Material Science Quiz Review
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
stress
the internal distribution of forces within a body that balance and react to the loads applied to it
(Stress is the force inside a material that pushes back against an external load.)
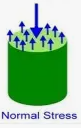
direct stress
force is perpendicular to the surface
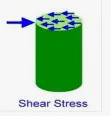
sheer stress
force is parallel to the surface
force is what type of quantity?
Vector quantity: has magnitude + one direction
stress is what type of quantity?
Tensor quantity: has magnitude + direction + the plane or orientation it acts on
strain
a measure of distortion of a material
plastic strain
permanent deformation — the material does not return to its original shape after the load is removed
elastic strain
temporary deformation — the material returns to its original shape when the load is removed
Poisson contraction
when a material is stretched in one direction, it becomes thinner in the other directions
direct strain
Deformation due to stretching or compressing along the length of a material
shear strain
Deformation due to sliding layers of a material over each other, changing its shape
uniform shear strain
A deformation in which all layers of the material are displaced uniformly, so the angular distortion is constant throughout.
allowable stress
The maximum stress that a material or structure can safely withstand under service conditions.
strength
amount of stress material can withstand before yielding
stiffness
resistance to elastic deformation
toughness
ability to absorb energy before fracture (strength + ductility)
hardness
resistance to scratching / indentation / wear
ductility
amount of strain before breaking (stretchability)
impact energy
energy absorbed during fracture (fast toughness indicator)
yield stress
beginning of the plastic deformation
elastic region
linear
reversible
UTS (ultimate tensile stress)
highest stress before necking
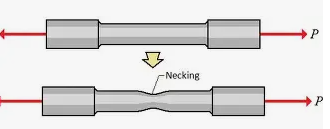
necking
when a material starts to become thinner at a specific region (usually the middle) because it is being pulled
Fluids (liquids & gases)
Flow resistance depends on flow rate, not total deformation.
This resistance = viscosity.
Viscoelastic materials
Act part solid, part fluid.
Deform under stress, partly return to shape, partly stay deformed.
Non-linear behavior
Stress and strain are not proportional.
Response can change over time.
Thermo-viscoelasticity
Material behavior changes with temperature.
Non-Newtonian fluids
Shear thickening: Gets thicker when stressed more.
Shear thinning: Gets thinner when stressed more.
tension
positive stress
compression
negative stress
solids
elastic → then plastic → then fracture
fluids
cannot resist shear → constant deformation (flow)