Indirect Taxes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
indirect tax
A tax levied on expenditure on goods or services
They reduce the supply of the good by artificially increasing the cost of production
E.g. Value added tax (VAT) & excise duties such as those on cigarettes or petrol
Different to a 'direct' tax, which is a tax charged directly to an individual based on a component of income
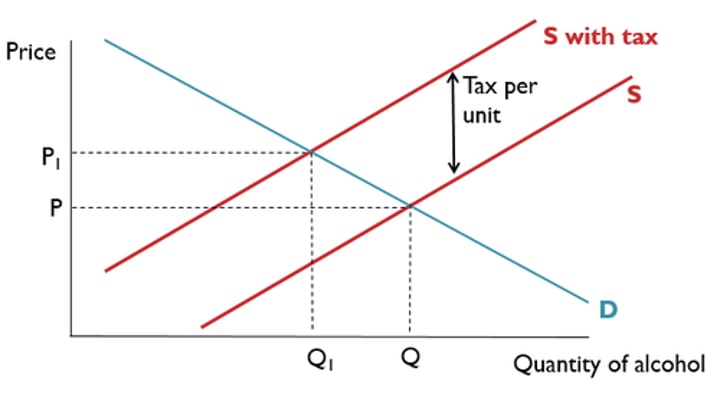
Specific taxes definition
a fixed tax per unit of the good or service produced
Shifts the supply curve inwards and maintains gradient
E.g. Air passenger duty of £12 per flight for domestic flights
Specific taxes diagram
Ad Valorem taxes diagram
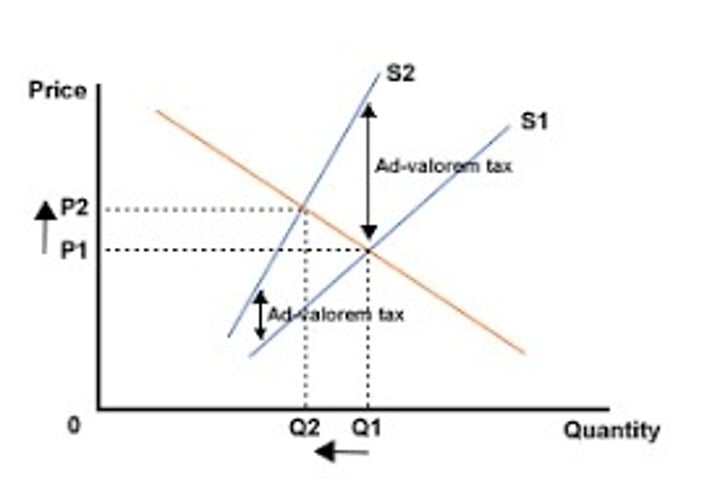
Ad Valorem taxes definition
a percentage tax of the unit cost of a good
Pivots the supply curve inwards and increases gradient
E.g. VAT (currently at 20% in the UK)
Impact of Indirect taxes
Indirect taxes lead to an increased price and reduced quantity traded of the good or service
Why would a government want to implement an indirect tax?
To raise tax revenue to fund government spending
To change (a) the level of demand and (b) the pattern of demand for different goods and services
Indirect taxes are flexible - easy to change
To raise tax revenue to fund government spending
Indirect taxes can be a powerful fiscal policy tool
To change (a) the level of demand and (b) the pattern of demand for different goods and services
To deter and reduce the consumption of goods and services considered to be harmful (de-merit goods and negative externalities)
To encourage the longer-term conservation of scarce economic resources (e.g. fuel)
Indirect taxes are flexible - easy to change
Allowing governments to quickly intervene in markets when necessary
Also harder to avoid
Economic Incidence (or burden)
Indicates the extent to which someone is made worse off by the tax, i.e. the amount they pay.
incidence of tax diagram
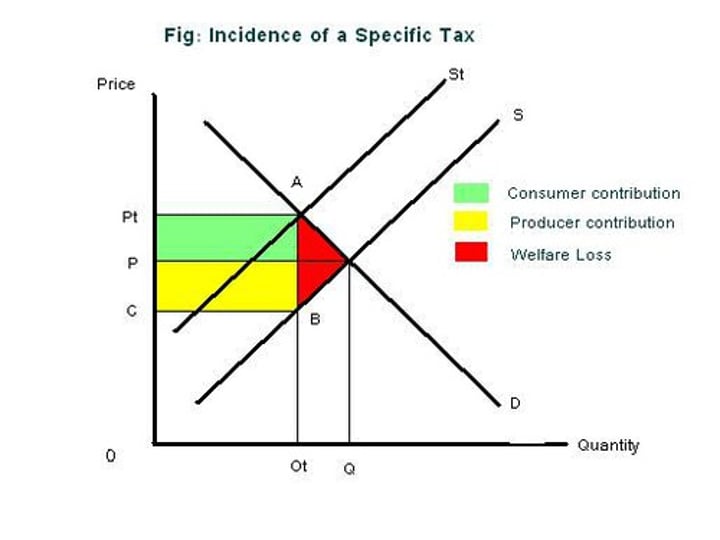
who pay's most of the tax based on PED?
Elastic PED: Producers pay most of the tax
Perfectly Elastic PED: Producers pay all the tax!
Inelastic PED: Consumers pay most of the tax
Perfectly Inelastic PED: Consumers pay all the tax!
Limitations of Indirect Taxes
Indirect taxes can be regressive
Inflation
Gov failure
Can be ineffective
Uncertain government revenue
Loss of economic welfare
Indirect taxes can be regressive
The implementation of indirect taxes on certain goods can mean that poorer individuals pay a greater proportion of their income on these taxes
The tax burden is heaviest on poorer households, meaning a more unequal distribution of income
E.g. Alcohol duties
If a person earning £200 a week buys two pints of lager on a Friday and pays about £1 in total in beer duties, representing 0.5% of their income
But a richer person earning £600 a week buys four pints of the same lager, paying £2 in total in beer duties, representing only 0.33% of their income, despite consuming twice as much!
Inflation
Higher taxes leads to higher prices as suppliers pass on part of the tax by raising prices
Particularly an issue when PED is inelastic
Gov failure
If indirect taxes are set too high, it creates an incentive to avoid taxes through "boot-legging" and smuggling
These boot-legged goods can often be even more harmful are less likely to be made to same standards as legitimate products.
Can be ineffective
If demand is inelastic, indirect taxes have little effect on the amount consumed
The tax just pushes up prices, potentially further worsening income equality through their regressive nature
Uncertain government revenue
If a market is volatile, the amount raised from indirect taxes can be uncertain
Particularly during a recession / downturn
Loss of economic welfare
Higher prices and lower output causes a loss of consumer and producer surplus
The fall in CS and PS outweighs the gain in government revenue, leading to a DWL