Physiology Exam 1 Review Doc Flashcards
1/258
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all questions from the review doc except for the ones only regarding memorization of a diagram (cell membrane, fluid mosaic model, neuron, and sarcomere structure diagrams)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
259 Terms
Why are all carbohydrates broken down into single sugars/monosaccharides?
so they can enter the blood
What are the components of disaccharides?
2 monosaccharides and glucose
What is the main source of energy for the brain?
carbohydrates
What is a part of all disaccharides?
glucose
What is the storage form of carbohydrates in the body?
glycogen
Where is glycogen in the body?
mostly in muscle, rest in liver
What does the glycemic index measure?
quality of carbohydrates
What type of carbohydrates have a high glycemic index?
easily digestable carbohydrates that immediately raid blood glucose
What type of carbohydrates have a low glycemic index?
slow to digest carbohydrates that don’t spike blood glucose
What does glycemic load measure?
quantity and quality of carbohydrates
Will one food have the same glycemic load and glycemic index?
no
How are lipids stored in the body?
triglycerides
What is a triglyceride?
glycerol bound to fatty acid chains
Where are triglycerides found?
adipose tissue and skeletal muscle
Why are lipids stored as triglyceride instead of in fat?
more efficient and compact
How are saturated fats different than unsaturated fats?
no double bonds between carbons, tightly packed
Why are saturated fats tightly packed?
no double bonds
Are saturated fats solid at room temperature?
yes
Why do saturated have a high melting point?
tight packing
How are unsaturated fats different from saturated fats?
contain one or more double bonds
Why are unsaturated fats nonlinear and loosely packed?
double bonds
Are unsaturated fats solid at room temperature?
no
Why do unsaturated fats have low melting points?
loosely packed
How do NSAIDs stop pain?
block COX 1 and 2 to stop production of prostaglandin
Why is it preferable to have NSAIDs that only block COX2 not COX1?
COX1 is responsible for homeostasis, blocking it can cause GI distress
What is an example of an NSAID that doesn’t block COX1 commonly used by people who chronically use NSAIDs?
Celebrex
What are complete/high quality proteins?
contains all essential amino acids, generally found in animal products
What are incomplete/low quality proteins?
lack one or more essential amino acids, generally found in animal products
How can incomplete/low quality proteins be consumed to make them a complete protein?
consume multiple at same time
what are the 4 levels of organization?
cells, tissue, organ, and organ system
describe the cell level of organization
smallest unit with a function
describe the tissue level of organization
tissues with specialized functions
Give 4 examples of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, and neural
describe the organ level of organization
combination of tissues
describe the organ system level of organization
organs interacting in a system
Name the 3 body fluid compartment/cavities
cranial, thoracic, and abdominopelvic cavities
Describe the physical barrier function of the cell membrane
Separates intracellular from extracellular fluid
Describe the gateway for exchange function of the cell membrane
controls entry of ions and nutrients, removes waste, and releases hormones
Describe the communication function of the cell membrane
primary location for hormone receptors
describe the cell structure/cytoskeleton function of the cell membrane
internal scaffolding and support
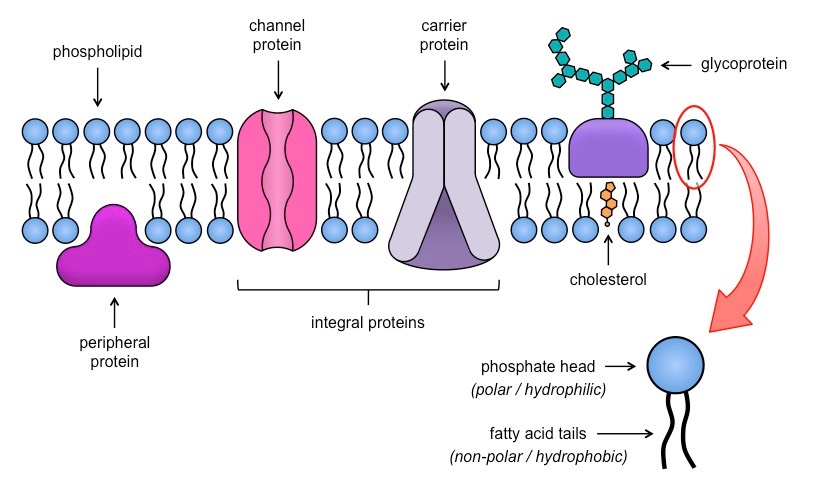
What is pictured in this diagram?
the fluid mosaic model showing structure of cell membrane
What is the overall structure of the cell membrane?
made up of phospholipid bilayer with cholesterol and protein inserts

What is the purpose of cholesterol inserts in the cell membrane?
increases cell membrane flexibility
What is synthesized in the smooth ER
fatty acids, steroids, and lipids
What are the 2 functions of the smooth ER?
synthesis and detoxification of drugs in kidney and liver
Why is the rough ER “rough”?
covered in ribosomes
What is the function of the rough ER?
protein assembly and modification
What are the 4 types of tissue in the body?
epithelia, connective, muscle, and nervous
What is the function of epithelia tissue?
protecting internal environment, regulating exchange
How does epithelia tissue regulate exchange?
all substances entering or exiting the body must cross epithelia
What is the function of connective tissue?
strength and support
What are 2 examples of connective tissue?
cartilage and bone
What is the function of muscle tissue?
movement and contractility
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
cardiac, skeletal, and smooth
What is the function of nervous tissue?
control and communication
What are 2 examples of nervous tissue?
neurons and glial cells
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
Define bioenergetics
energy transfer in living organisms
How is energy acquired?
from food/nutrition
Where is energy stored in the body?
tissues
Why is energy conversion/transfer important?
non-useful energy converted to useful energy
What factor limits power?
rate ATP is turned into power
What is the function of enzymes?
Lower activation energy and serve as reaction catalysts
Are enzymes consumed in reactions?
no
Do enzymes produce energy?
no
How do co-enzymes assist enzyme activity?
by binding substrate to enzyme
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
enzymes work faster at higher temperatures up to a certain point
How does substrate availability affect the speed of reactions?
availability speeds up reaction to a certain point
What are catabolic/exergonic reactions?
reactions that release energy through breakdown
What are anabolic/endergonic reactions?
reactions that use energy through synthesis
Does the PCr pathway occur in the presence of oxygen?
no
What is the fuel for the PCr pathway?
phosphocreatine
What does phosphocreatine do in the PCr pathway?
provide phosphate to form ATP
Where does the PCr pathway take place?
cytoplasm
Does energy created from PCr last a long time?
no
Where does glycolysis take place?
cytoplasm
Where does the Kreb’s/citric acid cycle take place?
mitochondria
Where does the electron transport chain take place?
mitochondria
What is the end product of anaerobic glycolysis?
lactic acid
What is the end product of aerobic glycolosis?
pyruvate for oxidative phosphorylation
Why are two of the fates of lactate to be reconverted to pyruvate?
to be used for energy by aerobic tissues or in the heart
In what conditions is lactate reconverted to pyruvate?
presence of oxygen, or in heart
What reconverts lactate to pyruvate?
lactate dehydrogenase
What happens to lactate in the liver?
converted to glucose
What is the primary function of the citric acid cycle?
bring electrons NADH/FADH to the electron transport chain
How does the electron transport chain generate ATP?
electrons move against concentration gradient and are pumped through ATP synthase
What is the final electron acceptor in oxidative phosphorylyzation (end of electron transport chain)?
oxygen
Why are electrons forced to go through ATP synthase in the electron transport chain?
membrane isn’t permeable to electrons
What is the 1st step of triglyceride breakdown to Acetyl CoA?
digested by lipases into glycerol
What is the 2nd step of triglyceride breakdown to Acetyl CoA?
glycerol used for glycolysis to create pyruvate and fatty acids
What is the 3rd step of triglyceride breakdown to Acetyl CoA?
fatty acids move to mitochondrial matrix where the acyl units are chopped off by beta oxidation
What is the 4th step of triglyceride breakdown to Acetyl CoA?
acyl units become acetyl CoA to be used in citric acid cycle
Rank the capacity (amount) of the ATP generating pathways from highest to lowest
oxidative phosphorylation, anaerobic glycolysis, PCr
Rank the power (speed) of the ATP generating pathways from highest to lowest
Pcr, anaerobic glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation
Describe autocrine communication in the neuroendocrine system?
local communication, cell targets itself
Describe signaling across gap junction communication in the neuroendocrine system?
local communication, targets connected cell
Describe paracrine communication in the neuroendocrine system?
local communication, targets nearby cell
Describe endocrine communication in the neuroendocrine system?
long-distance communication, targets through bloodstream
What are amine hormones derived from?
tryptophan and tyrosine
Are most of the bodies hormones amine or protein?
protein