BIOL 109 – Chapter 15 Respiratory System
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts from Chapter 15 of the Human Respiratory System (BIOL 109) including structures, functions, and processes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What are the five functions of the respiratory system?
Provides gas exchange surface, moves air, protects surfaces, produces sound, aids smell.
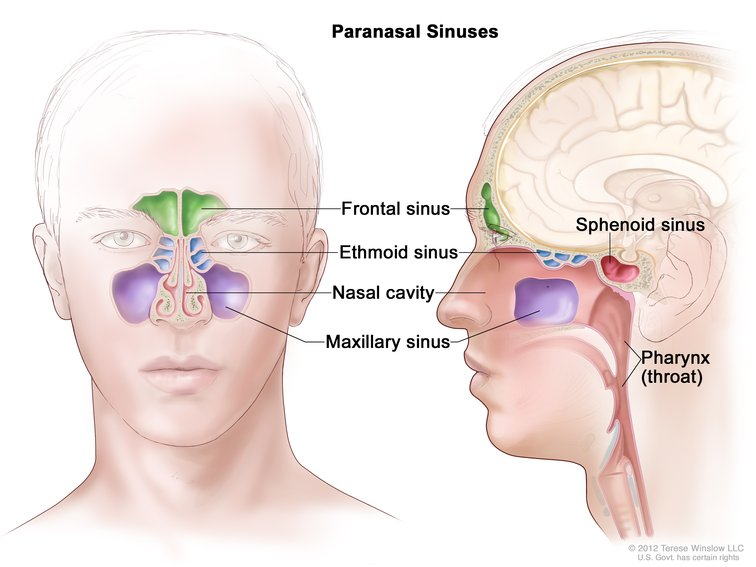
What structures belong to the upper respiratory system?
Nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx.
What structures belong to the lower respiratory system?
Larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli.
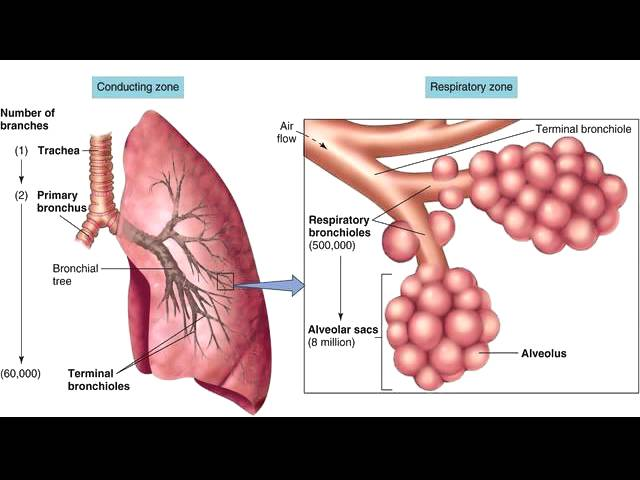
What is the main job of the conducting zone?
Carry, warm, filter, and humidify air.
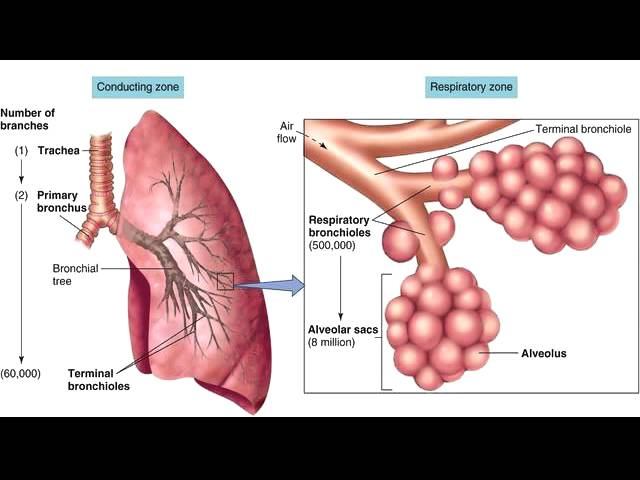
What is the respiratory zone?
Smallest bronchioles + alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
What type of tissue lines most of the conducting zone?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with many mucus cells.
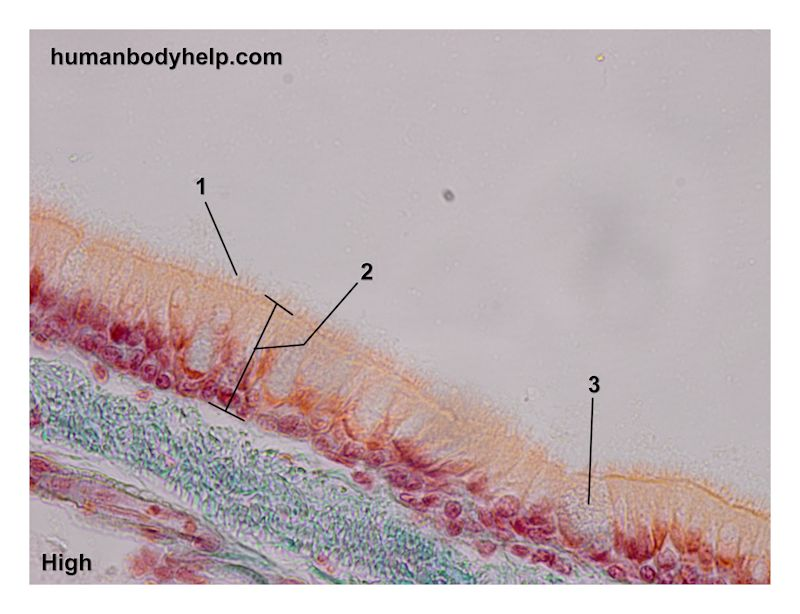
What supports the respiratory epithelium?
The lamina propria.
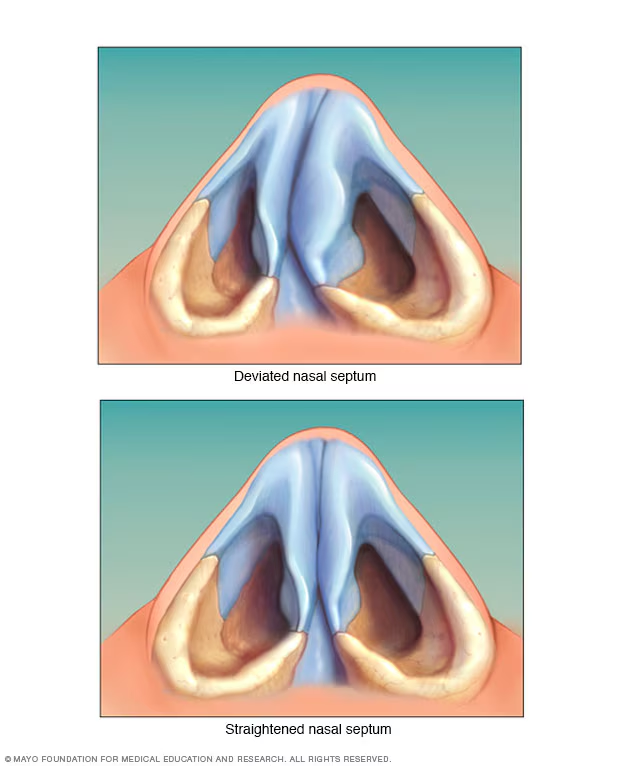
What structure divides the nasal cavity?
Nasal septum.
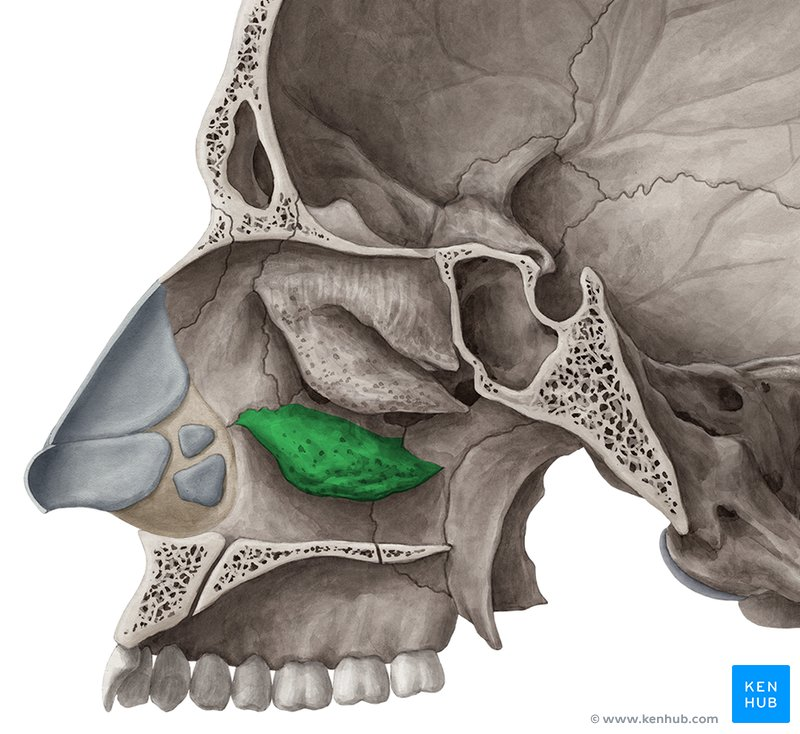
What structures increase turbulence and warm air?
Nasal conchae.
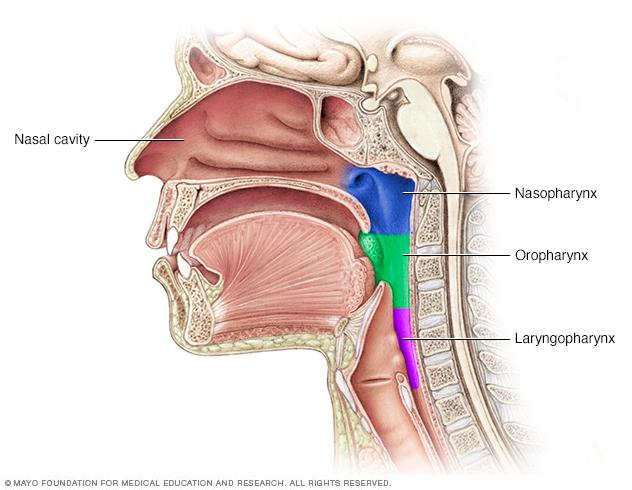
What are the three parts of the pharynx?
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx.
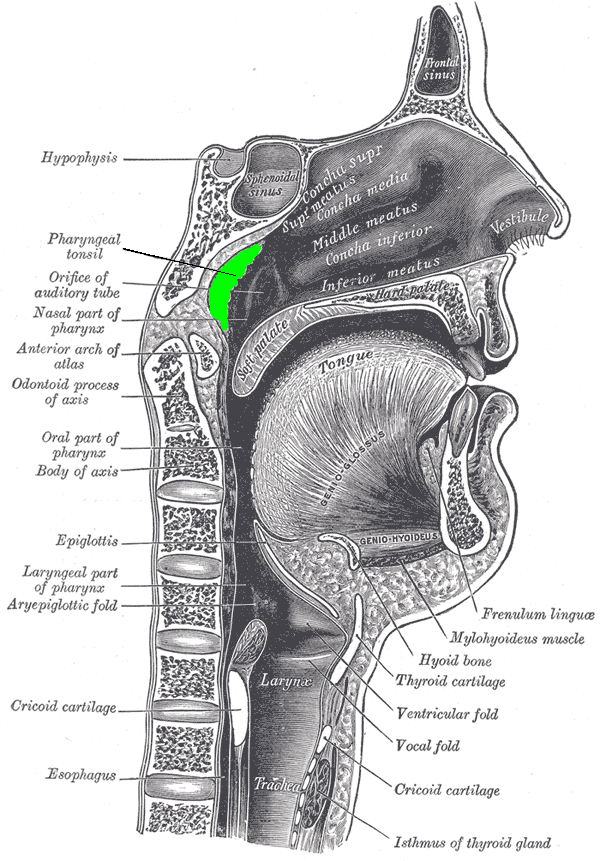
What tonsil is found in the nasopharynx?
Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid).
What tonsils are found in the oropharynx?
Palatine tonsils.
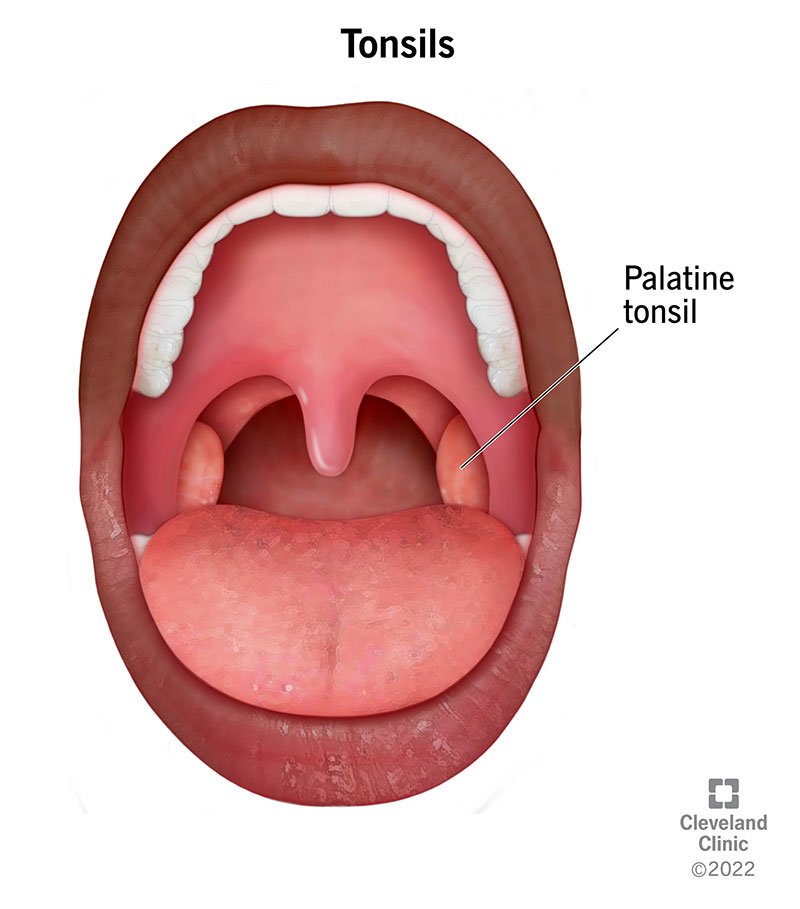
What structure begins the lower respiratory system?
The larynx.
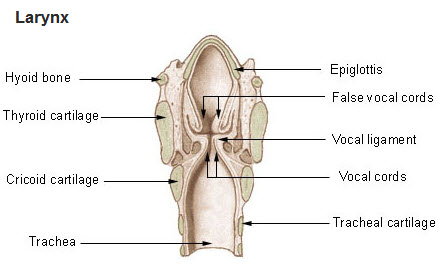
What cartilage covers the glottis during swallowing?
Epiglottis.
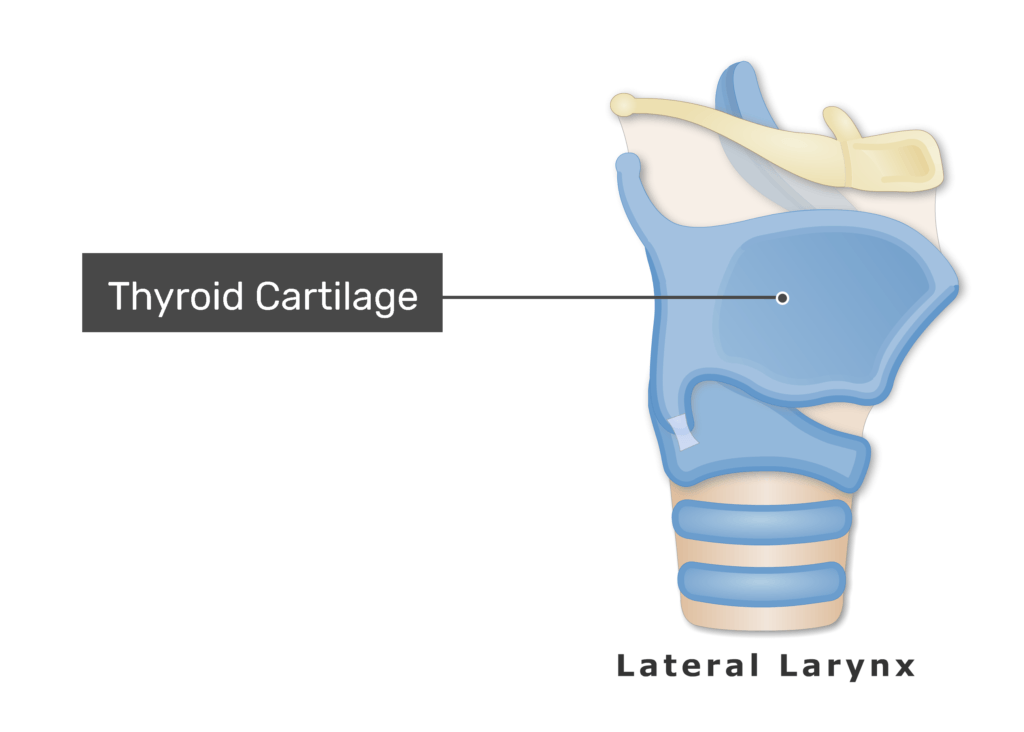
What cartilage forms the “Adam’s apple”?
Thyroid cartilage.
Which cartilage forms the base of the larynx?
Cricoid cartilage.
What do false vocal cords do?
Protect the true vocal cords and block debris.
What do true vocal cords do?
Produce sound.
What muscle lines the posterior trachea?
Trachealis muscle.
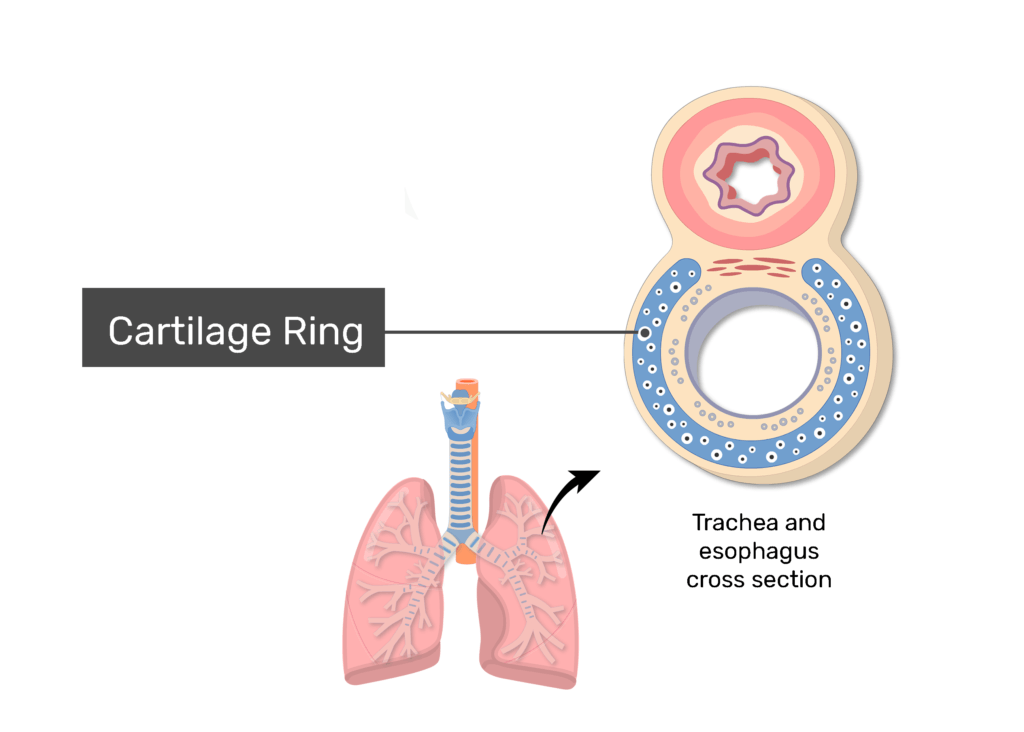
Why are tracheal cartilages C-shaped?
To allow esophagus to expand while swallowing.
Which primary bronchus is wider and more vertical?
Right primary bronchus.
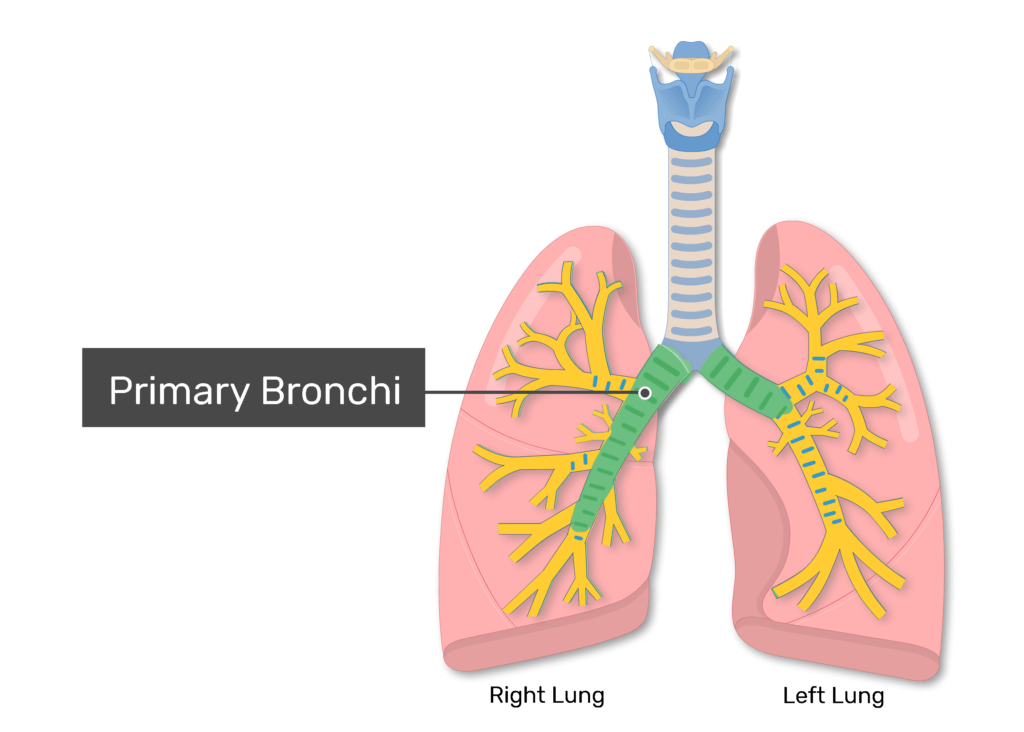
Name the bronchial tree branches in order.
Primary → secondary → tertiary bronchi → bronchioles.
Do bronchioles have cartilage?
No; they contain smooth muscle only.
What does sympathetic stimulation cause in bronchioles?
Bronchodilation.
What does parasympathetic stimulation cause?
Bronchoconstriction.
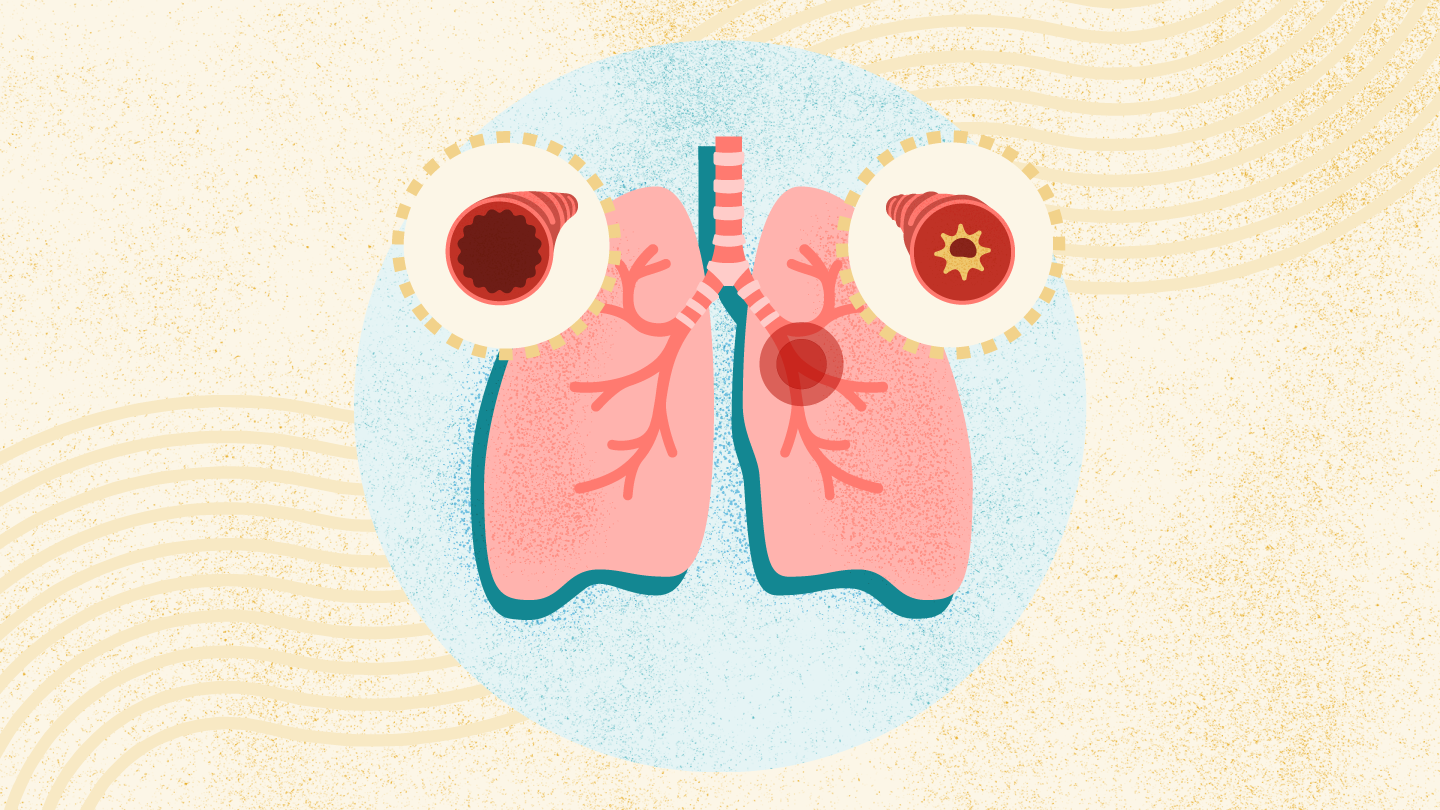
What is an asthma attack?
Extreme bronchoconstriction + inflammation.
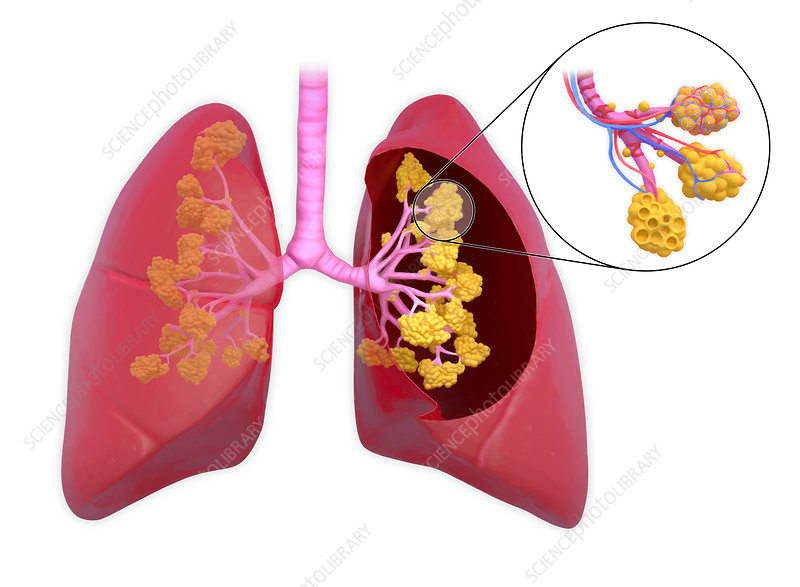
What are alveoli?
Tiny sacs where gas exchange occurs.
What type of epithelium is found in alveoli?
Simple squamous epithelium.
What do Type I pneumocytes do?
Gas exchange.
What do Type II pneumocytes do?
Produce surfactant.
What does surfactant do?
Reduces surface tension to prevent alveoli from collapsing.
What happens without surfactant?
Respiratory distress syndrome.
What cells clean debris from the alveoli?
Alveolar macrophages.
What are the three layers of the respiratory membrane?
Alveolar epithelium, fused basement membrane, capillary endothelium.
Which lung has three lobes?
Right lung.
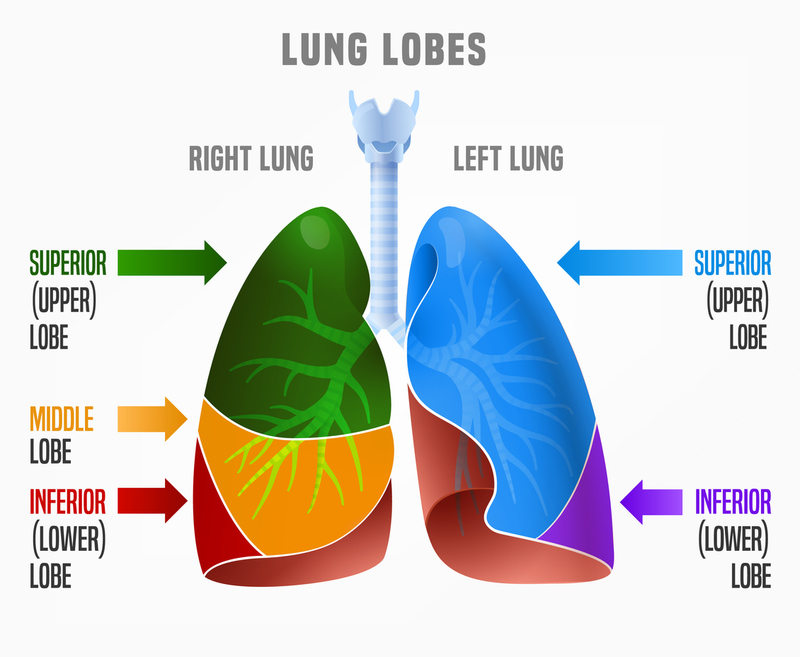
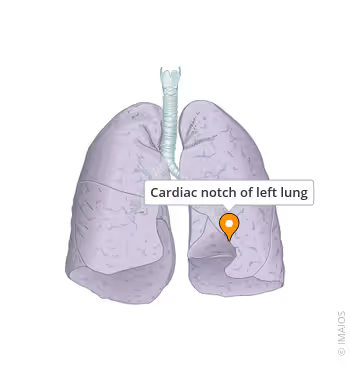
Which lung has a cardiac notch?
Left lung.
What are the pleural layers?
Parietal and visceral pleura.
What is pleural fluid for?
Reduces friction.
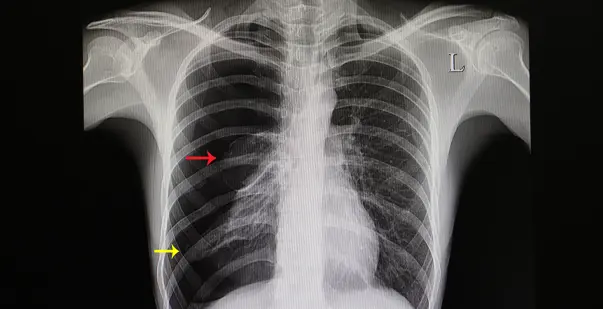
What is pneumothorax?
Air entering pleural cavity → lung collapse.
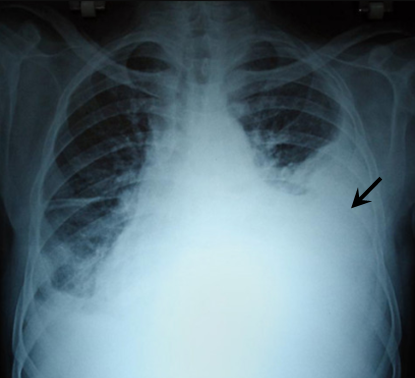
What is hemothorax?
Blood in pleural cavity.
What is pulmonary ventilation?
Movement of air in and out of lungs.
What happens to pressure when lung volume increases?
Pressure decreases.
What happens during inhalation?
Diaphragm contracts → thoracic volume increases → air enters.
What happens during exhalation?
Diaphragm relaxes → thoracic volume decreases → air exits.
What is compliance?
Ease of lung expansion.
What reduces compliance?
RDS, arthritis, fibrosis.
What increases compliance excessively?
Emphysema.
What is eupnea?
Normal quiet breathing.
What is apnea?
Temporary breathing stop.
What is tidal volume (TV)?
Air moved per quiet breath (≈500 mL).
What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)?
Extra air you can inhale.
What is expiratory reserve volume (ERV)?
Additional air you can exhale.
What is vital capacity?
TV + IRV + ERV.
What is residual volume?
Air left after max exhale.
What is total lung capacity?
Vital capacity + residual volume.
What is external respiration?
Gas exchange between alveoli and blood.
What is internal respiration?
Gas exchange between systemic capillaries and tissues.
What is hypoxia?
Low oxygen in tissues.
What is anoxia?
No oxygen → tissue death.
How is oxygen transported?
Mostly bound to hemoglobin.
How is carbon dioxide transported?
Dissolved in plasma, bound to hemoglobin, bicarbonate ions.
What is carbaminohemoglobin?
CO₂ bound to hemoglobin.
What reaction forms bicarbonate?
CO₂ + H₂O → H₂CO₃ → H⁺ + HCO₃⁻.
What is the chloride shift?
Bicarbonate leaves RBC as chloride enters.
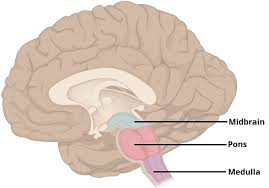
Where are breathing centers located?
Medulla and pons.
What gas primarily triggers breathing?
CO₂.
What is hypercapnia?
High CO₂ due to hypoventilation.
What is hypocapnia?
Low CO₂ due to hyperventilation.
What is COPD?
Group of disorders that restrict airflow.
What is chronic bronchitis?
Long-term inflammation + mucus overproduction.
Why are chronic bronchitis patients called 'blue bloaters'?
Low oxygen → blue skin; fluid retention.
What is emphysema?
Alveoli enlarge + lose elasticity.
Why are emphysema patients called 'pink puffers'?
Overexpanded lungs + heavy breathing.
What is the major cause of lung cancer?
Smoking.
What is the risk for nonsmokers living with smokers?
20–30% higher lung cancer risk.
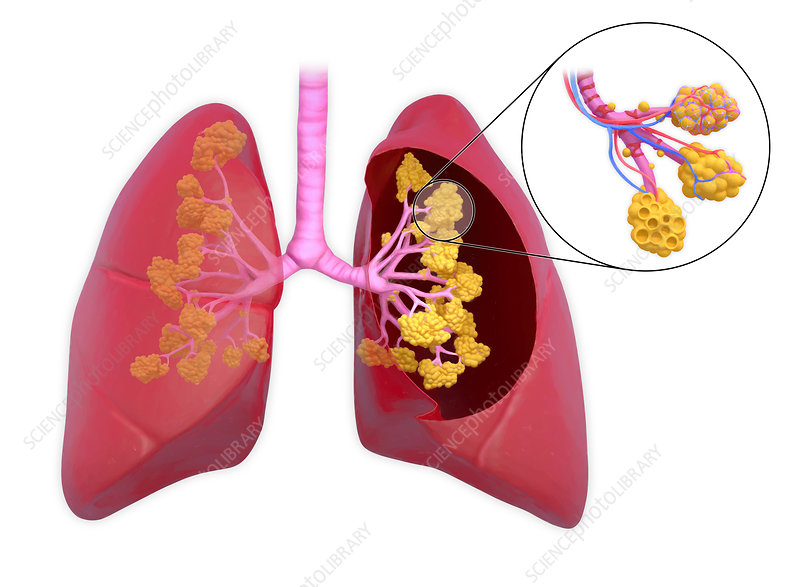
Which structure collapses first without surfactant: bronchi or alveoli?
Alveoli.
Which lung will collapse if the LEFT pleura is punctured?
Left lung.
Which pressure must remain negative to keep lungs inflated?
Intrapleural pressure.
Which primary bronchus is more likely to receive a foreign object?
Right.
Does emphysema increase or decrease lung compliance?
Increase.
Which air space participates in gas exchange: dead space or alveoli?
Alveoli.
During hyperventilation, what happens to CO₂ levels?
They decrease.
What happens to blood pH during hyperventilation?
It rises (respiratory alkalosis).
What happens to blood pH during hypoventilation?
It falls (respiratory acidosis).
Which gas binds more strongly to hemoglobin: O₂ or CO?
CO.
What separates the nasal and oral cavity?
Hard palate.
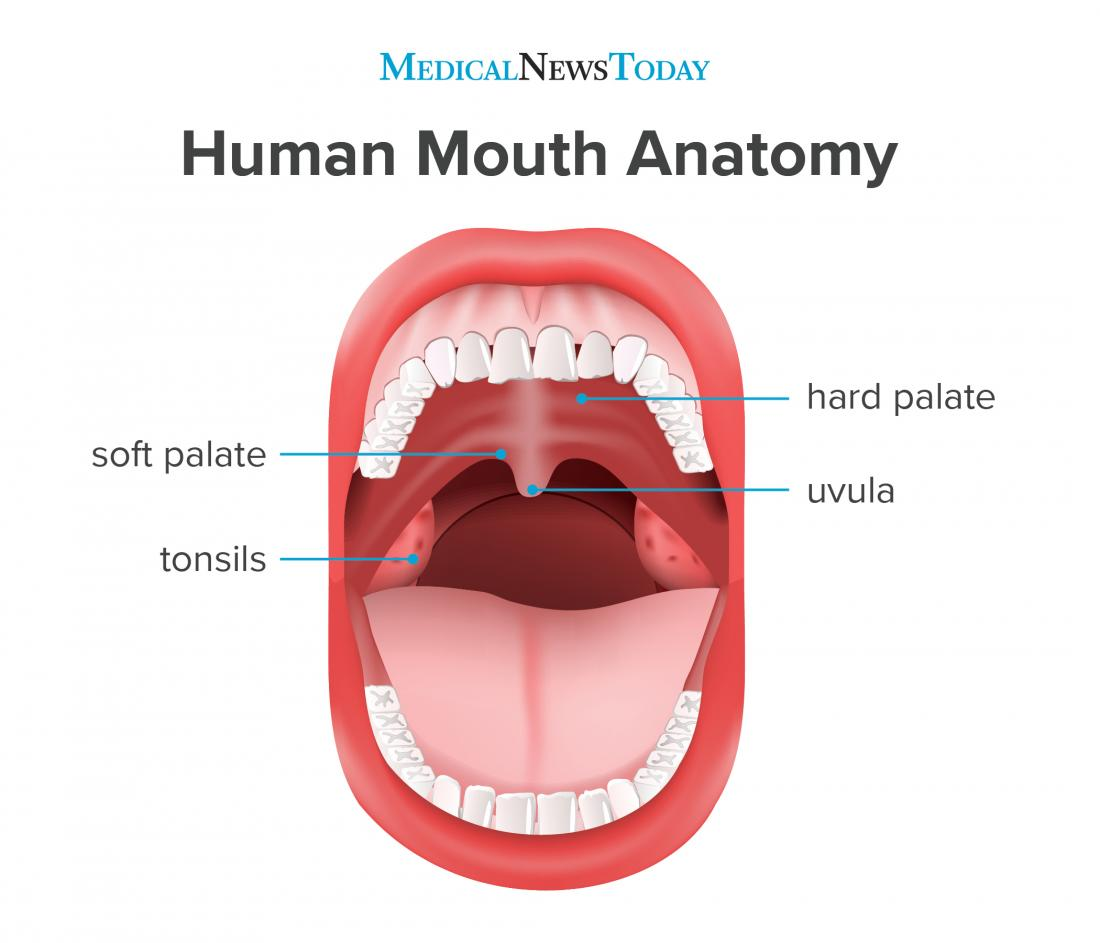
What moves during swallowing?
Soft palate.
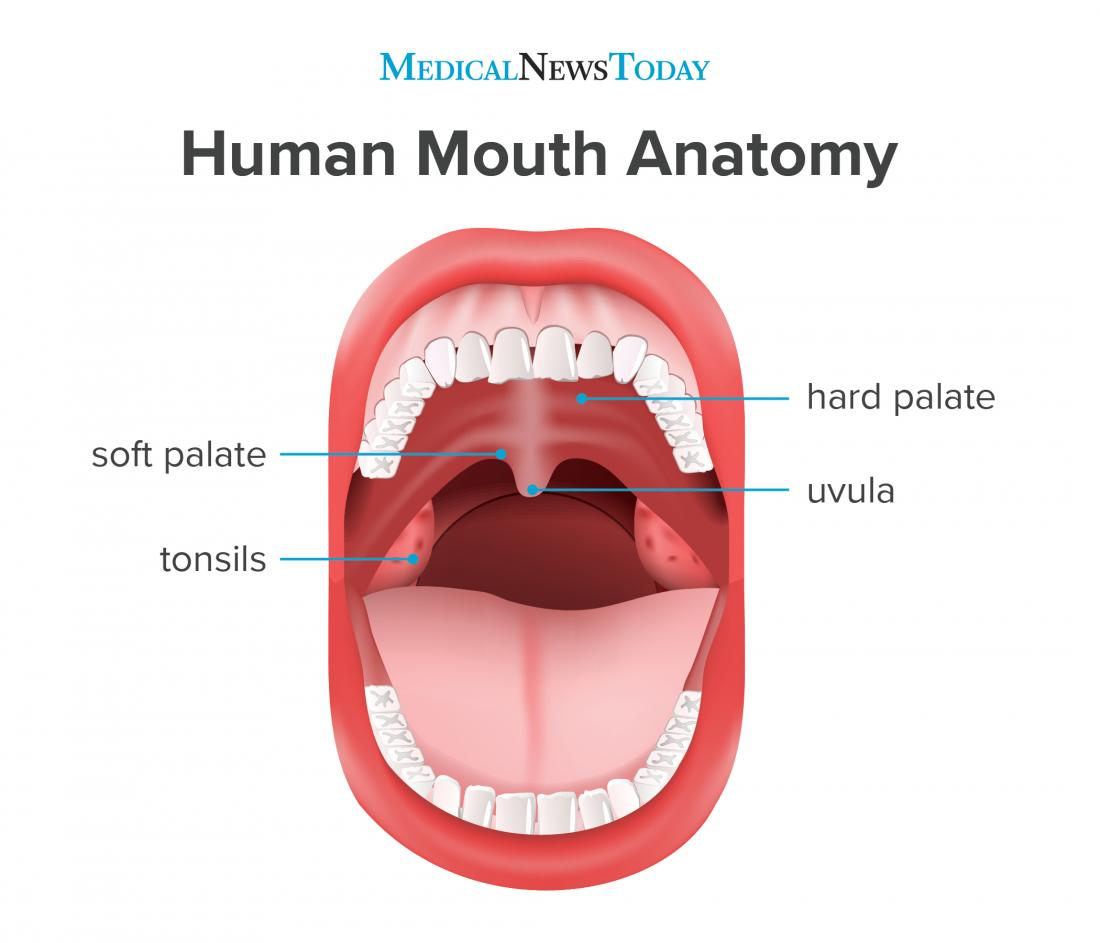
What increases vocal pitch?
Vocal cord tension increases.
What controls airflow resistance?
Bronchioles.
What cleans debris in lungs?
Alveolar macrophages.
What drives gas exchange?
Diffusion.
What do Type II cells make?
Surfactant.
What causes inhalation?
Diaphragm contraction.
What is minimal volume after lung collapse?
Exists after lung collapse.
How much is dead space?
≈150 mL.
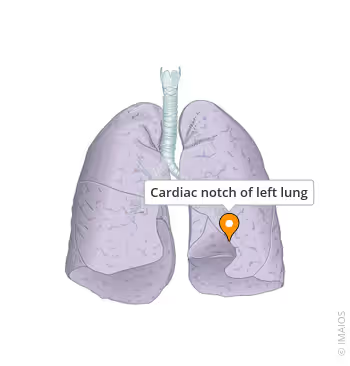
Where is the cardiac notch?
On left lung.
Where does external respiration occur?
In lungs.
Where does internal respiration occur?
In tissues.
Where does oxygen bind?
To heme units.
How is CO₂ transported predominantly?
As bicarbonate.