AP Bio-Unit &: DNA vocab
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
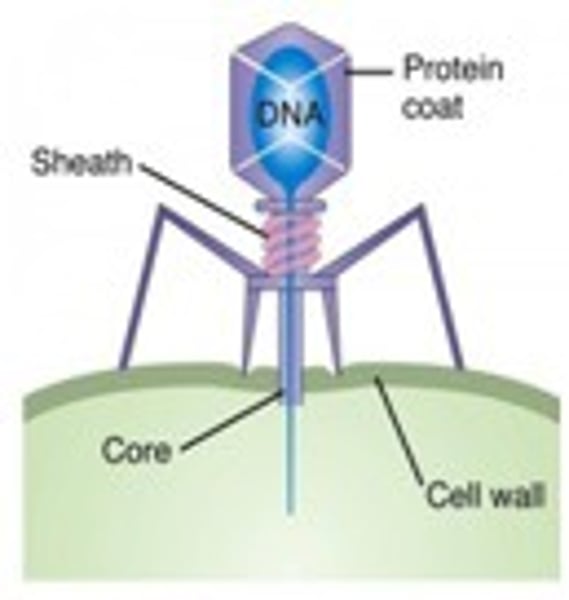
phages
viruses that infect bacteria
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule *5'->3'*
mismatch repair
The cellular process that uses specific enzymes to remove and replace incorrectly paired nucleotides.
primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.
nuclease
An enzyme that cuts DNA or RNA, either removing one or a few bases or hydrolyzing the DNA or RNA completely into its component nucleotides.
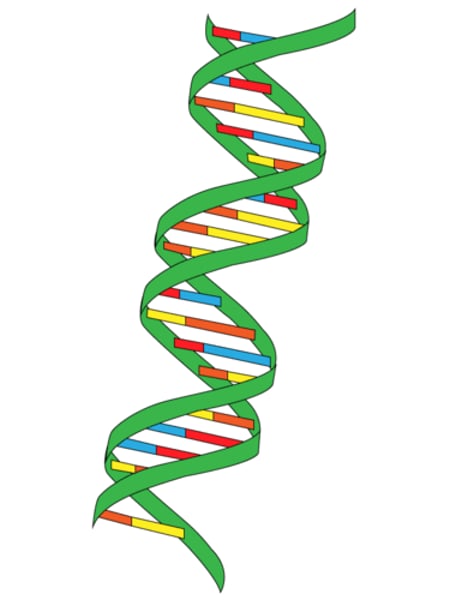
double helix
Shape of DNA
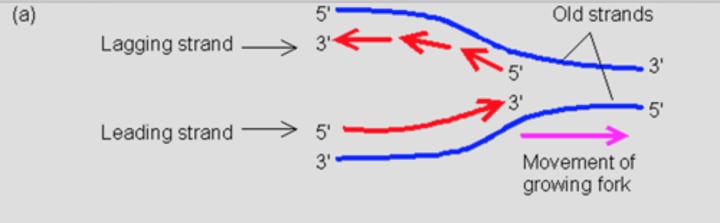
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks.
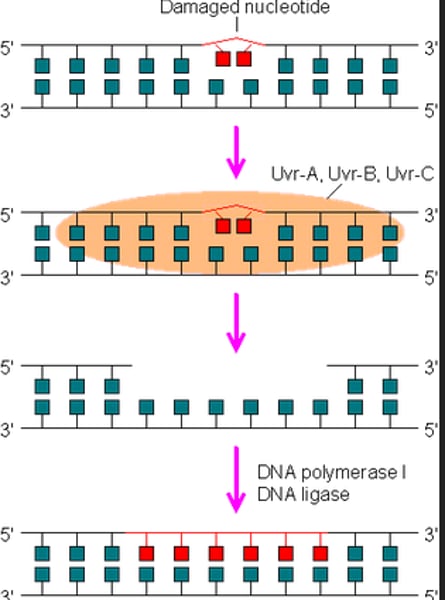
excision repair
locates and repairs incorrect sequence by removing a segment of the DNA and then adding the correct nucleotides
semi-conservative model
Type of DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand, derived from the old molecule, and one newly made strand.
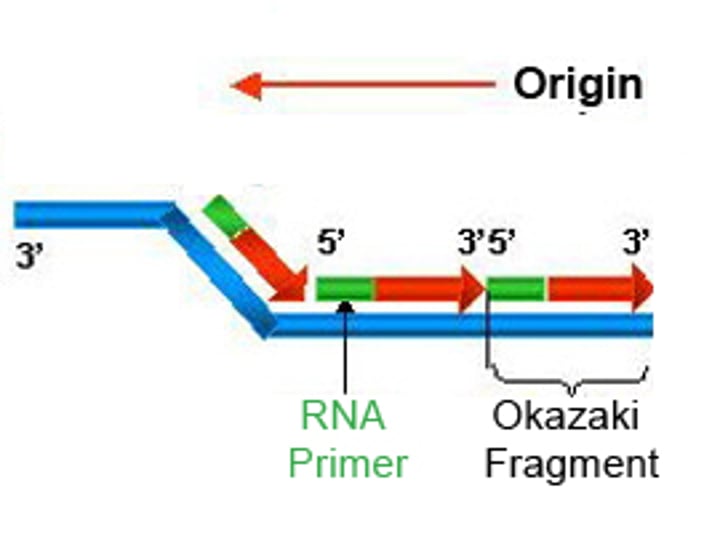
lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
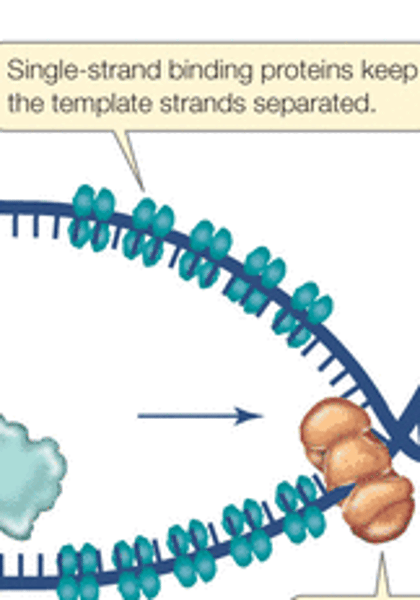
single-stranded binding proteins
Proteins that act as scaffolding, holding two DNA strands apart during replication
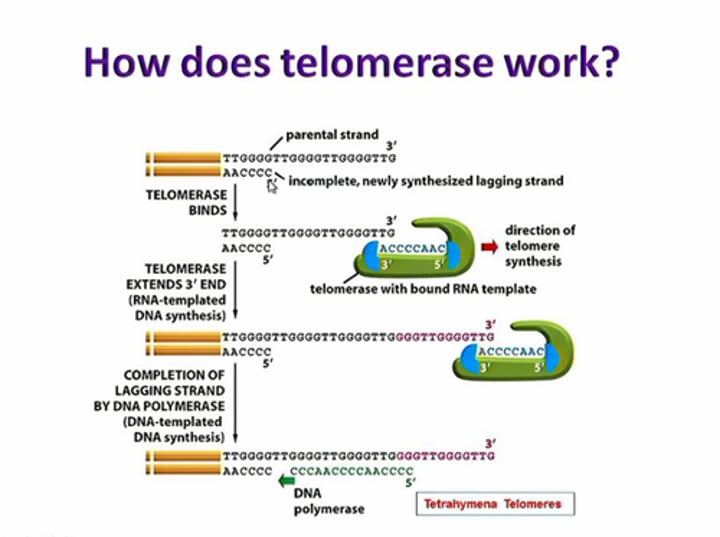
telomerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in eukaryotic germ cells.
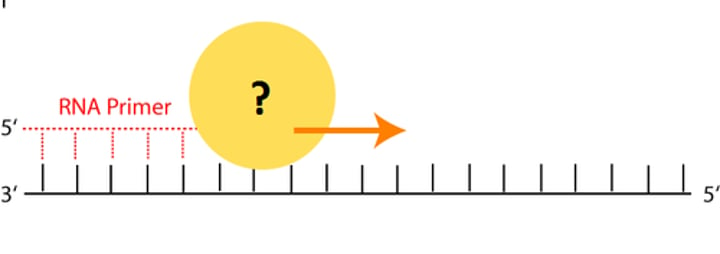
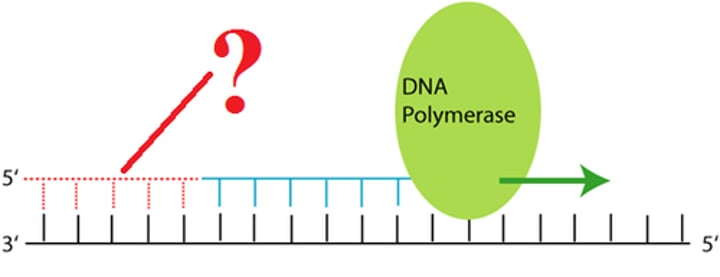
primer
a short stretch of RNA with a free 3' end, bound by complementary base pairing to the template strand and elongated with DNA nucleotides during DNA replication
DNA ligase
A linking enzyme essential for DNA replication; catalyzes the covalent bonding of the 3' end of a new DNA fragment to the 5' end of a growing chain.

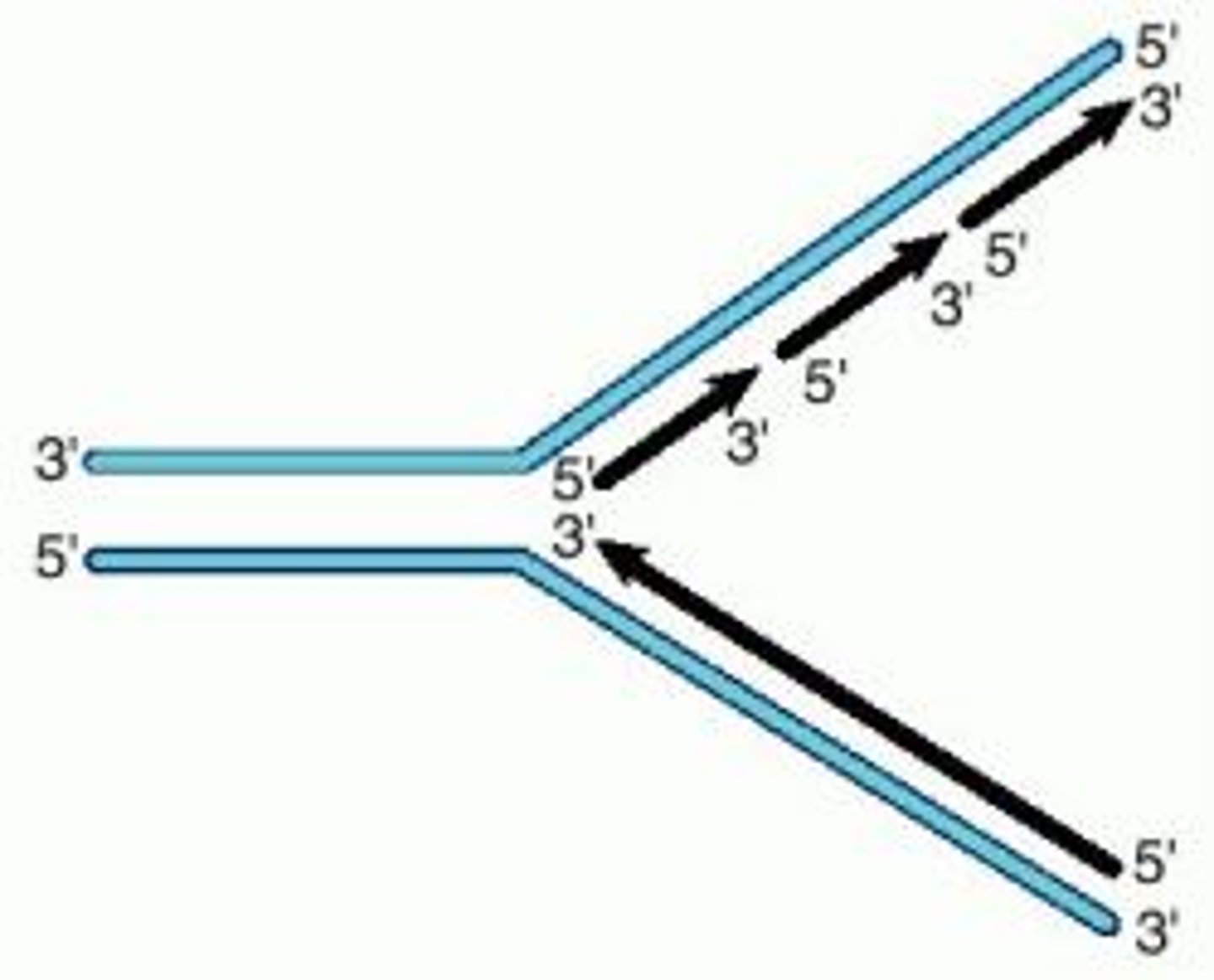
Replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing.
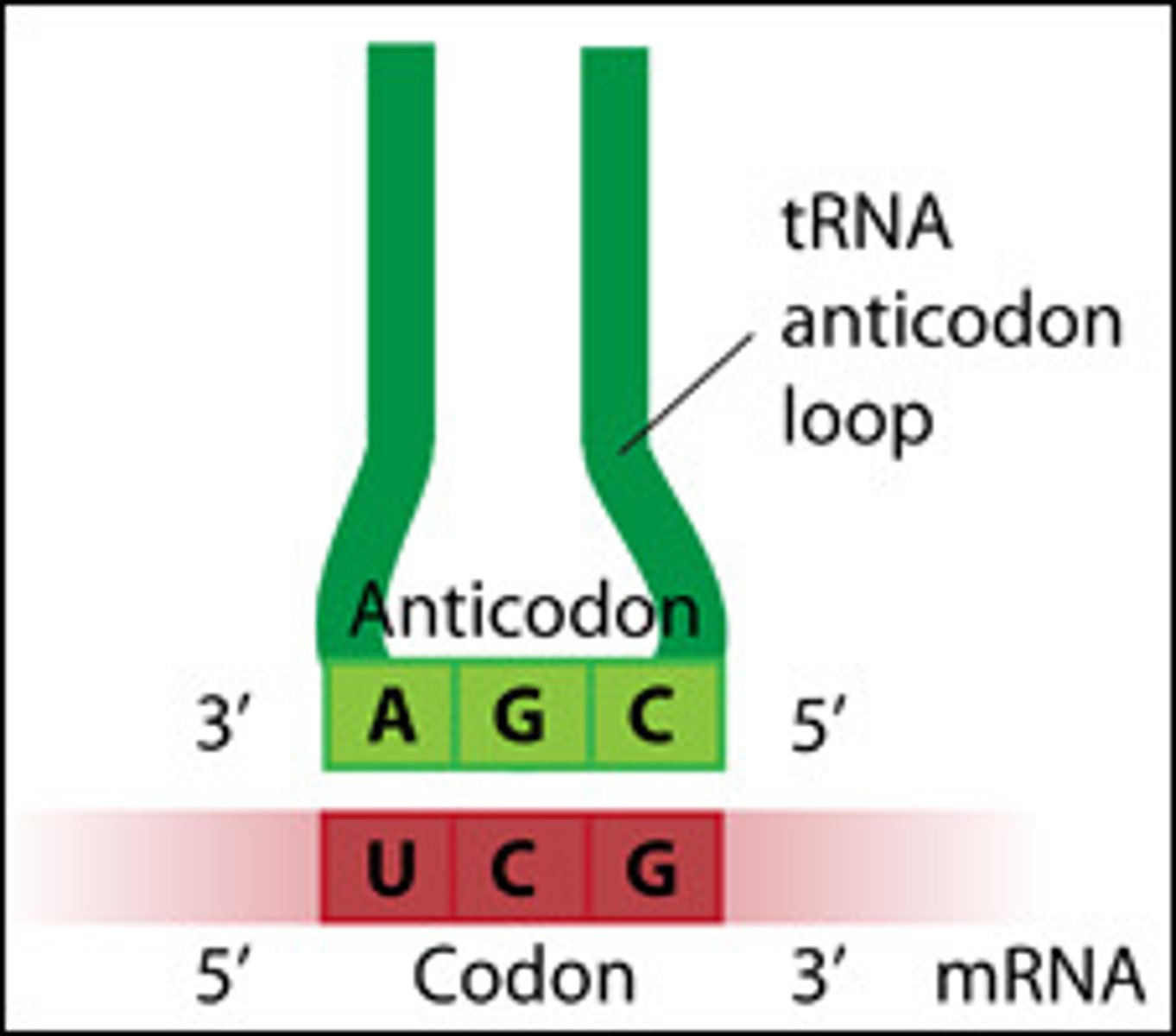
anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
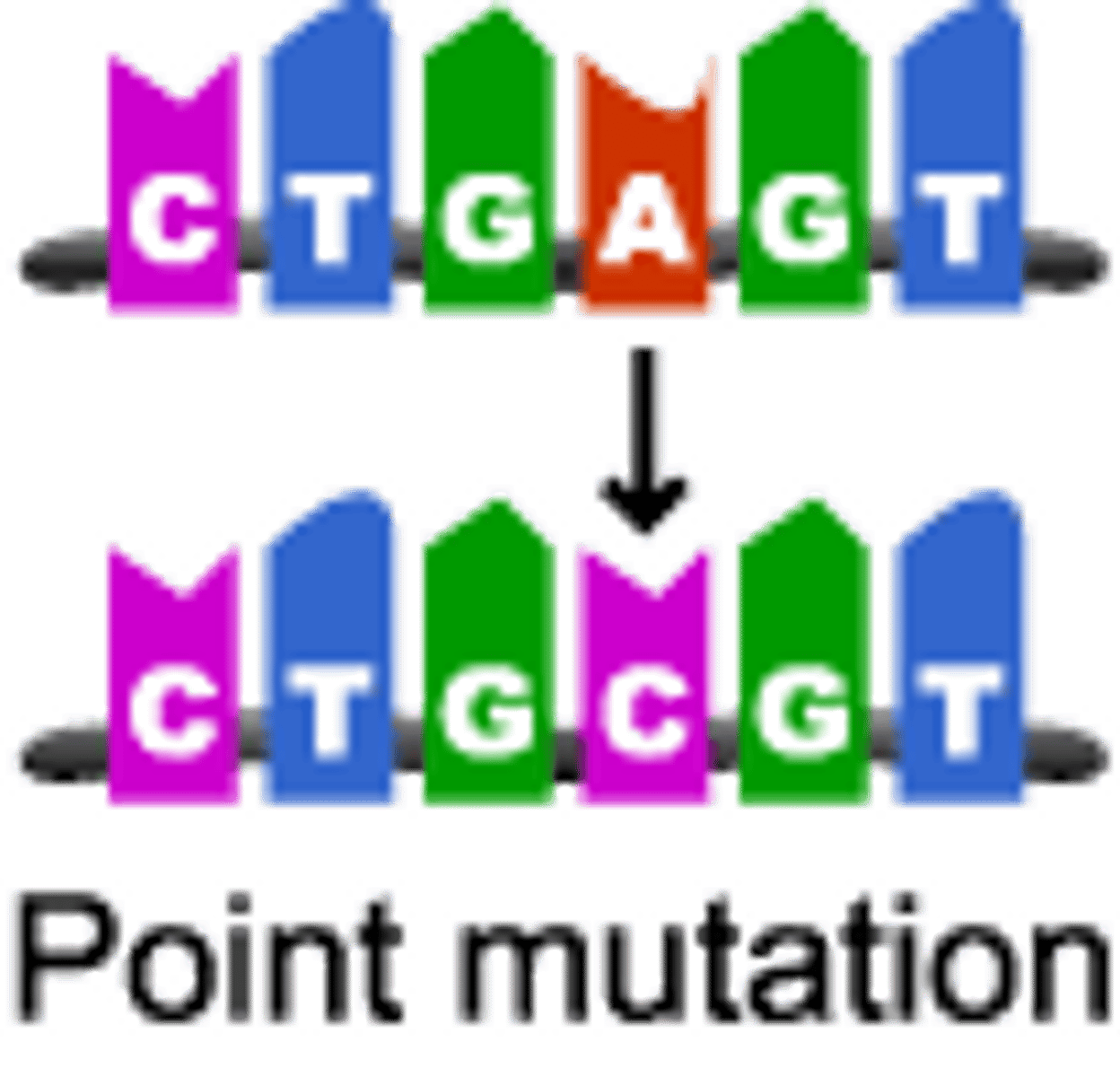
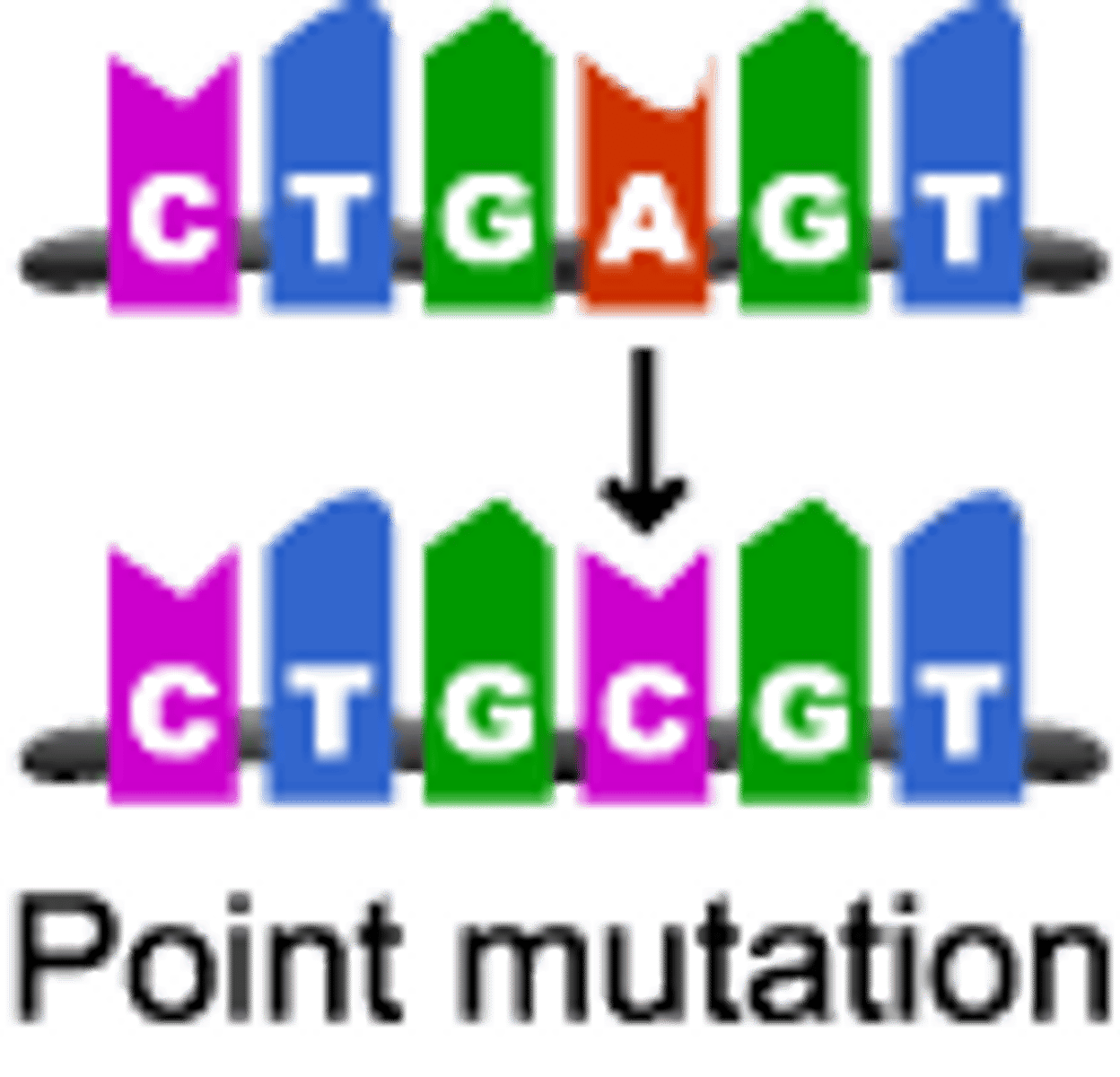
point mutation
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed
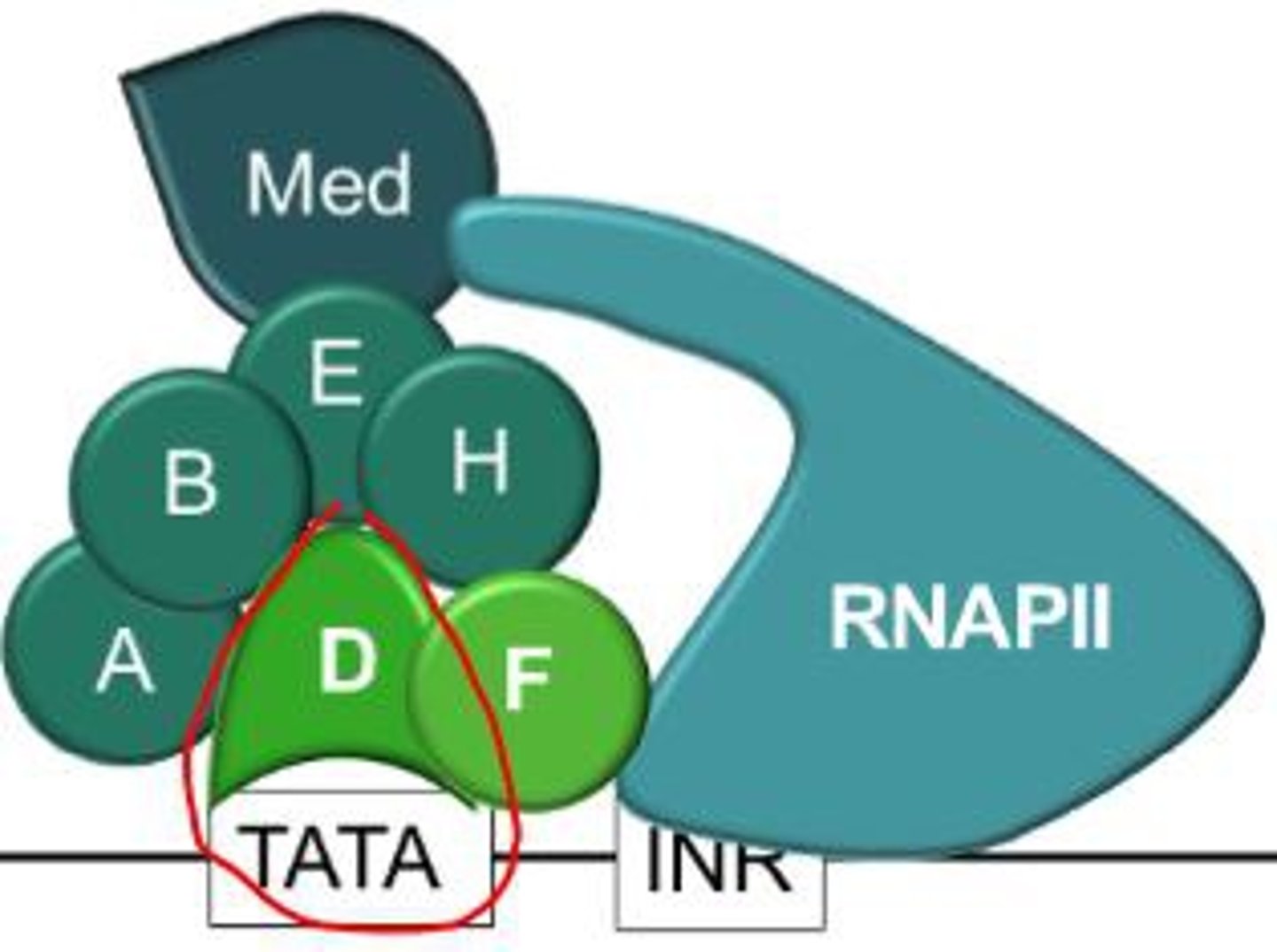
transcrption factors
A regulatory protein that binds to DNA and affects transcription of specific genes (turns them on or off)
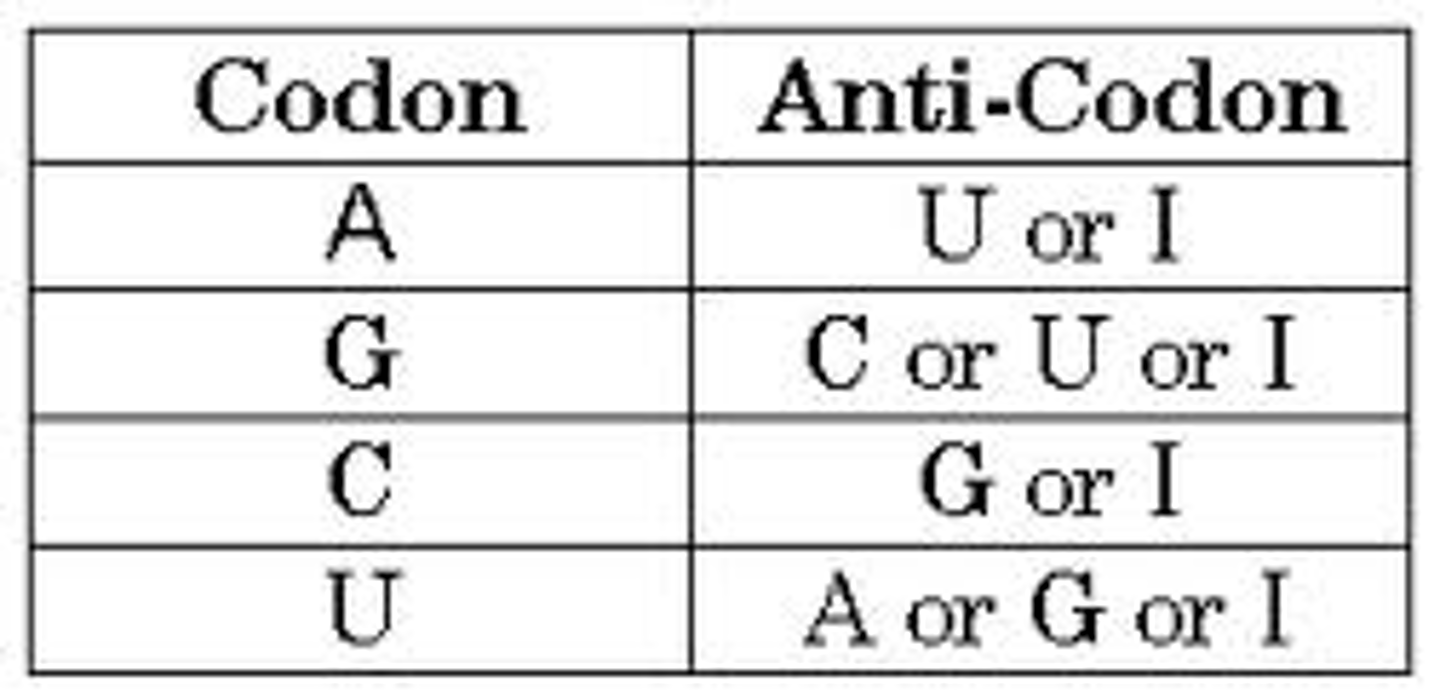
wobble
Flexibility in the base-pairing rules in which the nucleotide at the 5' end of a tRNA anticodon can form hydrogen bonds with more than one kind of base in the third position of a codon.
base-pair substitution
A type of point mutation; the replacement of one nucleotide and its partner in the complementary DNA strand by another pair of nucleotides.
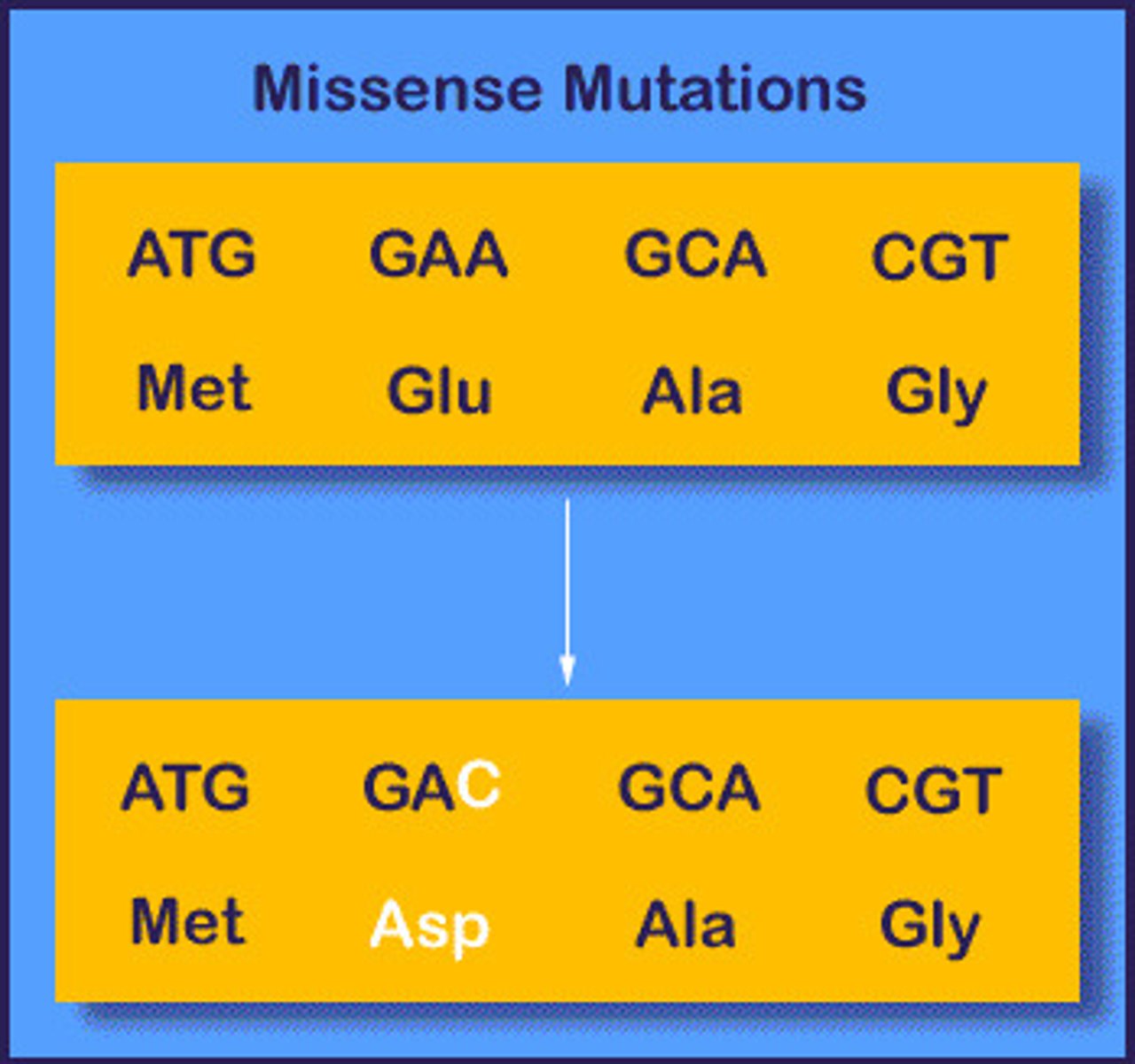
missense mutation
A base-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
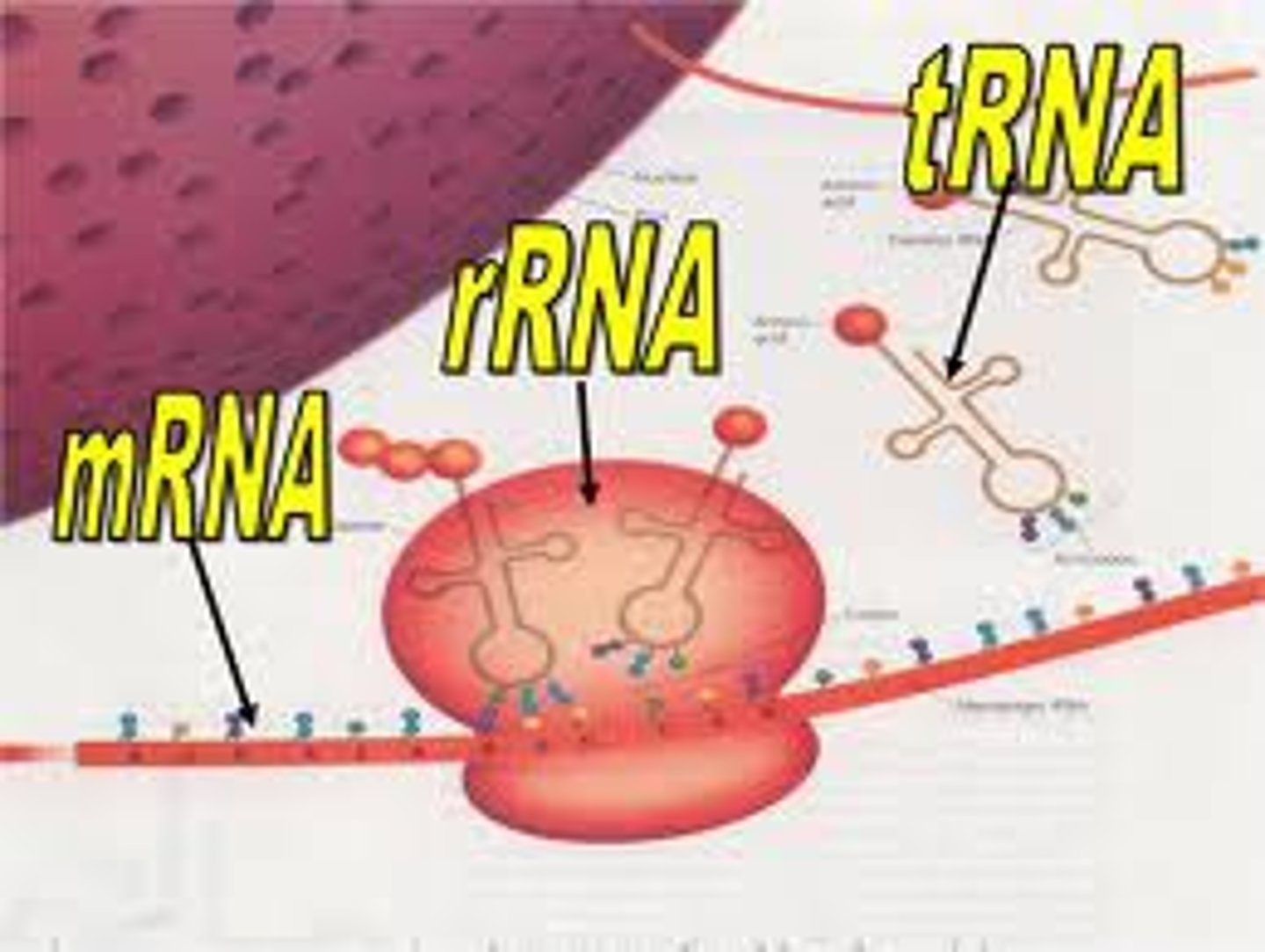
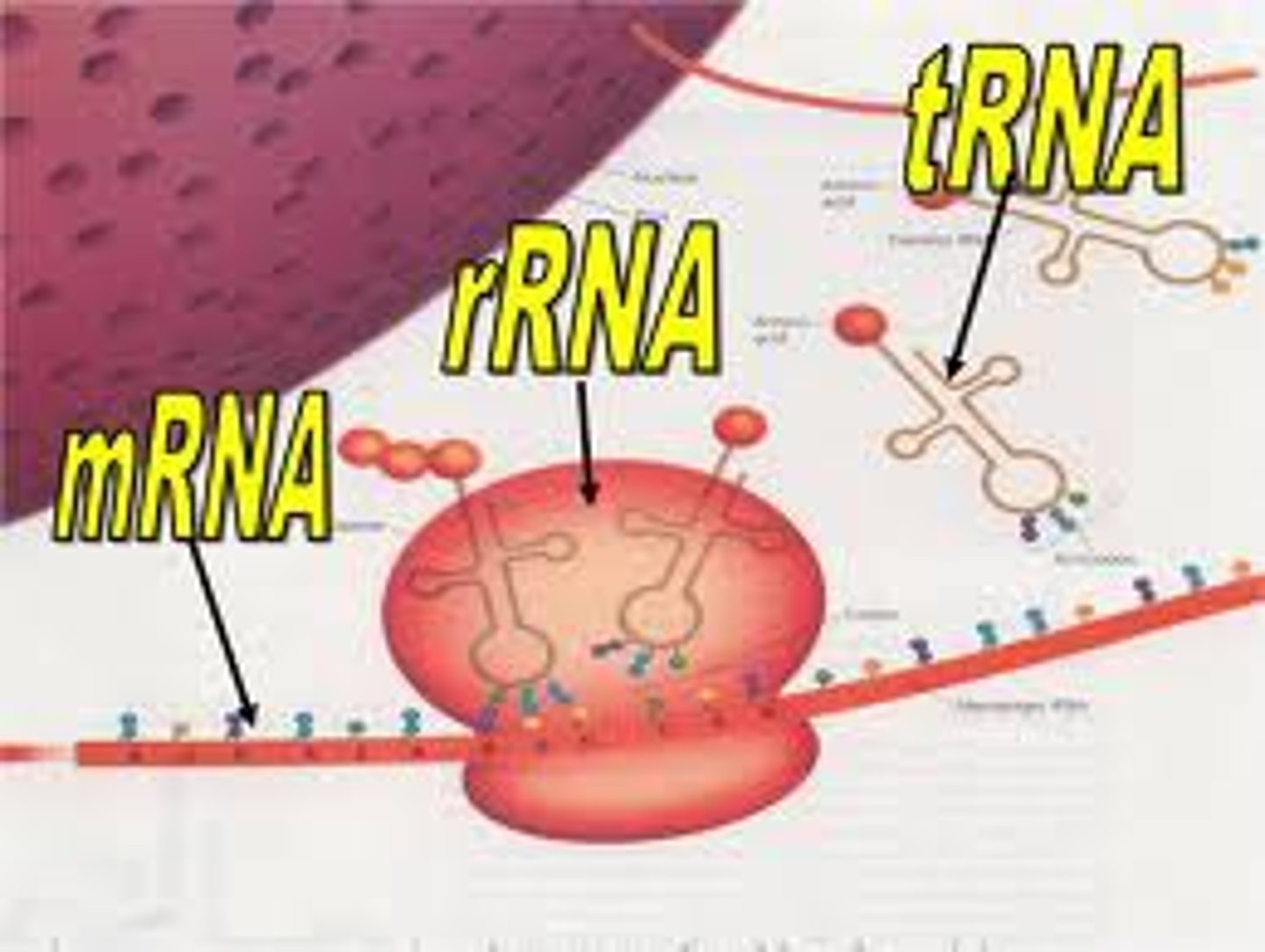
messenger RNA (mRNA)
A type of RNA, synthesized from DNA and attached to ribosomes in the cytoplasm; it specifies the primary structure of a protein.
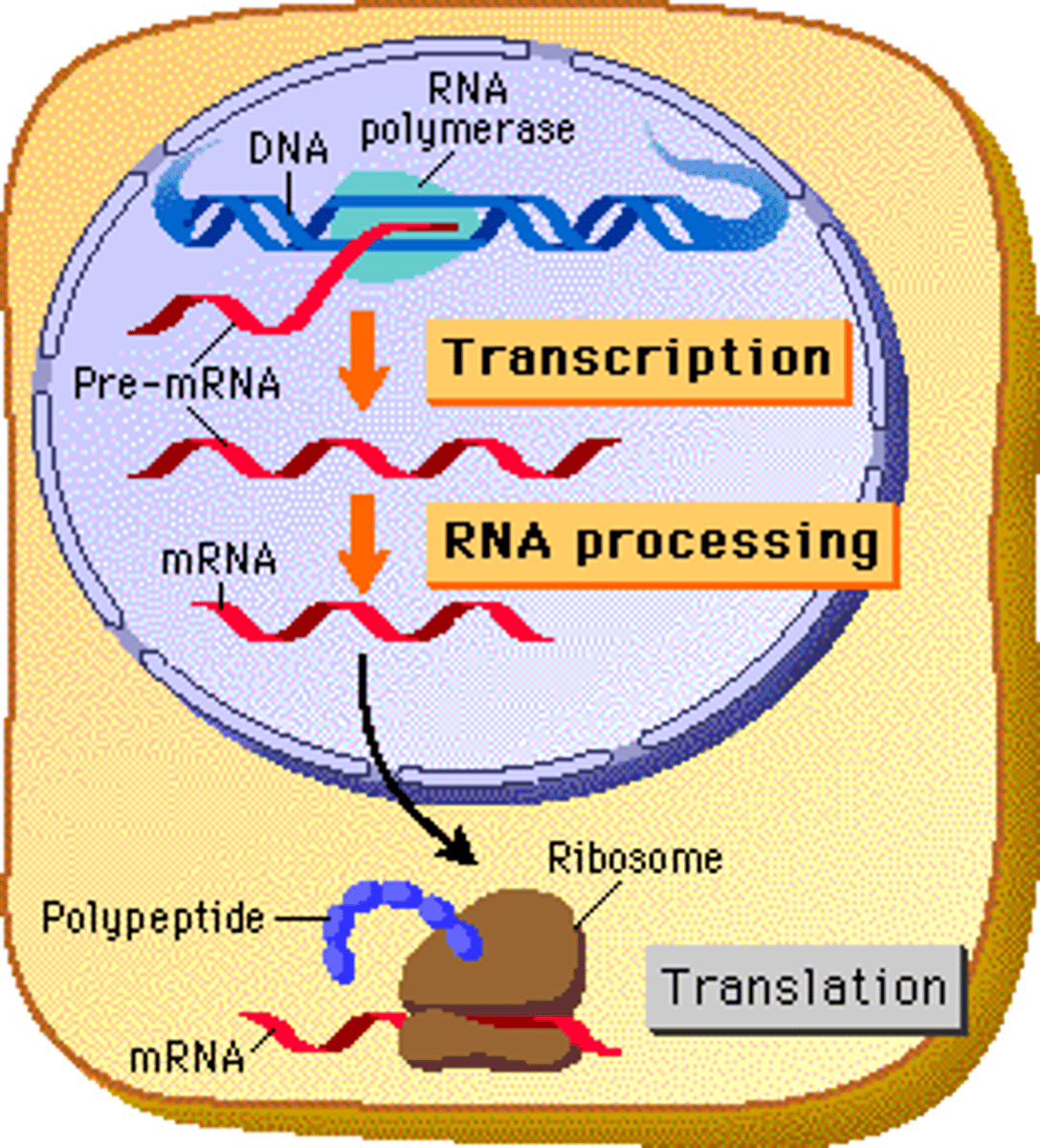
transcription
the process of making RNA from instructions in DNA
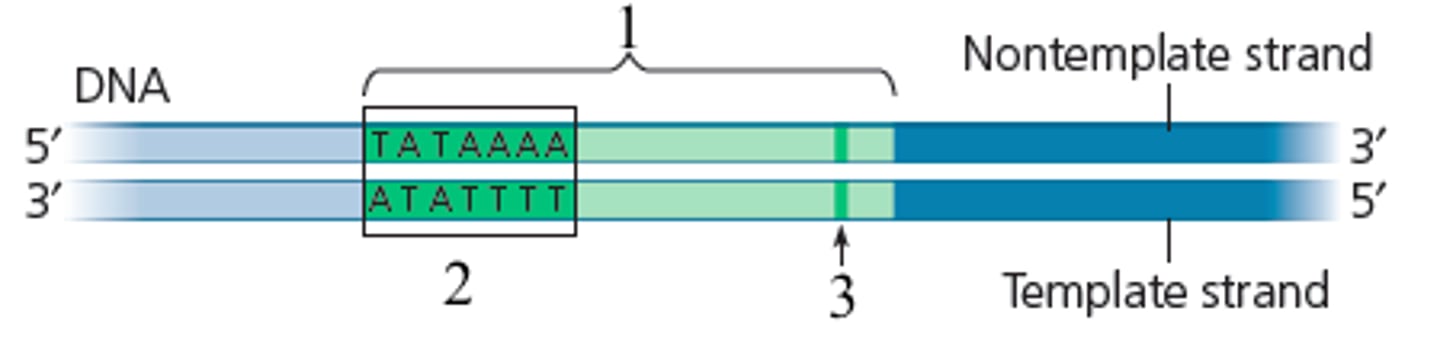
TATA box
A promoter DNA sequence crucial in forming the transcription initiation complex.
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
type of RNA that combines with proteins to form ribosomes
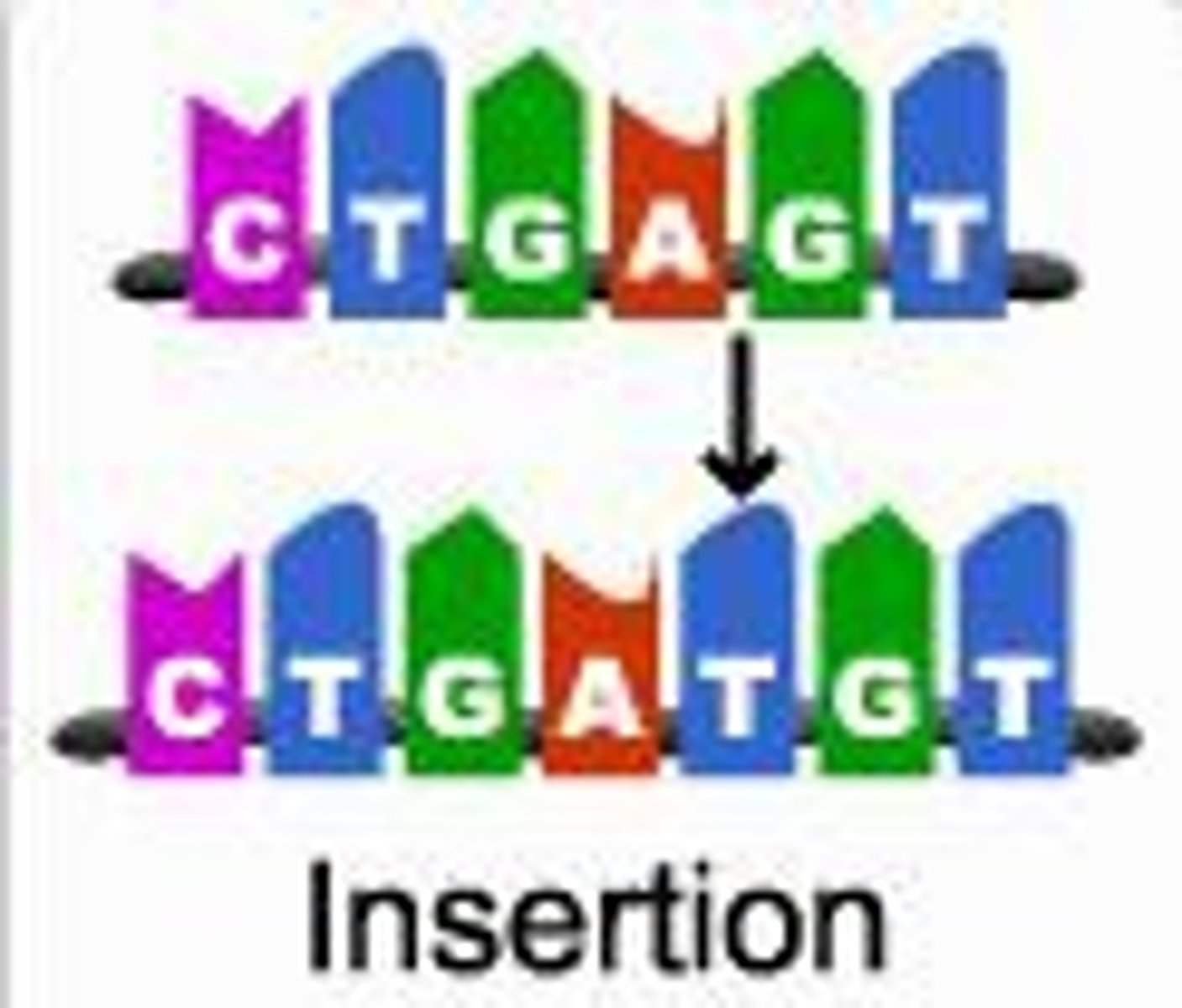
insertion
A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene.
transfer RNA
type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis
deletion
A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is removed.

Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
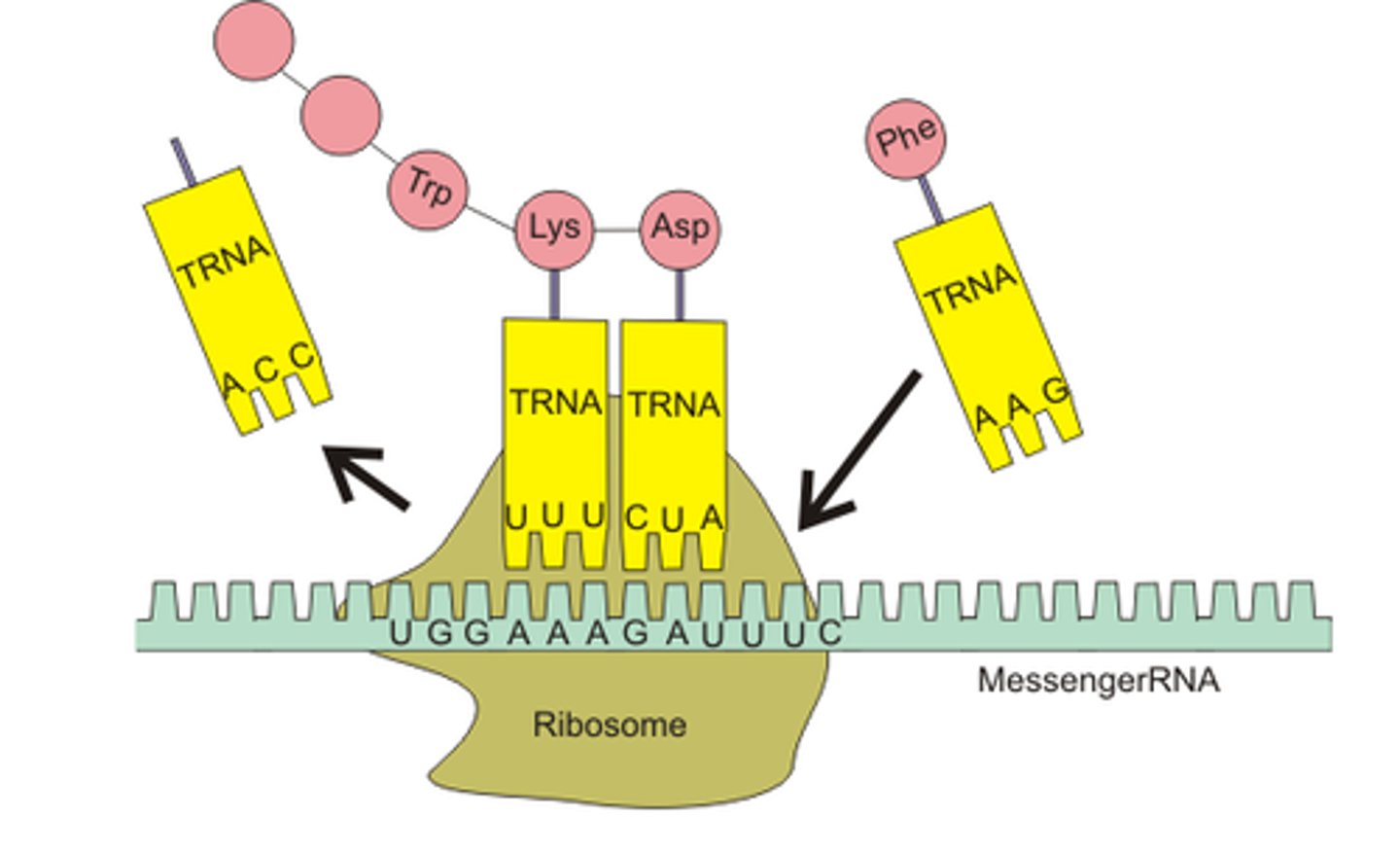
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs)
these enzymes cut out introns and splice together eons in the pre-RNA to create a functional mRNA
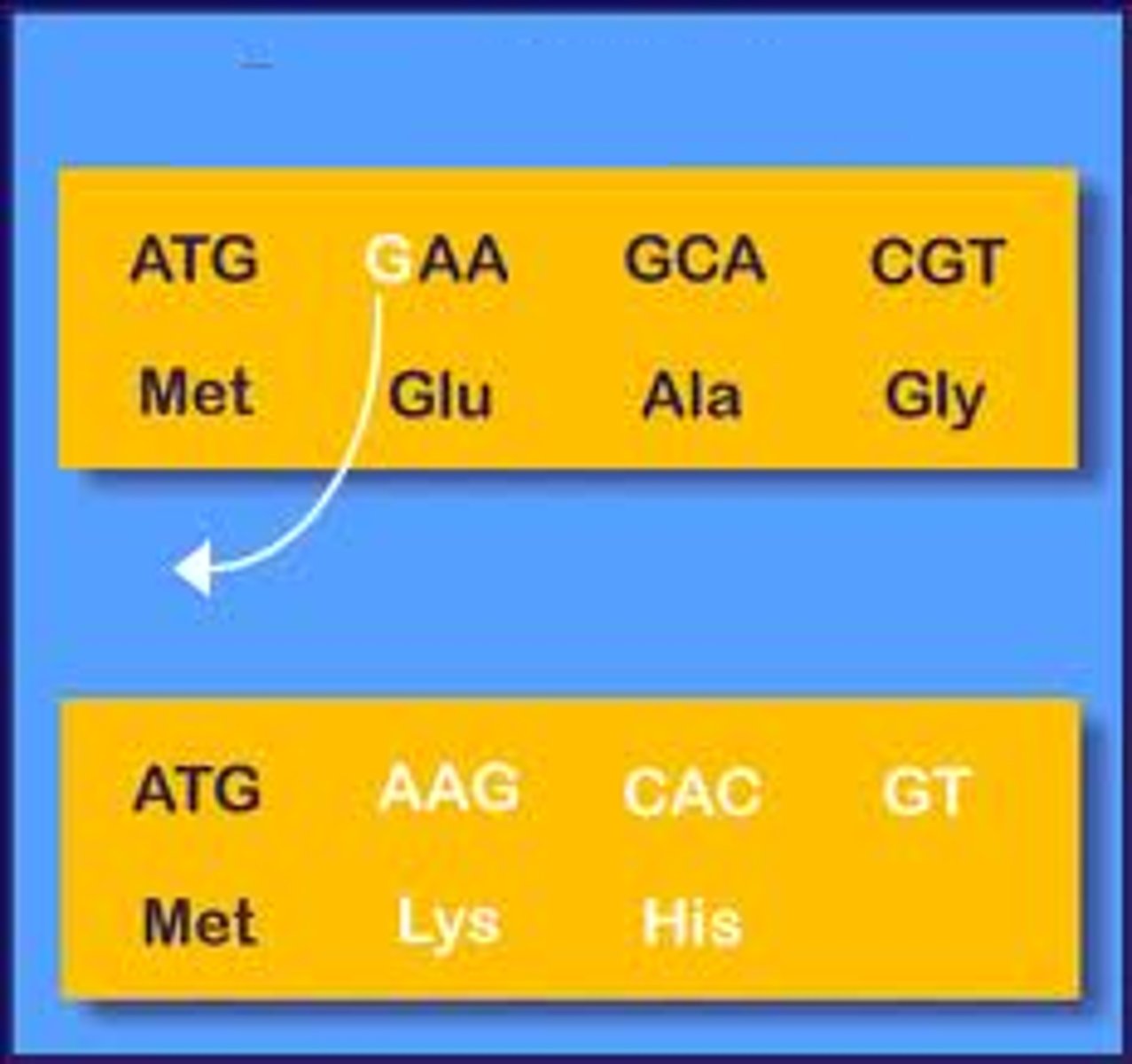
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
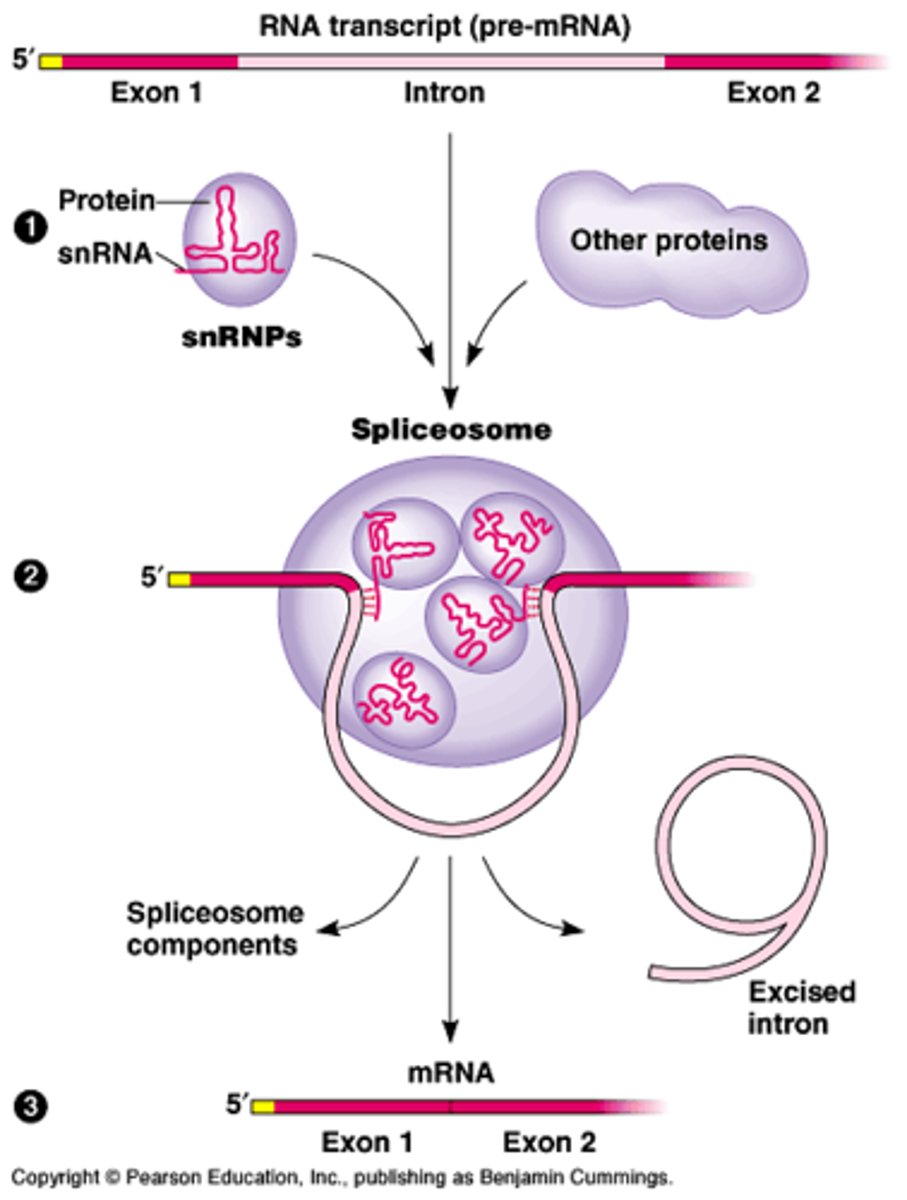
RNA processing
The modification of mRNA before it leaves the nucleus that is unique to eukaryotes.

small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
RNA molecule of around 200 nucleotides that participates in RNA splicing
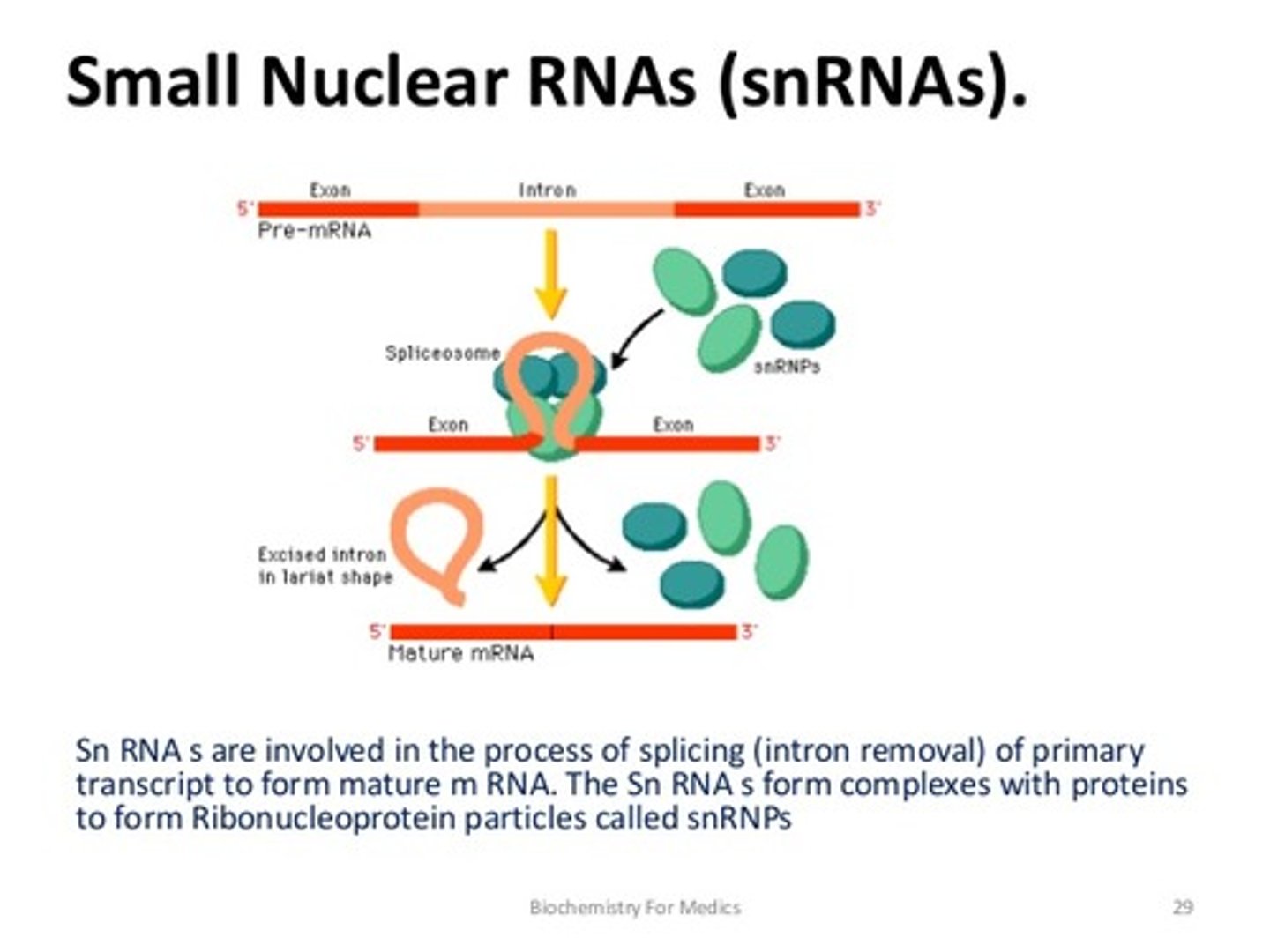
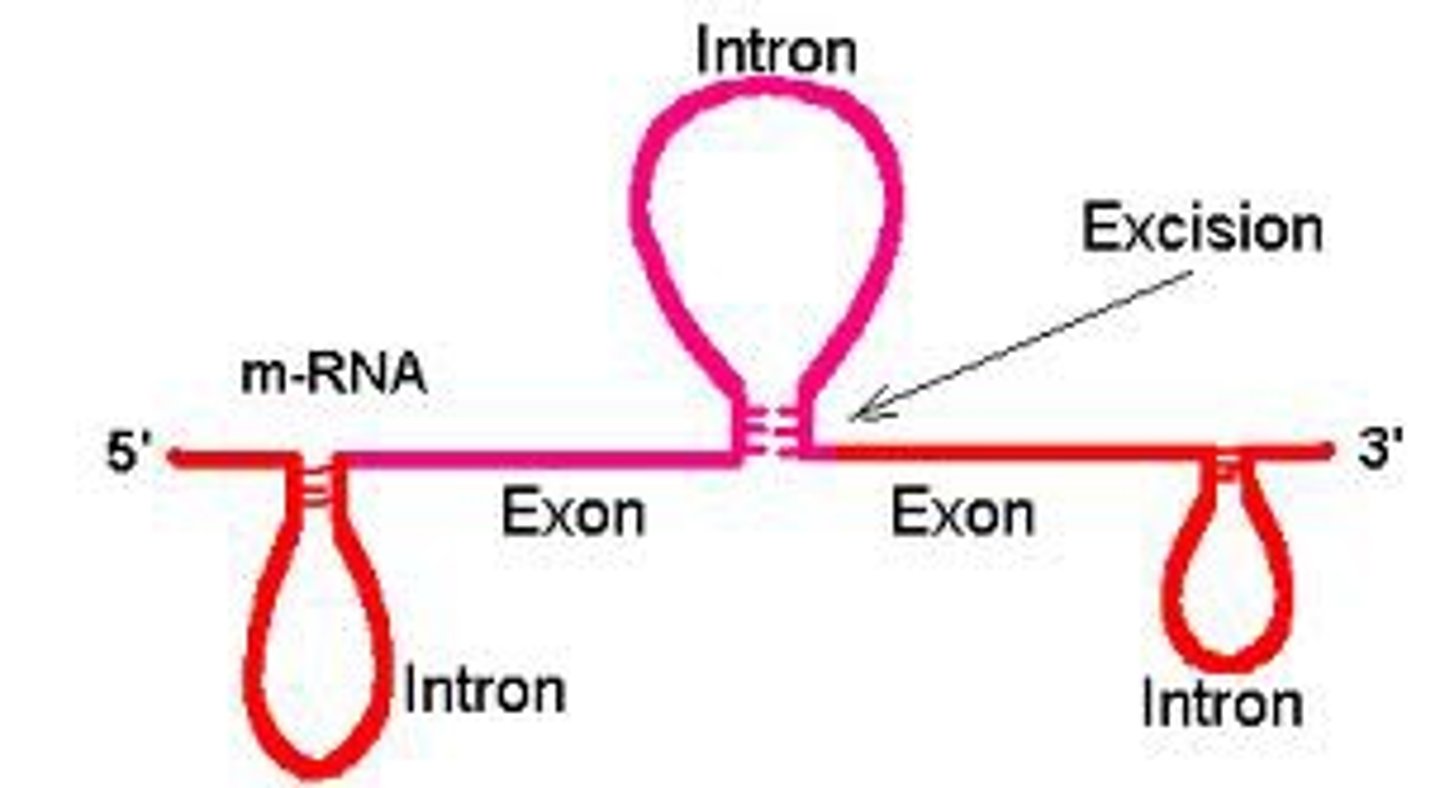
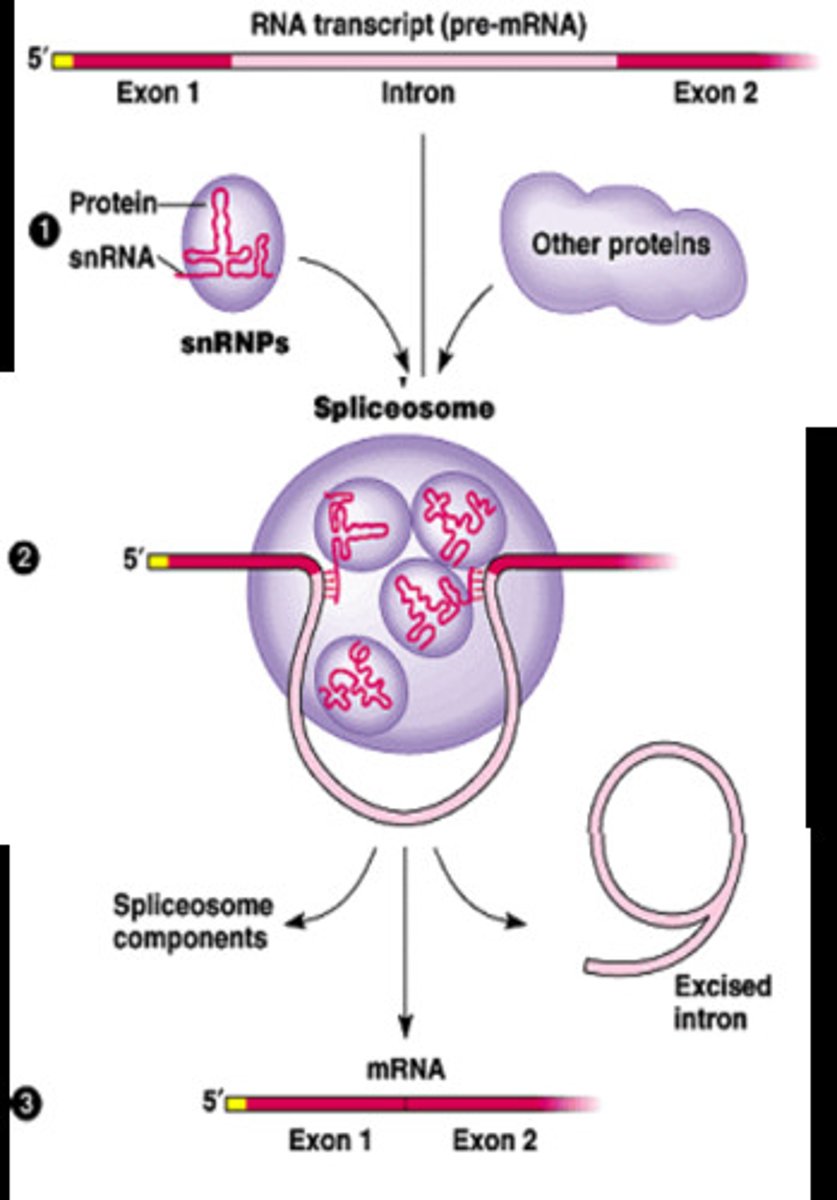
RNA splicing
Process by which the introns are removed from RNA transcripts and the remaining exons are joined together.
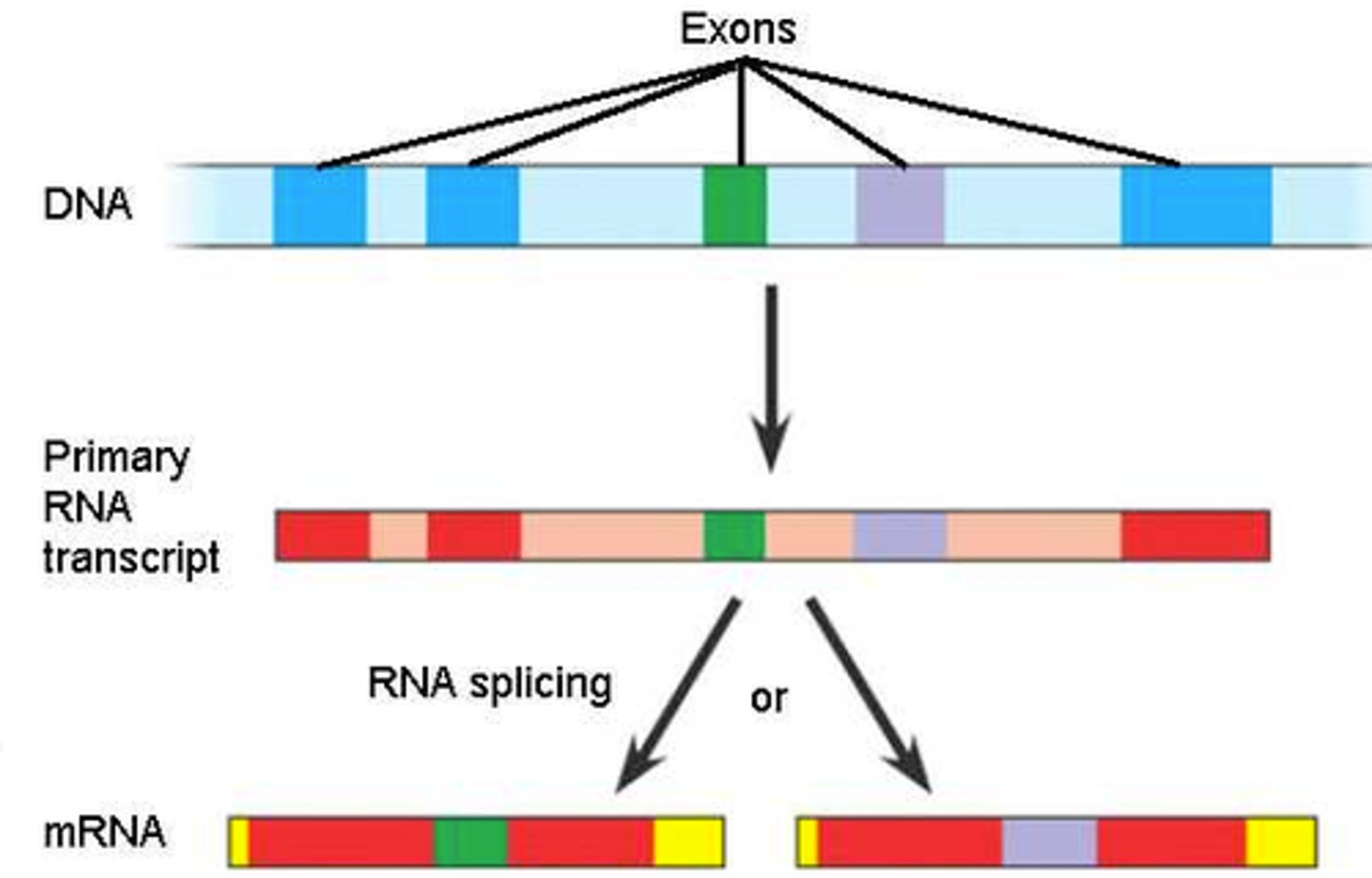
triplet code
A set of three-nucleotide-long words that specify the amino acids for polypeptide chains.
intron
sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein
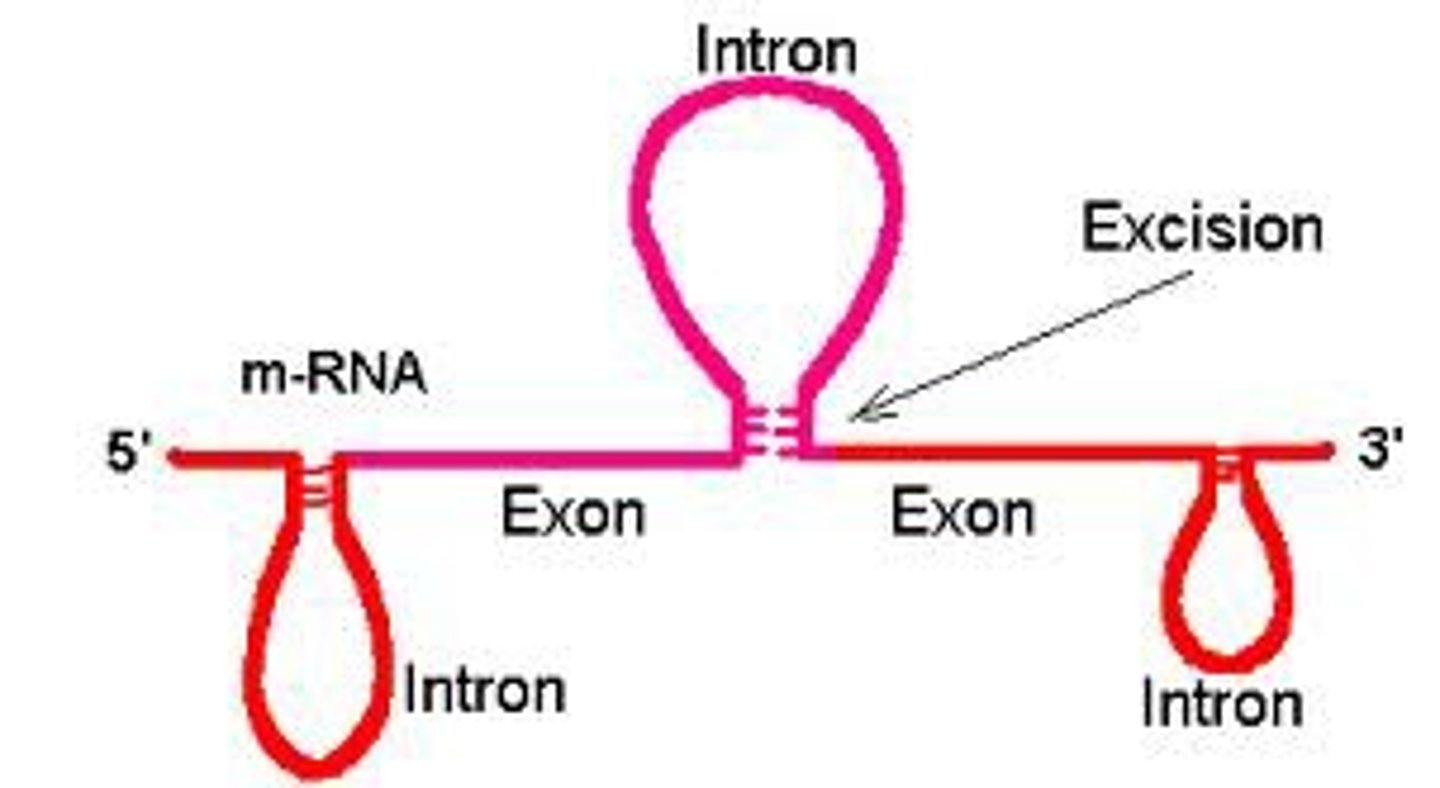
exon
expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein
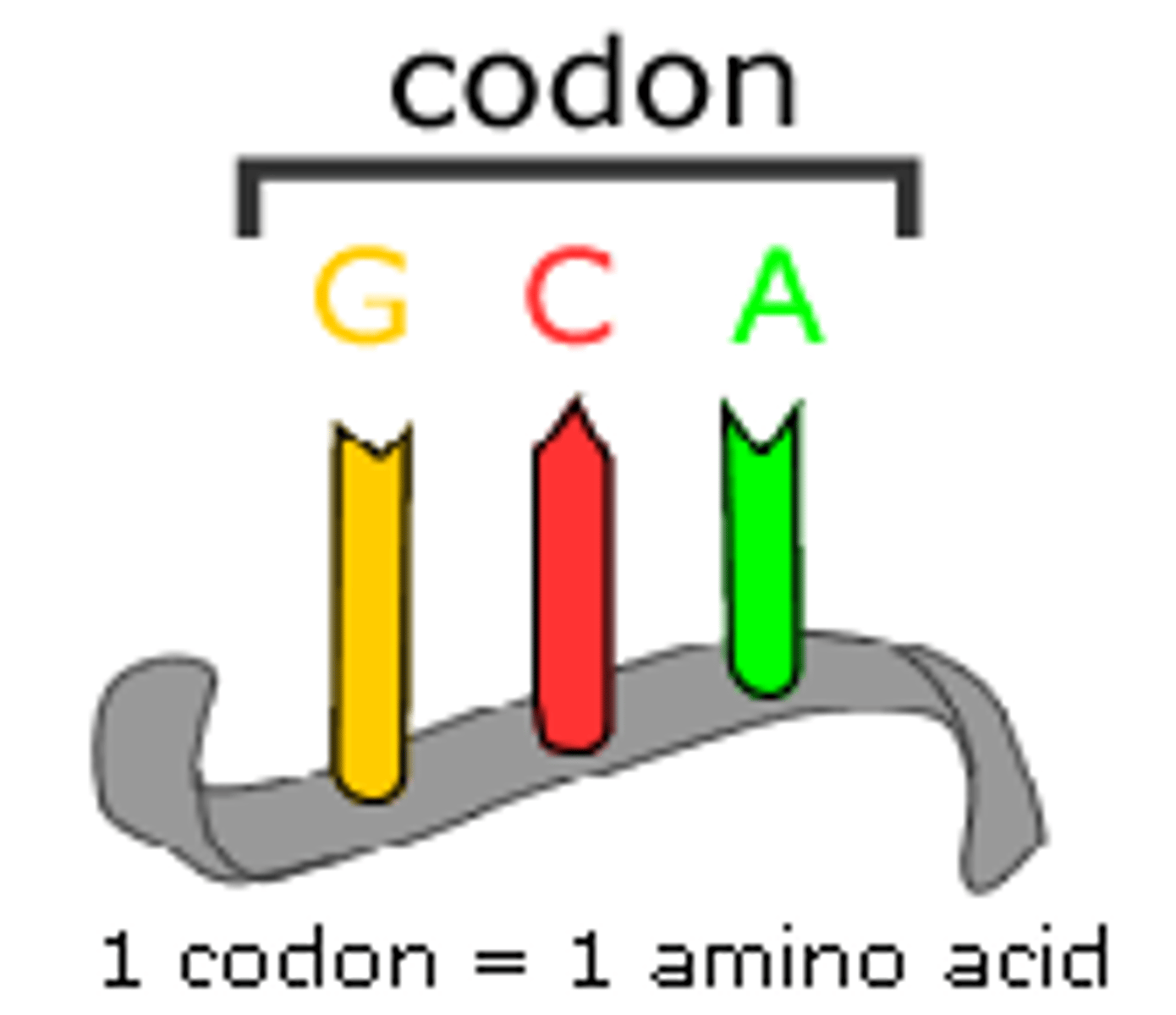
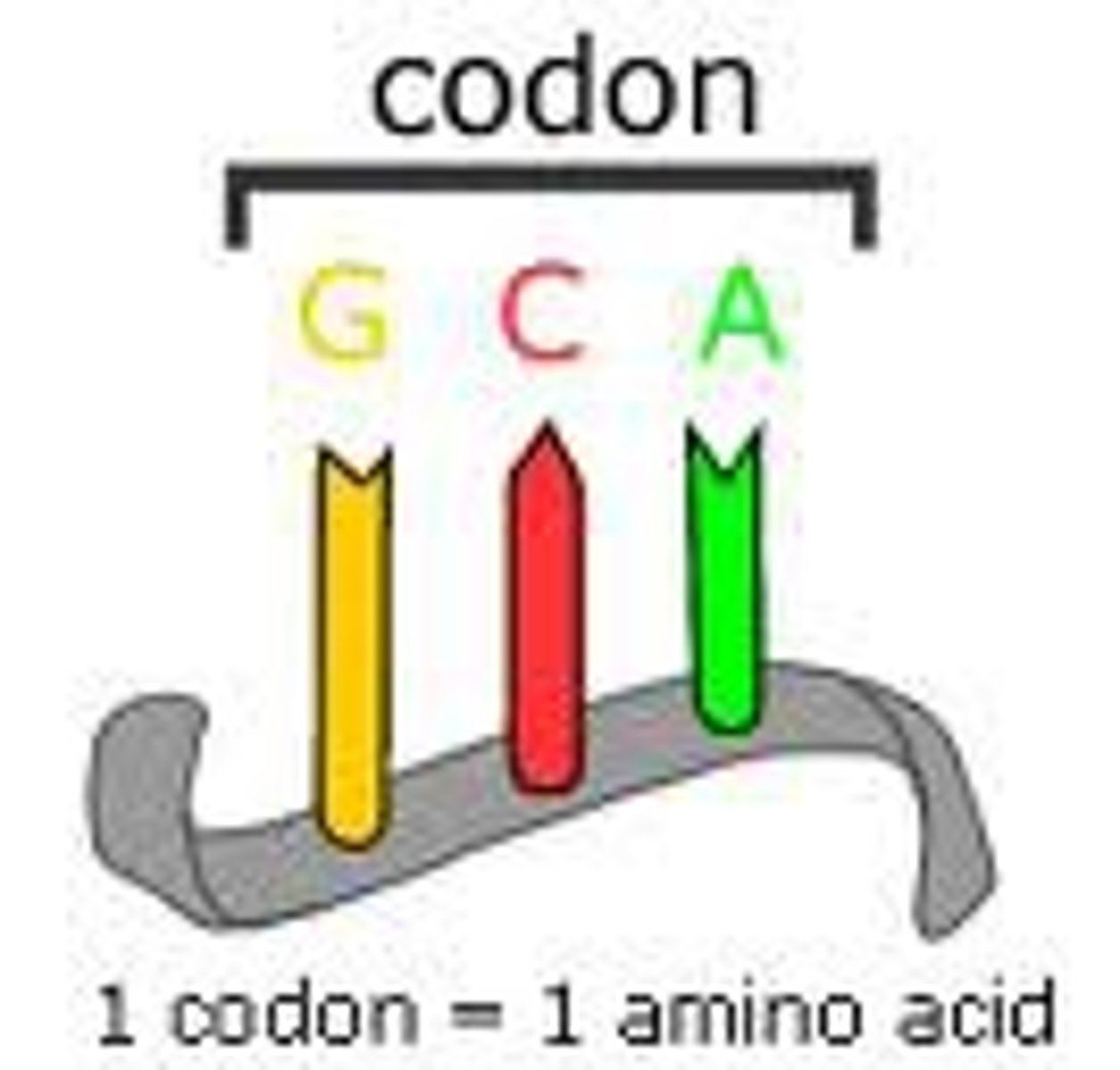
codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid
splicesome
a complex of specialized RNA and protein subunits that removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA segment.
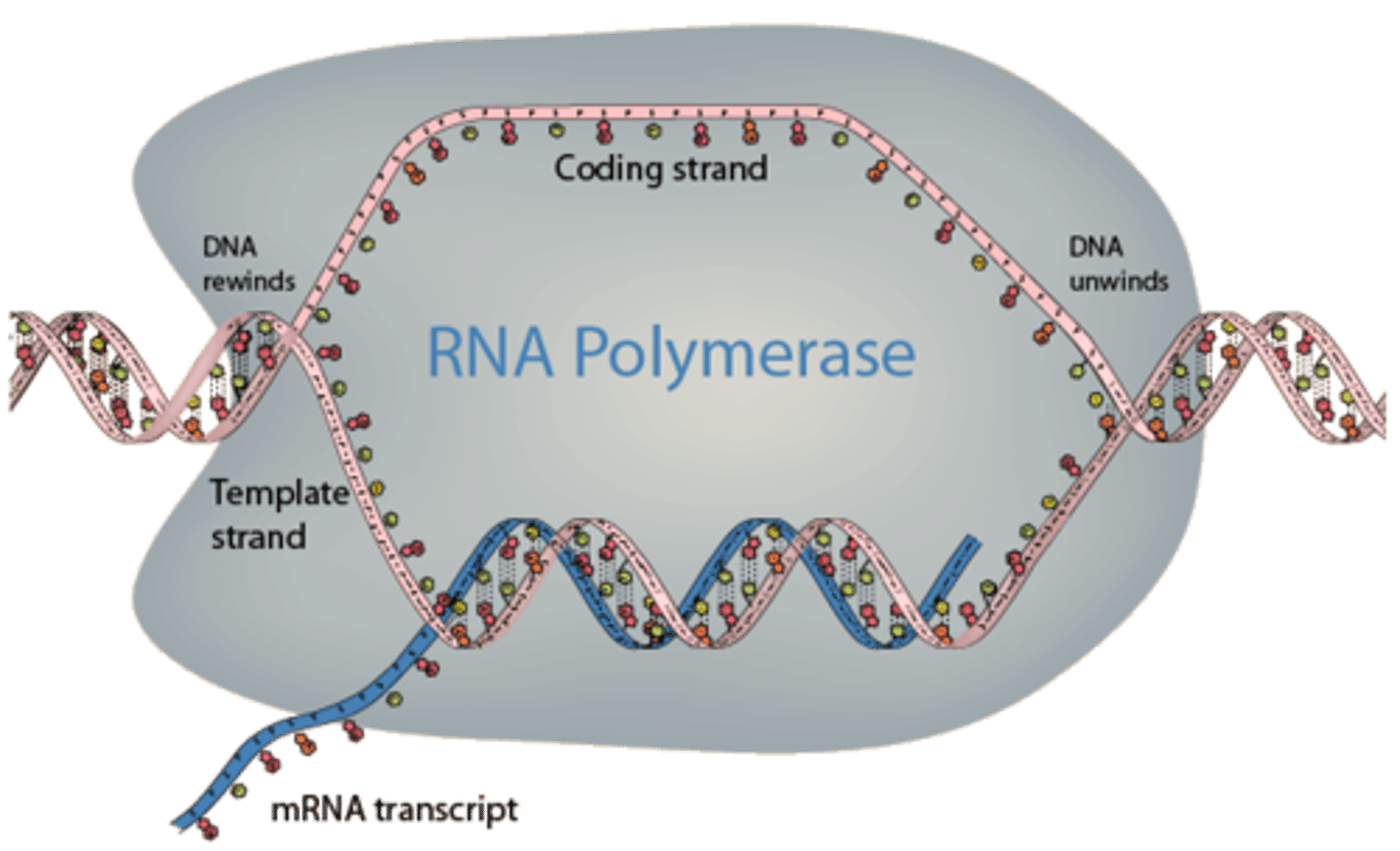
RNA polymerase
Enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription