Exam 1 Plant Phys (ALA 1-7)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What does the RNA hypothesis state?
The RNA hypothesis states that RNA was the primary genetic material and catalyst in early life, preceding DNA and proteins.
Define a plant in a unifying way.
Plants are multicellular photosynthetic organisms.
Name a bryophyte and where it can be found in Houston.
Mosses.
Name an angiosperm and where it can be found in Houston.
Magnolia trees.
Name a monocot and where it can be found in Houston.
Corn.
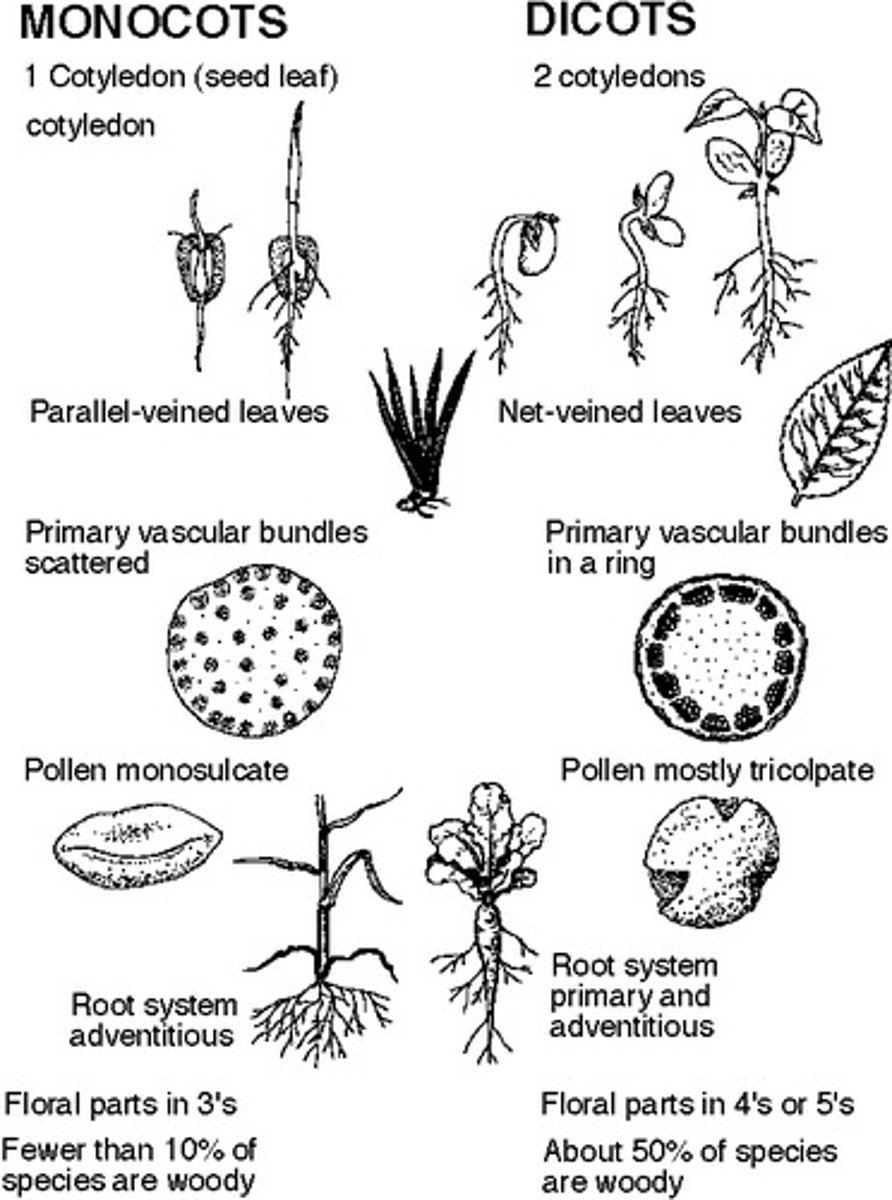
Name a eudicot and where it can be found in Houston.
Soybean.
Where can lipids be found in a plant cell?
In the plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, nuclear envelope, vesicles, vacuole, lipid bodies, chloroplast, and mitochondrial membranes.
What types of amino acids are expected in a transmembrane protein?
All types; uncharged and non-polar in the middle, charged at the ends interacting with the cell exterior.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in plant cells?
It receives mRNAs from the nucleus, facilitates ribosome docking and translation, translocates polypeptides, and packs them into vesicles.
What is the role of peroxisomes in plant cells?
They are the site of fatty acid beta-oxidation, production of plant hormones, and breakdown of toxic metabolites like H2O2.
What is the function of vacuoles in plant cells?
They store water, pigments, noxious chemicals, and hydrolytic enzymes, maintaining osmotic gradient and turgor pressure.
What is the primary function of the nucleus in plant cells?
Storage of DNA and the site of DNA replication and transcription.
What is the function of chloroplasts?
They are the site of photosynthesis found in the cytoplasm.
What is the role of mitochondria in plant cells?
They are the site of cellular respiration found in the cytoplasm.
What is the function of the cytoskeleton in plant cells?
It reinforces the cell and permits transport of subcellular organelles.
What is the role of the cell wall in plant cells?
It provides structural support for growth, protection, and transport.
What are plasmodesmata?
Structures in the cell wall that connect adjacent plant cells.
Where does transcription occur in a plant cell?
In the nucleus.
Where does translation occur in a plant cell?
In the cytoplasm.
What evidence supports the endosymbiotic theory of organelle evolution?
Organelles have metabolic functions similar to bacteria, possess two membranes, have bacterial-like genomes, and divide by fission.
Describe the structure and contents of a vacuole.
A membrane-bound compartment containing water, ions, sugars, amino acids, pigments, and enzymes, maintaining turgor pressure.
What is an example of a non-bilayer membrane in plant cells?
The membrane surrounding oil bodies is a monolayer due to the nonpolar center of the oil body.
What is cytoplasmic streaming?
A process facilitated by cellular machinery that allows the movement of cytoplasm within plant cells.
What role do kinesins and ABPs play in cytoplasmic streaming?
They hydrolyze ATP to power movement along the cytoskeleton, facilitating organelle transport.
What are apical meristems and where are they located?
Regions of cells capable of division and growth found at the tips of roots and shoots, responsible for the extension of the primary plant body.
What are the three anatomical sections of the root?
1) Zone of Division: actively dividing cells; 2) Zone of Elongation: cells increase in length; 3) Zone of Differentiation: cells mature into specialized types.
What is the purpose of the root cap?
To protect the root from environmental stress and assist in gravity perception.
What gases are exchanged in the leaf and their directions?
CO2 enters the leaf, while H2O and O2 exit.
How do trichomes benefit plants?
They increase surface area, reduce water loss, insulate against frost, and protect from herbivores.
What is vascular cambium and its function?
A ring of secondary meristematic cells that increases the diameter of stems and roots and forms woody tissue.
What are the benefits of plastid transformation in crop development?
Simplified breeding, more powerful traits, higher yields, easy trait stacking, and trait containment.
Why is only ~10% of genes expressed in a given cell at any time?
Each cell type requires different genes to be active based on its specific functions.
How can controlling plasmodesmata help plants respond to stresses?
Closing plasmodesmata can prevent virus spread during infection, while opening them can facilitate nutrient transfer during biotic stress.
What is the role of transvacuolar strands in cytoplasmic streaming?
They allow tethered organelles to move across the plane of a cell, aiding in streaming.
What is the function of guard cells in leaves?
To regulate the opening and closing of stomata, controlling gas exchange and water loss.
What is the significance of the palisade mesophyll in leaves?
It is the primary site for photosynthesis due to its high chloroplast density.
What is the function of the spongy mesophyll in leaves?
To facilitate gas exchange and allow for the diffusion of CO2 to the palisade mesophyll.
What is the role of xylem in plants?
To transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.
What is the role of phloem in plants?
To transport sugars and nutrients produced by photosynthesis from leaves to other parts of the plant.
What is the function of bundle sheath cells?
To protect vascular tissue and regulate the flow of substances between the mesophyll and the vascular system.
How do environmental factors influence cytoplasmic streaming?
Cytoplasmic streaming often occurs in response to light and during cell growth.
What is the impact of chloroplast traits being maternally inherited?
It eliminates the risk of transgene escape via pollen, addressing environmental and regulatory concerns.
Why might chloroplast transformation speed up time to market for crops?
It reduces the breeding process to one cross, as chloroplast traits are inherited only through seeds.
What is the benefit of higher trait expression in chloroplasts?
It results in a higher dose of traits, making them more effective against pests and reducing resistance development.
What is the significance of the upper and lower cuticle in leaves?
They provide a protective barrier against water loss and environmental stress.
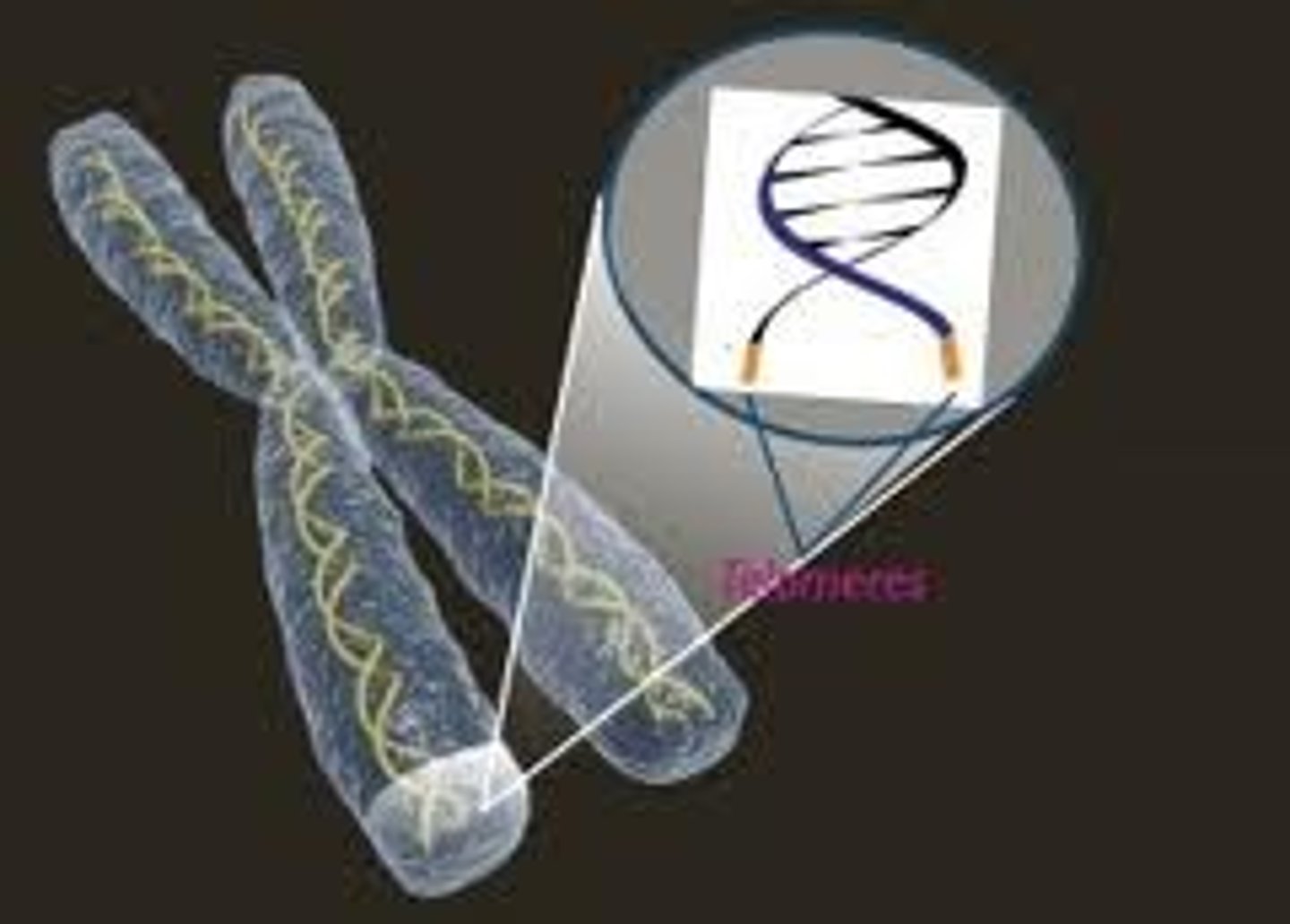
Where is the centromere?
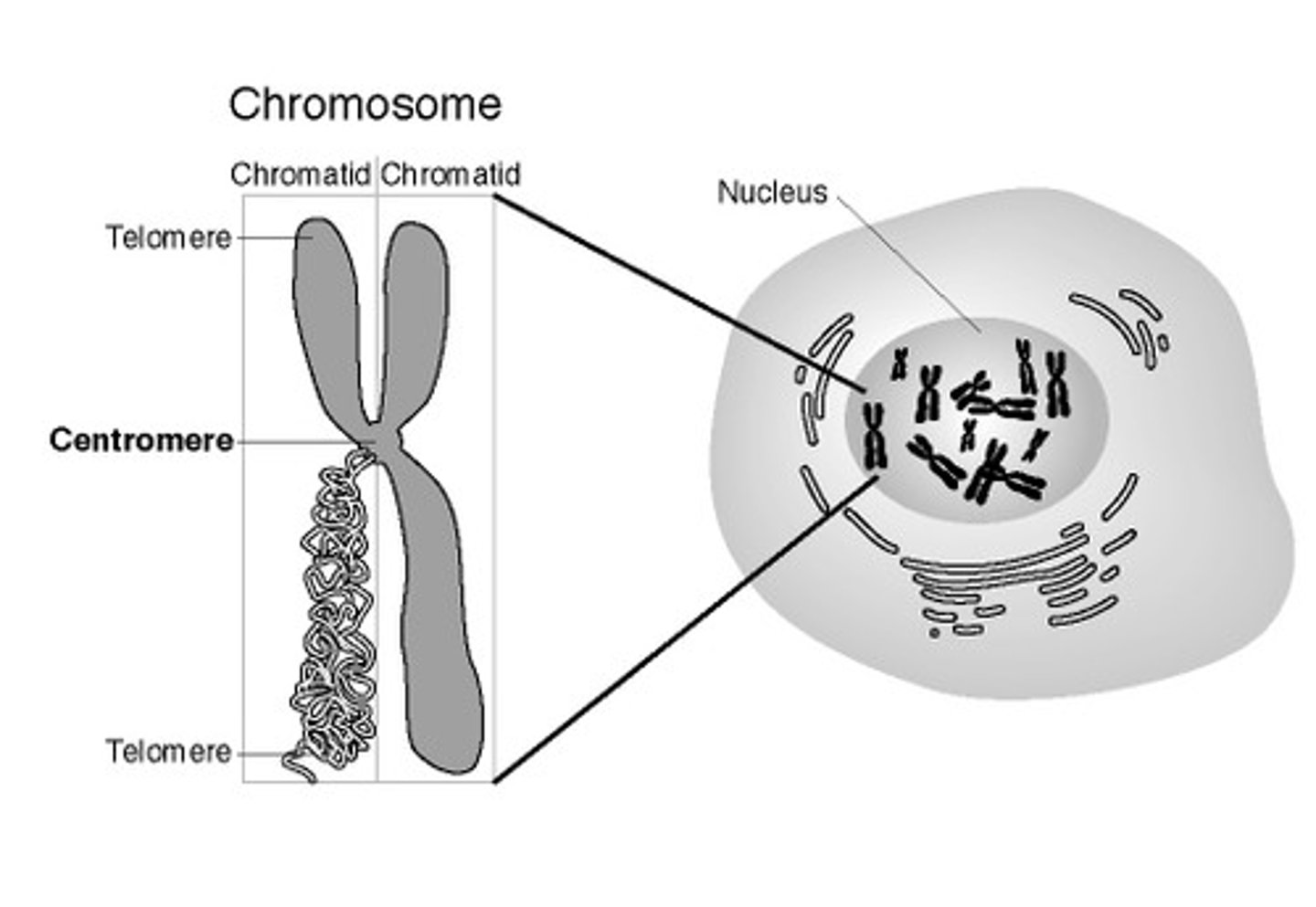
where is the telomeres?
What is an example of an allopolyploid plant?
Strawberry, wheat, peanut, coffee, blackberries.
What is an example of an autopolyploid plant?
Potato, sweet potatoes, banana (can be both).
What does the C-value paradox refer to?
The lack of correlation between genome size and gene number across different organisms.
Why might larger genomes not correlate with higher gene numbers?
Larger genomes often contain non-protein coding DNA, repetitive DNA, and transposable elements.
What determines the complexity of an organism if not the number of genes?
Gene expression and the regulation by transcription factors.
What is the role of Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization (FISH)?
To mark specific regions of the genome using fluorescently labeled probes.
How do plants regulate transposon activity?
Through epigenetic regulation, silencing, DNA methylation, and small RNAs.
What are the consequences if plants cannot regulate transposon activity?
It can lead to genome instability, large-scale rearrangements, and altered gene expression.
Why is meiosis I crucial for genetic diversity?
It allows crossing over of homologous chromosomes and random alignment of chromosomes.
What challenges do plant genomes present compared to animal genomes?
They are often larger, highly repetitive, polyploid, and subject to structural rearrangements.
How does polyploidy complicate genome assembly?
High sequence similarity between subgenomes can lead to misassignment of reads.
What is the primary reason bananas are threatened by Panama disease?
They are clonally propagated, leading to a lack of genetic diversity.
What is the significance of the term 'clonally propagated' in relation to bananas?
It means all bananas are genetically identical, increasing vulnerability to diseases.
What is the impact of non-coding regions on genome complexity?
Non-coding regions make up most DNA and contribute to the regulation of gene expression.
What types of DNA are likely found in larger genomes?
Non-protein coding DNA, repetitive DNA, and transposable elements.
What is the role of small RNAs in plants?
They mediate post-transcriptional gene regulation and help silence transposons.
What happens during anaphase I of meiosis?
Crossing over occurs, leading to new combinations of alleles.
What is the significance of random chromosome alignment during Metaphase I?
It ensures that each gamete receives a random mix of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
What are activators in gene expression?
Positively acting transcription factors that bind to DNA and increase gene expression, usually by recruiting RNA Pol II.
What is the function of enhancers in gene regulation?
Distal regulatory sequences that can be located kilobases away from the promoter, where transcription factors bind to promote transcription.
What role do repressors play in gene expression?
Negatively acting transcription factors that bind to DNA and repress gene expression.
Define cis-acting elements.
DNA sequences adjacent to the gene they regulate, which are bound by transcription factors.
What are trans-acting elements?
Transcription factors that bind to cis-acting elements to drive transcription.
What epigenetic marks are associated with repressive gene models?
DNA methylation and histone methylation marks that inhibit transcription.
What activating marks might be found in active gene models?
Histone acetylation and DNA demethylation, which can lead to gene activation.
What is the role of small RNAs like miRNAs and siRNAs in gene regulation?
They function in post-transcriptional gene regulation, with miRNAs cleaving target mRNAs or inhibiting translation, while siRNAs are involved in RNA-directed RNA methylation or silencing.
How are miRNAs generated?
Encoded in the genome, transcribed by RNA Pol II into pri-miRNA, then processed into pre-miRNA and cleaved into mature miRNAs by DICER-LIKE proteins.
What is the effect of phosphorylation on protein function?
Phosphorylation generally activates protein function, influences protein shape, localization, interactions, and can mark proteins for degradation.
What region of the primary transcript is removed by a spliceosome?
Introns (Region E).
Where is the TATA box located?
In the promoter region (Region B).
Where is the poly (A) tail added to the transcript?
At the 3' UTR (Region F).
Where is the 5' cap added to the transcript?
At the transcriptional start site (Region C).
What type of regulation occurs in Gene A during drought stress?
Transcriptional activation, as both RNA and protein levels increase.
What type of regulation is observed in Gene B during drought stress?
Post-transcriptional regulation, where RNA levels are stable but protein is produced only under drought conditions.
What happens to Gene C during drought stress?
Both RNA and protein levels decrease, indicating transcriptional repression or post-transcriptional silencing.
What occurs with Gene D's RNA and protein levels during drought stress?
RNA levels remain stable, but protein abundance decreases, suggesting translational regulation.
What does it indicate if Gene E's RNA and protein levels are steady during drought?
The gene may not be regulated by drought stress or could be subject to post-translational modification.
Why do viruses evolve proteins that block RNA silencing?
To inhibit the siRNA-mediated mechanisms that recognize and degrade viral RNA, allowing for infection.
Why is it beneficial for plants to regulate flowering through epigenetic switches?
Epigenetic regulation is faster and reversible compared to permanent DNA mutations, allowing for adaptation to environmental cues.
Why might protein degradation be preferred over shutting off transcription?
Degradation is faster and more effective in stopping a protein's function than merely turning off transcription, which leaves RNA available for translation.
How do agrobacteria contribute to transgenic crop formation?
Agrobacteria infect plants by inserting a region of their genome (T-DNA) into the host genome, allowing scientists to insert genes of interest.
What are sequence-specific nucleases (SSNs) and their role in genetic modification?
SSNs lead to single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or small indels through DNA repair mechanisms like homologous repair (HR) and non-homology end joining (NHEJ).
How do Bt crops function?
Bt crops contain a gene encoding an endotoxin that kills pests like the European corn borer when ingested.
What effect does targeting the promoter region with CRISPR gRNA have?
Mutations in the promoter can affect transcription, potentially leading to lost expression or increased activity of the gene.
What happens if CRISPR gRNA targets the start codon?
Mutations at the start codon would likely prevent translation of the gene.
What is the impact of targeting an intron with CRISPR gRNA?
Mutations within an intron probably would not affect the gene product or protein.
What occurs when CRISPR gRNA targets the exon-intron junction?
Mutations at the splice site can result in mis-splicing, leading to intron retention or cryptic splice sites.
What is the consequence of targeting the stop codon with CRISPR gRNA?
Mutations at the stop codon likely prevent translation termination, resulting in a longer, potentially non-functional protein.
What is the significance of the AaMYB1 gene in artemisinin production?
The AaMYB1 gene promotes trichome formation and artemisinin synthesis in sweet wormwood (Artemisia annua).
How can the production of more MYB1 mRNA be achieved?
Modifying the promoter of the MYB1 gene would likely increase mRNA production.
What components are needed in a transgene/T-DNA for Agrobacterium infiltration?
A transgene/T-DNA includes the gene of interest (e.g., MYB1), an antibiotic resistance gene, and left and right borders (LB and RB).
What historical plant-derived compound has been used to combat malaria?
Quinine, isolated from the bark of the Cinchona plant, has been used for centuries as an antimalarial drug.
What is the role of artemisinin in malaria treatment?
Artemisinin, extracted from sweet wormwood, is an integral therapy for controlling malaria infections and transmission.