Krebs Cycle Flashcards
1/11
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is the source of the carbon atoms released as CO2 in the Krebs cycle?
The carbon atoms from acetyl-CoA.
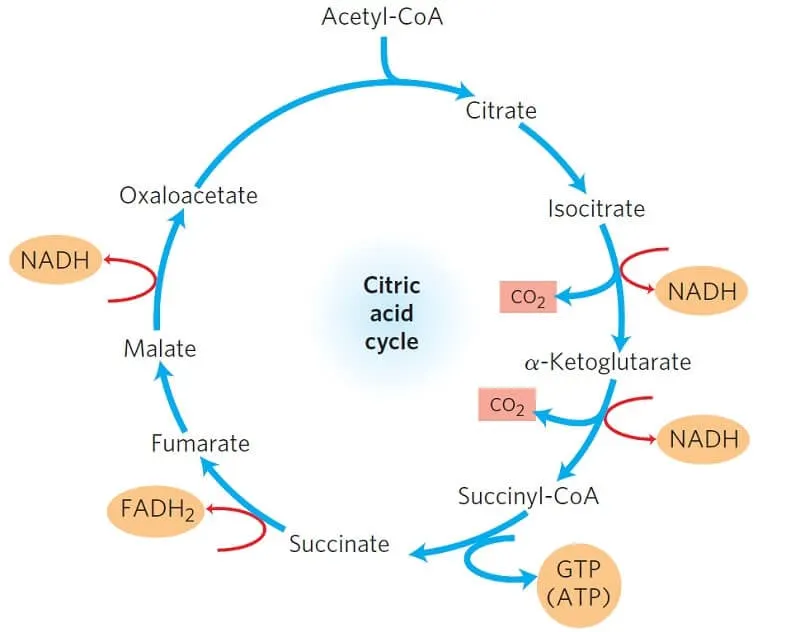
What high-energy electron carriers are reduced during the Krebs cycle?
NAD+ and FAD.
What type of phosphorylation generates ATP in the Krebs cycle?
Substrate-level phosphorylation.
Is oxygen directly used in the Krebs cycle?
No, but the cycle depends on oxygen indirectly because NADH and FADH2 must transfer electrons to the ETC.
What happens to oxaloacetate at the end of the cycle?
It is regenerated to begin the cycle again.
Where does the Krebs cycle occur in eukaryotic cells?
In the mitochondrial matrix.
What molecule enters the Krebs cycle?
Acetyl-CoA (a 2-carbon molecule derived from pyruvate).After pyruvate oxidation
What 4-carbon molecule combines with acetyl-CoA to begin the cycle?
Oxaloacetate.
What 6-carbon molecule is formed when acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate combine?
Citrate.
How many turns of the Krebs cycle occur per glucose molecule?
Two turns (one per acetyl-CoA).
What are the main products of one turn of the Krebs cycle?
3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP (or GTP), and 2 CO2.
How many total NADH molecules are produced from one glucose molecule during the Krebs cycle?
6 NADH (3 per cycle × 2 cycles).