueduct, pain perception, site of opiate receptors
82
New cards
Reticular formation
* involved with sleep and arousal
* Running from hindbrain through midbrain
* Running from hindbrain through midbrain
83
New cards
Hindbrain
* Certain vital body functions are controlled by the brainstem
* If we damage the hindbrain you are dead
\
* Cerebellum
* Pons
* Medulla
* If we damage the hindbrain you are dead
\
* Cerebellum
* Pons
* Medulla
84
New cards
Cerebellum
* big structure on back
* Coordination and control
* Participates in come types of learning
* Coordination and control
* Participates in come types of learning
85
New cards
Pons (bridge)
* fiber crossings
* Axons going from left ot right side and vise versa
* Origin of some cranial nerves
* Axons going from left ot right side and vise versa
* Origin of some cranial nerves
86
New cards
Medulla
* Transition from brain to spinal cord
* Essential processes such as respiration and heart rate
* Origin of some cranial nerves
* Essential processes such as respiration and heart rate
* Origin of some cranial nerves
87
New cards
Ways to study the brain: based on structure
* CT/CAT scans
* MRI scans
* MRI scans
88
New cards
Ways to study the brain: based on function
* fMRI
* PET
* TMS
* MEG (Magnetoencephalography)
* DTI
* EEG
* PET
* TMS
* MEG (Magnetoencephalography)
* DTI
* EEG
89
New cards
CT/CAT scans
* (computerized tomography)
* Telling you what the brain looks like
* Image
* Measure of X-ray absorption at several position
* Telling you what the brain looks like
* Image
* Measure of X-ray absorption at several position
90
New cards
MRI scans
* (magnetic resonance imaging)
* Uses magnets
* Uses magnets
91
New cards
fMRI
* (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
* MRI, but looking at function
* Where in the brain is there a lot of activity
* Using oxygen
* MRI, but looking at function
* Where in the brain is there a lot of activity
* Using oxygen
92
New cards
PET
* (Positron Emission Tomography)
* Only at high medical center
* Only at high medical center
93
New cards
TMS
* (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)
* Using magnet to control what is going on in the brain
* Using magnet to control what is going on in the brain
94
New cards
DTI
* (Diffusion Tensor Imaging)
* Shows the circuits
* Looking at fiber tracts (measuring water in the brain)
* Shows the circuits
* Looking at fiber tracts (measuring water in the brain)
95
New cards
EEG
* (Electroencephalography)
* Put the electrodes on head
* Useful when measuring sleep patterns
* Put the electrodes on head
* Useful when measuring sleep patterns
96
New cards
Senses, understanding, how we understand:
* **Detection** of sense requires **receptors**, specialized for that stimulus modality
* A protein that whatever the stimulus is can react
* Ex: hair cells moving can detect wind
* Stimulus must be **transduced** (changed) into the language that the neurons can speak
* Neurons speak through action potential
* The “language” of sensory input is in the form of chemicals, sound waves, temperature, etc.
* The “language” of neurons includes action potentials, depolarization, hyperpolarization
* The concept of **labeled lines(what she drew)** says that the brain recognizes distinct senses because action potentials travel along separate nerve tracts.
* When information gets to the brain it will based on method of **coding**
* Coding is done in the cerebral cortex!!!!
* A protein that whatever the stimulus is can react
* Ex: hair cells moving can detect wind
* Stimulus must be **transduced** (changed) into the language that the neurons can speak
* Neurons speak through action potential
* The “language” of sensory input is in the form of chemicals, sound waves, temperature, etc.
* The “language” of neurons includes action potentials, depolarization, hyperpolarization
* The concept of **labeled lines(what she drew)** says that the brain recognizes distinct senses because action potentials travel along separate nerve tracts.
* When information gets to the brain it will based on method of **coding**
* Coding is done in the cerebral cortex!!!!
97
New cards
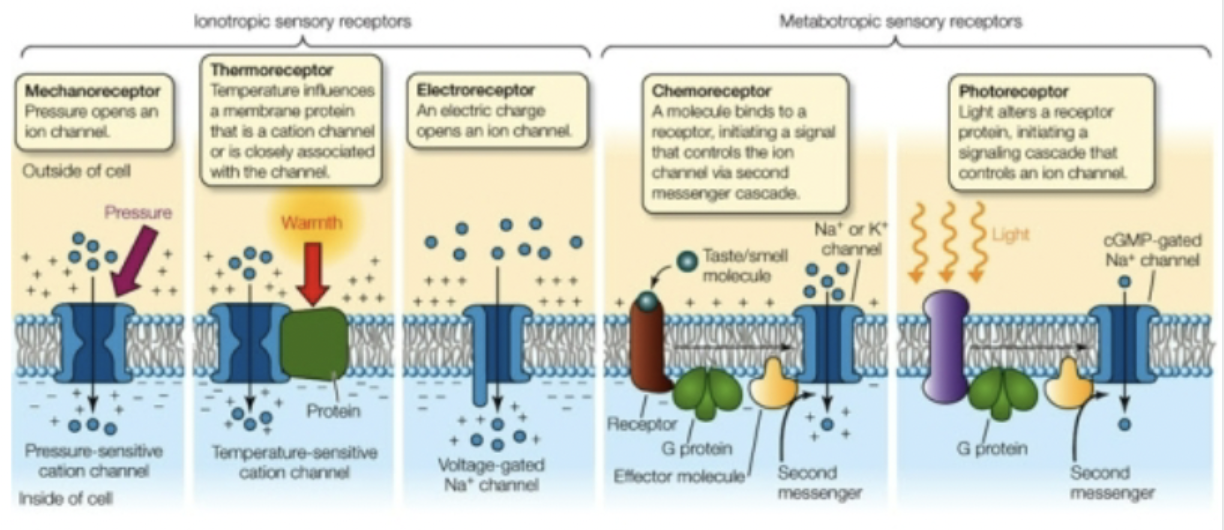
Sensory transduction
* The detector is able to take stimulus energy and convert it to polarization or depolarization
* Uses ionotropic or metabotropic receptors
* **Generator potentials** = local changes in membrane potential, resemble EPSPs
* Uses ionotropic or metabotropic receptors
* **Generator potentials** = local changes in membrane potential, resemble EPSPs
98
New cards
Labeled lines
* Sensory information going to the brain to be coded
* Stimulus binds to a receptor to allow ion channels to open, action potentials start happening then labeled lines
* Stimulus binds to a receptor to allow ion channels to open, action potentials start happening then labeled lines
99
New cards
Pacinian corpuscle
* Related to the **touch to skin**
* Before touched, at rest
* A stimulus to the corpuscle opens sodium channels and produces a graded generator potential
* Smaller stimulus, smaller response
* Bigger stimulus, bigger response
* If the potential is big enough, a threshold is reached, and an action potential is **generated**.
* Responds to vibration and pressure
* Before touched, at rest
* A stimulus to the corpuscle opens sodium channels and produces a graded generator potential
* Smaller stimulus, smaller response
* Bigger stimulus, bigger response
* If the potential is big enough, a threshold is reached, and an action potential is **generated**.
* Responds to vibration and pressure
100
New cards
Vestibular system
* Related to sound
* Receptors respond to **mechanical stimuli** which indicate position and movement of head
* Also helps with balance
* Could have spontaneous action potential firing, moving head can increase or decrease it
* Vestibular neuron normally active
* Activity increases or decreases, depending on which direction hair cells bend
* Receptors respond to **mechanical stimuli** which indicate position and movement of head
* Also helps with balance
* Could have spontaneous action potential firing, moving head can increase or decrease it
* Vestibular neuron normally active
* Activity increases or decreases, depending on which direction hair cells bend