CHEM43A Final
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
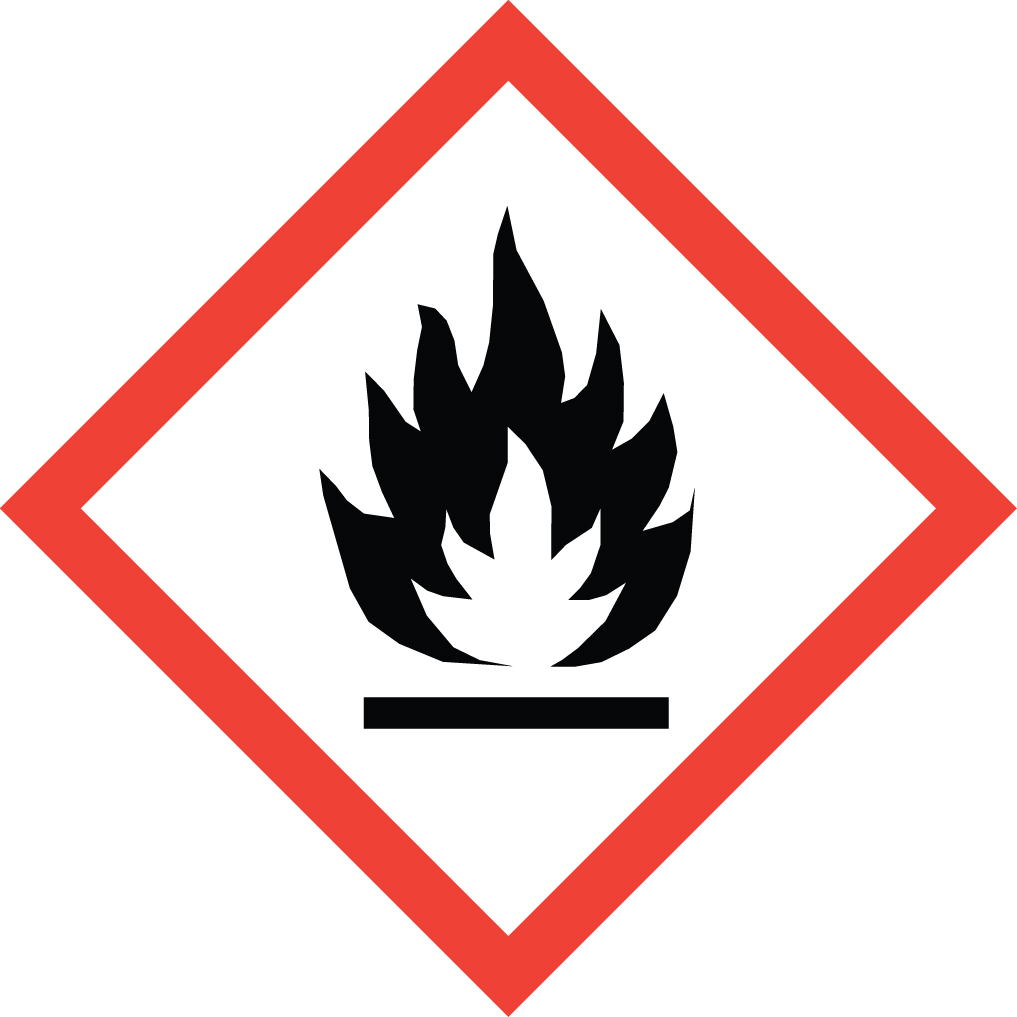

Flammables

Explosives
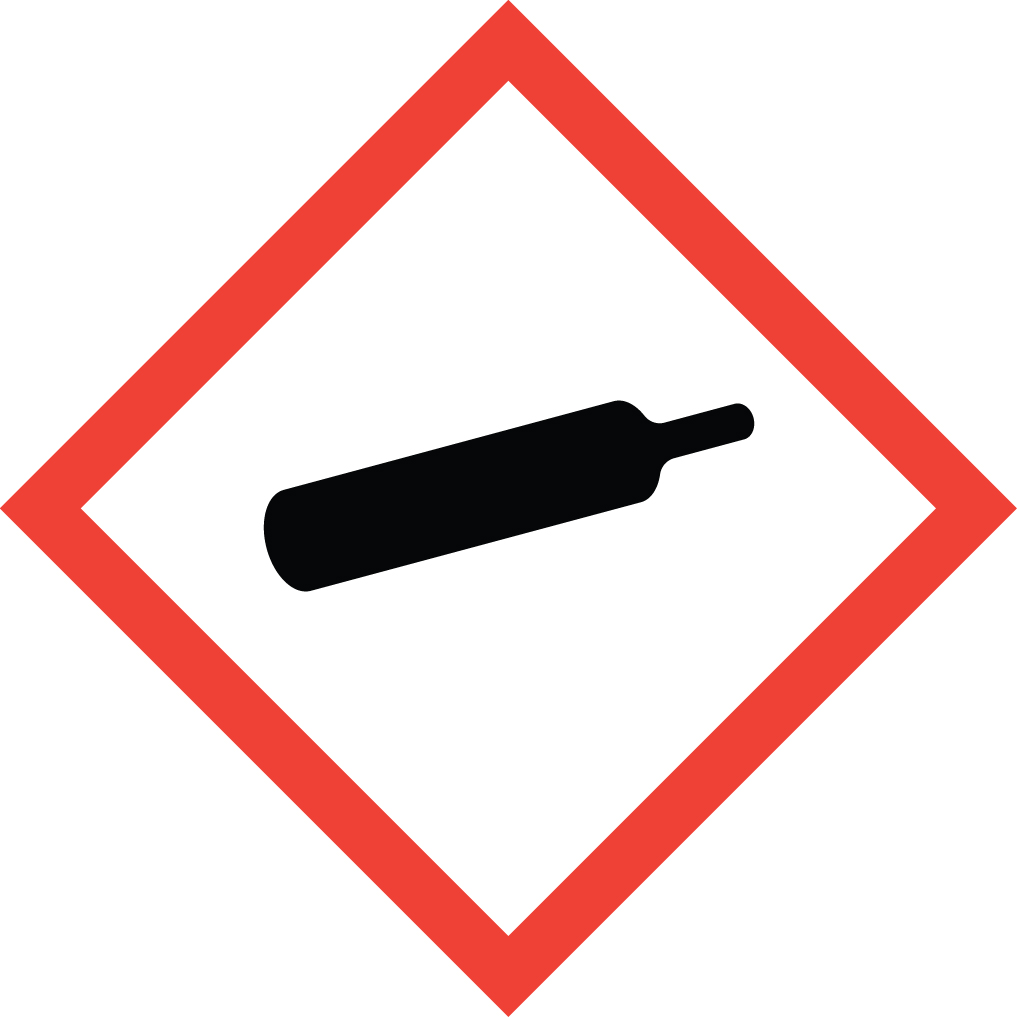

Gases under pressure
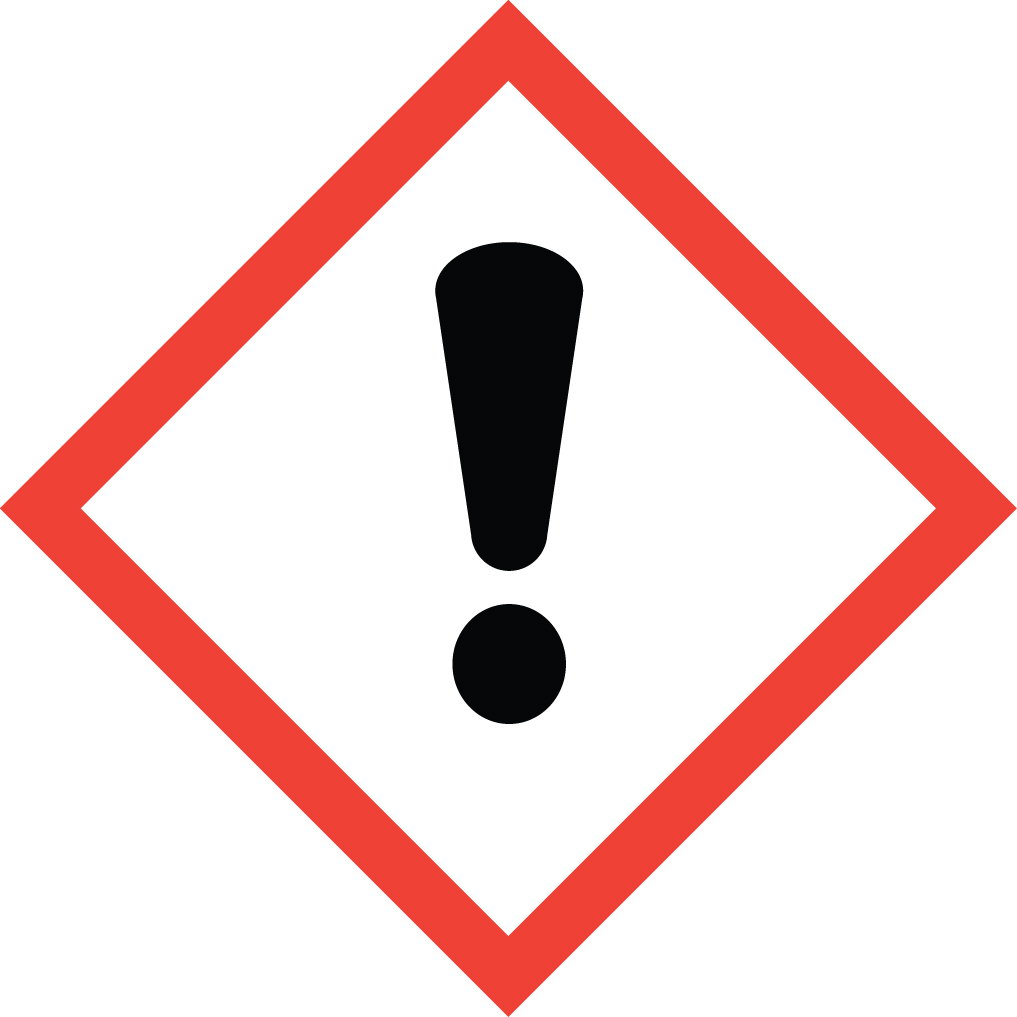

Irritant (skin and eye), acute toxicity
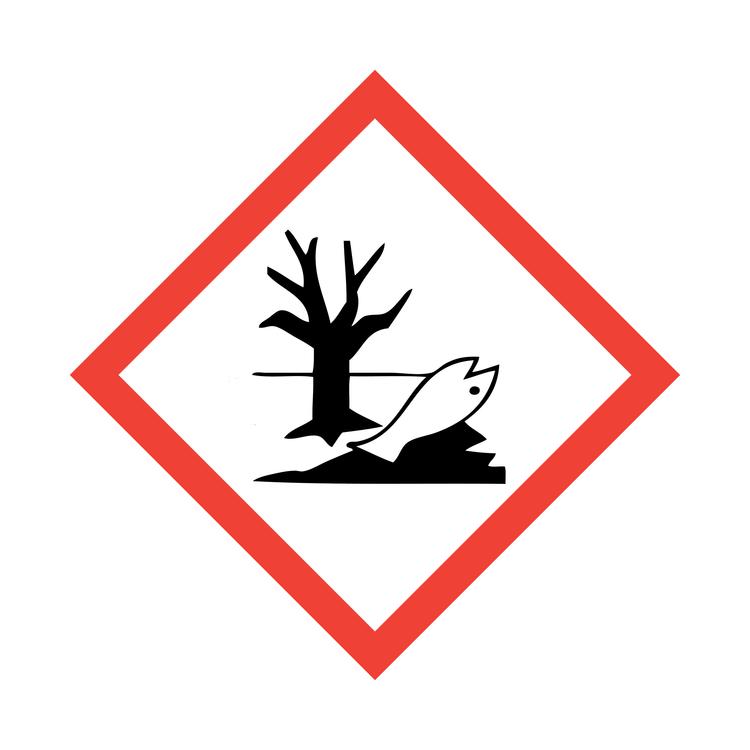

Aquatic toxicity
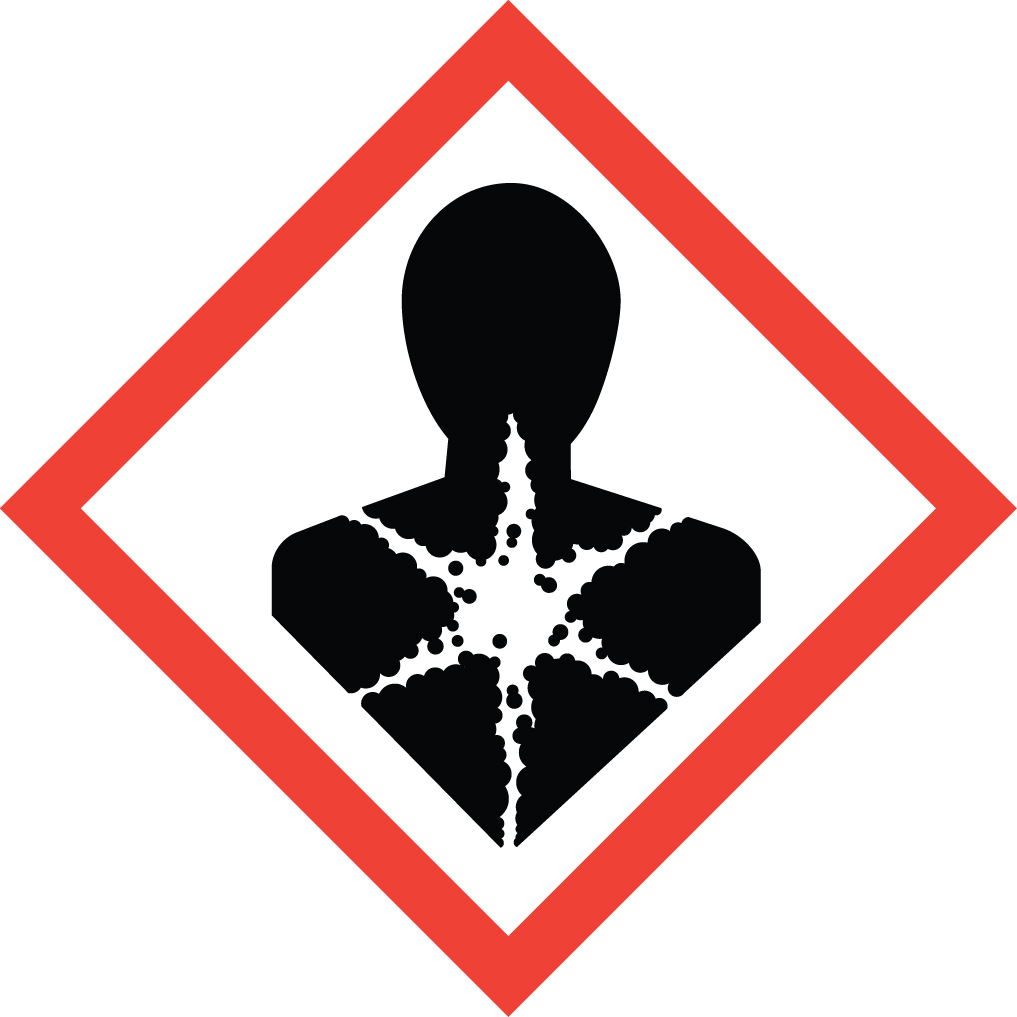

Health hazard; carcinogen
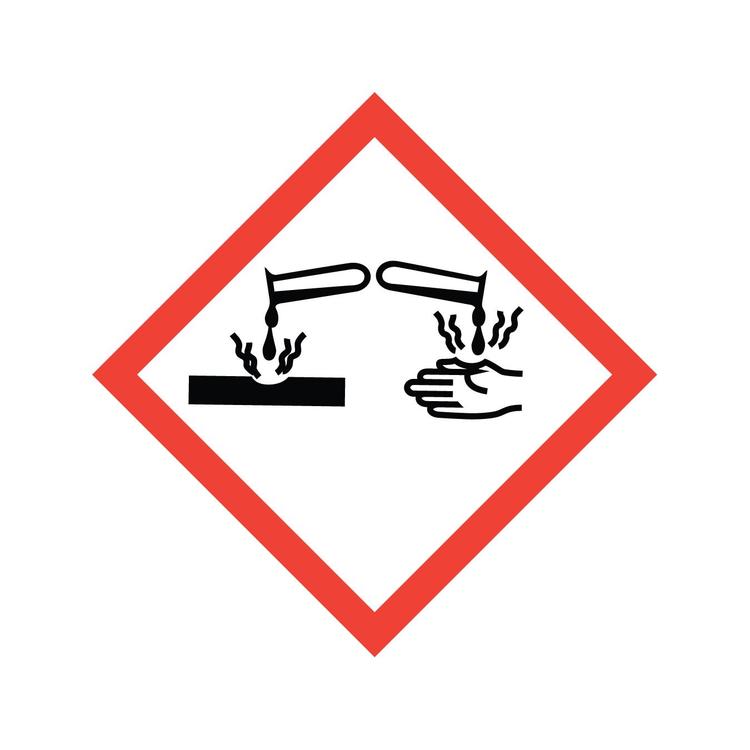
Corrosive, eye damage
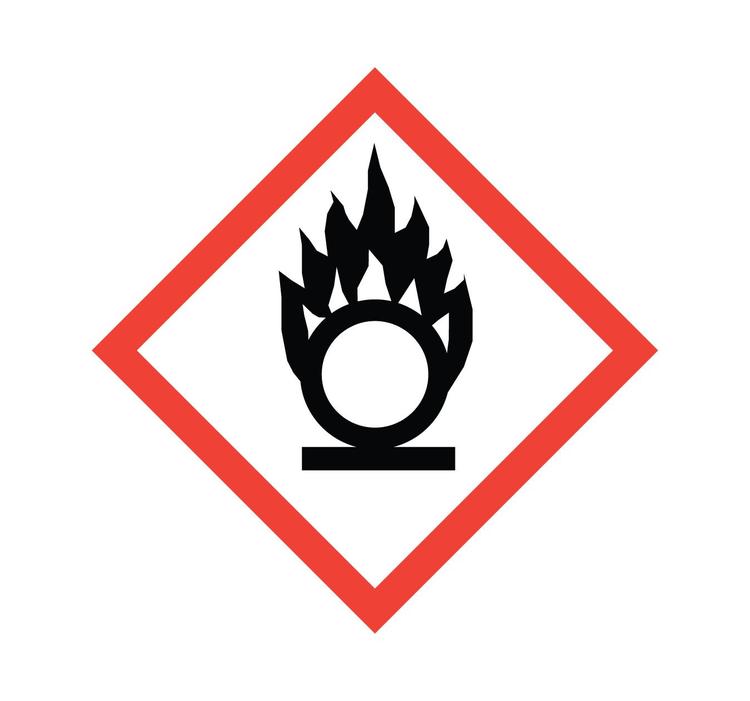

Oxidizers
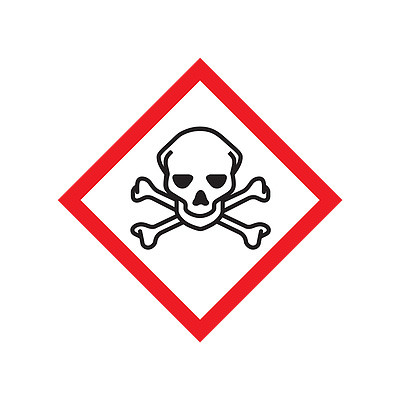

Acute toxicity (fatal or toxic)
Melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid.
E0 Procedure
Determine crude mp range for unknown and utilize range to find precise melting point.
Calibrate the melting point apparatus and calculate the correction factor.
Apply mixed melting points to confirm identity of unknown.
How to calculate CF and how to apply it.
CF = (avg. mp of literature) - (avg. mp of observed)
if observed is higher than literature, subtract
5 types of interactions for solids (strongest → weakest)
ionic bonds: cations + anions = strong lattice
covalent bonds: network of shared e- between atoms throughout solid
metallic bonds: delocalized e- and charged (+) metal ions
dipole-dipole: attractive forces between partial + / -
Van Der Waal: attractions between non-polar e-
What is bumping and why does it happen?
Liquid expels from container due to uneven heating or heating too quick.
How to prevent bumping?
Addition of boiling chips that have porous materials to trap air and provide nucleation sites to allow even heating.
How does charcoal get rid of impurities?
Charcoal adsorbs impurities due to its high surface area and porous structure, allowing it to trap molecules and remove them from liquids or gases.
Why is pure crystal formation slow?
Molecules have more time to arrange into strong lattice