Speech Anatomy Exam 1
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
Skeletal structure (ribs)
12 ribs, give roundness to breathing apparatus, most connect to sternum through costal cartilage, lowest two pairs “float”
Pectoral Girdle
Clavicle and Scapulae
Pelvic Girdle
Ilium (coxal/hip bone), sacrum, coccyx
How many vertebrae are there
34
Cervical Vertebrae
7, in the neck
Thoracic Vertebrae
12, in the chest
Lumbar Vertebrae
5
Sacral Vertebrae
5
Coccygeal Vertebrae
5
Breathing Apparatus
Chest Wall + Pulmonary Apparatus
What makes up the chest wall
rib cage wall, abdominal wall, diaphragm, abdominal content
What makes up the rib cage wall
Thoracic vertebrae, ribs, costal cartilage, sternum, pectoral girdle
What makes up the abdominal wall
lumbar, sacral, coccygeal vertebrae. pelvic girdle, connective tissue, large muscles
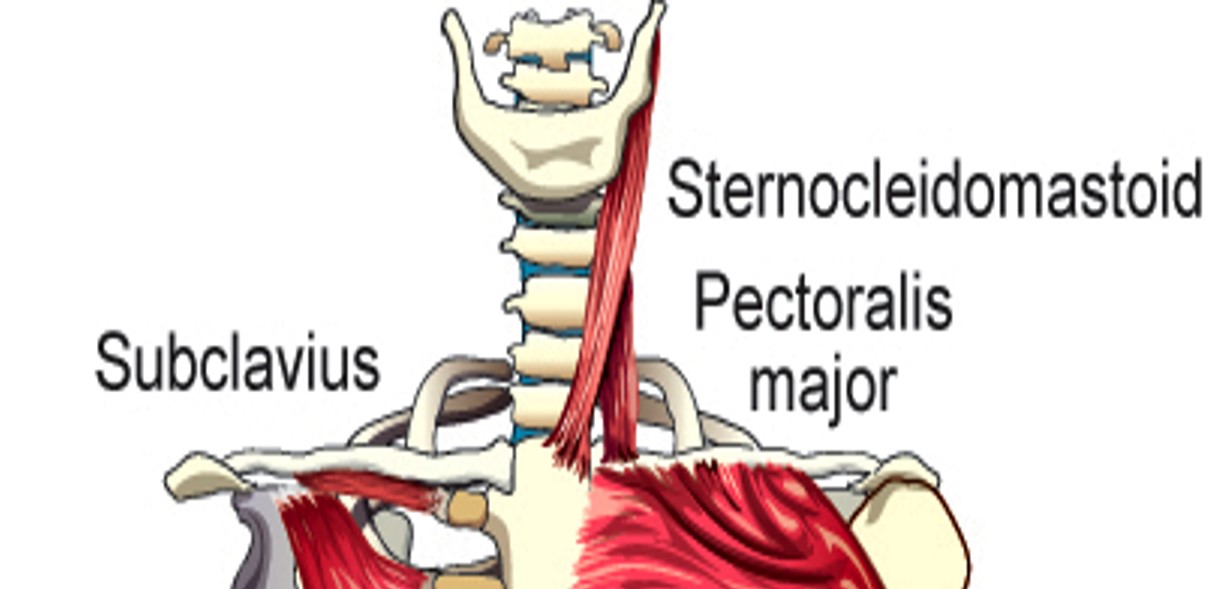
Sternocleidomastoid
elevates sternum, clavicle, and ribs
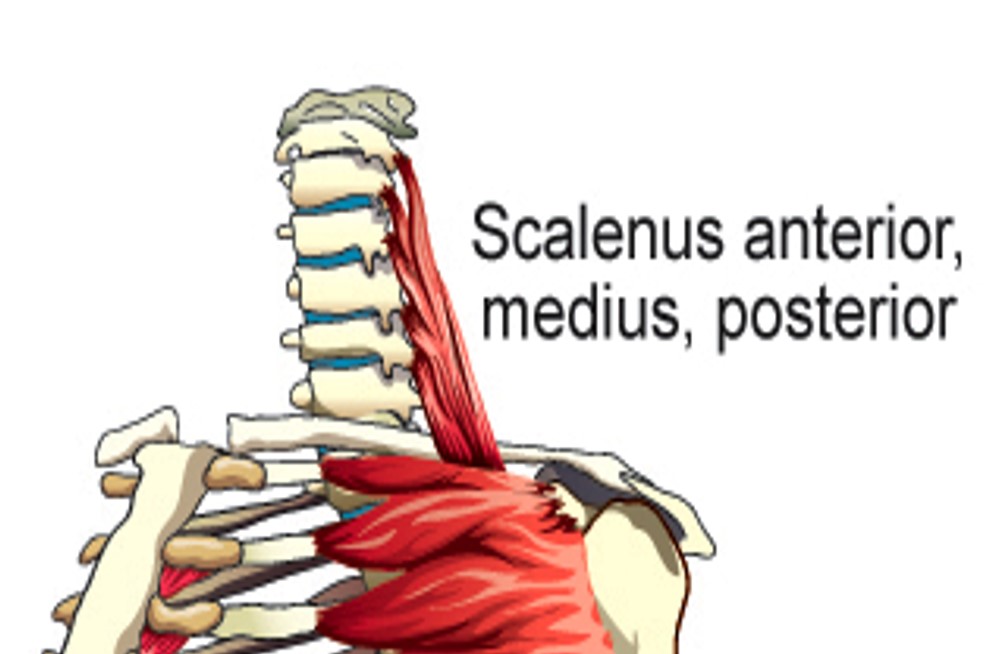
Scalenus Anterior
elevates first rib
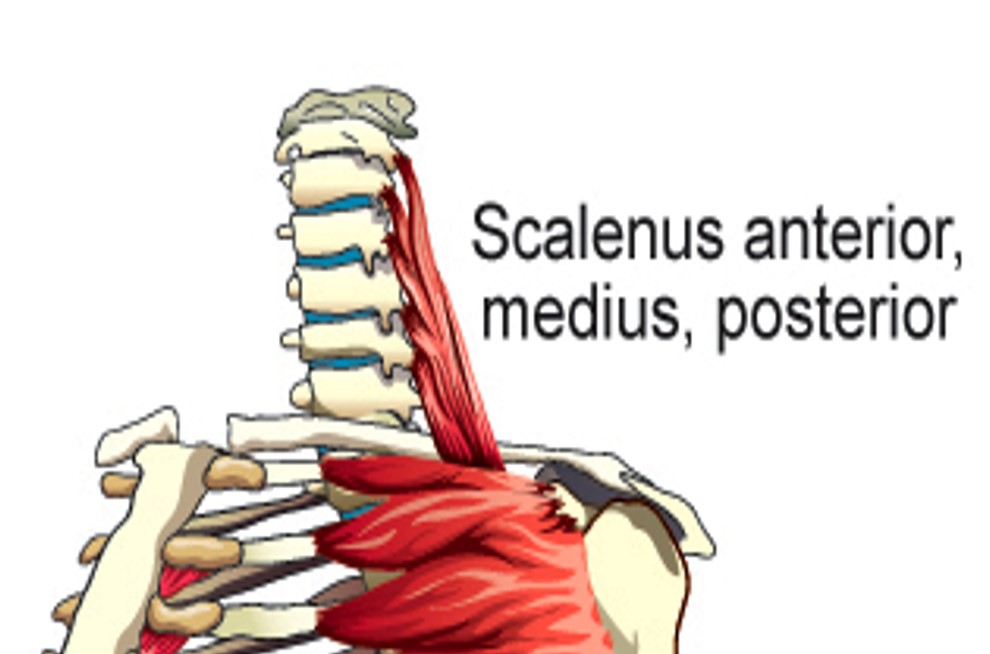
Scalenus Medius
Elevates first rib
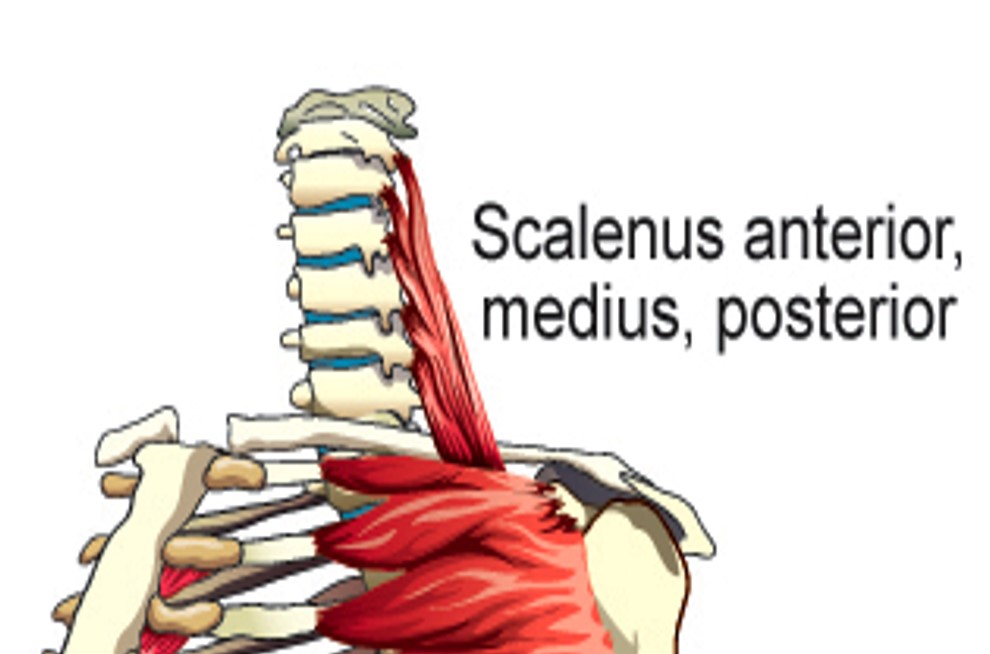
Scalenus Posterior
Elevates 2nd rib
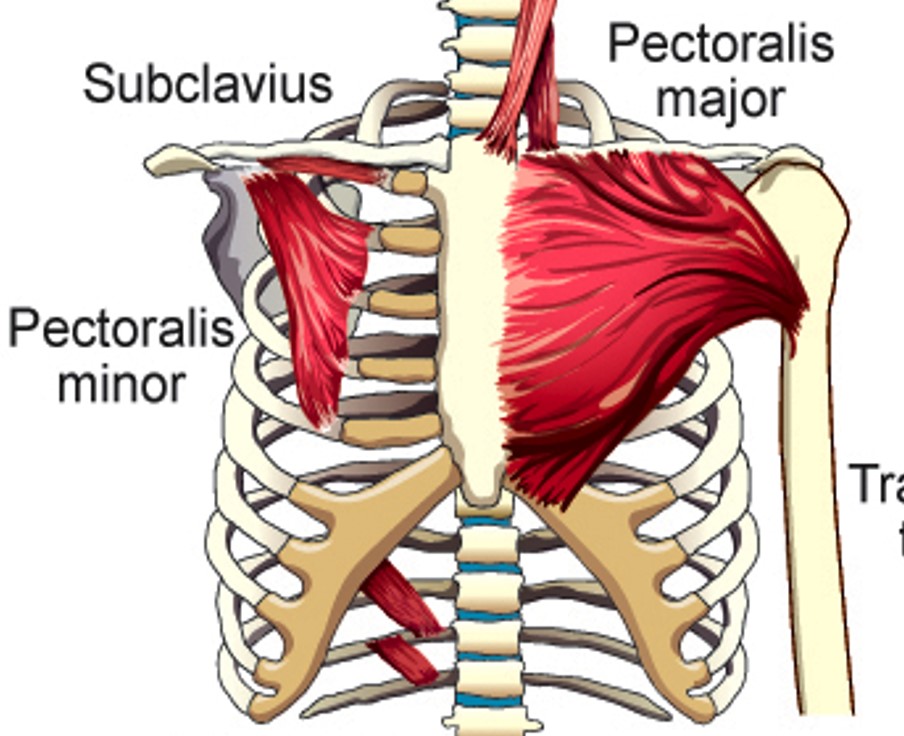
Pectoralis Major
Pulls Sternum and ribs up
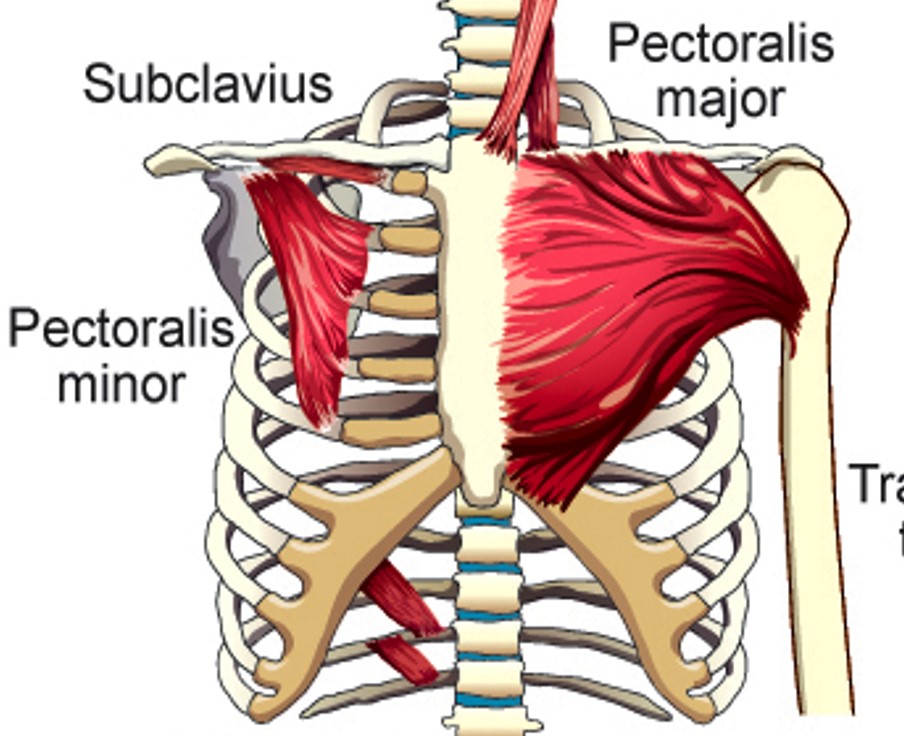
Pectoralis Minor
Elevates 2nd-5th ribs
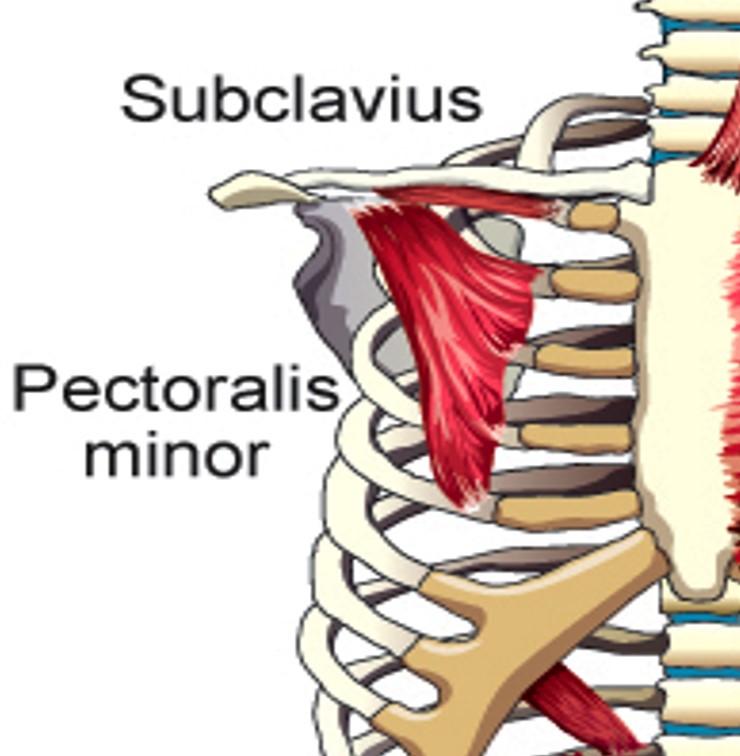
Subclavius
Elevates first rib
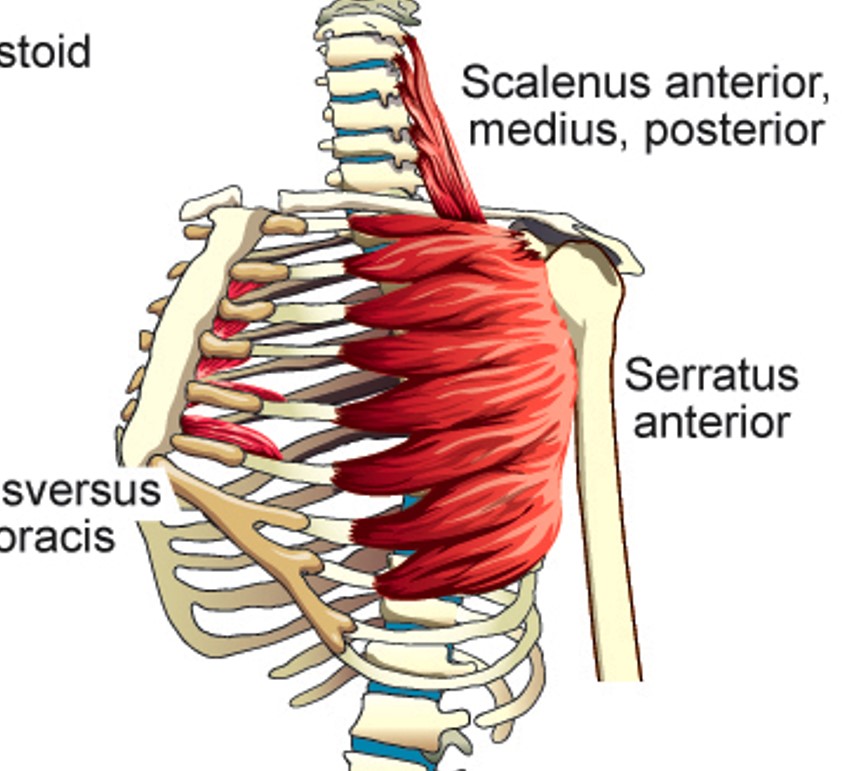
Serratus Anterior
Elevates upper ribs
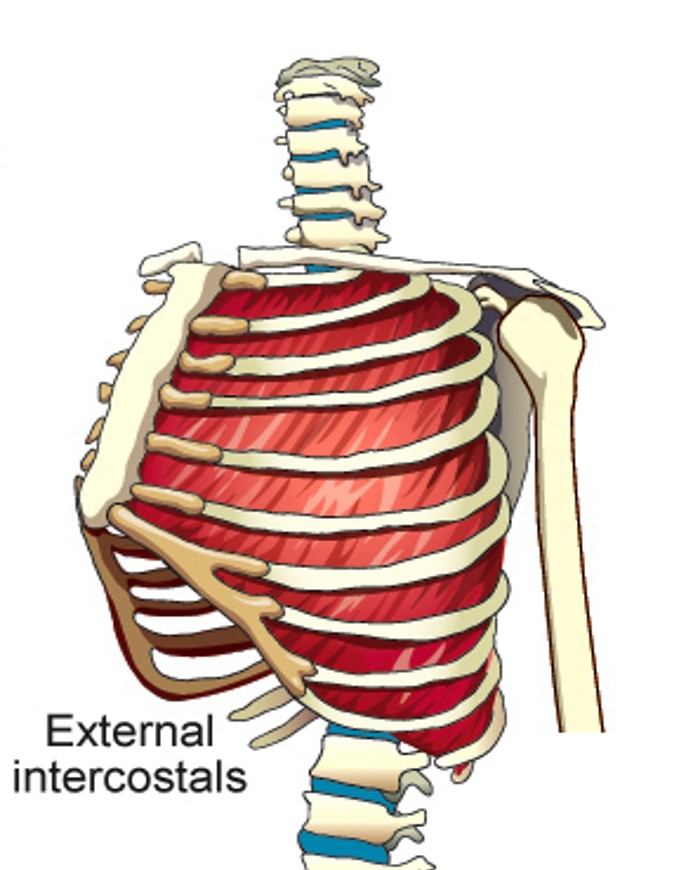
External intercostals
Each elevates the rib immediately below the one it is attached to
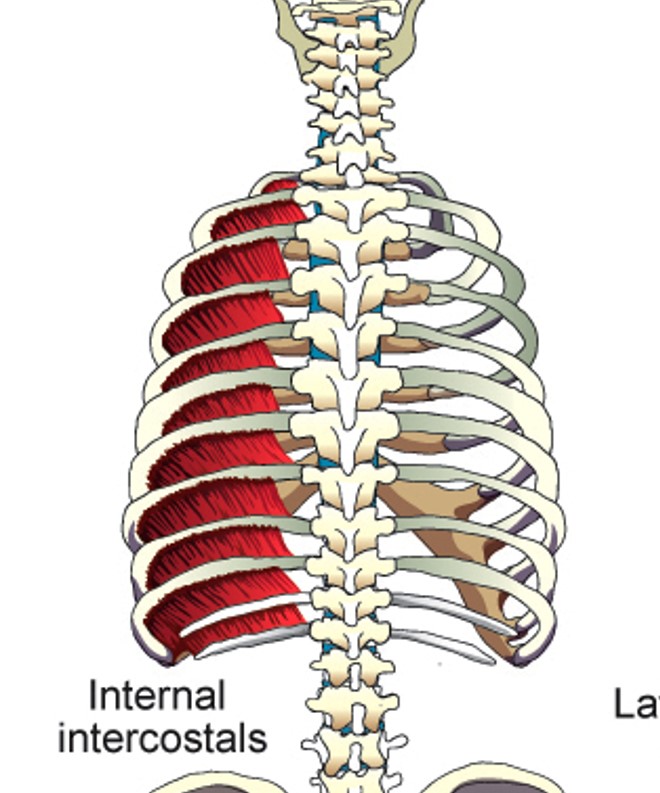
Internal Intercostals (Interosseus portion)
depresses ribs and stiffens space between them
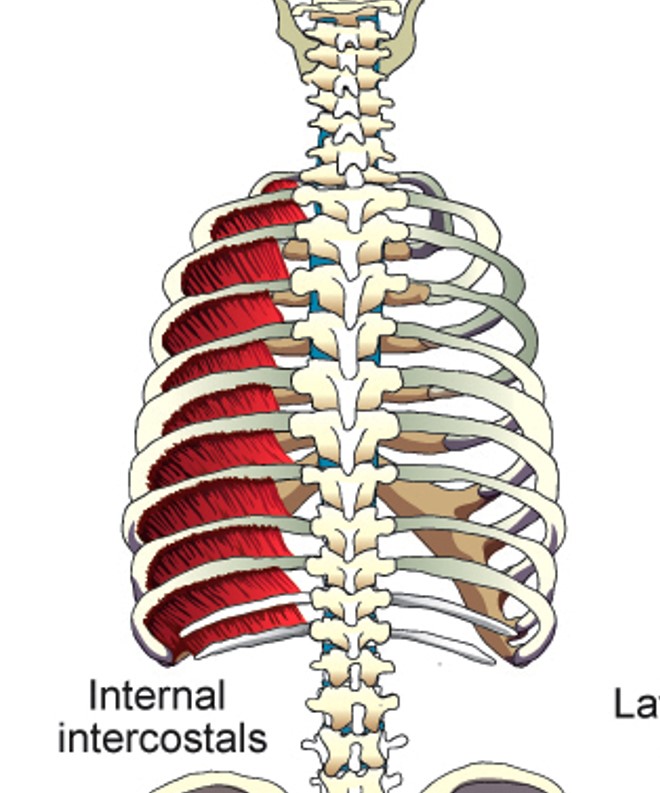
Internal Intercostals (Intercartilagenous portion)
elevates ribs
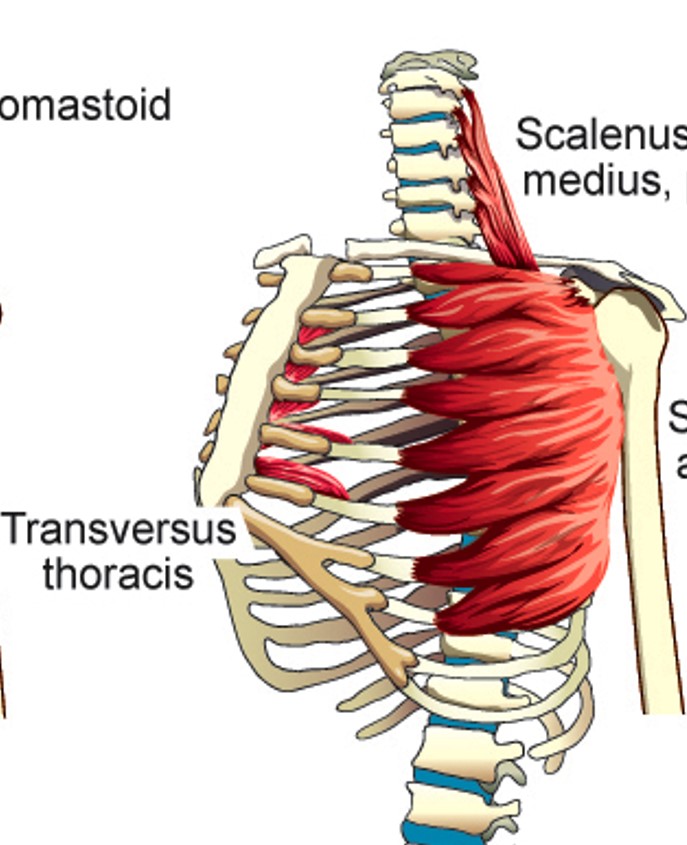
Transversus Thoracis
Depresses 2nd - 6th ribs
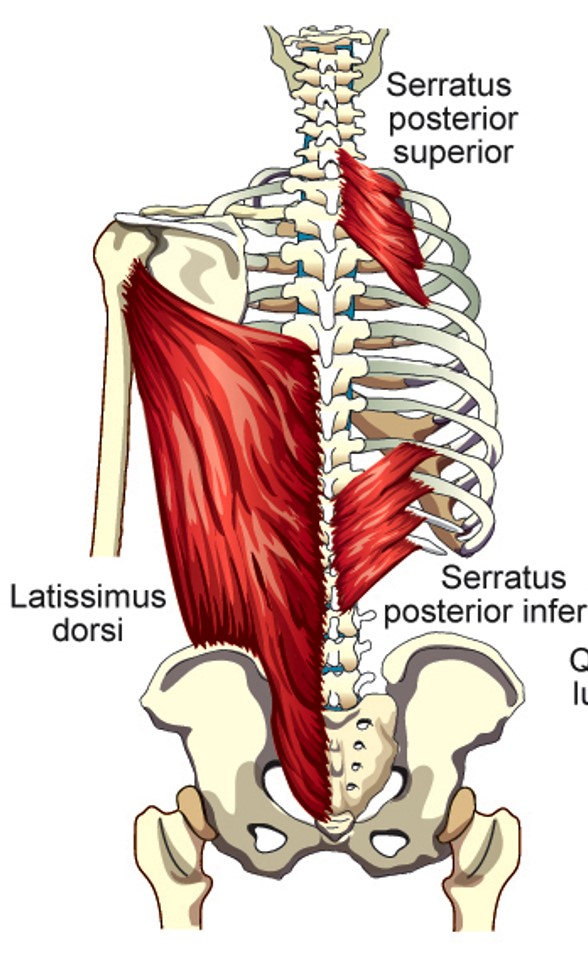
Latissimus Dorsi
Compresses the lower portion of the rib cage (can elevate lower ribs when humerus is fixed)
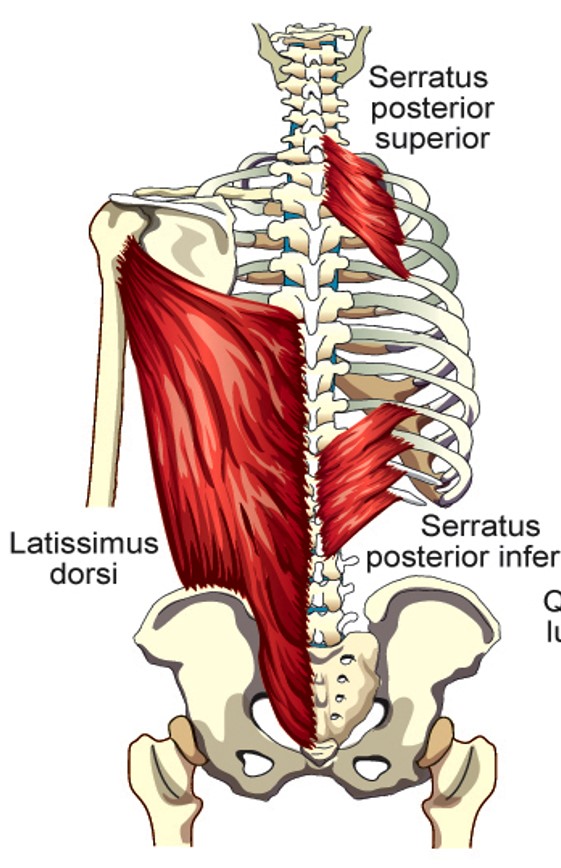
Serratus Posterior Superior
Elevates 2nd - 5th ribs
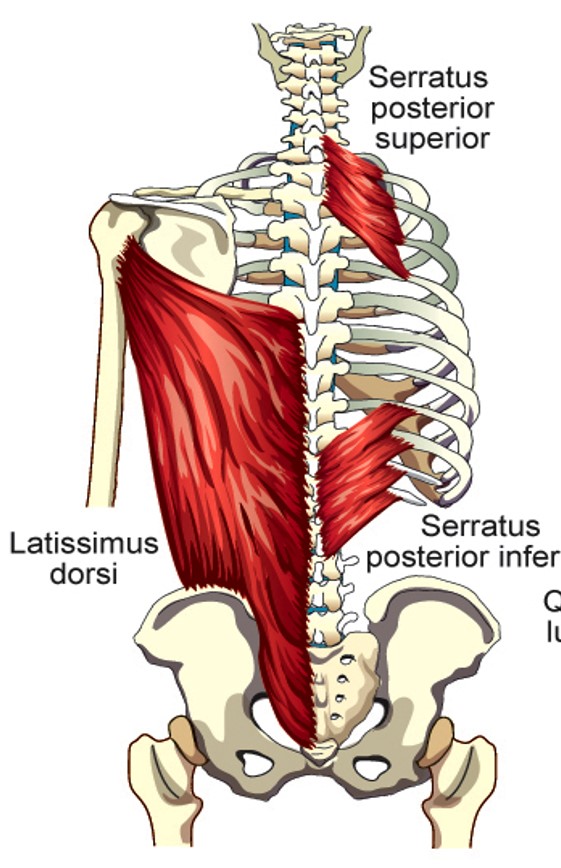
Serratus Posterior Inferior
depresses lower four ribs
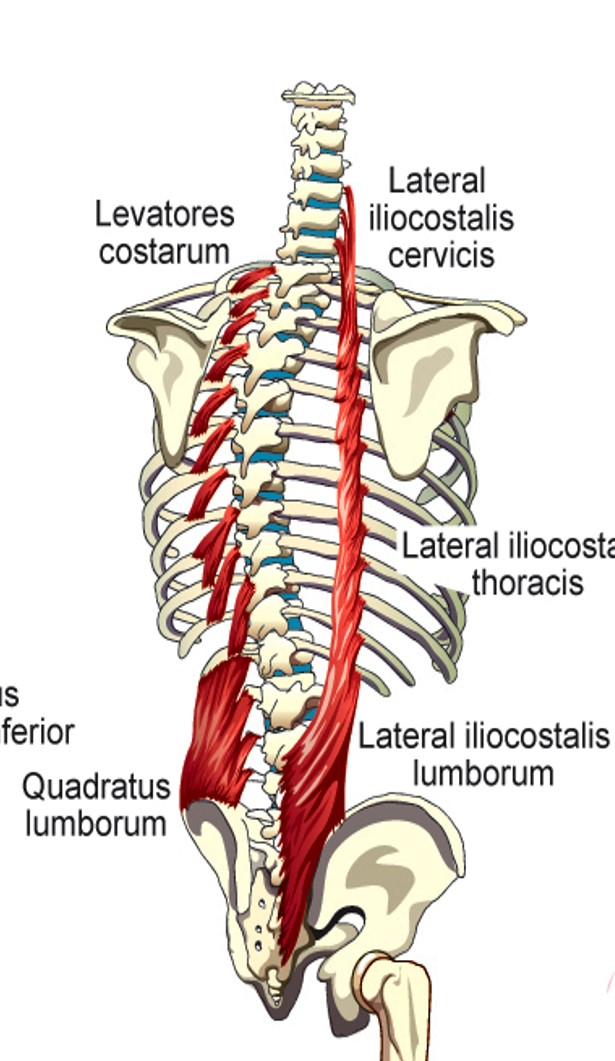
Lateral Iliocostalis (cervicis)
elevation of 3-6th ribs
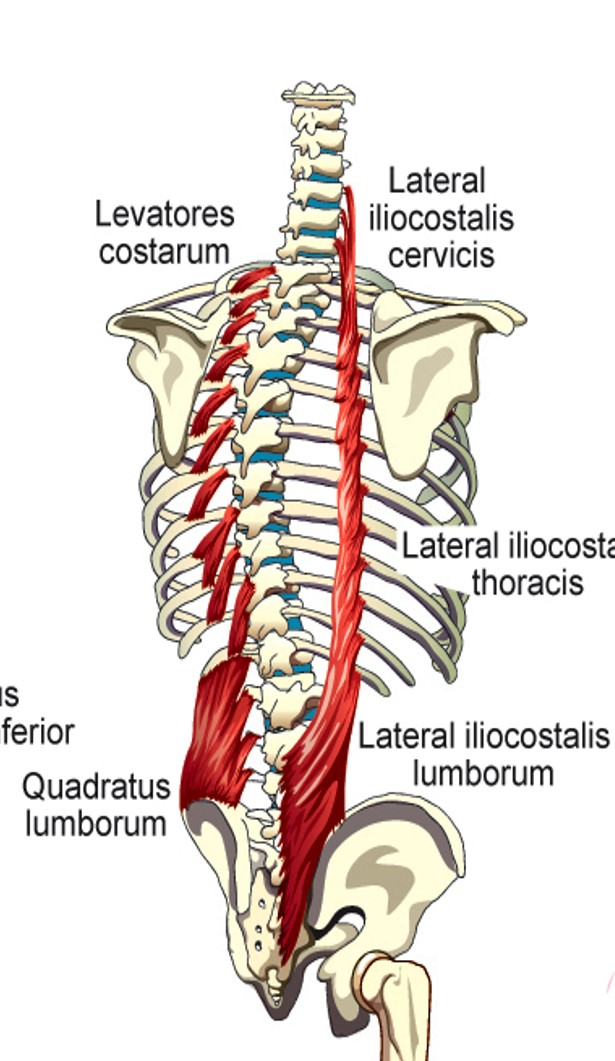
Lateral Iliocostalis (thoracis)
stabilizes large muscle segments of the back of the rib cage wall and makes them move with the rib elevation/depression
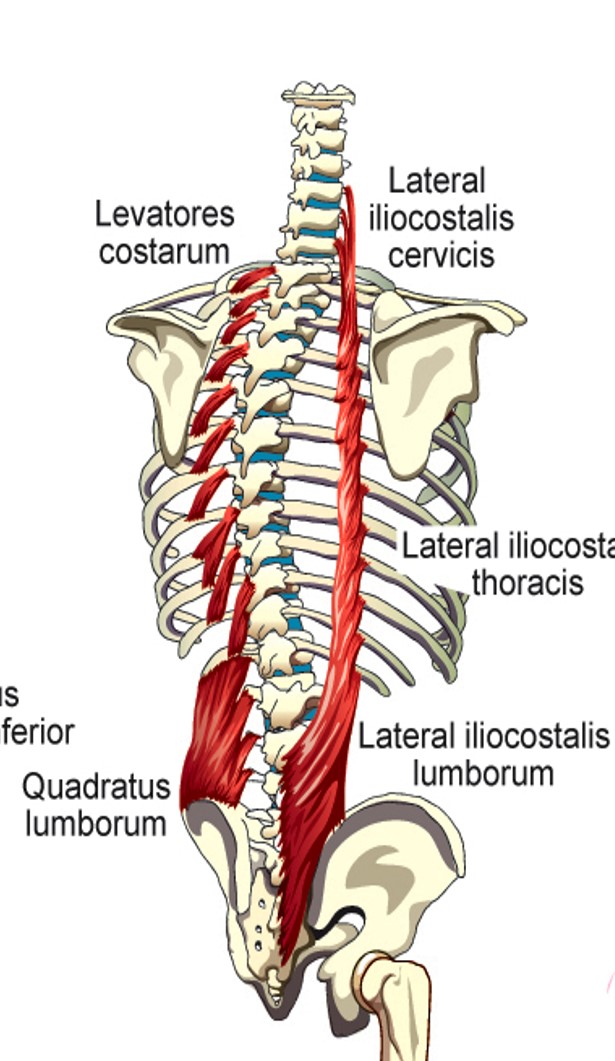
Lateral Iliocostalis (lumborum)
depression of lower 6 ribs
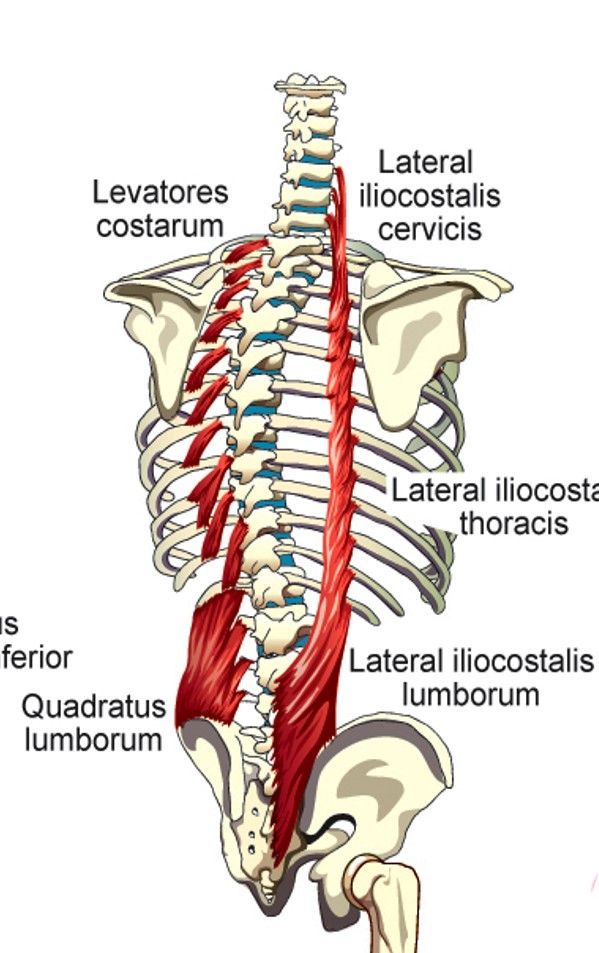
Levatores Costarum
lifts individual ribs or elevates whole rib cage
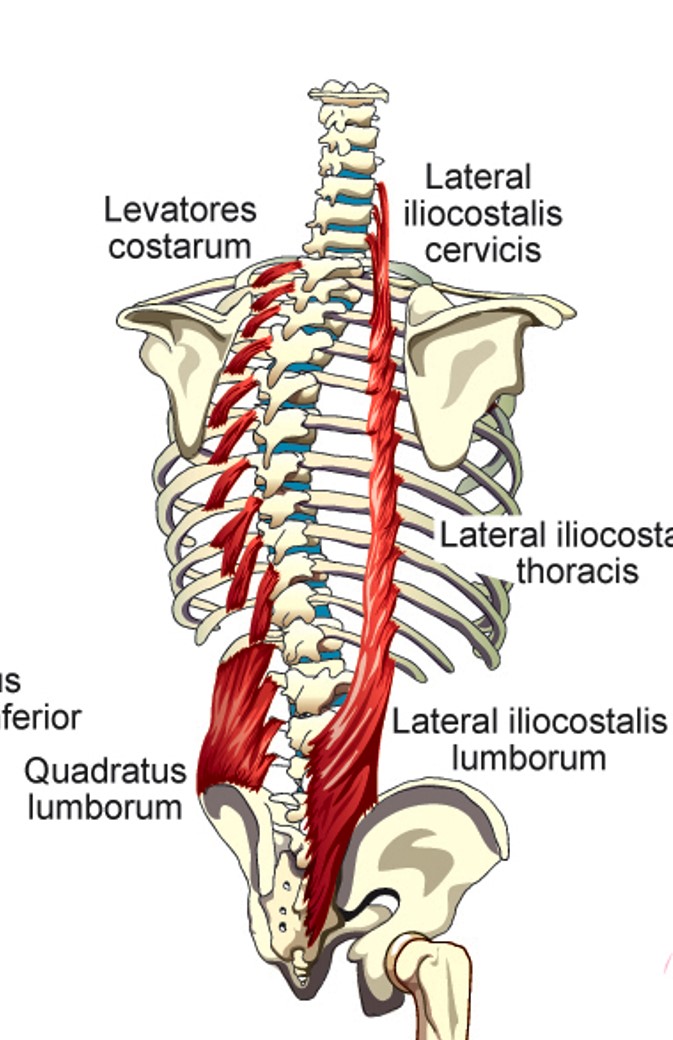
Quadratus Lumborum
pulls down on lowest rib
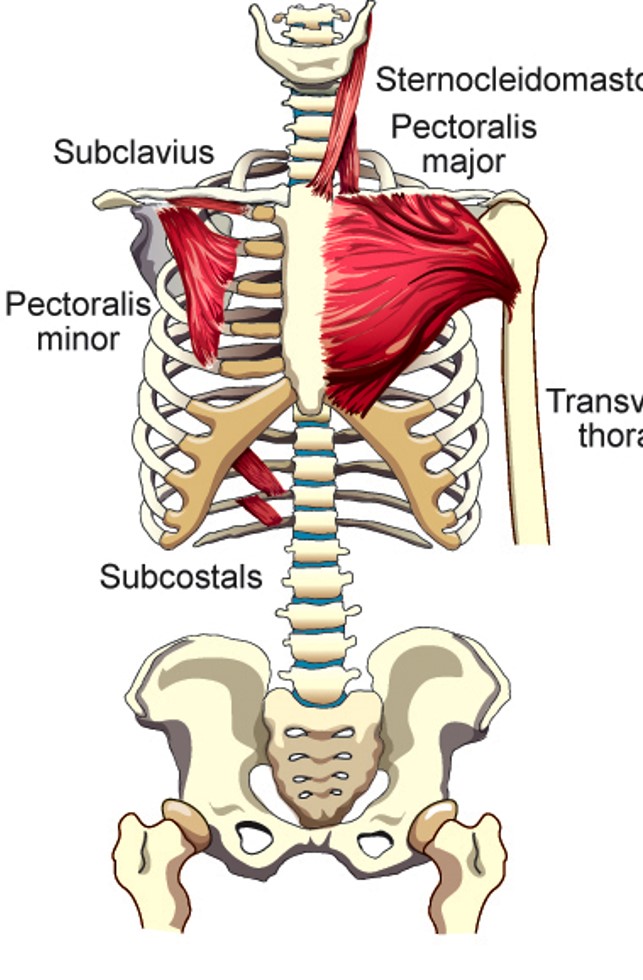
Subcostal Muscles
pulls down on ribs they are attached to
Diaphragm
primary driver of inspiration
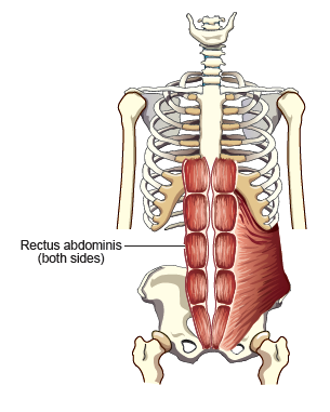
Rectus Abdominus
Pulls lower ribs and sternum down. Forces front of abdominal wall inward
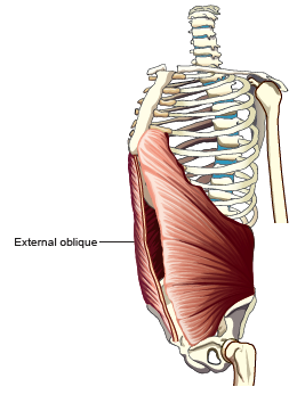
External Oblique
Pulls lower ribs down. Forces front and side of abdominal wall inward
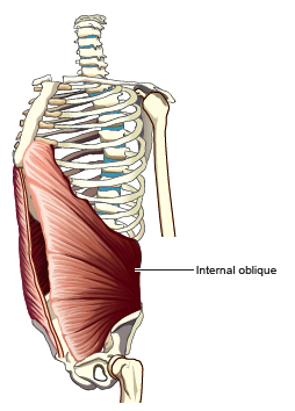
Internal Oblique
pulls lower ribs down. forces front and side of abdominal wall inward
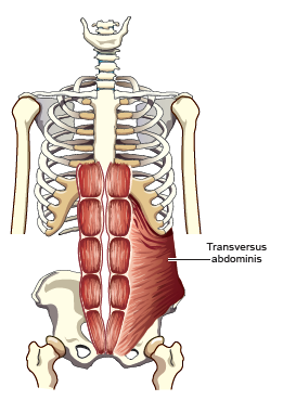
Transversus Abdominus
Pulls front and side of abdominal wall inward
Joint types in the rib cage wall
•Costosternal joints
•Costovertebral joints
Tidal Volume
Volume of air inspired or expired during the breathing cycle
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Maximum volume of air that can be inspired from the tidal end-inspiratory level
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
Maximum volume of air that can be expired from the tidal end-expiratory level
Residual Volume
Volume of air remaining at the end of a maximum expiration
Lung inspiratory capacities
the maximum volume of air that can be inspired from the resting end-expiratory level
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Maximum volume of air that can be inspired from the tidal-end inspiratory level
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
maximum volume of air that can be expired from the tidal end-expiratory level
Residual volume
the volume of air remaining at the end of a maximum expiration
Vital Capacity
maximum volume of air that can be expired after max inspiration or vice versa
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
Amount of air in the pulmonary apparatus
Total Lung capacity
volume of air in the pulmonary apparatus after a maximum inspiration
Inspiratory capacity made from
TV + IRV
Vital capacity made from
IC + ERV
Functional residual capacity made from
ERV + RV
Total Lung capacity made from
VC + RV
Cranial Nerves involved in breathing
IX (glossopharyngeal), X (Vagus), XII (Hypoglossal), and XI (Accessory)
Which cranial nerves elevate the rib cage?
XI (Accessory)
Which cranial nerves dilate the larynx and stiffen the upper airway?
IX (glossopharyngeal), X (Vagus), and XII (Hypoglossal)
Spinal Nerves through the rib cage wall
C1-L2
Spinal nerves through the diaphragm
C3-C5
Spinal nerves through the abdominal wall
T7-L1
Medulla
Controls tidal breathing
Chemoreceptors location
Front and side of the medulla (central) and common carotid arteries (perioheral)
Mechanoreceptors location
chest wall (muscle length), and pulmonary apparatus (muscle smoothness)
Controls special acts of breathing
Higher brain centers
Tidal Breathing purpose
ventilation and gas exchange
Forms of speech breathing
extended steady utterances and running speech
extended steady utterances
deepest inspiration until moveable air is gone
Checking action
causes a slower release of air
extended steady utterance
changes muscle activities to maintain pressure
Running speech
uses twice the resting Tidal Volume. Fast inspirations, slow expirations
High drive to breathe
breathy speech; fewer syllables per breath; increased air-flow; larger tidal lung, rib cage, and abdominal wall volume
Larynx functions
airway protection, phonation
parts of the larynx
skeleton, laryngeal joints, internal topography
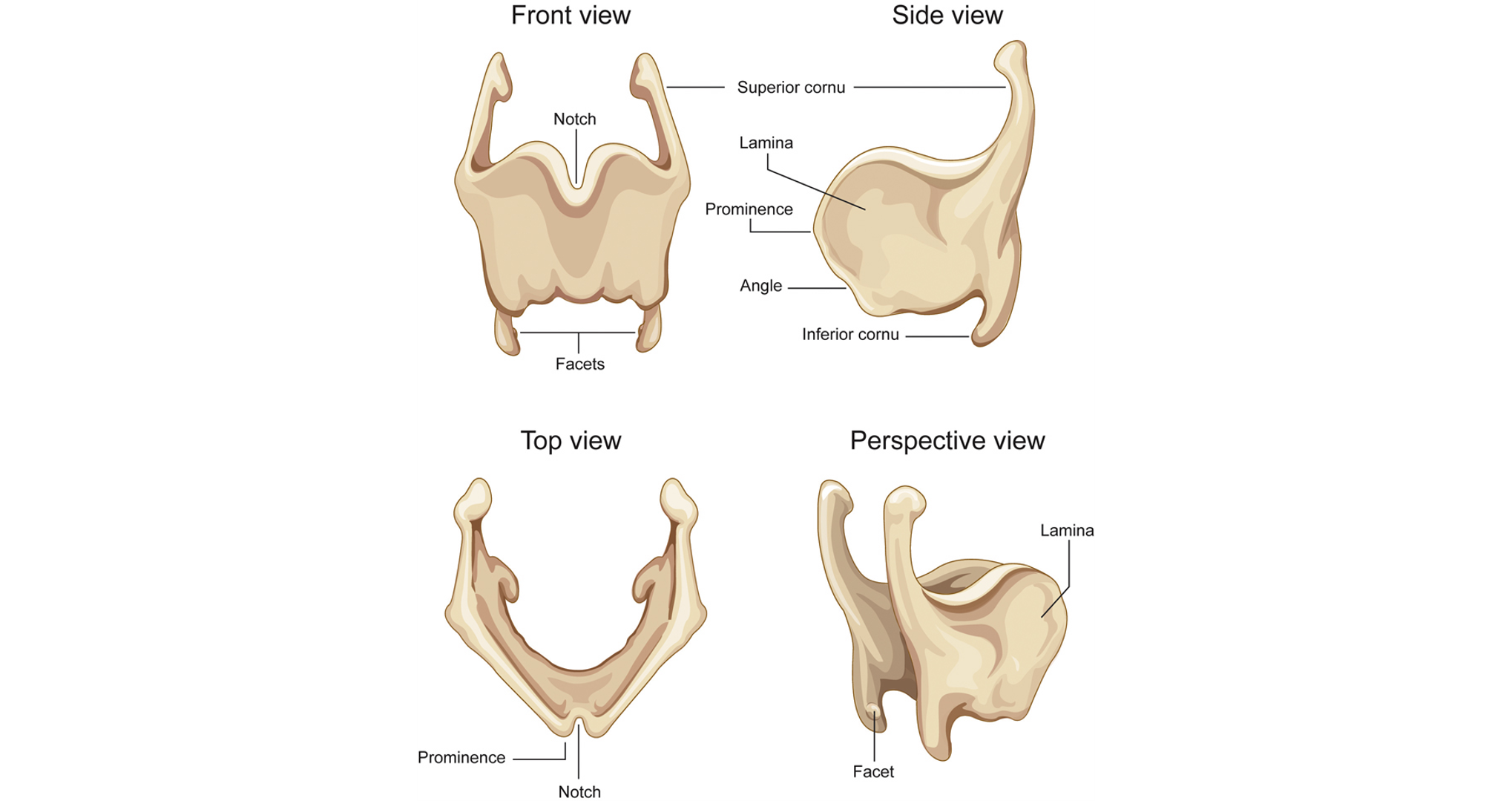
Thyroid cartilage
largest laryngeal cartilage, composed of two plates (thyroid laminae)
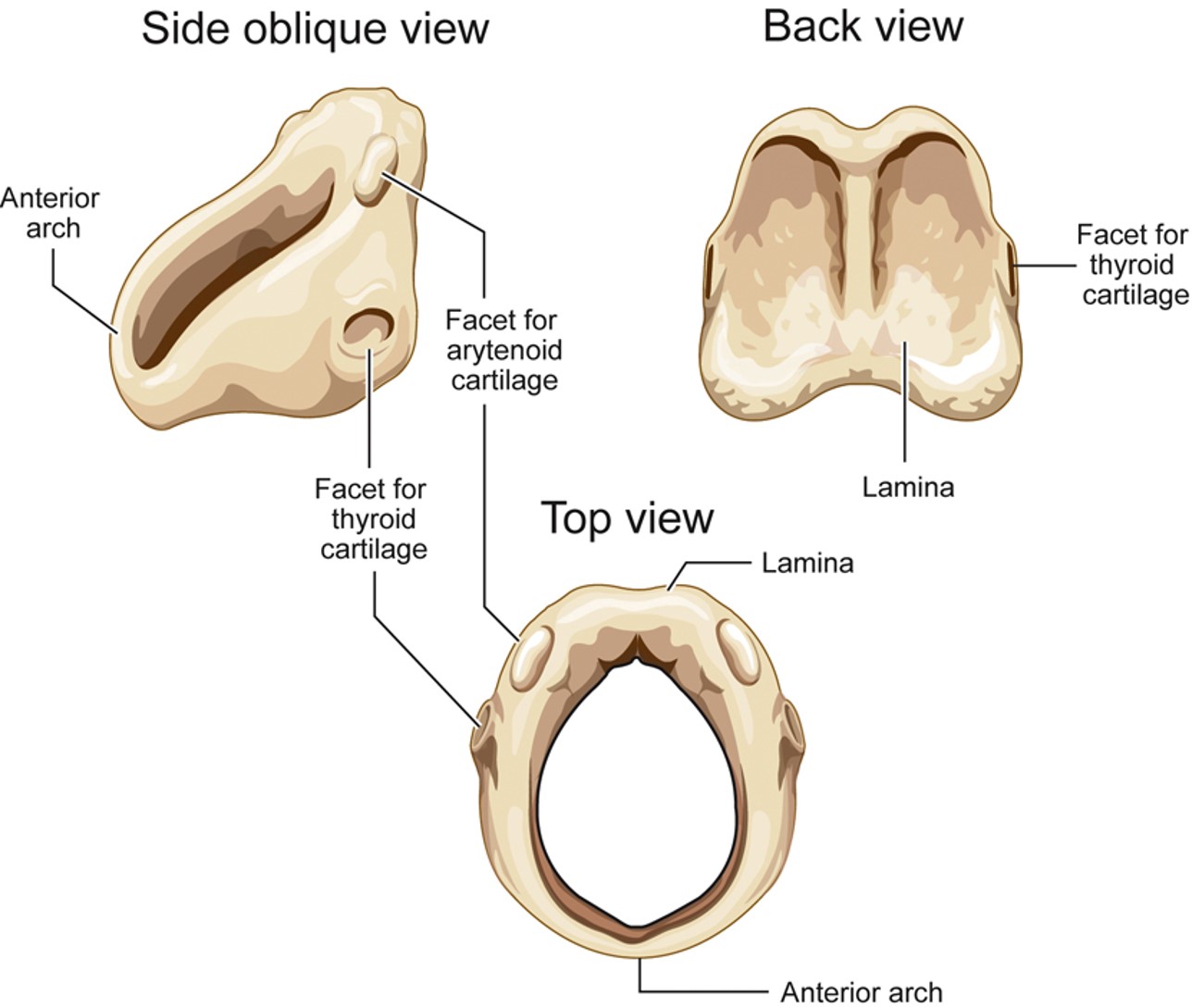
Cricoid Cartilage
beneath thyroid cartilage, ring shaped, 4 facets for thyroid cartilage and arytenoids
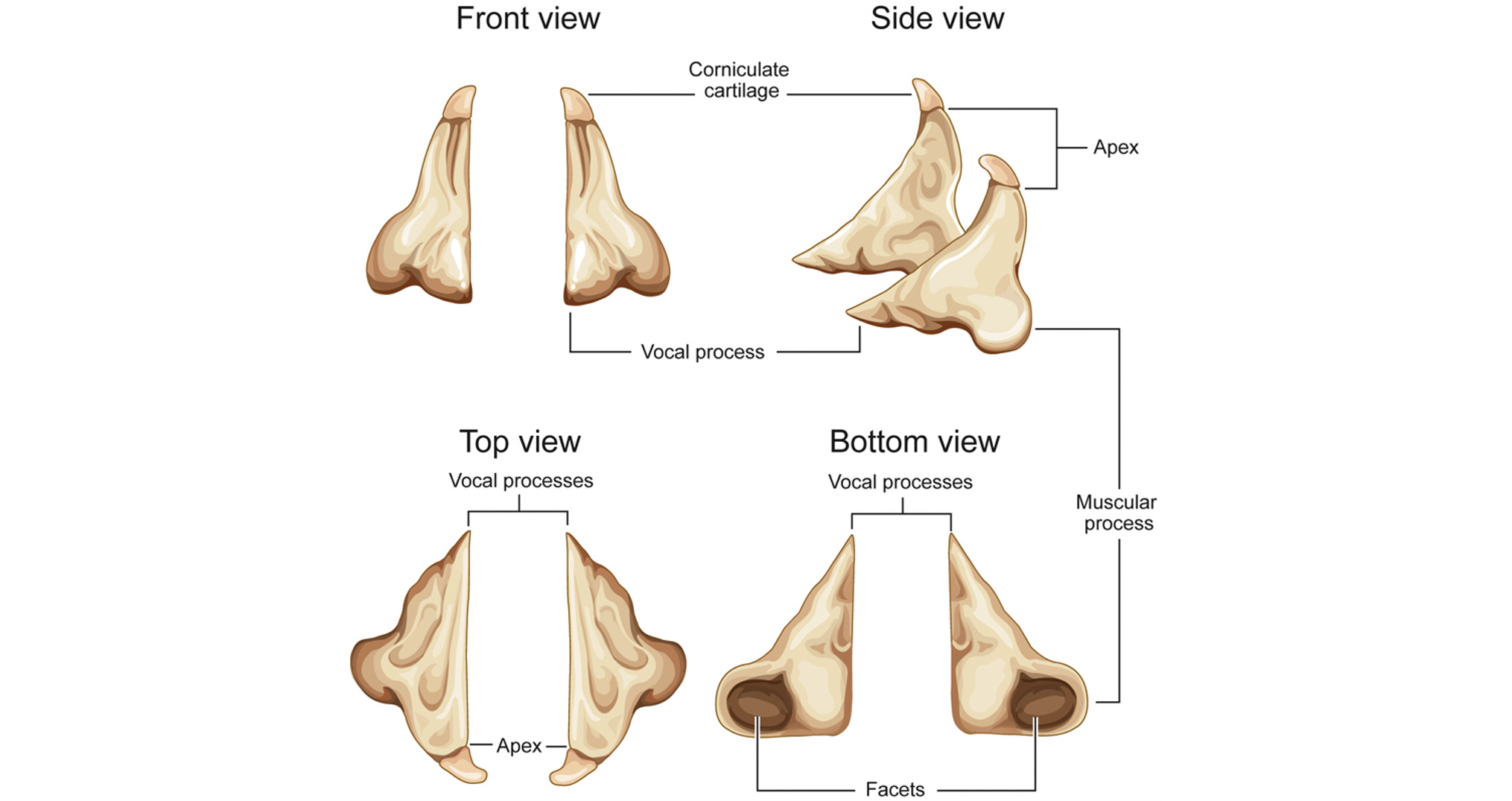
Arytenoid Cartilages
2 pyramid structures, on top of the posterior lamina of cricoid
epiglottis
leaf-shaped cartilage beneath the hyoid bone and root of tongue
Hyoid bone
NOT part of larynx. free floating, positioned horizontally in the neck above larynx
Cricothyroid joints
Laryngeal joints. restrict movement of the cricoid and thyroid cartilages.
cricoarytenoid joints
on top of cricoid cartilage. Two ligaments bind and restrict movement of the joint. joint rocks and slides.
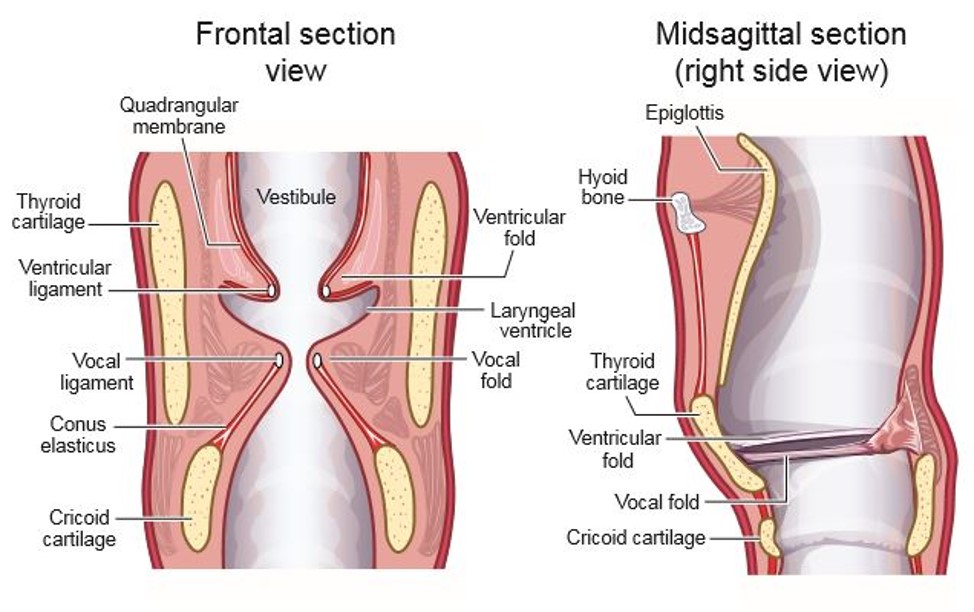
Laryngeal vestibule upper region
laryngeal aditus. made of arytenoid cartilages, side of epiglottis, and aryepiglottic folds (run between the arytenoid cartilages and the epiglottis)
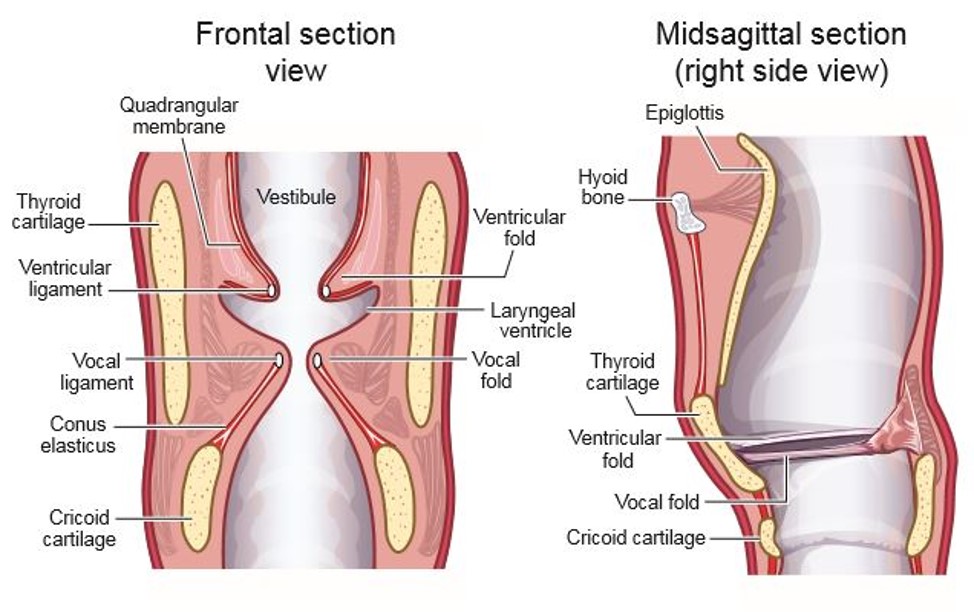
Laryngeal vestibule middle region
ventricular folds
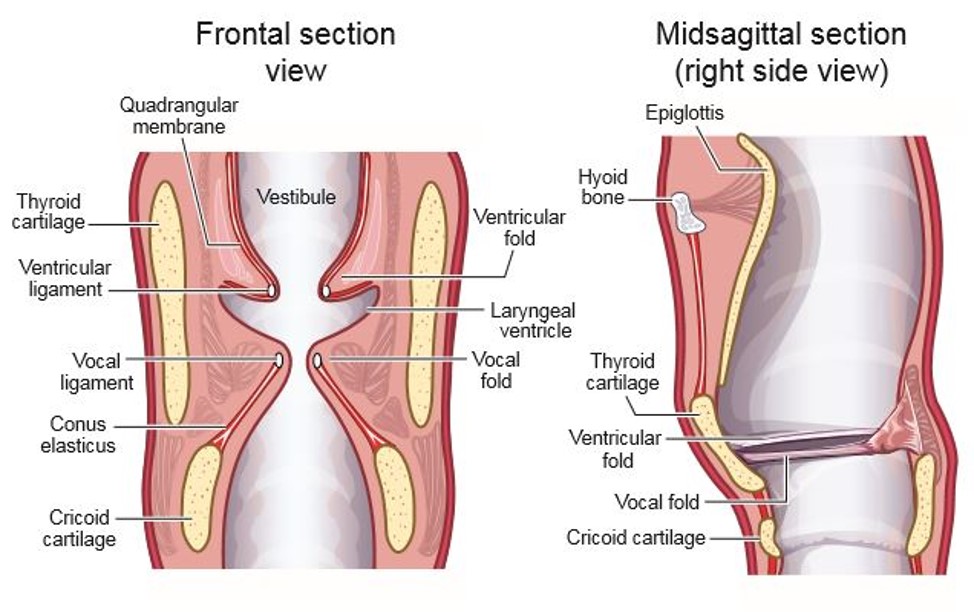
Laryngeal vestibule lower region
vocal folds and cricoid cartilage
Vocal fold layer 1
squamous epithelium - determines outer shape of the vocal fold
Vocal fold layer 2 (superficial layer of lamina propria)
loose fibrous matrix
Vocal fold layer 3 (intermediate layer of lamina propria)
elastic fibers
Vocal fold layer 4 (deep layer of lamina propria)
collagen fibers
Vocal fold layer 5 (innermost)
muscle fibers - make up the bulk of the vocal folds
Membranous glottis
front 60% of the glottis
cartilaginous glottis represents the ____ _____ of the glottis
back 40%
ventricular folds
false folds. lie above vocal folds
laryngeal ventricles
sinus between the ventricular folds and the vocal folds
Conus elasticus (cricothyroid ligament)
intrinsic ligament
Middle cricothyroid ligament
intrinsic ligament
Vocal ligaments
intrinsic ligament
Thyroepiglottic ligament
intrinsic ligament
ventricular ligaments
intrinsic ligament
lateral cricothyroid membranes
intrinsic ligament
quadrangular membrane
intrinsic ligament