Neurological Dysfunction: Module 8 - Adult Spinal Cord Injuries fully solved questions with 100% accurate solutions(Latest Update)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Hippocrates
In 400BC, Who correlated visceral dysfunction with Spinal Cord Injuries?
males
(Males or Females?) have a higher mortality risk associated with spinal cord injuries
Tetraplegia
Quadriplegia is an old term for ________________
True
True or False: The paraplegia category of SCIs can include conus medullaris and cauda equina syndrome
Incomplete
(Incomplete or Complete?) Spinal Cord Injuries are more common
Incomplete Tetraplegia
Most common classification of Spinal cord injuries (not sure if this means occurrence or number of individuals with it) (slide 9)
C5
A _____ Burst Fracture is highlighted as a common fracture of the spine
T12, L1, L2
a "Chance" Fracture ("Seatbelt Fracture") is a Spinal Fracture that commonly occurs at what 3 spinal segments?
A, C
Which of the following tract(s) crosses at the brainstem and therefore any pathologic effects involving them will be ipsilateral below the level of injury?
A) Dorsal Column
B) Lateral Spinothalamic
C) Corticospinal
(Listed as the letter(s))
B
Which of the following tract(s) crosses at the spinal cord and therefore any pathologic effects involving them will be contralateral below the level of injury?
A) Dorsal Column
B) Lateral Spinothalamic
C) Corticospinal
(Listed as the letter(s))
2/3
The Anterior Spinal Artery provides blood flow to how much of the spinal cord? (fraction)
True
True or False: Skeletal level of injury with a SCI does not always equate to the severity or level of neurological effects
Skeletal
(Skeletal or Neurologic?) Level of Injury = Radiologically greatest vertebral damage
Neurologic
(Skeletal or Neurologic?) Level of Injury = Most caudal level where both motor & sensory modalities are intact bilaterally
B
Motor Complete + Sensory Incomplete = ASIA (A or B?)
A
Motor Complete + Sensory Complete = ASIA (A or B?)
True
True or False: AIS C & D are defined as motor & sensory incomplete
complete
Motor (Complete or Incomplete) + Sensory Complete = AIS B
3
ASIA Scale Scoring: For an individual to be scored as a "C", they must have a majority of the muscles below the level of injury be less than a _____/5 MMT
E
ASIA Scale Scoring: ____ = Neurologically Intact
False
True or False: A person that never had a spinal cord injury would be scored as an ASIA E because they are neurologically intact
D
ASIA Scale Scoring: If an individual has a majority of muscles below the level of injury rated as a 3/5 MMT, then they are an ASIA (C or D?)
3
ASIA Scale Scoring: In order to distinguish between an ASIA B and ASIA C, the individual would need to have motor preservation greater than ____ levels below the motor level of injury to be considered an ASIA C
Neurologic Level of Injury
What does NLI stand for?
Zone of Partial Preservation
What does ZPP stand for?
Zone of Partial Preservation
Definition: Dermatome & Myotomes caudal to the Neurologic Level of Injury that remain partially intact
False (it was updated to not have to be an ASIA A this year)
True or False: The term Zone of partial preservation is only applicable if the person is an ASIA A
C1-T1
Complete SCIs: The classification of tetraplegia is used for an injury that occurs within what spinal segment range? (slide 25)
T2
With Complete SCIs, the term Paraplegia is applied to individuals with a level of injury that is _____ and below (spinal segment) (slide 25)
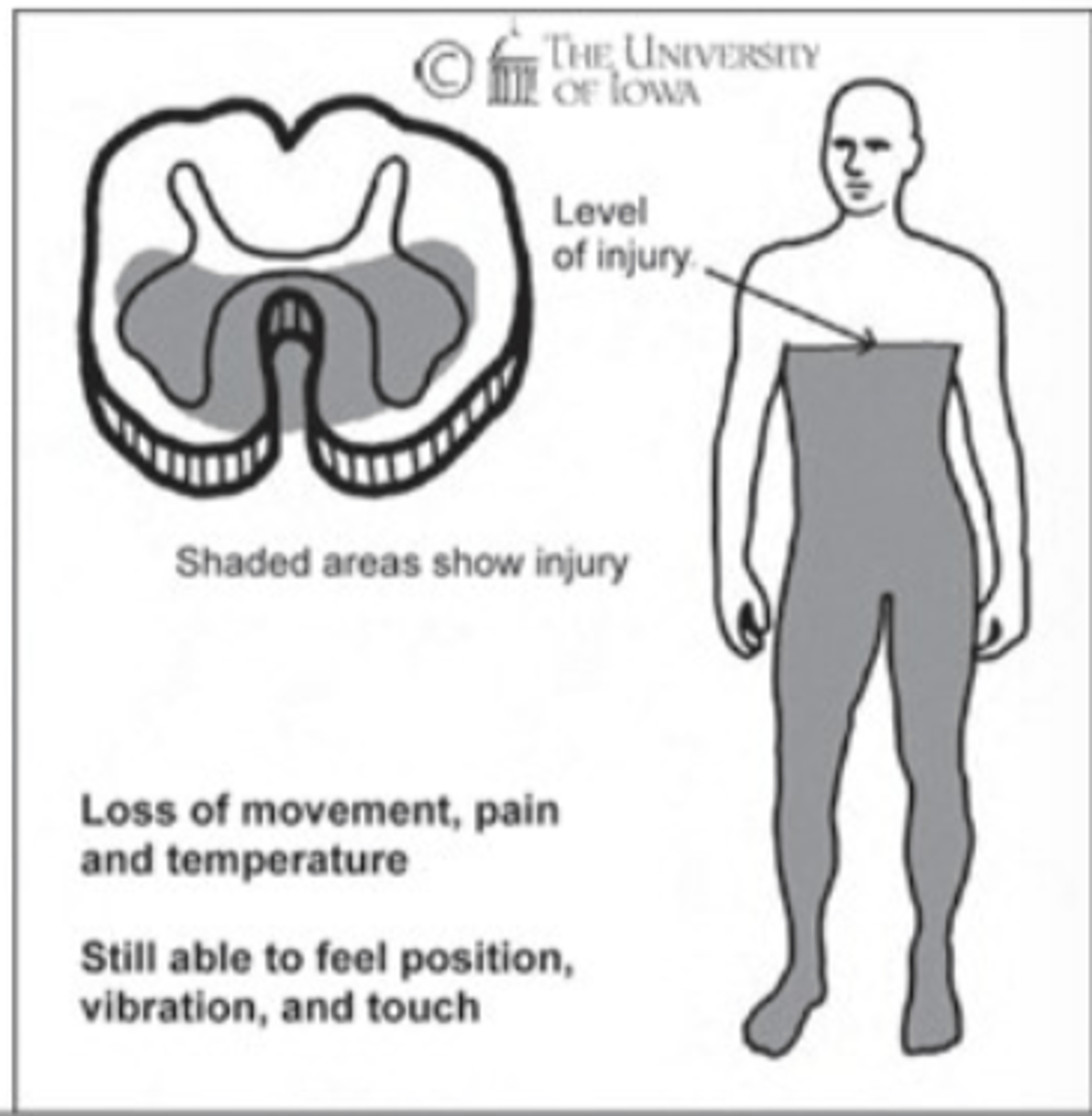
Anterior Cord Syndrome
This image depicts the damage associated with which Incomplete SCI Syndrome?
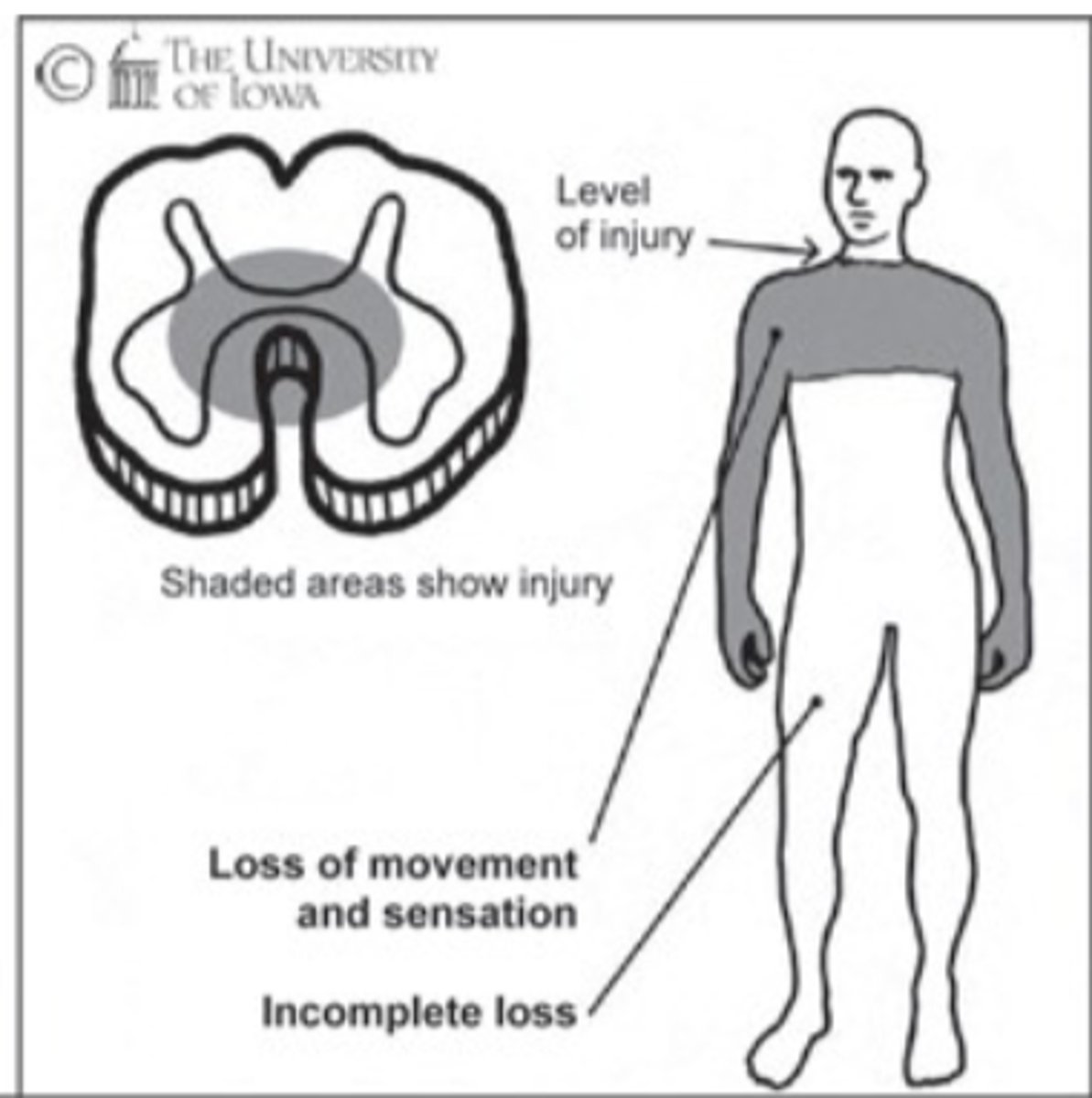
Central Cord Syndrome
This image depicts the damage associated with which Incomplete SCI Syndrome?
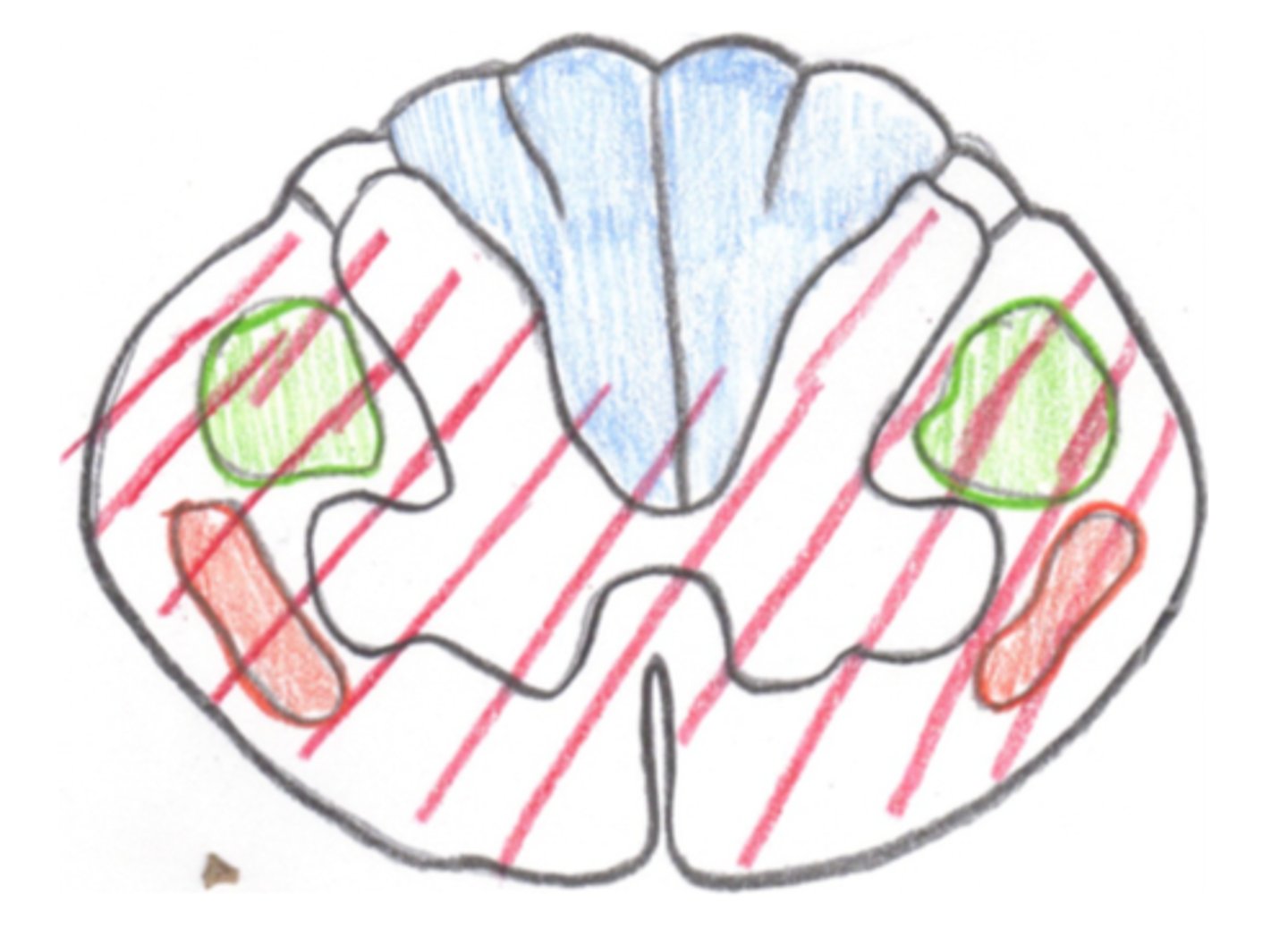
Anterior Cord Syndrome
This image depicts the damage associated with which Incomplete SCI Syndrome?
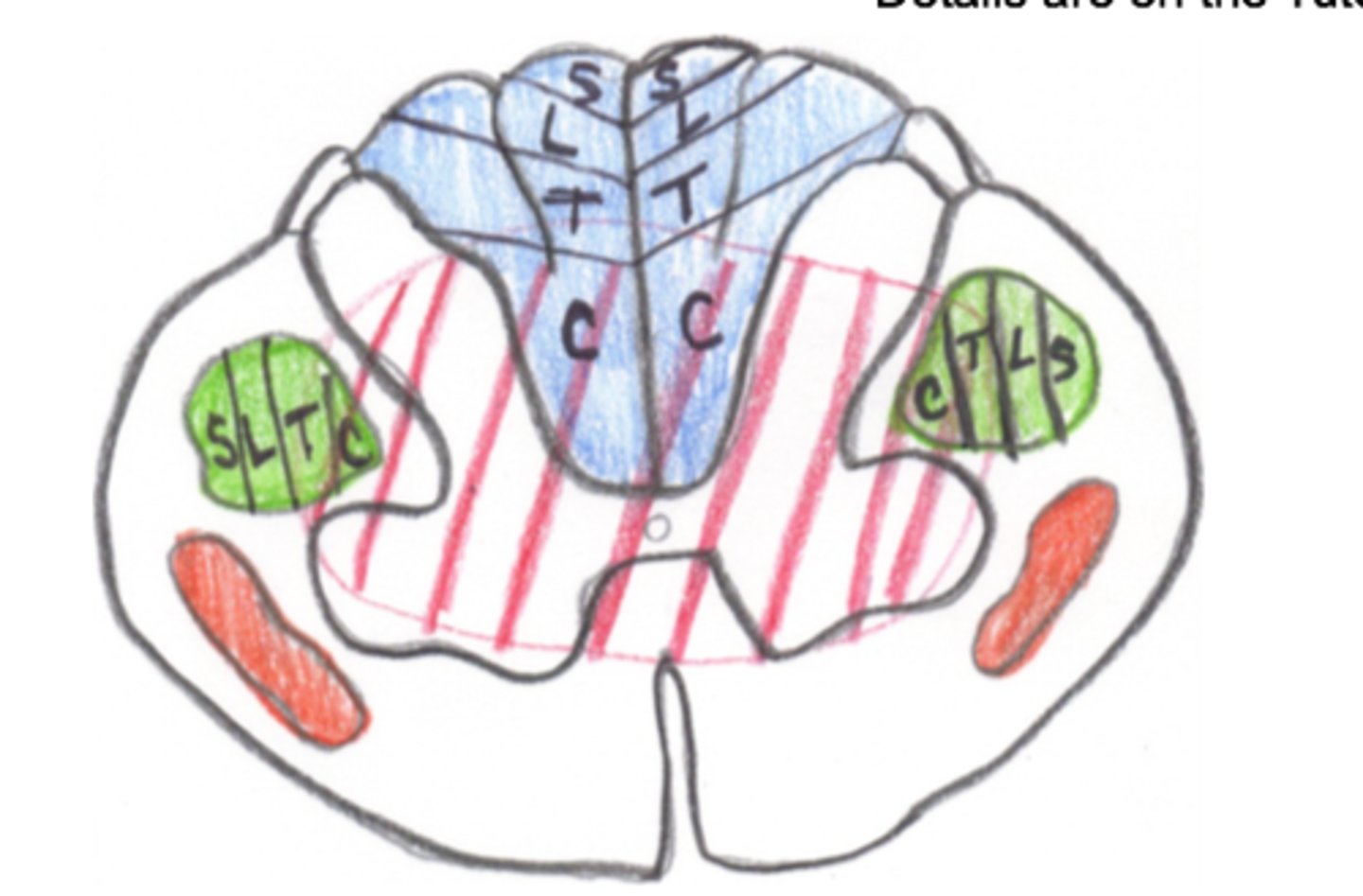
Central Cord Syndrome
This image depicts the damage associated with which Incomplete SCI Syndrome?
position, vibration, touch
What 3 things are preserved below the NLI with Anterior Cord Syndrome? (slide 27)
movement, pain, temperature
What 3 things are NOT preserved below the NLI with Anterior Cord Syndrome? (slide 27)
Brown Sequard Syndrome
This image depicts the damage associated with which Incomplete SCI Syndrome?
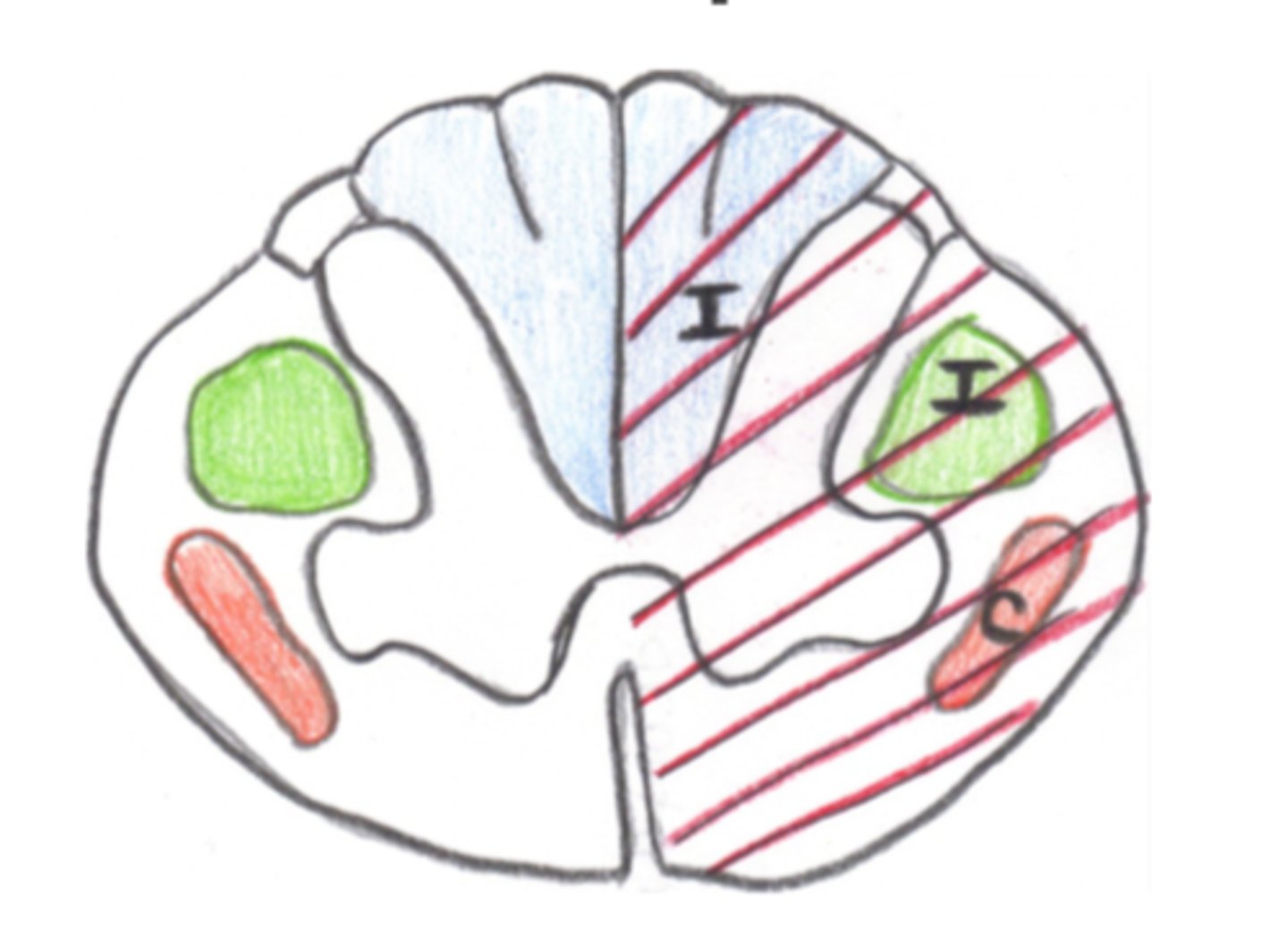
Brown Sequard Syndrome
This image depicts the damage associated with which Incomplete SCI Syndrome?
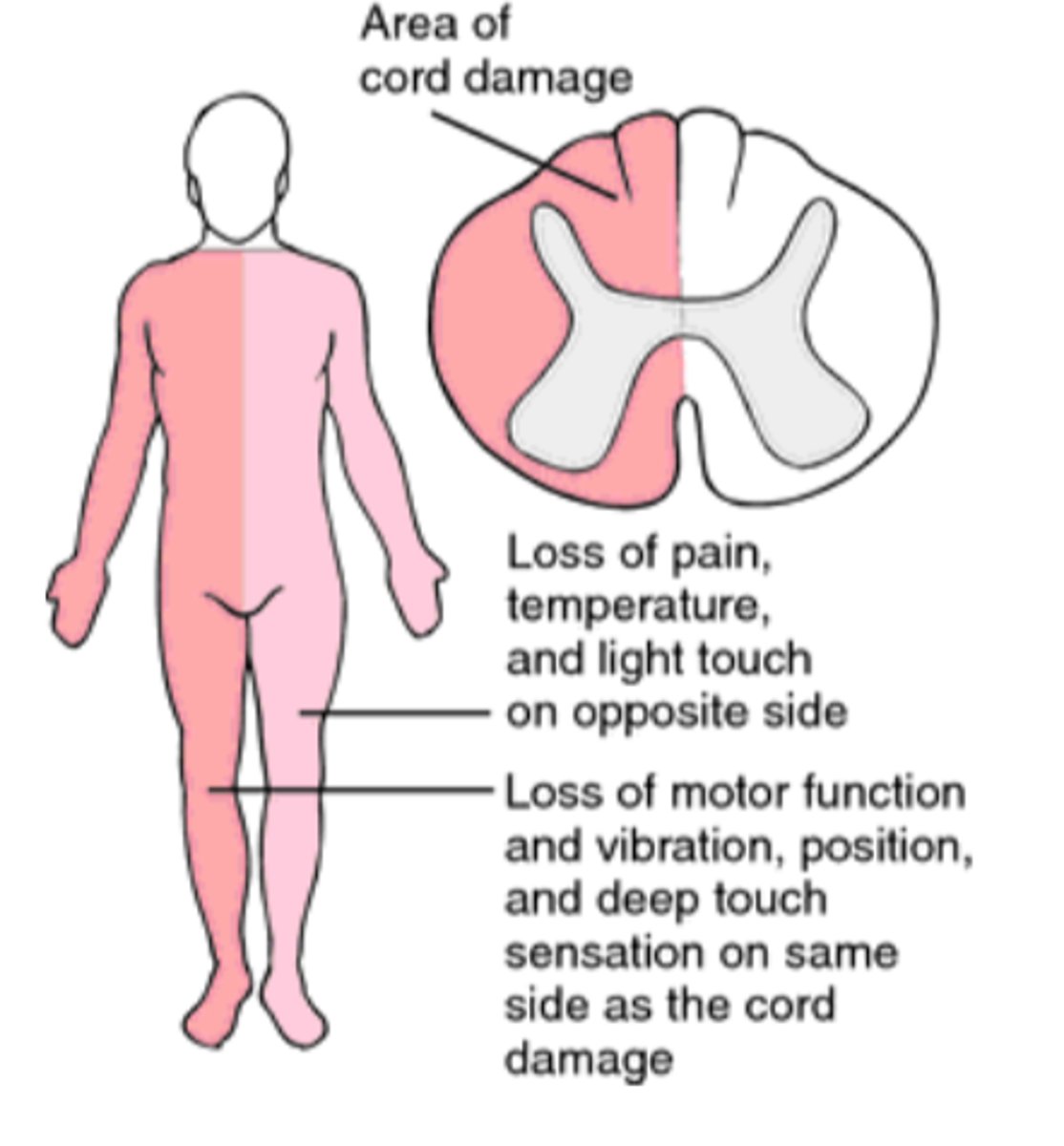
pain, temperature, light touch
With Brown Sequard Syndrome, there is a contralateral loss from the side of injury of what 3 things? (slide 29)
motor function, vibration, position, deep touch
With Brown Sequard Syndrome, there is an ipsilateral loss from the side of the injury of what 4 things? (slide 29)
L1
The Conus Medularis is the terminal segment of the spinal cord that lines up with which vertebra?
L1
Cauda Equina pathology involves a lesion below which skeletal vertebra segment?
S2-S4/5
Conus Medularis injuries affect what range of spinal cord segments? (slide 30)
Conus Medularis (likely has LMN component too)
(Conus Medularis or Cauda Equina?) is an Upper Motor Neuron Lesion
Cauda Equina
(Conus Medularis or Cauda Equina?) is not technically a spinal cord injury. It is a spinal nerve injury (minute 07:20 SCI Part 3)
Glutamate
Any upper motor neuron problem or trauma will initiate a "__________ Bomb". This neurotransmitter is an excitatory neurotransmitter (Part 3 Voice over minute 7)
Conus Medularis
(Conus Medularis or Cauda Equina?) = LE strength may remain intact
L2-S2
Cauda Equina will cause LE motor weakness & atrophy of muscles that are contributed to by what range of spinal segments? (slide 30)
Conus Medularis
(Conus Medularis or Cauda Equina?) will always have saddle anesthesia
Cauda Equina
(Conus Medularis or Cauda Equina?) will result in possible sparing of perineum sensation
Cauda Equina
(Conus Medularis or Cauda Equina?) will result in Areflexia/hypotonia
Cauda Equina
Pain is listed as a sign of (Conus Medularis or Cauda Equina?). The other one may also involve pain but idk
LMN
(UMN or LMN?) Lesion will result in present fasciculations
UMN
(UMN or LMN?) Lesion will result in absent fasciculations
C7
If a person with a SCI is a _____ or above, you want to preserve tenodesis grip (spinal segment)
external rotation
What motion of the shoulder can effectively lock out the elbow if a person does not have innervation of their triceps?
110
When working with an adult with a spinal cord injury, you want them to have Hamstring Length that is greater than ____ degrees to allow for lower extremity dressing
True
True or False: One positive aspect of a person will a spinal cord injury having increased muscle tone is that it assists with venous return
0
Clonus Ratings: _____ = no reaction
1
Clonus Ratings: _____ = mild, clonus was maintained for less than 3 seconds
2
Clonus Ratings: _____ = moderate, clonus persisted between 3-10 seconds
3
Clonus Ratings: _____ = severe, clonus persisted for greater than 10 seconds
Clonus, Flexor Spasms (Pinprick), Extensor Spasms (hip/knee extension)
What are the 3 components of the Spinal Cord Assessment Tool for Spastic Reflexes (SCAT)? (slide 34)
30
A TLSO, if ordered by a physician, should be worn whenever the patient is out of bed or the head of bed is elevated greater than ____ degrees
supine
In what position should the patient be to don a TLSO?
True
True or False: If the patient is in a Halo Brace then you should ensure that they are not laying on a pillow
C4
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: ______ = Level when the person is breathing without a vent
glossopharyngeal
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: A C1-C3 Level injury will result in ventilation to be required for breathing but the person may be able to wean for very short periods of time by using the ______________ Nerve for breathing (slide 38)
Diaphragm, Trapezius, Levator Scapulae, Rhomboids
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: 4 Muscles available when a C4 Level Injury is present (not including muscles available from injuries above this level)
Deltoid, Biceps brachii, Brachialis, Brachioradialis, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor, Supinator
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: 7 Muscles available when a C5 Level Injury is present (not including muscles available from injuries above this level)
C5
A _____ Level Complete SCI could possibly use a manual wheelchair by utilizing shoulder external range of motion but it would require alot of energy
Pectoralis Major Clavicular Portion, Serratus Anterior, Latissimus Dorsi, Extensor Carpi Radialis, Pronator Teres
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: 5 Muscles available when a C6 Level Injury is present (not including muscles available from injuries above this level)
Pectoralis Major Sternal Portion, Triceps, Flexor Carpi Radialis, Extensor Pollicis (Longus and Brevis), Extrinsic Finger Extensors
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: 5 Muscles available when a C7 Level Injury is present (not including muscles available from injuries above this level) (one of them is a muscle group not a specific muscle)
Extrinsic Finger Flexors, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris, Flexor Pollicis (Longus and Brevis), Intrinsic Finger Flexors
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: 4 Muscles available when a C8-T1 Level Injury is present (not including muscles available from injuries above this level) (one of them is a muscle group not a specific muscle)
C8-T1
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: A _______ Level (range) Injury will no longer need a tenodesis grip
T2-T6
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: A _____ Level (range) of Injury will result in a person being able to use some Back Extensors
T7-L1
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: A _____ Level (range) of Injury will result in a person being able to use Abdominal Muscles (extent depends on where they are in this range though)
L2-L5
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: A _____ Level (range) of Injury is when Ambulation becomes a feasible goal with assistive devices & LE Bracing
SCI
Look at this image of Motions Available to a L2-L5 range Complete Spinal Cord Injury. The answer to this slide is SCI

S1-S2
Typical Presentation by Level of Injury with COMPLETE SCIs: A _____ Level (range) of Injury is when Community ambulation with minimal to no bracing or assistive device becomes likely
30
Patients should shift position every _____ minutes if they are in a wheelchair to prevent sores
2
Patients should shift position every _____ hours if they are in a bed to prevent sores
ASIA
Look at this image of Ambulation Prognosis based on ASIA level. The answer to this slide is ASIA

Community
Ambulation Categories: ___________ = unassisted outside with or without device/bracing
Household
Ambulation Categories: ___________ = within home independently, but not outside for longer distances/on uneven surfaces
Exercise
Ambulation Categories: ___________ = requires assistance to walk and walks purely for weight bearing/strengthening
C3-C5
The Diaphragm is innervated by what range of spinal segments?
T1-T7
What spinal segment range supplies Sympathetic input to the heart? (slide 62)
parasympathetic
With Autonomic Dysreflexia, there is (sympathetic or parasympathetic?) input ABOVE the level of Injury
sympathetic
With Autonomic Dysreflexia, there is (sympathetic or parasympathetic?) input BELOW the level of Injury
250-300
With Autonomic Dysreflexia, patients can have their SBP reach higher than _________mmHg (range) (slide 64)
seated
If a patient is experiencing Autonomic Dysreflexia, you should put them in a (seated or supine?) position
2
If there is no resolution of autonomic dysreflexia within ____ hours the patient needs to be sent to the ICU
T6-T8
If a SCI NLI is above ________ (spinal segment range) then they will have problems with thermoregulation
Poikilothermia
Definition: Term for a person with a SCI above T6-T8 having thermoregulatory issues (slide 67)
Renal Disease
Prior to 1970, what was the #1 cause of death in individuals with a spinal cord injury (slide 68)
100-150
How much Urine Can you Hold: First sensation of filling = about __________mL (range)
250
How much Urine Can you Hold: Desire to void = ______mL
300-400
How much Urine Can you Hold: Strong Urge to Void = __________mL (range)
Parasympathetic (S2-S4)
(Parasympathetic or Sympathetic?) Dominance = Voiding
Sympathetic (T11-L2)
(Parasympathetic or Sympathetic?) Dominance = Storage