Reflection and Refraction of Light Concepts
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Explain the frequencies and energy on the electromagnetic spectrum
At the start
Lower frequency
Lower energy
At the end:
Higher frequency
Higher energy
Microwaves
Overlap with radio waves
Ex. Microwaves, cell phones, wifi
Use Anti Nodes (max), And Nodes (low)
Infrared
Felt as heat by skin
Night vision, remote controls
Visible light
ROGBIV is the order of frequencies
How does frequencies effect visible light
Diff. frequencies=diff colors
How does amp effect color
Diff. Amps = Diff intensities of color
Ultraviolet
Higher energy waves that can be dangerous to humans (damage DNA)- makes vitamin d in our skin
Used to:
Black lights
sterilizing medical equipment
Tanning beds
X-Ray
Can damage human cells
Used for medical imagining, airports, cancer treatment
Gamma ray
Highest energy, most dangerous
Smallest wavelength
Used for nuclear radiation and cancer treatments.
Explain how light travels
Light travels in a straight line but in order to see something light must "bounce" off an object into our eyes
What is a reflected ray
The ray of light that bounces off a surface
Incident ray
an incoming ray of light (before it is reflected or refracted)
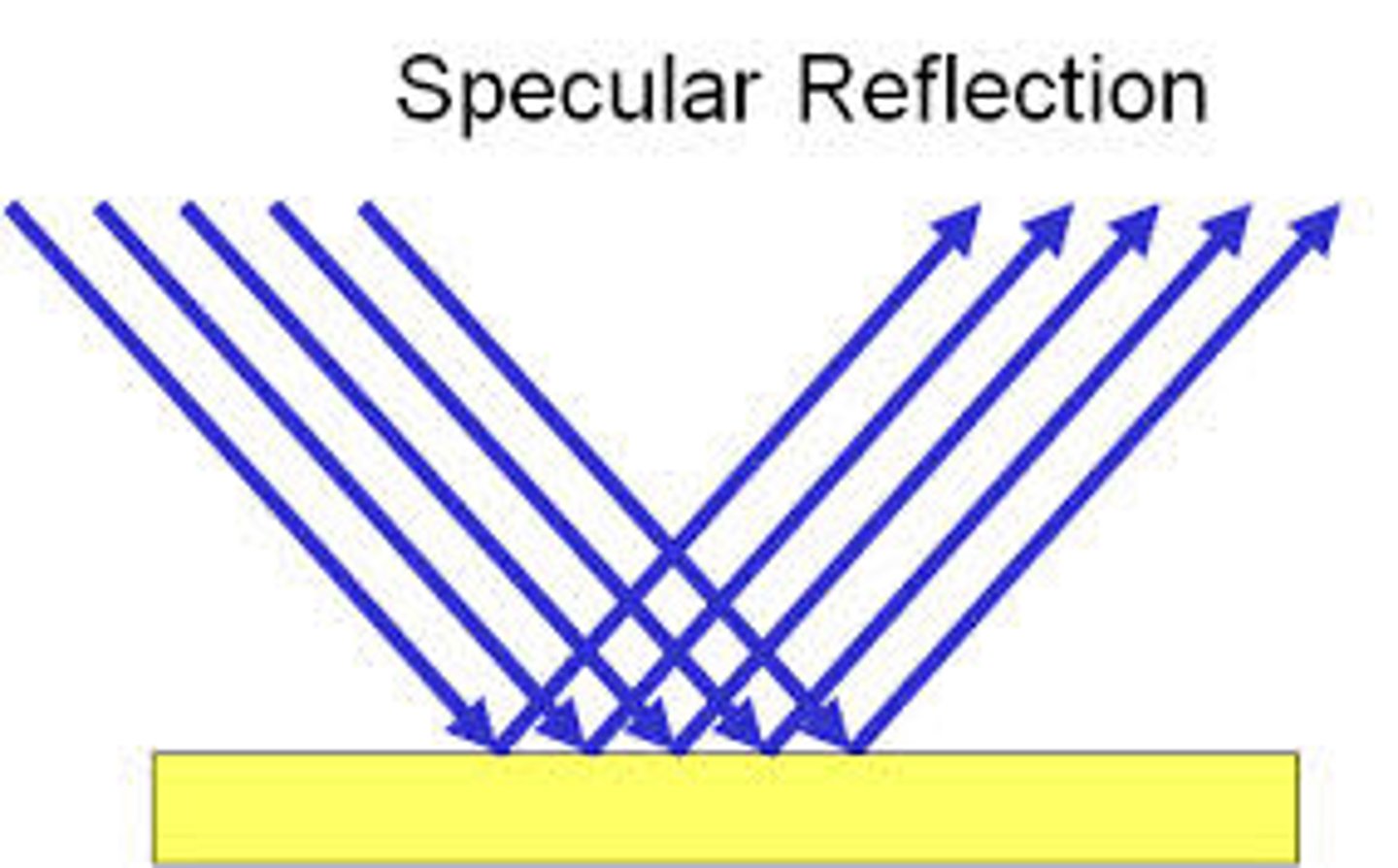
Specular Reflection
a reflection produced by a smooth surface in which parallel light rays are reflected in parallel
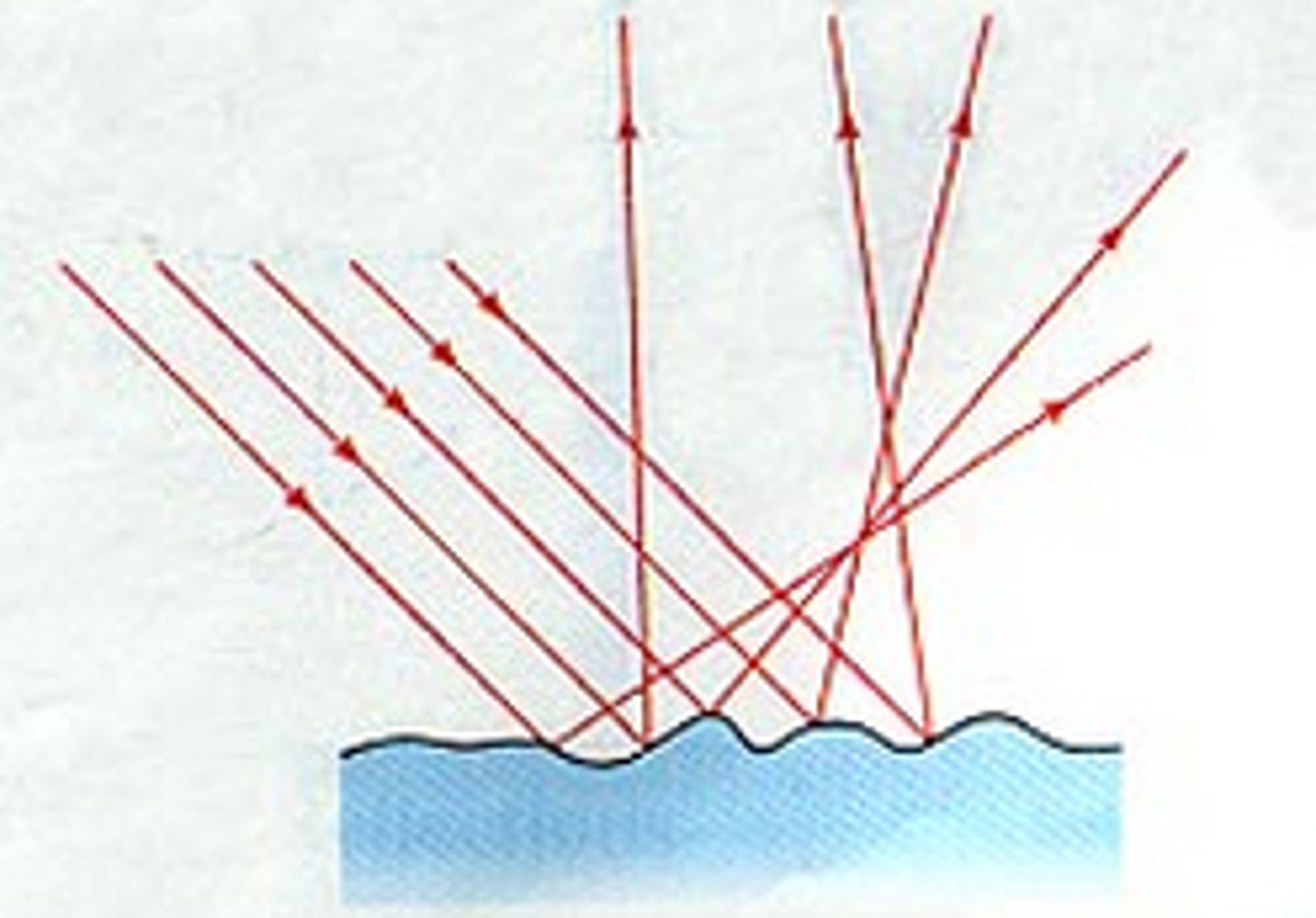
Diffuse Reflection
Reflection that occurs when parallel rays of light hit a rough surface and all reflect at different angles
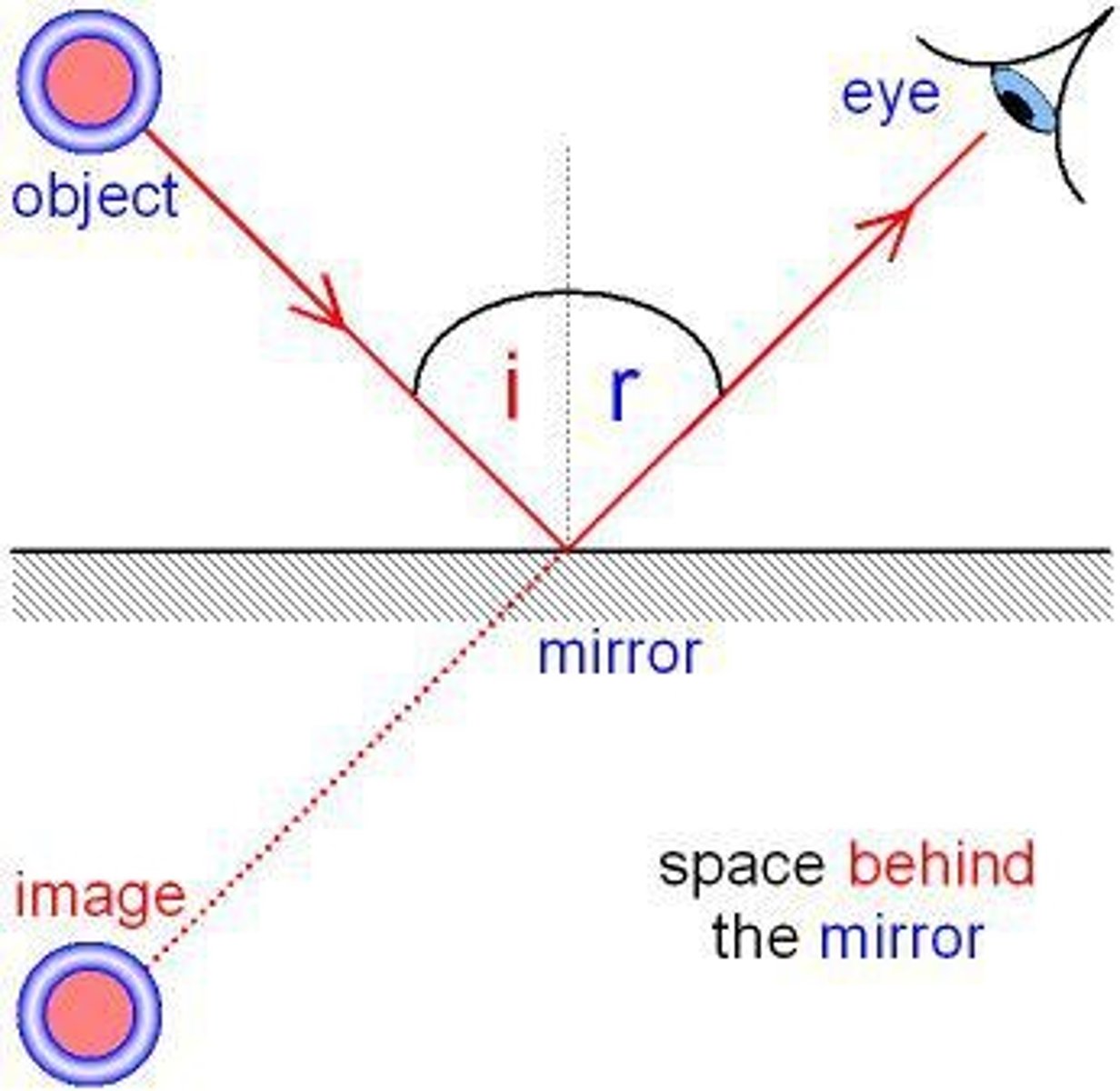
Reflected Images and Plane mirror
The virtual image is:
The same size as the object
Upright
Left-right reversed
As far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror
Lights speed
Vacuum, gas, liquid, solid
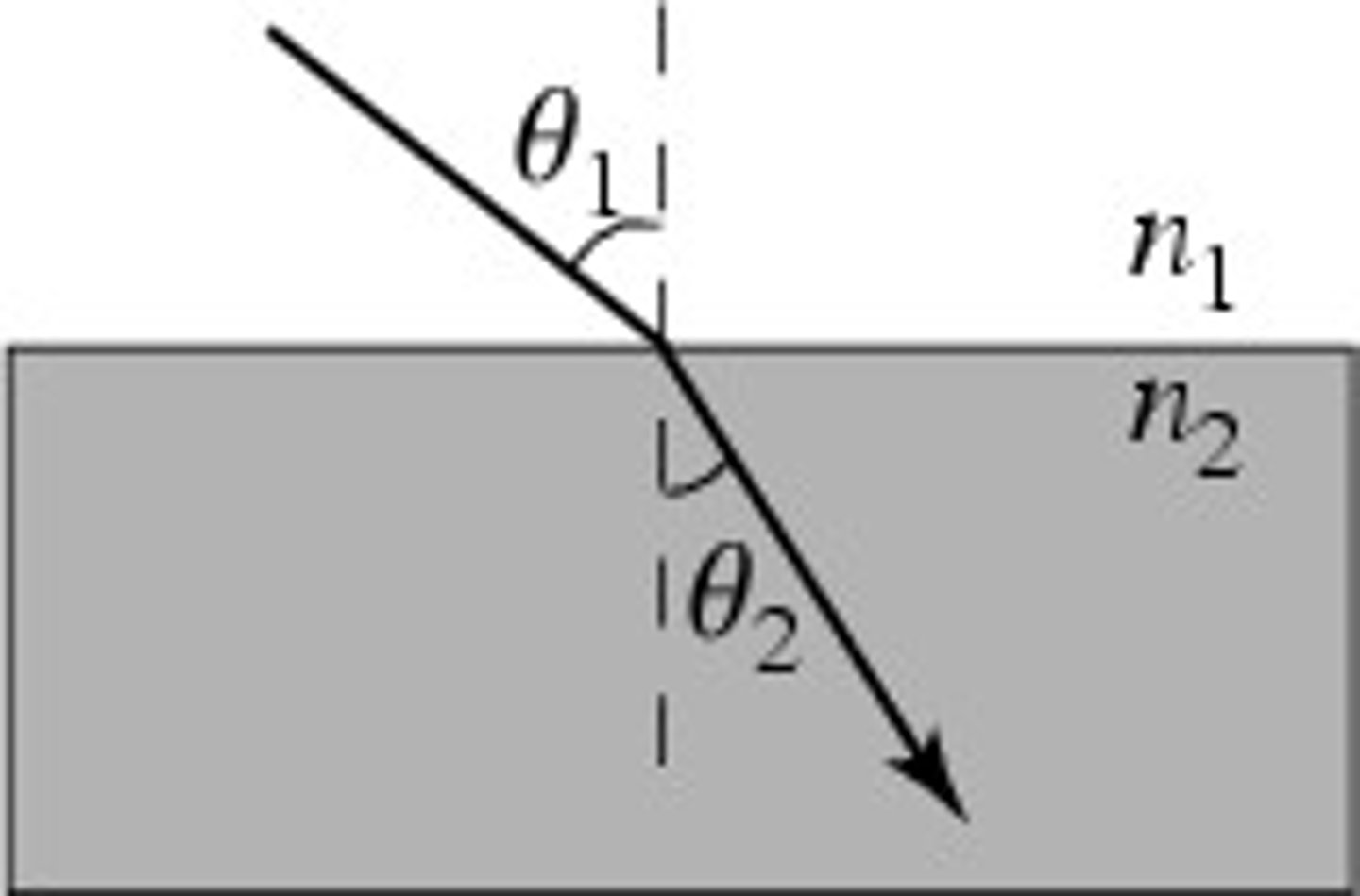
Snell's Law
n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2. When n2>n1, light bends toward the normal. When n2
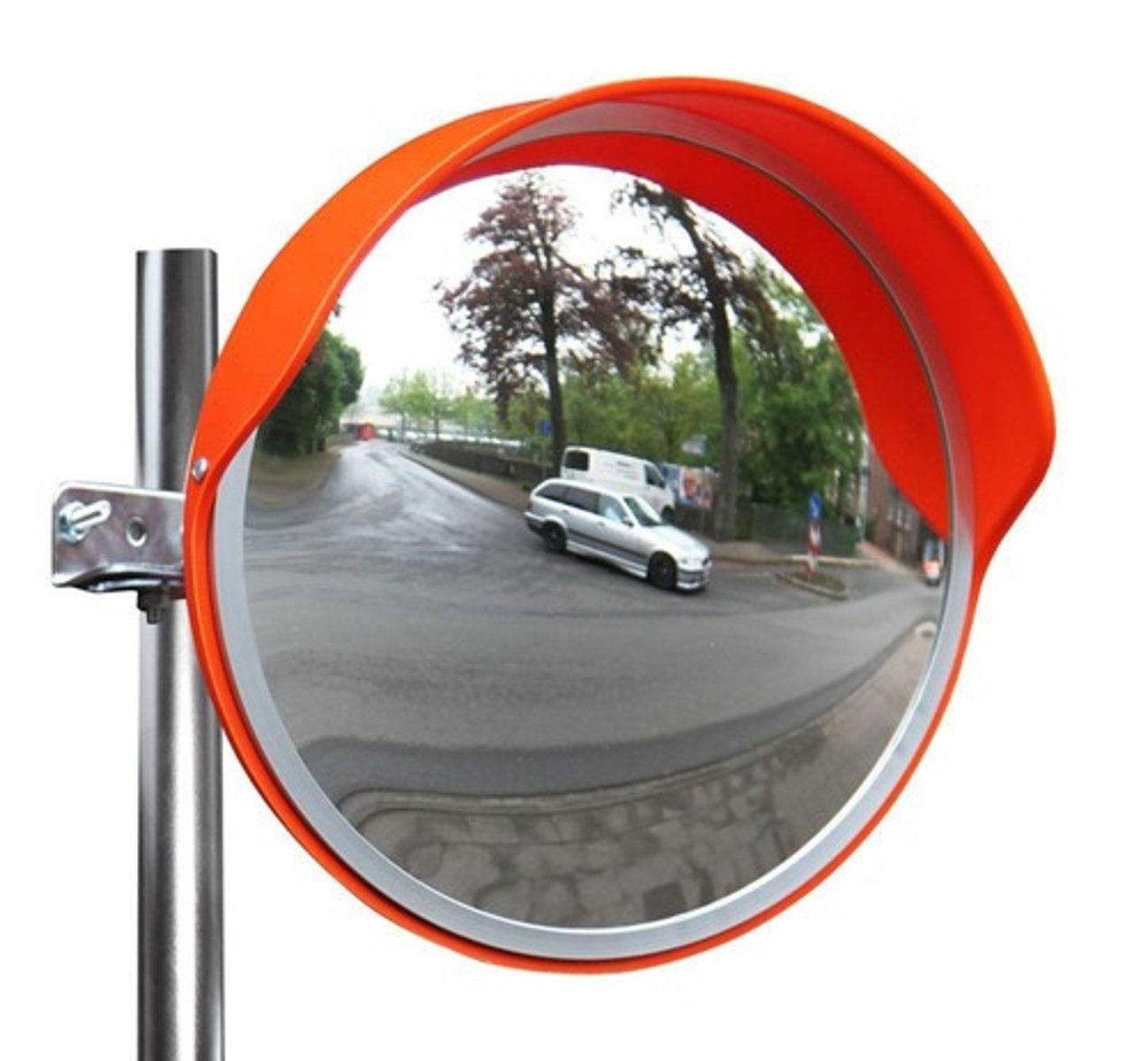
Convex Mirror
A mirror that curves outward and reflects light outward.

Concave Mirror
A mirror that curves inward and can focus light to a point.
Index of Refraction (n)
The ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium.
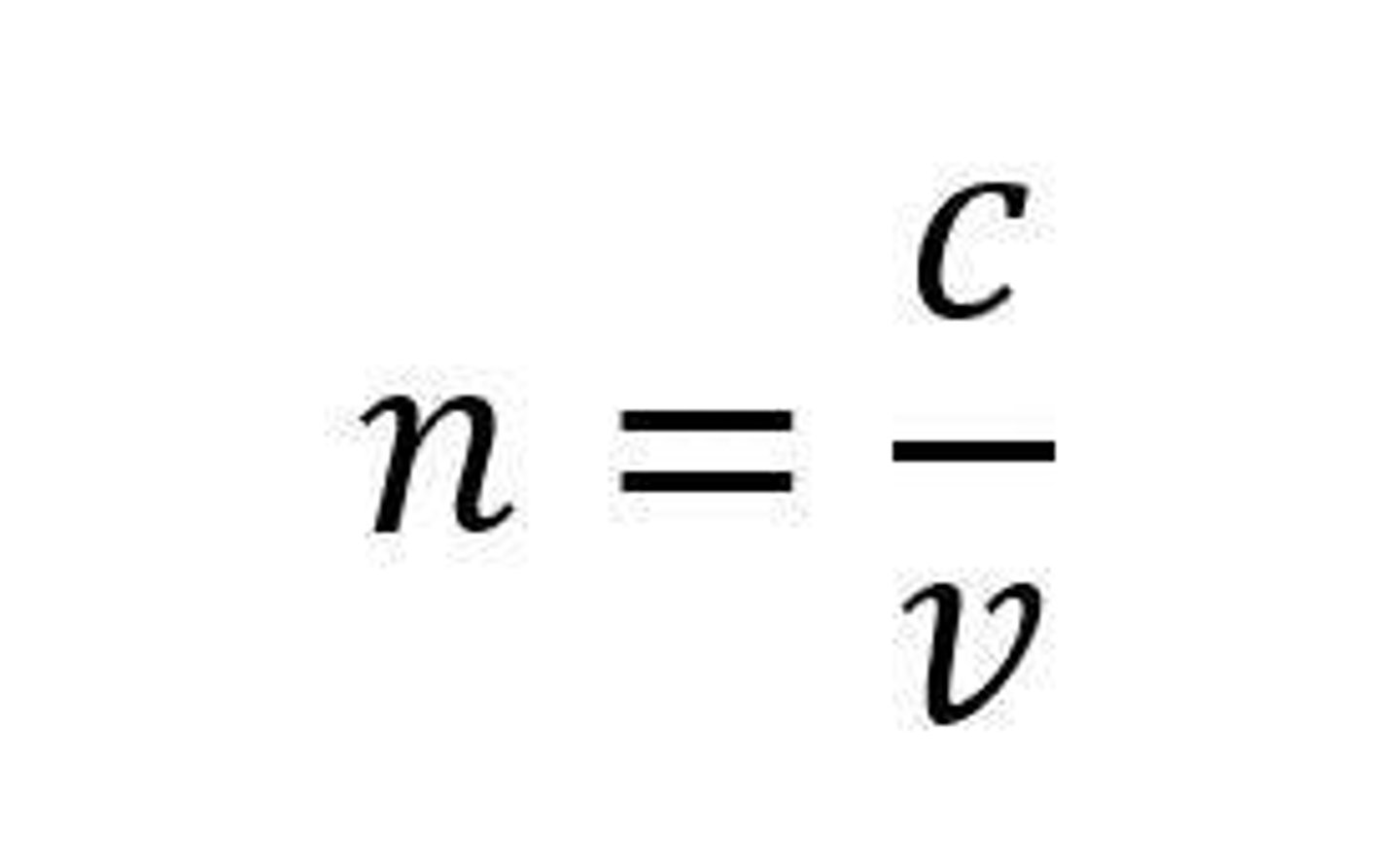
Speed of light in vacuum
3 x 10^8 m/s
Speed of light in diamond
1.25 x 10^8 m/s
Why do diamonds sparkle?
Light changes speed when it enters a new medium.

Bending of Light
Light bends towards the normal when it goes from less dense to more dense and away from the normal when it goes from more dense to less dense.
Refraction
The change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed.
Angle of Incidence (𝜃1)
The angle between the incident ray and the normal line at the boundary of two media.
Angle of Refraction (𝜃2)
The angle between the refracted ray and the normal line at the boundary of two media.
Critical Angle (θc)
The angle of incidence above which total internal reflection occurs, defined by θc = sin-1(n2/n1).Fno
Total Internal Reflection (TIR)
The complete reflection of a light ray back into a medium when it hits the boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle.
Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Normal Line
An imaginary line perpendicular to the boundary at the point of incidence.
What is differaction
Waves bend around obstacles in their path
What is poissons spot
A bright spot that appears at the center of a circular object's shadow, proving light behaves like a wave due to diffraction and constructive interference
Polorazation
Polarization is when light waves are filtered so they vibrate in only one direction. This only happens with transverse waves, like light, and is evidence that light behaves as a wave, not a particle
Photoelectric Effect
The emission of electrons from a material when light of certain frequencies shines on the surface of the material
Photons either supply enough energy to eject an electron or they don't- light can behave as particles
Explain threshold frequency and amp.
Any light above the threshold frequency gives electrons enough energy to eject
Amplitude doesn't affect electrons unless above threshold frequency. Then, amplitude only increases the number of ejected electrons, not their energy.
Wave Particle Duality
Light behaves like a wave when it spreads, bends, and interferes, and like a particle when it transfers energy in small, exact packets called photons.