Charged Particles
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What do charged particles have associated to them?
Electromagnetic field
Which atoms do charged particles interact with?
Move through medium and interact with the electrons/nucleus of every atom they pass.
The type of interaction that occurs depends on proximity. Which interaction takes place depending on proximity ?
Close = hard collision (bremsstrahlung)
Far = soft collision ( excitation & ionisation )
Describe what happens during hard collision ?
Distance from atom is small.
Incident electron knocks out orbital electron.
This imparts significant K.E to the ejected electron.
Sometimes known as “delta rays” .
Few collisions happen this way but total K.E is low this way.
What kind of interaction happens when charged particles passes close to the nucleus ?
Elastic collision - electrons may scatter, negligible energy loss BUT changes direction.
Or
Bremsstrahlung - interacts with nucleus
Dependent on atomic number
Inversely dependent on atomic mass
Describe what occurs during soft collisions ?
further from atom.
More likely to happen
Many small collision all losses
Either ionisation or excitation occurs
Define excitation
Atomic electron mover to a higher shell then returns with emission of photon.
Define ionisation
atomic electron is ejected
Net effect is transfer of a few electron volts of energy to the medium.
Small amounts of energy are transferred
The incident photon will continue to travel till it loses all K.E
Any ejected electron stays locally.
Describe 2 qualities of the stopping power of a material by ionisation interaction ?
PROPORTIONAL to the square of the particle’s charge.
INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to the square of its velocity .
Why is the depth dose curve of an electron different to other charged particles ?
electrons are lighter than proton and heavy ions used in particle therapy.
They scatter.
Draw a electron depth dose curve (including Bremsstrahlung tail)
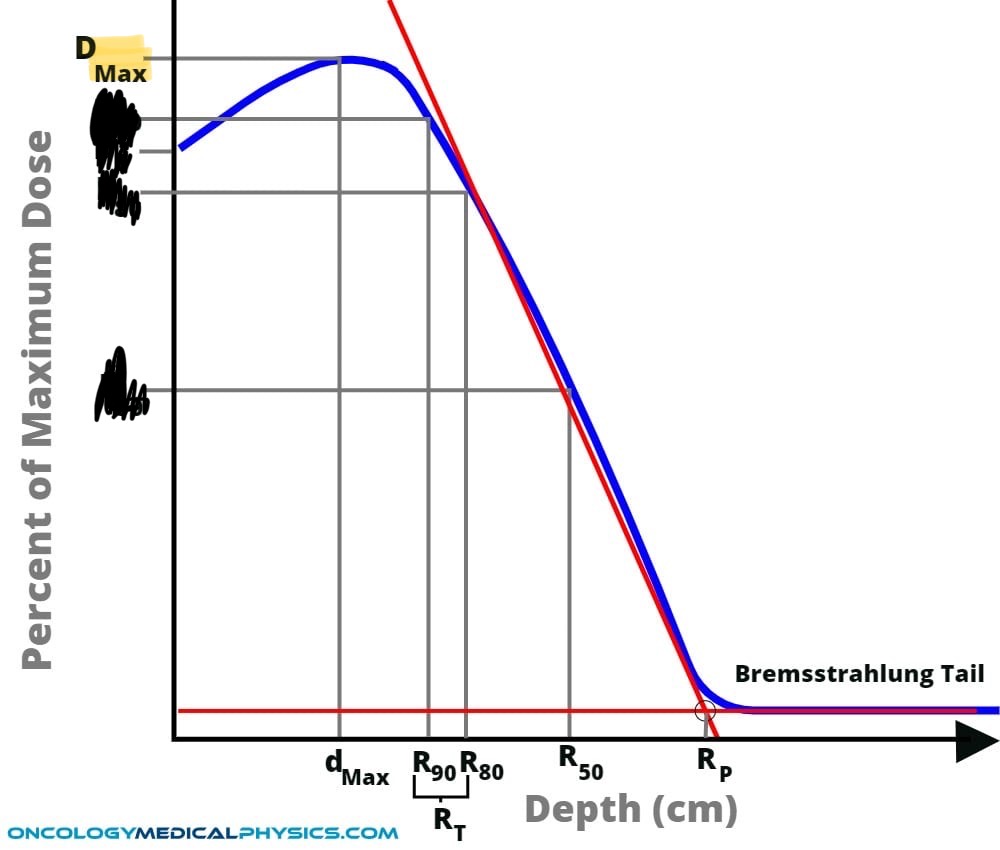
What are 4key features of the electron % depth dose curve ?
high surface dose INCREASES with energy (opp to protons)
Build up to Dmax (which can be broad at high electron energies)
Rapid dose fall off beyond Dmax.
Low value dose bremsstrahlung tail - which INCREASES slightly for high energy beams).
What happens if the depth (Dmax) increases ?
Electrons have less energy.
Scatter more easily.
More path length in a fixed increment of depth (more distance travelled, same drop down)
What happens to electrons if energy is deposited in successive layers ?
Energy deposited in successive layers INCREASES until electrons are fully diffused (Dmax).
After Dmax electrons start to be lost from beam.
What happens to surface dose at low energies ?
Electrons travel a longer distance, for the same increase in depth near the surface.
More scatter
Dose builds up more rapidly and over a shorter distance.
What happens to surface dose at high energies ?
Less scatter
More gentle change in dose deposited between surface and Dmax.
Higher surface dose relative to Dmax.
Describe what happens at the fall off region.
Electrons are being lost from beam
Depth dose fall (almost) linearly
Describe what happens at the Bremsstrahlung tail.
Large proportion come from machine (scattering foil)
Draw a proton depth dose curve.
Name 4 features of a proton depth dose curve.
No scattering
DD similar in shape to stopping power.
Low entry dose
Brag peak - sharp increase in dose at well defined depth (rapid dose fall off after Dmax)
The Bragg peak is sharp and not wide enough to cover treatment volume. How is this overcome?
Superimpose a series of Bragg peaks (w decreasing energies + varying weights )) to cover greater volume.
This is known as as “Spread out Bragg peaks” (SOBP).