National 5 Business Management - Management of Marketing and Operations
1/201
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
Marketing
The process of identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer needs while achieving business goals.
Purpose of Marketing
To satisfy customer needs, inform about products, increase sales, and improve image.
Importance of Marketing
Helps businesses meet customer needs and promote products effectively using the 4Ps.
Successful Marketing Mix
The right product, sold at the right price, in the right place, with the right promotion.
4Ps of Marketing (Marketing Mix)
Product, Price, Place, Promotion – the main elements of a marketing strategy.
Market Share
The percentage of total sales in a market made by one company.
Market growth
The increase in total sales or size of a market over time.
Customer
The person or organisation that buys and uses a product or service.
Target market
A specific group of customers a business aims its products or services at.
Benefits of Target Marketing
Improves customer satisfaction, loyalty, pricing accuracy, and marketing efficiency.
Market Segmentation
Dividing customers into groups based on characteristics such as age, gender, income, religion/culture, lifestyle.
Segmentation by Age
Products targeted at specific age groups (e.g., toys for children).
Segmentation by Gender
Products designed for men or women (e.g., perfume/aftershave).
Segmentation by Income
Products aimed at different income levels (e.g., luxury brands vs. discount stores, Waitrose target people with a higher income).
Segmentation by Religion/Culture
Products tailored for beliefs or cultures (e.g., halal meat).
Segmentation by Lifestyle
Products based on interests or hobbies (e.g., gym memberships).
Advantages of Market Segmentation
Products can be aimed at specific needs, increasing customer satisfaction and sales.
Disadvantages of Market Segmentation
More market research is required (costly); smaller target markets can limit sales volume.
Market Research
Gathering, analysing, and interpreting data about customers, competitors, and trends.
Purpose of Market Research
To identify customer needs, test new ideas, and gather competitor information.
Field Research (Primary)
Collecting new, first-hand information for a specific purpose.
Advantages of Field Research
Up-to-date, relevant, reliable, specific.
Disadvantages of Field Research
Expensive and time-consuming, requires trained staff.
Desk Research (Secondary)
Using existing information gathered by others.
Advantages of Desk Research
Cheap, quick, and readily available.
Disadvantages of Desk Research
May be outdated, biased, or irrelevant.
Methods of field research
Postal Survey, Telephone Survey, Focus Group, Personal Interview, Online Survey, Social Media Research, Loyalty Cards
Postal Survey
Questionnaire sent by mail – cheap but low response rate.
Telephone Survey
Questions asked over the phone – fast but may annoy customers.
Focus Group
Small group discussion for opinions – detailed feedback but costly.
Personal Interview
Face-to-face questions – in-depth information but time-consuming.
Online Survey
Digital questionnaire – quick and inexpensive but may miss some audiences.
Social Media Research
Gathering opinions from online users – wide reach but public.
Loyalty Cards
Track customer purchases for research – useful data but privacy issues.
Methods of desk research
Internal records, Newspapers, Magazines, Websites, Government Statistics, Social Media
Internal Records
Company data such as sales figures, invoices, and previous reports used for desk research.
Newspapers
Print or online daily/weekly publications used as a source of market news and trends.
Magazines
Periodicals (often specialist) used to find industry-specific information and adverts.
Websites
Online company, industry or news sites that provide up-to-date information and statistics.
Government Statistics
Official data (e.g., census, trade figures) used for reliable market facts.
Social Media (as desk source)
Public posts, pages and analytics used to spot trends and customer sentiment.
Distinguish between Desk Research and Field Research
Desk research uses existing sources and is cheaper/quick; field research gathers new, first-hand data and is more specific but costlier.
Product
The goods or services a business sells to meet customer needs.
Product Development
The process of creating, testing, and launching new products.
Stages in Product Development
Carry out market research → Generate the idea → Analyse the idea → Produce a prototype → Test the product → Alter/Improve the product → Launch/Produce the product.
Advantages of New Product Development
Meets customer needs and can increase profit.
Disadvantages of New Product Development
Time-consuming, expensive, and may fail.
Product Life Cycle
The stages a product goes through – Introduction, Growth, Maturity, Decline.
Introduction Stage
New product launched, few sales, heavy promotion.
Growth Stage
Rapid sales increase, profits rise.
Maturity Stage
Sales peak, high competition, stable profit.
Decline Stage
Sales fall, product withdrawn.
Price
The amount of money customers are willing to pay for a product.
Factors Affecting Price
Production costs, competition, quality, profit margin, and market demand.
Cost-plus Pricing
Adding a percentage profit to the cost of making the product.
Competitive Pricing
Setting prices similar to competitors.
Price Skimming
High price at product launch, then reduced later.
Penetration Pricing
Low initial price to attract customers, then increased later.
Promotional Pricing
Temporary low price to boost short-term sales.
Destroyer Pricing
Very low prices to eliminate competitors.
Psychological Pricing
Making prices appear cheaper (e.g., £9.99 instead of £10).
Premium Pricing
Setting a higher price to create a luxury image.
Advantages of Competitive Pricing
Attracts price-sensitive customers; avoids price wars.
Disadvantages of Competitive Pricing
Limits profitability; less differentiation.
Brand
A name, symbol, or design used to identify a product or business.
Advantages of Branding
Creates recognition and loyalty; allows higher prices; helps launch new products.
Disadvantages of Branding
Expensive to create and maintain; damage to one product can harm the brand image.
Own Brand Products
Goods sold under a retailer’s own name (e.g., Tesco Finest).
Advantages of Own Brand Products
Cheaper for customers; no expensive advertising.
Disadvantages of Own Brand Products
May be seen as lower quality; poor product can hurt reputation.
Packaging
The materials and design used to protect, promote, and present a product.
Advantages of Packaging
Protects products, attracts customers, provides legal and product information.
Disadvantages of Packaging
Adds cost, can harm the environment, may require strict labelling.
Consequences of Poor Packaging
Damaged goods, customer complaints, reduced sales, poor reputation.
Place
Where and how a product is made available to customers.
Business Location Factors
Proximity to customers, transport links, skilled workers, grants, competition, parking.
Advantages of Good Location
Attracts more customers; reduces delivery costs.
Disadvantages of Poor Location
Lower sales, higher transport costs.
Methods of distribution
Road, Rail, Air, Sea
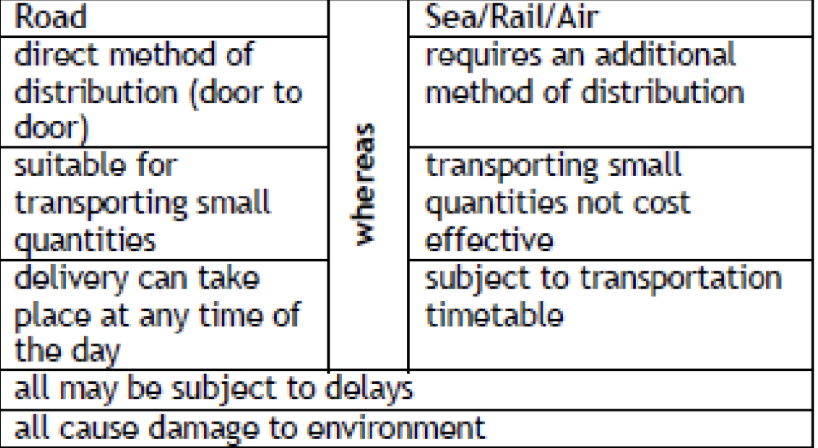
Road
The road network is used to transport goods using large trucks, lorries and vans.
Road Advantages
Can be cheaper than other methods, Many types of good can be delivered, can be delivered to the customer’s door.
Road Disadvantages
Speed limits mean goods may be delayed, Fuel costs are high, Traffic jams and road works can cause delays.
Rail
The rail network is used to transport goods.
Rail Advantages
Less delays than road, Large orders can be transported.
Rail Disadvantages
Train station may not be close to delivery destination.
Air
Goods are delivered by aircraft
Air Advantages
Goods can be delivered world-wide, Quicker than by sea.
Air Disadvantages
Can be expensive, Airports may not be close to destination.
Sea
Goods are delivered by sea/boat/ship
Sea Advantages
Goods can be delivered world-wide, Can transport large products.
Sea Disadvantages
Can be expensive, Can be time-consuming.
Factors Affecting The Method Of Distribution
Size, Distance, Time Required, Product Perishability
The size of the product
large items may often be delivered by rail as they cannot travel safely by road.
The distance of the delivery
if an item is to travel abroad then it is likely to go by air or sea as road will take too long.
How quickly the item is required
UK items will be delivered by road as they can go directly to the location/railway stations are not found in every town.
The perishability of the product
the method of transport must be capable of keeping the item in a safe way such as refrigerated lorries.
Comparing Methods of Distribution

E-Commerce
Selling goods online 24/7 to a global market.
Advantages of E-Commerce
24/7 availability, global reach, reduced costs, customer data collection.
Disadvantages of E-Commerce
Website setup costs, delivery delays, cybersecurity risks.