Astronomy
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Galaxy
clsusters of a few million to 400 billion stars
ex: Milky Way galaxy
small galaxies may orbit larger ones
three shapes
spiral galaxies: flattened disks with spiral or barred spiral arms
elliptical galaxies: spherical in shape with no spiral arms
irregular galaxies: no distinct shape
Universe
enormous collection of matter
solar system
planets, moons, etc circling a star
Planets
Mercury: terrestrial
Venus: terrestrial
Earth: terrestrial
Mars: terrestrial
Jupiter: gas
Saturn: gas
Uranus: ice
Neptune: ice
Wave
a repeating disturbance that transfers energy through matter or space
ex: ocean waves, sound waves, seismic waves, light waves
frequency (waves)
number of waves per unit of time
Parts of a Wave
Crest: highest point on a wave
through: lowest point on a wave
amplitude: distance between where the wave begins and where it ends
wavelength: the distance between two waves
Newton’s findings regarding light
1666
studies light traveling through a prism & saw a spectrum of colors: ROYGBIV
Hugenns’ findings regarding light
1670s
determined light travels in waves; shorter wavelengths are refracted (bent) more than longer wavelenghts
this discovery led to the creation of spectroscopy
spectroscopy
the study of the properties of light
radiation (light) released or reflected by distant objects allows scientists to study the universe
electromagnetic spectrum
the continuum of radiation released by celestial objects
Electromagnetic waves
travel at the speed of light-300,000 km/s
transfer energy
travel through space
types of electromagnetic radiation
Gamma (CT scans)
X-Rays
UV light = sunburns
infrared = heat
microwaves & radio ______
Speed of light
speed of light (c) - relationship between frequency and wavelength
3 × 10^8 meters/sec (186,000 miles per sec!)
c = f(λ)
speed of light (m/s) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m)
this equation can be used to find wavelength or frequency of different types of light when we know the speed of light
traveling at the speed of light you could circle the Earth 7 times in less than a second
What is energy measured in? What are the two formulas to solve it?
Electron Volts (eV)
E=hf
E=hc/λ (Iambda)
h = Planck’s Constant = 6.626 × 10³4 Joules (J)/second
f = frequency
c = speed of light
λ = wavelength
The Big Bang Theory
Theory that the universe began as a singularity and has been expanding ever since
occured about 14 (13.7) billion years ago
singularity - zone of infinite density
what does this mean?
all matter squished into a tiny amount of space
Expansion of the Universe
Universe has two opposing forces:
Momentum of outward exxpansion
gravity pushing inward to slow expansion
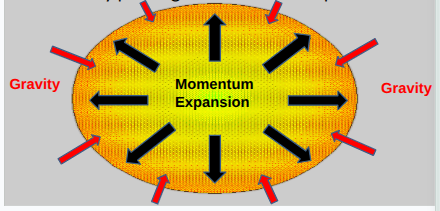
What would the possible outcomes of the universe be if a certain force became too strong?
depends on which opposing force is stronger
three possible possibilities:
Open
expansion will never stop
closed
expansion stops and begins to contract
flat
expansion slows to a halt, but does not contract


Contents of the Universe
universe expansion is accelerating (dark energy)
composition
dark energy (75%) (unknown)
dark matter (21%) (unknown subatomic particles)
luminous matter (4%)
What is Hubble’s Law?
42 miles/second : 3 million light-years
Einstein’s Theory of Relativity & Quantum Physics
math based theory that proves objects are moving away from a “singularity” (and relative to each other)
Cosmic background radiation
weak radiation left over from the early, hot stages of the Big Bang expansion
Cosmic Background Radiation
Discovered in 1965
(background noise in radio antenna)
Shorter wavelengths of light (when hot) that became longer (when cooled)
The “leftovers” of the Big Bang
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
Bigger wavelength = less frequency
smaller wavelength = more frequency
Doppler Effect
an apparent change in the frequency of waves when the observer or the source of the waves is moving relative to each other.
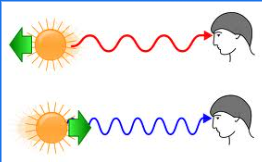
Measuring Doppler Shift
When an object in space is moving, its spectral lines will be shifted towards one end of the spectrum.
We can use this shift to determine how fast a star is moving.
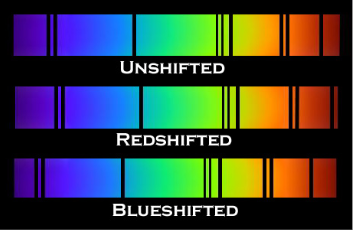
Describe Blueshift and Redshift
When objects are moving away from us, they show a red shift. When objects are moving towards us, they show a blue shift.
Interstellar Cloud/Nebula
clump of dust clouds mostly containing hydrogen and helium
Collapsing of Cloud (Contraction)
gravity (perhaps a nearby supernova explosion?) draws the matter together causing the cloud to collapse
collapsed cloud spins faster pushing dense material to the center (will become SUN)
When temps reach 15 billion degrees C, nuclear fusion begins →the Sun is born!
When spin slows the cloud will become a flat rotating disk