Periodic Table
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Group
Columns in the periodic table, Their valency is the same.
Period
The rows in the periodic table, the number of shells are the same
Valence Electrons
The number of electrons on the outermost shell
Oxidation Number
Valency with charge
Isotopes
Same element, same atomic number, but different mass number, and different neutrons
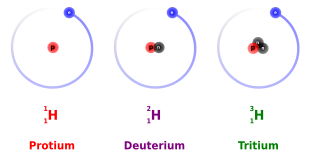
Ions
Electrically charges particles, either has gained electrons or lost electrons
Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell, from a gaseous atom, because it is easies to remove electrons in a gas state
Increases up the group, and right across the period (Upper right corner)
Electronic Affinity
It is the energy change that occurs when a neutral atom in the gaseous state gains an electron to form a negative ion. It is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts an extra electron and is typically expressed in units like kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol)
Electronegativity
The tendency to attract a shared pair of electrons
Increases from left to right across a period, increases up the group (Upper right-hand corner)
Metals
Substances that can lose electrons (electropositive)
Non-Metals
Substances that can gain electrons (electronegative)
Alkali Metal Physical Properties
Soft, Silvery Metals
Low melting and boiling points
Low density
All properties of metals
Alkali Metals Chemical Properties
Highly Reactive
Form 1+ Ions
Reacts with oxygen and water
Transition Metal, Physical Properties
High Density
High melting and boiling points
Metallic Properties
Halogens, Physical Properties
Non-metals
Colored Gases
They are all soluble in organic solvents
Halogens, Chemical Properties
Highly Reactive
Strong oxidizing agents
In nature, they exist as diatomic particles
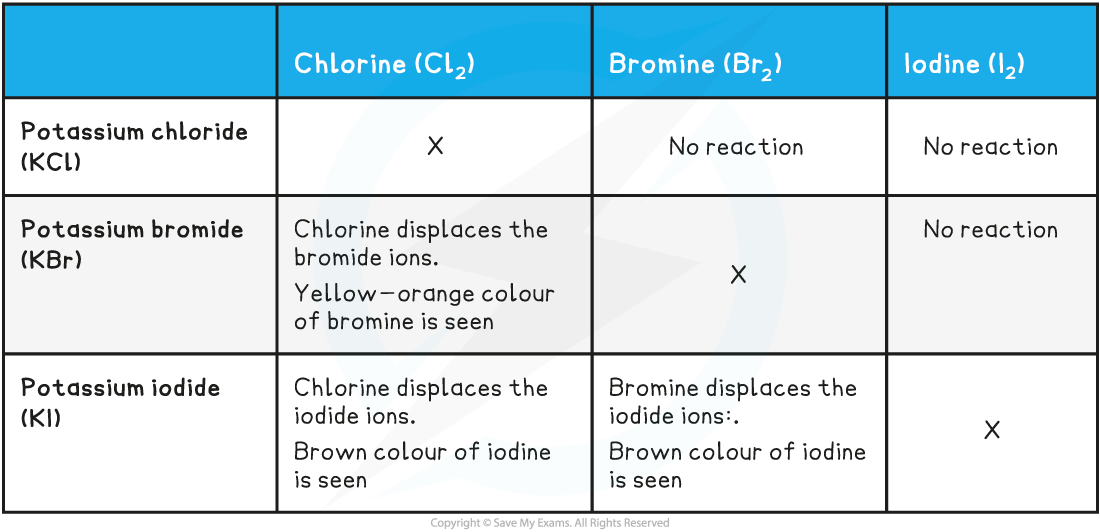
Bromine - Orange
Chlorine - Yellow-Green
Noble Gases
Colorless, Odorless, Tasteless
Under standard conditions, they are gases
Low solubility
Low melting/boiling points
Highly stable
Inert
Monatomic
Metal and Non-Metal Bonding
Ionic Bonding - transfer of an electron from a metal to a non-metal
They are non actually bonded but, have a very strong electrostatic force of attraction
Properties: Crystalline Solids, High melting and boiling points, Molten/Solution conducts electricity
Non-Metal and Metal
Covalent Bonds - no electrons are lost, both non-metals share them
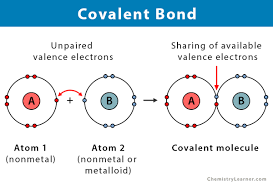
Properties: Are liquids/gases at RTP, Low melting/boiling points, Don’t conduct electricity
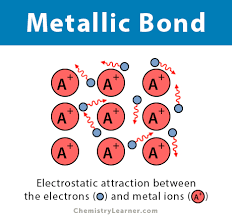
Metal and Metal
Metallic Bonding - attraction between the negatively charged, mobile electons
Electrons are free-roaming in the sea of electrons
Always the same element
Ammonium
NH4 Valency: +1
Hydroxide
OH Valency:-1
Sulfate
SO4 Valency: -2
Sulfite
SO3 Valency: -2
Carbonate
CO3 Valency:-2
Phosphate
PO4 Valency:-3
Nitrate
NO3 Valency:-1