FMR_WOOD
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Wood
organic material
comes from fiber part of a tree, rather than the bark
has grain, used for transporting water and nutrients from roots to the leaves
grain
makes each piece of natural wood unique - no two trees are identical
growth rings
Created as trees increase in diameter.
Each ring represents one year of growth.
Some trees may have multiple growth rings in one year if they grow in more than one season.
Annual rings
Rings formed by trees growing in one season, producing one ring per year.
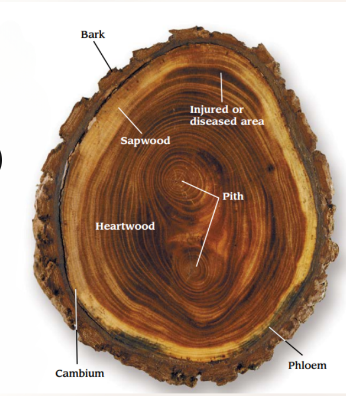
Heartwood
The inner part of wood.
may be darker in color than the sapwood (does not effect strength)
sapwood
outer part of the wood
knots
caused when a branch grows from the side of the tree
considered imperfection by some
can be unique of decorative feature
anatomy of a tree
timber
Wood that has been prepared for use in construction or carpentry.
hardwoods
softwoods
wood classifications
softwood
Type of wood derived from gymnosperm trees (coniferous trees).
may be called evergreen
Generally lighter in color and less dense compared to hardwood.
Commonly used in construction, furniture, and paper production.
Examples include pine, cedar, and spruce.
hardwood
Type of wood derived from angiosperm trees (broadleaf trees).
Typically denser and harder than softwood.
Often used for high-quality furniture, flooring, and decorative purposes.
Examples include oak, maple, and cherry.
angiosperms
A group of plants whose seeds are enclosed within an ovary.

conifers
A group of gymnosperm plants characterized by cones and needle-like or scale-like leaves.

Endgrain
The section where a board is typically viewed on its end.
Often referred to as the most useful plane for wood identification.
Sometimes called the transverse surface or cross-section in processed lumber.
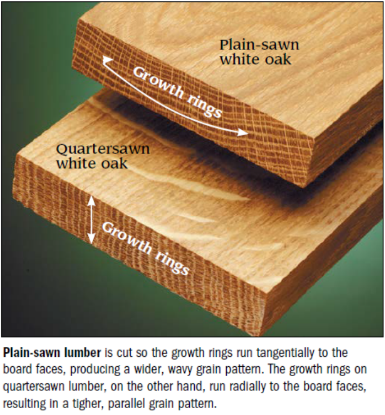
Quartersawn Section
Radial Surface - Wood surface that radiates out from the center of the log like spokes on a wheel.
Crosses the growth rings at a 90-degree angle.
Also known as vertical grain.
Provides distinctive grain patterns and stability in woodworking
Flatsawn Section
Tangential Surface - Wood surface more or less tangent to the growth rings.
Often results in a distinctive grain pattern characterized by cathedral-like arches.
Typically exhibits more variation in grain pattern compared to quartersawn sections.
Commonly used in woodworking for its aesthetic appeal.
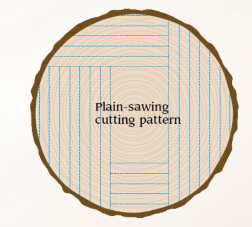
Plain-sawing
Flat-sawing
Cutting the log to maximize lumber without including the center pith area.
Involves rotating the log to make successive cuts around the pith.
Economical method for producing lumber for construction and woodworking.
Cuts are made tangentially to the growth rings, leading to increased wood movement.
Lumber is more prone to distortion compared to quartersawn lumber.
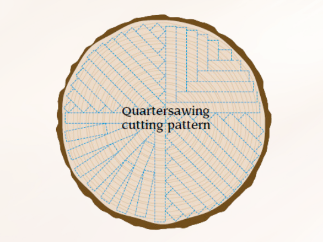
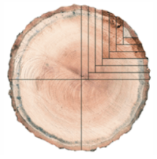
Quartersawing
A method to produce dimensionally stable lumber by rotating a log in quarter-turn increments and cutting around the center pith area.
Less efficient in maximizing board yield compared to plainsawing.
Results in lumber with increased dimensional stability.
Prominent medullary rays are displayed in quartersawn oak, which may not show if the boards were plainsawn.
kk
kk
Rift sawn
A method of cutting wood that produces a unique linear or vertical grain pattern with no flecking.
Annual growth rings are typically between 30 and 60 degrees.
flooring are aesthetically more appealing due to minimal grain activity.
Results in more dimensionally stable flooring compared to other cuts.
Live sawn
A method of cutting wood that starts with a straight cut through the log, providing a full range of the wood's natural characteristics.
Results in a varied grain pattern, with vertical grain on the edges.
Produces a naturally beautiful floor, showcasing the full range of wood's characteristics.
The wider the plank, the more uniquely beautiful the grain pattern.


bet
bet

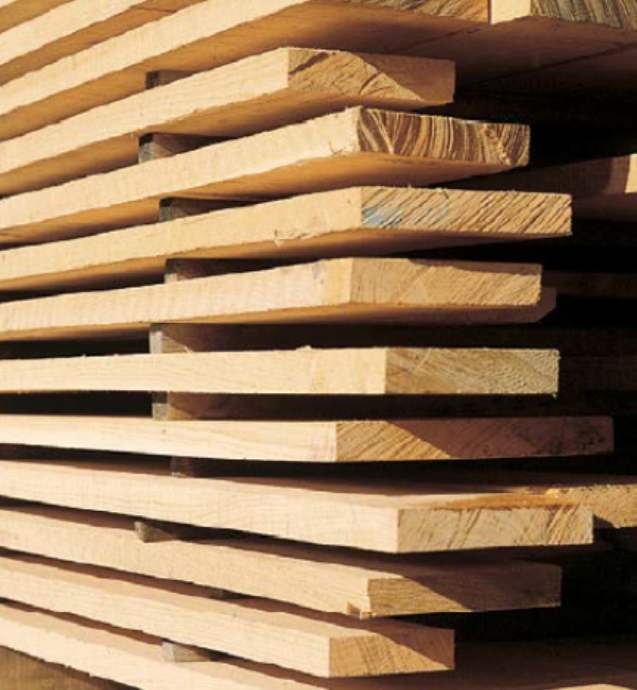
air-drying
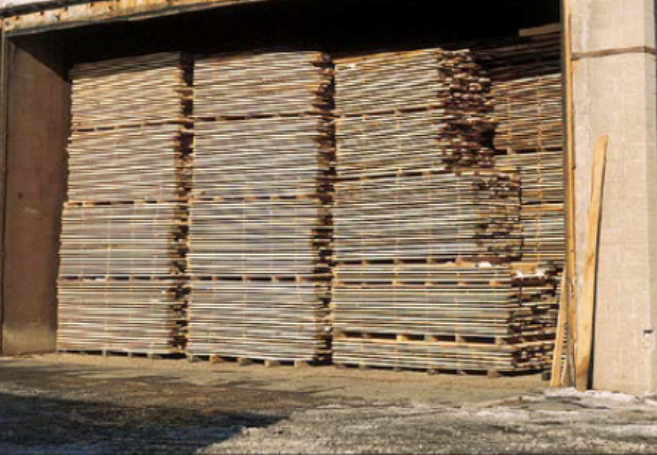
kiln-drying
lumber drying methods
air-drying
short lengths of scrap wood (called stickers) are inserted between each board in a stack to allow air to circulate all around the board
may take months or years
without stickers, lumber may dry unevenly and attract mold

kiln-drying
once stickered lumber is loaded to this, it will be closed up and heated evenly for several weeks until the moisture inside is reduced to acceptable levels
drying time may vary on the grade of lumber
faster method of producing general-purpose lumber

gets
gets
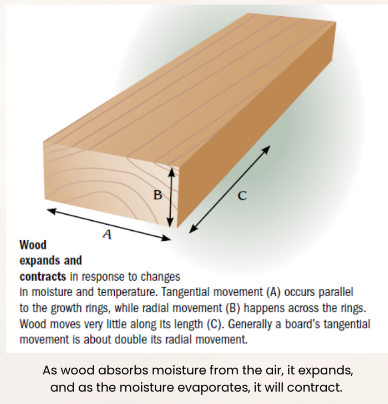
lumber defects
knot
split
twist
check
shake
wane
spalling
case-hardened boards

done
done
lumber distortion
bow
crook
cup
twist

bow
flat width
face curves lengthwise
crooked
flat across the face
curves along the edges in one direction
like the rocker of the rocking chair
cupping
flat along it’s edges
curls across it’s width
twist
one or both ends of the board twist
faces are no longer flat
wow
wow
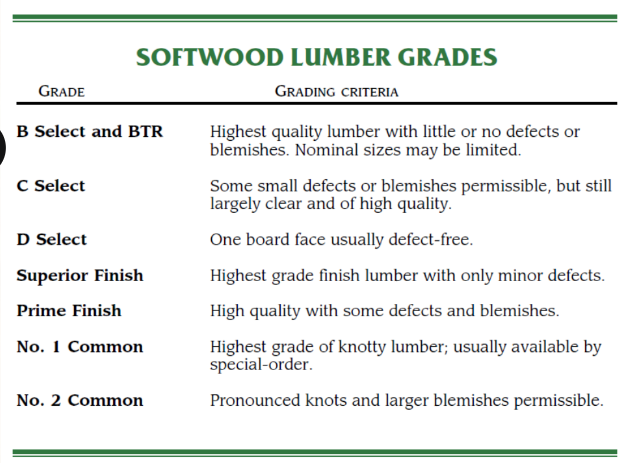
grabe
grabe
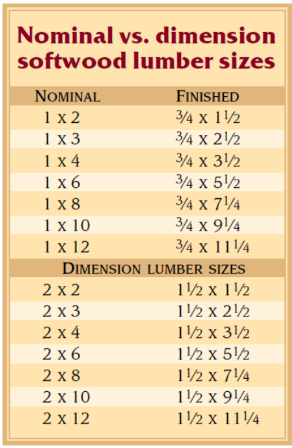
tamad
tatamad na ko magtype

plywood
fashioned from sheets of wood veneer, primarily pine and fir
Orienting the wood grain of each laminated sheet so adjacent sheets are perpendicular.
Results in a product capable of withstanding greater stress compared to construction lumber of the same thickness.
Offers increased dimensional stability due to its crosswise orientation of wood grains.
Often used in construction for its strength and stability.
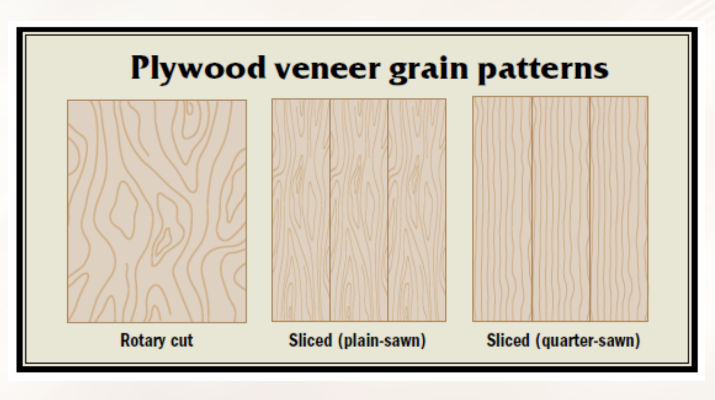
Particleboard
Engineered wood product
Made from wood particles and binder
Dimensionally stable
Suitable for countertops and tabletops
Smooth surface for laminate
Wide range of thicknesses and sizes
Inexpensive
Lacks stiffness and shear strength
Poor screw-holding ability
Degrades in moisture
Coarse core, hard to shape
Heavy
Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF)
Similar to particleboard
Denser and heavier
Smooth and dense surface
Good substrate for veneered projects
Bonds cleanly with thin wood veneer
Layers can be laminated to create structural components
Increasing popularity in trim molding applications
Melamine board
Particleboard core
Plastic laminate faces
Thicknesses range from 1⁄4 to 3⁄4 inch
Stock colors limited to white, gray, almond, and sometimes black
Panels oversized by 1 inch for edge chipping prevention
Fresh edges may need trimming due to brittleness
veneer
Thin layer of wood sliced or peeled from a log
Used to cover surfaces for decorative purposes
Provides the appearance of solid wood
Can be applied to plywood, particleboard, or MDF substrates
Offers a wide range of wood species and finishes
High Pressure Laminate (HPL)
Produced by saturating multiple layers of kraft paper with phenolic resin
Decor paper layer placed on top before pressing
Fused together under heat and pressure (more than 1,000 PSI)
Curing process transforms resin and paper sheets into a single, rigid laminated sheet
Common thickness: 1.2mm
Standard size: 2.4m
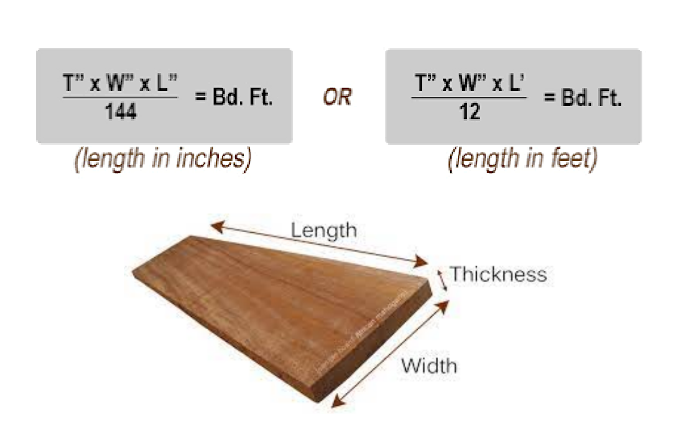
Board Measure
Standard unit for measuring the volume of lumber
Represents the volume of a board 1 inch thick, 12 inches wide, and 1 foot long
Used primarily for softwood lumber, particularly in commercial and industrial contexts
Board Footage
Measurement unit for the volume of lumber
Represents the volume equivalent to a board that is 1 foot long, 1 foot wide, and 1 inch thick
Used to quantify the amount of lumber, particularly in purchasing and selling transactions

Surface Measure
Measures the surface area of lumber
Typically used for calculating the amount of material needed for projects like flooring, paneling, or siding
Expressed in square feet or square meters
Lineal Measure
Measures the length of lumber in linear units, typically feet or meters.
Used for determining the length of lumber pieces, such as boards or beams.
formula