Unit 1
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on Geography lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Cartographer
A person who creates maps.
Data Aggregation
The process of gathering and expressing data in a summarized form, for statistical analysis.
Spatial Patterns
The arrangement of objects on the Earth's surface in relationship to one another.
Spatial Perspective
Observing variations in geographic phenomena across space.
Reference Maps
Maps that show the absolute location of places and geographic features.
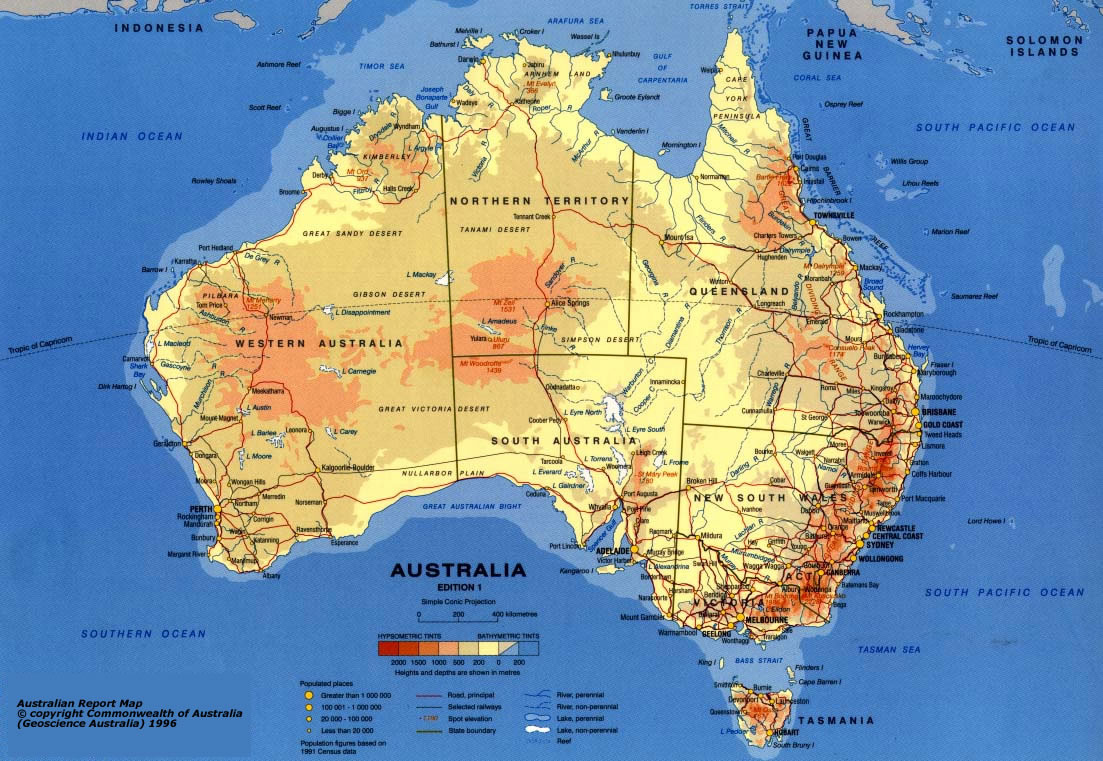
Thematic Maps
Maps that tell a story about the degree of an attribute, the pattern of its distribution, or its movement.
Dot density
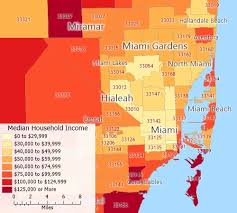
cloropleth map
Cartogram
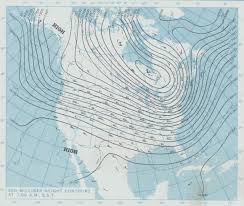
Isoline
Absolute Distance
A precise measure of the separation between two points using a standard unit.
Relative Distance
A measure of the social, cultural and/or economic connectivity between places.
Clustered
Objects that are closely arranged or grouped together.
Dispersed
Objects that are scattered or spread out.
Map Projections
A systematic transformation of the latitudes and longitudes of locations from the surface of a sphere or an ellipsoid into locations on a plane.
Distortion
The misrepresentation of shape, area, distance, or direction of or between geographic features when compared to their true measurements on the curved surface of the earth.
Mercator Projection
A cylindrical map projection presented by the Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569.
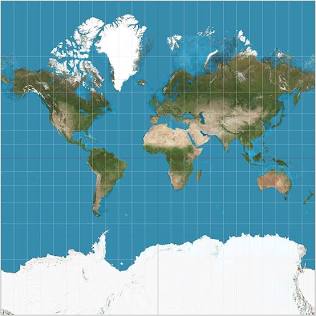
Peters Projection
A cylindrical map projection that attempts to retain the correct sizes of all areas on the Earth.
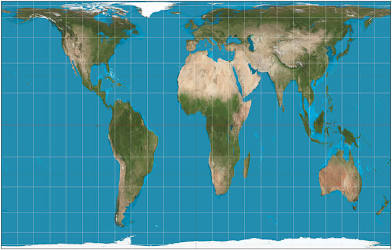
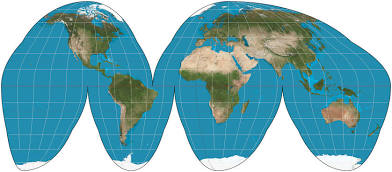
Goode Projection
A pseudocylindrical, equal area, composite map projection used for world maps.
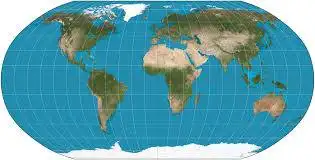
Robinson Projection
A map projection of a world map which shows the entire world at once.
Census
A complete enumeration of a population.
Fieldwork
The study of geographic phenomena by visiting places and observing how people interact with and thereby change those places.
Absolute Location
The exact position of an object or place, measured within the spatial coordinates of a grid system.
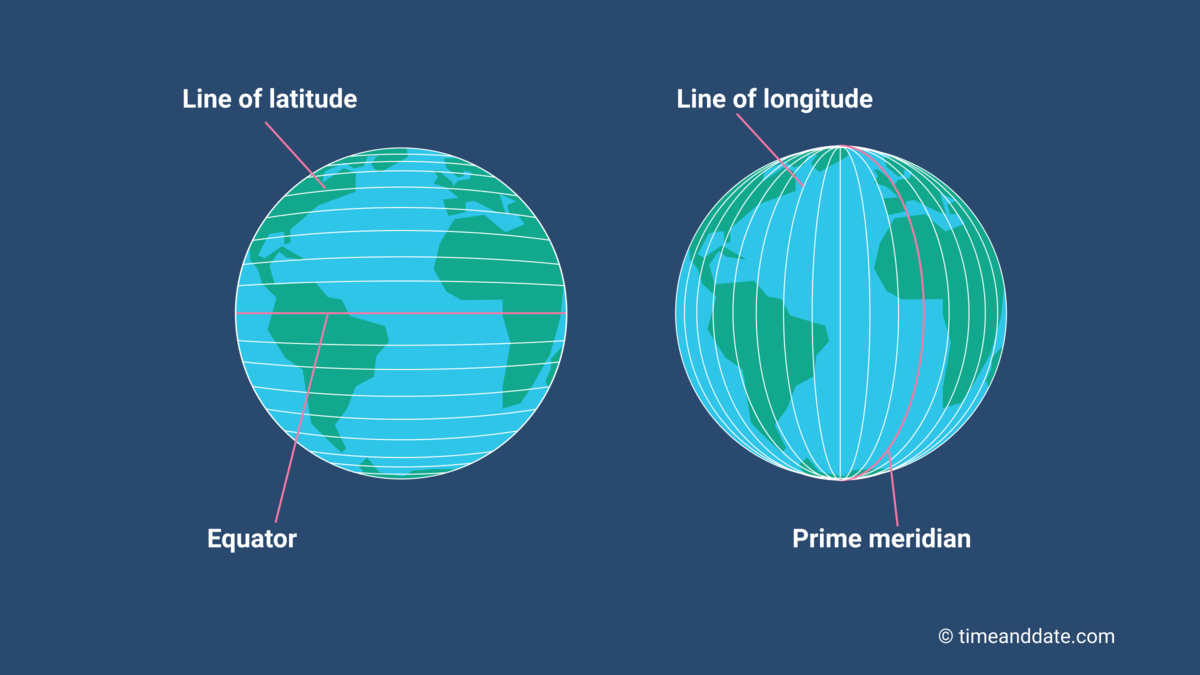
Latitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of parallels drawn on a globe and measuring distance north and south of the Equator.
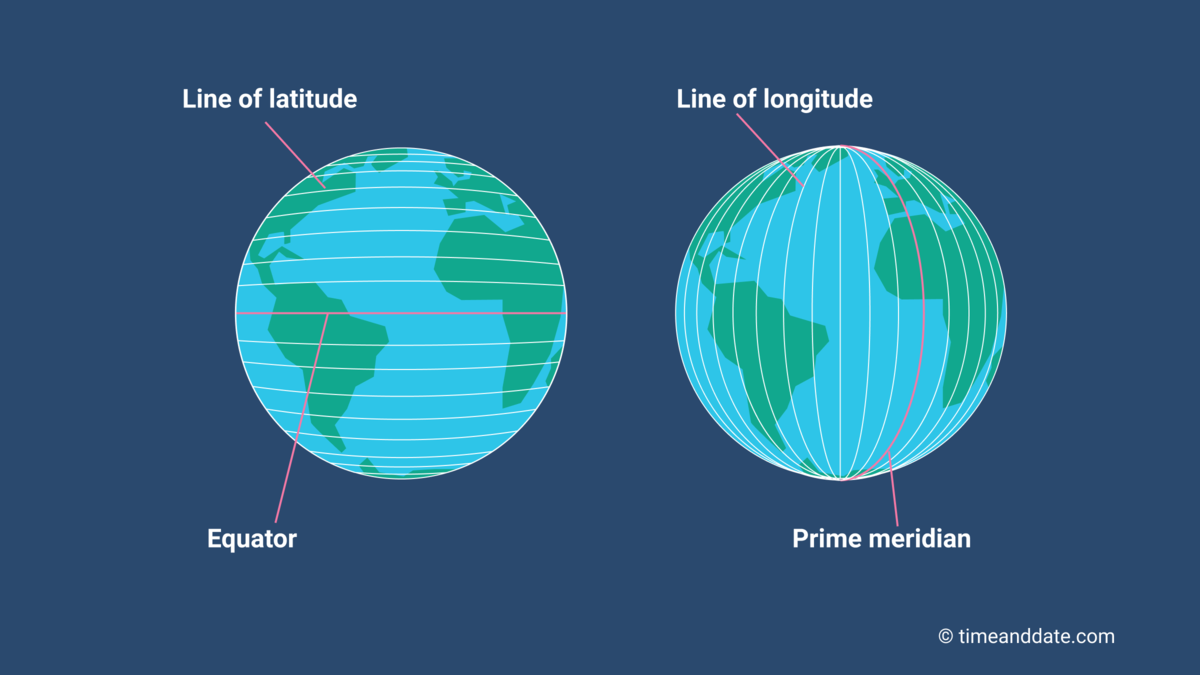
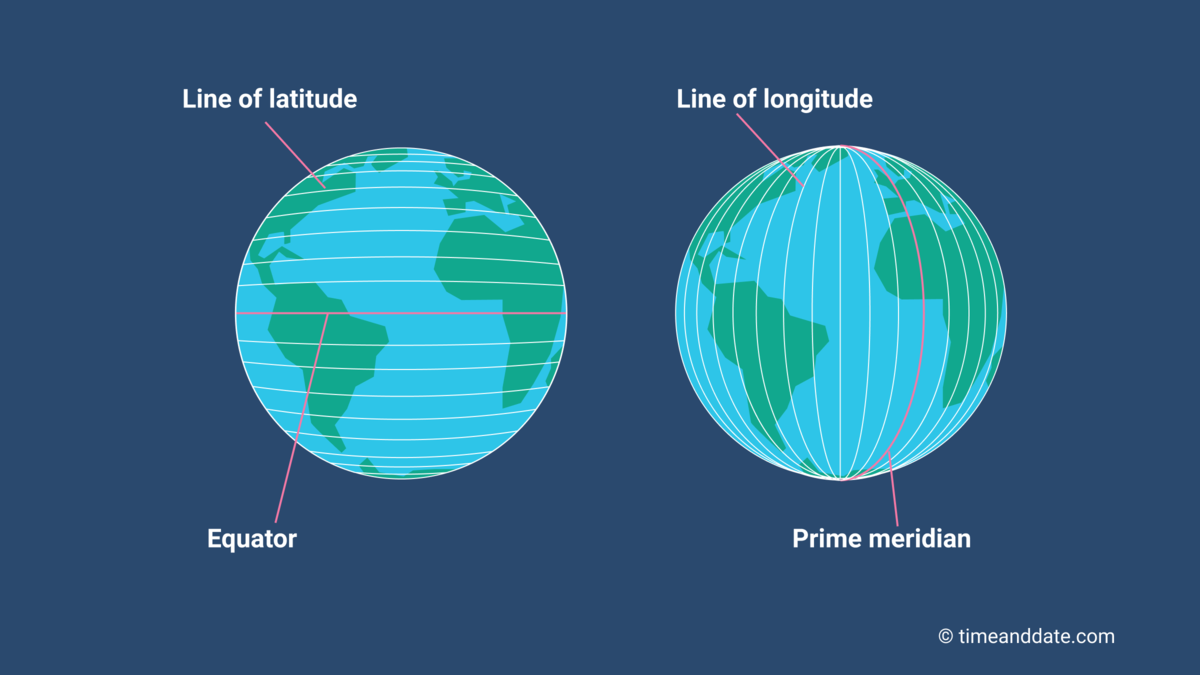
Longitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians drawn on a globe and measuring distance east and west of the Prime Meridian.
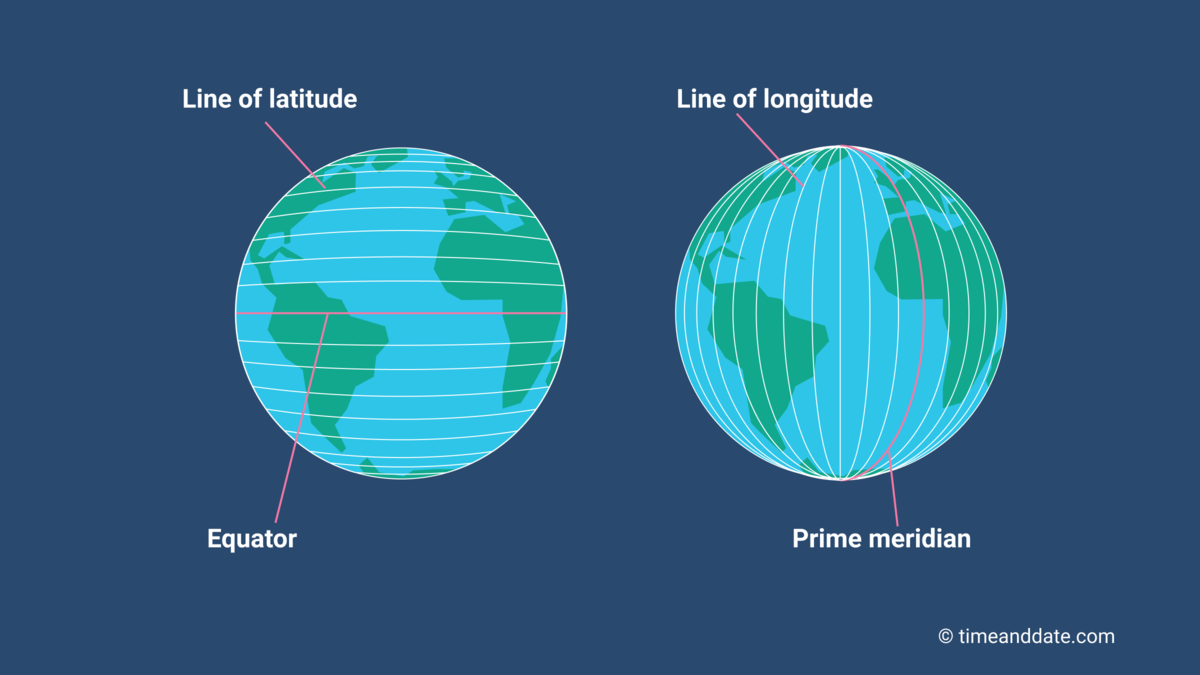
Equator
An imaginary line that circles the earth equally distant from both poles, dividing the earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and constituting the parallel of latitude 0°.
Prime Meridian
The meridian, designated at 0° longitude, which passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
Aerial Photography
The taking of photographs of the ground from an elevated position.
Satellite Imagery
Images of Earth collected by satellites operated by governments and businesses.
Relative Location
The regional position of a place relative to other places.
Space
The physical gap or interval between two objects.
Place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular character.
Cultural Landscape
The visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape.
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
Time-Space Compression
The reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation systems.
Time Distance Decay
The declining degree of acceptance of an idea or innovation with increasing time and distance from its origin.
Interdependence
A relationship between countries in which they rely on one another for resources, goods, or services.
Diffusion
The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time.
Cultural Ecology
A geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships.
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Environmental Perception
The way people interpret and understand their surroundings.
Natural Hazards
Events in the physical environment that can destroy human life and property.
Natural Resources
Materials or substances such as minerals, forests, water, and fertile land that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain.
Nonrenewable Resources
A resource of economic value that cannot be readily replaced by natural means on a level equal to its consumption.
Renewable Resources
A resource of economic value that can be replaced by natural means on a level equal to its consumption.
Greenhouse Gasses
Gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat near the surface.
Greenhouse Effect
The trapping of the sun's warmth in a planet's lower atmosphere due to the greater transparency of the atmosphere to visible radiation from the sun than to infrared radiation emitted from the planet's surface.
Environmental Determinism
The view that the natural environment has a controlling influence over various aspects of human life including cultural development.
Possibilism
The theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives.
Global Scale
Interactions occurring at the scale of the world, in a global setting.
Regional Scale
Interactions occurring within a region, in a regional setting.
National Scale
Interactions occurring within a country, in a national setting.
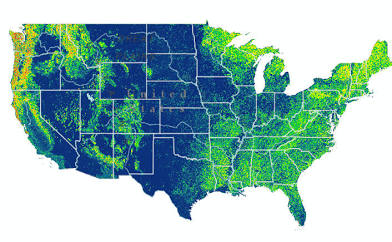
Local Scale
Interactions occurring within a community, in a local setting.
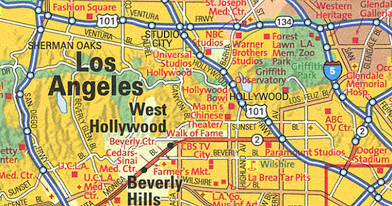
Glocal Perspective
Thinking about how events at a global scale affect local situations, and vice versa.
Region
An area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features.
Formal Region
An area which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics.
Functional Region
An area organized around a node or focal point.
Nodes
A central point in a functional region where functions are coordinated and directed.
Metropolitan Area
A major population center made up of a large city and the smaller suburbs and towns that surround it.
Perceptual/Vernacular Region
An area that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity.
Sense of Place
State of mind derived through the infusion of a place with meaning and emotion by remembering important events that occurred in that place or by labeling a place with a certain character.
Regional Identity
An awareness of being part of a group of people living in a particular region.
Contested Boundaries
Boundaries, either physical or cultural, that are subject to claims by more than one group of people.
Regional Analysis
Studying the distinctiveness of regions.