combined set
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
A class of antidepressant medications that work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain.
Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
A class of antidepressant medications that work by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
A class of antidepressant medications that work by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Monoamine hypothesis of depression
A theory that suggests that depression is caused by a depletion in the levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine in the central nervous system.
Lesion studies
Studies that involve examining animals or humans with brain damage to understand the functions of different brain regions.
Structure determines function
The principle that the physical attributes and arrangement of a brain region determine its function.
Sertraline
An antidepressant medication sold under the trade name Zoloft.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood, appetite, sleep, and other functions.
Neurotransmitter
A chemical messenger that transmits signals between neurons in the brain.
Neuropeptides
A type of chemical messenger involved in chemical transmission in the brain, larger than neurotransmitters.
Electrical transmission
The transmission of signals between neurons through electrical impulses.
Synapse
The space between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released and received.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood and stress response.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter involved in regulating motivation, reward, and pleasure.
Pathophysiologic basis
The underlying physiological or biological mechanisms that contribute to a disease or disorder.1. Monoamine Hypothesis of Depression:The theory that suggests that a depletion in the levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine in the central nervous system is the underlying cause of depression.
Serotonergic neurons
Neurons that release serotonin as their primary neurotransmitter.
Tryptophan
An amino acid that is a precursor for serotonin synthesis.
Antidepressant
A substance or medication that is used to treat depression.
5-HT
Abbreviation for serotonin.
MAO Inhibitors
Medications that inhibit the activity of monoamine oxidase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Autoreceptor
A receptor located on the presynaptic neuron that regulates the release of neurotransmitters.
5-HT transporter
A protein responsible for the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic neuron.
Tricyclics
A class of antidepressant medications that inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine.
Noradrenergic neurons
Neurons that release norepinephrine as their primary neurotransmitter.
Tyrosine
An amino acid that is a precursor for norepinephrine synthesis.
COMT
Abbreviation for catechol-O-methyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down norepinephrine.
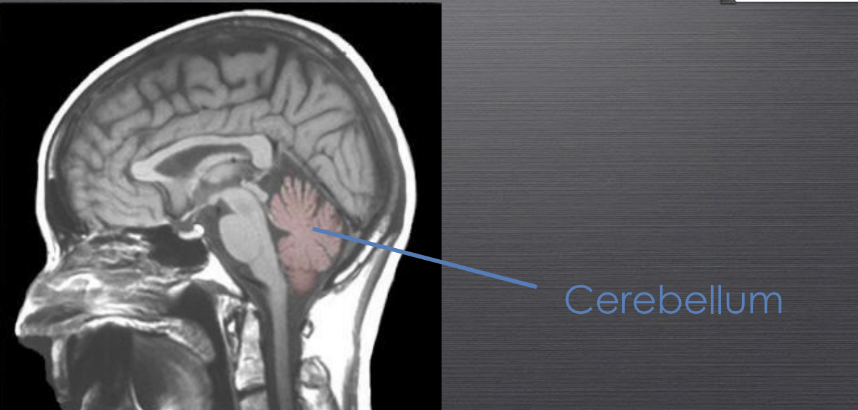
Cerebellum
A region in the brain responsible for muscle coordination and sense of equilibrium.
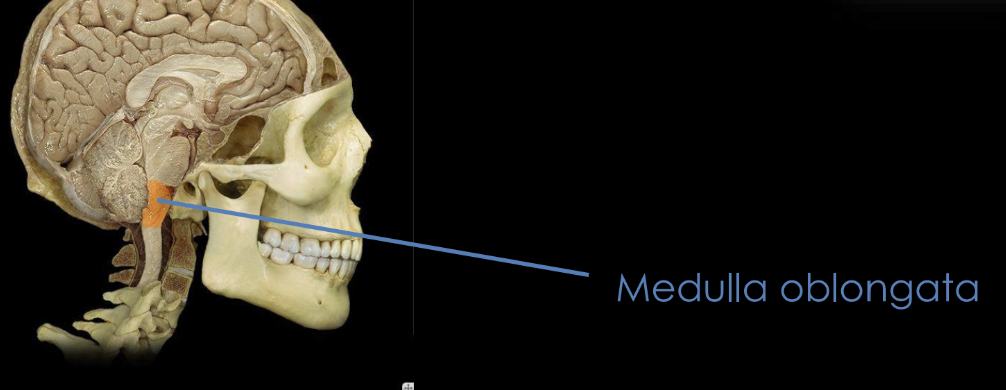
Medulla oblongata
A region in the brain responsible for controlling breathing.
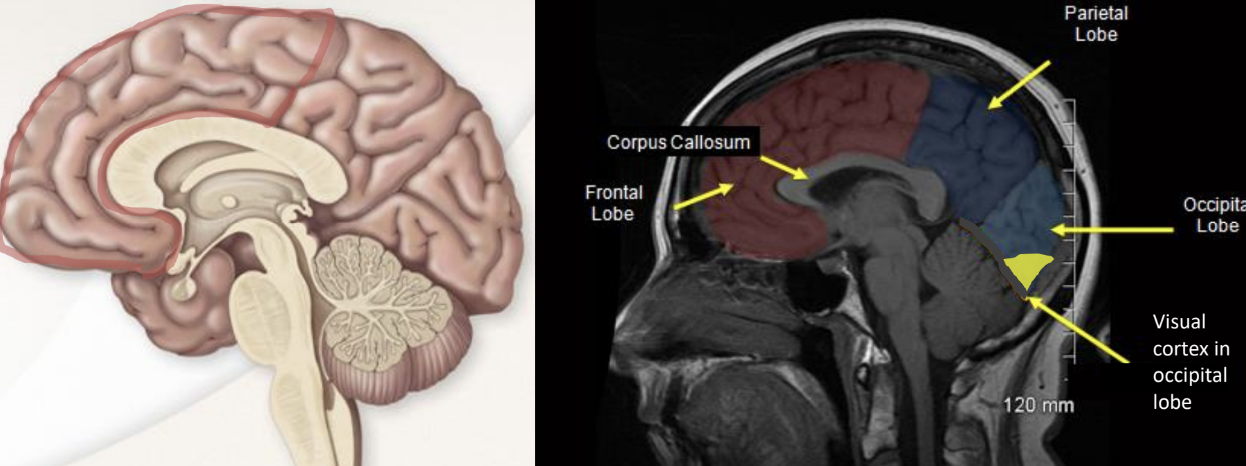
Frontal lobe
A region in the brain responsible for executive functions such as planning, organizing, and managing time.
Lobotomy
A surgical procedure that severs the connection between the frontal lobe and the thalamus, often resulting in changes in behavior.
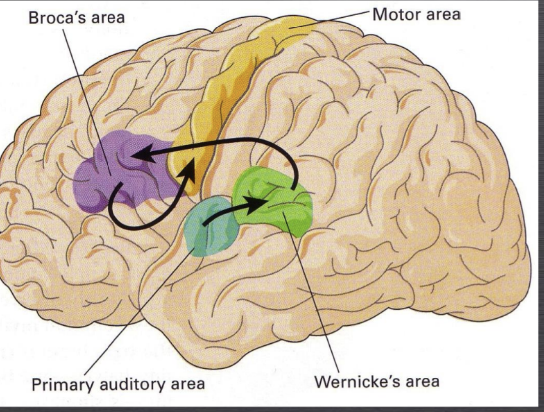
Broca's area
A region in the brain responsible for language production.
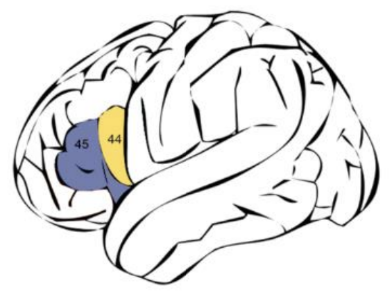
Wernicke's area
A region in the brain responsible for language comprehension.
Phrenology
A field developed by Franz Josef Gall that claimed personality traits could be predicted based on the size of bumps on the skull.
Homogenous mass
The idea that the brain is a uniform mass of tissue without specialized regions for different behaviors.
Thalamus
A relay center in the brain for sensory systems.
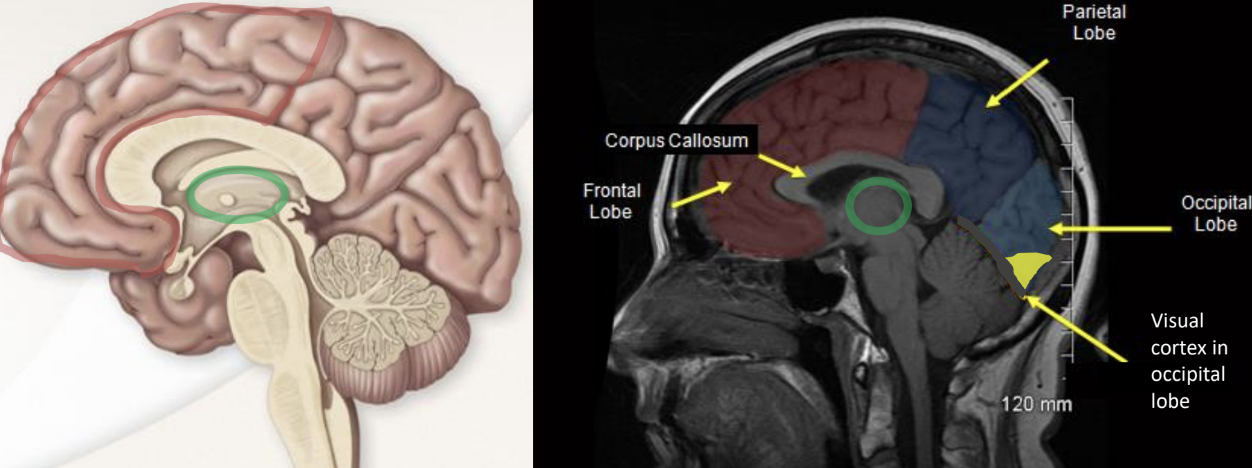
Occipital lobe
A region in the brain responsible for visual processing.
Motor coordination
The ability to coordinate and control movements.
Phineas Gage
A case study of a man who experienced a severe brain injury that resulted in significant changes in his behavior. Previously Gage was a shrewd, energetic, posses well-balanced mind, and persistent in executing all of his plans of operation. After he threw fits, could not see through his plans of operations, and more distracted often.
Primary auditory area
A region in the brain responsible for processing auditory information.
Motor cortex
A region in the brain responsible for controlling voluntary movements.
Axon
A long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body.
Axon terminal
The end of an axon where it forms a synapse with another neuron and transmits signals.
Cell body
The main part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles. It integrates and generates signals to transmit along the axon terminals.
Dendrite
A short, branched extension of a neuron that receives signals from other neurons.
Dendritic spines
Small protrusions on the dendrites that increase the surface area for receiving signals.
Botox
A neurotoxin that blocks the release of neurotransmitters by not allowing vesicles to fuse with the plasma membrane, leading to muscle paralysis.
Dynamin
A protein involved in vesicle fission that help pinch vesicles from the plasma membrane to release neurotransmitter.
fission
Vesicles split from plasma membrane (a larger split into 2 or more)
fusion
vesicles fuse with plasma membrane (join 2 or more into a larger one)
BOTOX INHIBITS VESICLES FROM FUSING TO THE
PLASMA MEMBRANE BY INHIBITING SNARE PROTEINS.
WHAT DOES BOTOX DO TO NEURAL TRANSMISSION?
Blocks exocytosis
DYNAMIN MUTANTS ARE MISSING A PROTEIN CALLED DYNAMIN. THESE MUTANTS HAVE BLOCKED VESICLE FISSION.
WHAT HAPPENS TO SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION?
BLOCKS ENDOCYTOSIS
WHY IS THE TYPICAL POSTSYNAPTIC RESPONSE SO MUCH STRONGER THAN THE RESPONSE TO A SINGLE VESICLE?
THERE IS A CONTINUOUS FUSION OF SINGLE VESICLES
what does exocytosis and endocytosis recycle?
the membrane
what does reuptake transporter recycle?
nerotransmitters
Neuron
A specialized cell that transmits electrical impulses in the nervous system.
Hyperpolarization
The process of making a neuron's membrane potential more negative, making it less likely to generate an action potential.
Action potential
When an electrical impulse travels down a neuron to relay information.
Step 1: Na+ channels open. This depolarizes the membrane potential positively towards Na+ equilibrium, away from resting potential
Step 2: K+ channels open. This hyperpolarizes the membrane negatively towards K+ equilibrium potential.
Step 3: After a delay, Na+ channels becomes inactive; therefore, allowing K+ channels to hyperpolarize the membrane potential towards the equilibrium potential for K+.
Membrane potential
The difference in electrical charges inside and outside a cell, creating a voltage difference
Describe how current is carried in a neuron
Current is carried in a neuron through charged ions.
depolarization
The process of making a neuron membrane more positive, making it more likely to generate an action potential.
resting membrane
when a neuron is at rest, there is still a voltage difference
WHAT CAUSES THE VOLTAGE DIFFERENCE (ALSO KNOWN AS POTENTIAL)ACROSS THE ACROSS?
Difference in ion concentrations
CONSIDERING THAT THE INSIDE OF THE CELL STARTS VERY NEGATIVE, WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF AN ACTION POTENTIAL?
QUICK DEPOLARIZATION
TETRODOTOXIN (TTX - a drug) BLOCKS VOLTAGE GATED SODIUM CHANNELS. WHAT DOES TTX DO TO NEURAL TRANSMISSION?
BLOCKS ACTION POTENTIALS
BOTOX INHIBITS VESICLES FROM FUSING TO THE
PLASMA MEMBRANE BY INHIBITING SNARE PROTEINS.
WHAT DOES BOTOX DO TO NEURAL TRANSMISSION?
BLOCKS EXOCYTOSIS
Monoamine hypothesis of depression
A theory that suggests that a depletion in the levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine in the central nervous system is the underlying cause of depression.
Mesolimbic pathway and what are two key components of the mesolimbic pathway of the reward center (add more info to the second)
Ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens. A neural pathway in the brain that is involved in the processing of reward and motivation.
Reward prediction-error signal
The role of dopamine in signaling the difference between expected and actual rewards in the brain.
Synaptic transmission
The process by which information is passed from one neuron to another across the synapse cleft.
Presynaptic neuron
The neuron that sends the signal across the synapse.
Postsynaptic neuron
The neuron that receives the signal across the synapse.
Neurotransmitter
A chemical substance that is released by a neuron and acts as a messenger to transmit signals to other neurons.
MAO (Monoamine oxidase)
An enzyme involved in the degradation of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
What does TTX block? (need to add more info)
TTX blocks action potential with a neuron.
What does BoTox block? (need to add more info)
BoTox blocks exocytosis also known as synaptic transmissions between neurons.
What does Endocytosis recycle?
The membrane
What does reuptake transporters recycle?
neurotransmitters
WHY ARE MANY ANTIDEPRESSANTS MONOAMINE
OXIDASE INHIBITORS (MAO-I)?
WHERE IN THE SYNAPSE DOES MAO-I WORK?
Mnay antidepressants are MAOI because monoamine oxidase are involved in the degradation of monoamines. Therefore, and inhibitor of MAO has the opposite effect, ultimately increasing the levels of monoamine, serving as an antidepressant. MAOI work in the presynatic cell.
WHY ARE MANY ANTIDEPRESSANTS SELECTIVE SEROTONIN
REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SSRI)?
WHERE IN THE SYNAPSE DO SSRI WORK? (need to check info)
Many antidepressants are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors because SSRIs prohibits the reuptake of neurotransmitters backs into the presynaptic cell; therefore, allowing the serotonin to continuously stay in the synapse, reactivating the postsynaptic receptors. SSRIs work in the presynaptic cell.
Describe an experiment that shows that dopamine
serves as a reward prediction-error signal (add def)
Monkey juice experiment. In the monkey juice experiment, there were 3 scenarios that dopamine serves as a reward prediction error signal. One of which was a predicted award in which a stimulus was played, and then the award was given. In this case, the dopamine levels spike when the stimulus was placed in. In a second scenario, it was a surprise award in which the stimulus was not played, but the award was given. In this case, the dopamine levels spiked when the award was given. In the last scenario, no reward was given; however, the stimulus was played. In this last case, the dopamine levels spiked when the stimulus was played but dipped after a delay when the expected award was not given.
Provide counterarguments which propose that the monoamine hypothesis of depression is wrong.
A) A SUCCESSFUL ANTIDEPRESSANT (TIANEPTINE) DOES NOT RAISE MONOAMINE LEVELS.
B) SOME PEOPLE WITH DEPRESSION DO NOT HAVE DECREASED LEVELS OF MONOAMINES.
C) LESIONING MONOAMINERGIC SYSTEMS DOES NOT ALWAYS INDUCE OR WORSEN DEPRESSION
Mesolimbic pathway
A neural pathway involved in the reward system of the brain.
Reward prediction-error signal
A signal generated by dopamine neurons that indicates a discrepancy between expected and actual rewards.
Prefrontal cortex
The part of the brain involved in regulating emotions and decision-making.
Amygdala
A brain structure involved in emotional processing and fear response.
Hypothalamus
A brain structure involved in regulating various bodily functions, including aggression.
Attack neurons
Neurons specific to the ventrolateral hypothalamus that are involved in aggression.
Gray matter
Brain tissue composed of unmyelinated cell bodies.
White matter
Brain tissue composed of myelinated axons.
Ventrolateral subdivision of the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMHvl)
An anatomical area within the hypothalamus involved in aggression.
Optogenetic activation
Using light-sensitive proteins to activate neurons.
Optogenetic silencing
Using light-sensitive proteins to inhibit or silence neurons.