6 Labour Markets
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Perfectly Competitive Labour Market
Where wages are set by supply and demand, and neither firms nor workers have market power — all are price (wage) takers.
Supply of Labour (to employer)
Supply curve of firm
Employer’s labour supply depends on market structure
If employer is wage taker, supply curve will be perfectly elastic (horizontal).
If employer is wage maker, supply curve will be upward sloping (less elastic)
Supply Curve = MCL = W (Horizontal)
Supply of Labour (to market)
Depends on
Number of qualified people
Non wage benefits/costs oj job and other jobs
What does wage elasticity of Labour Supply depend on
Depends on
Difficulty to change jobs (easier to change jobs, more elastic)
Whether long-run or short-run (more elastic in short run)
Demand for Labour (of Firm)
Shape of curve
Downward Sloping Curve
D = MRPL
MRPL = p x MPPL (Marginal Physical Product of Labour)
What is MRPL?
Marginal Revenue Product of Labour
MRPL = p x MPP
additional revenue a firm earns from hiring one more unit of labour, holding all else constant.
What is MPPL?
Marginal Product of Labour
additional output produced by hiring one more unit of labour, keeping all other inputs (like capital) constant.
Assumptions of Perfectly Labour Markets
Firms operate in Perfectly competitive market
Buy as much labour without affecting wage rate.
Wage takers, so w = MCL (Marginal Cost of Labour) = horizontal
Workers are Wage Takers
Complete information for buyers and sellers
Free Entry for Workers
Market Structure Perfectly Labour Market
S Many, Small firms
B Low Barriers to entry
D Undifferentiated Products
BU Many, Small Buyers
Find Profit Maximising Position (E) of an Individual firm: PLM
What happens to Labour Demanded (MRPL) if output price falls?
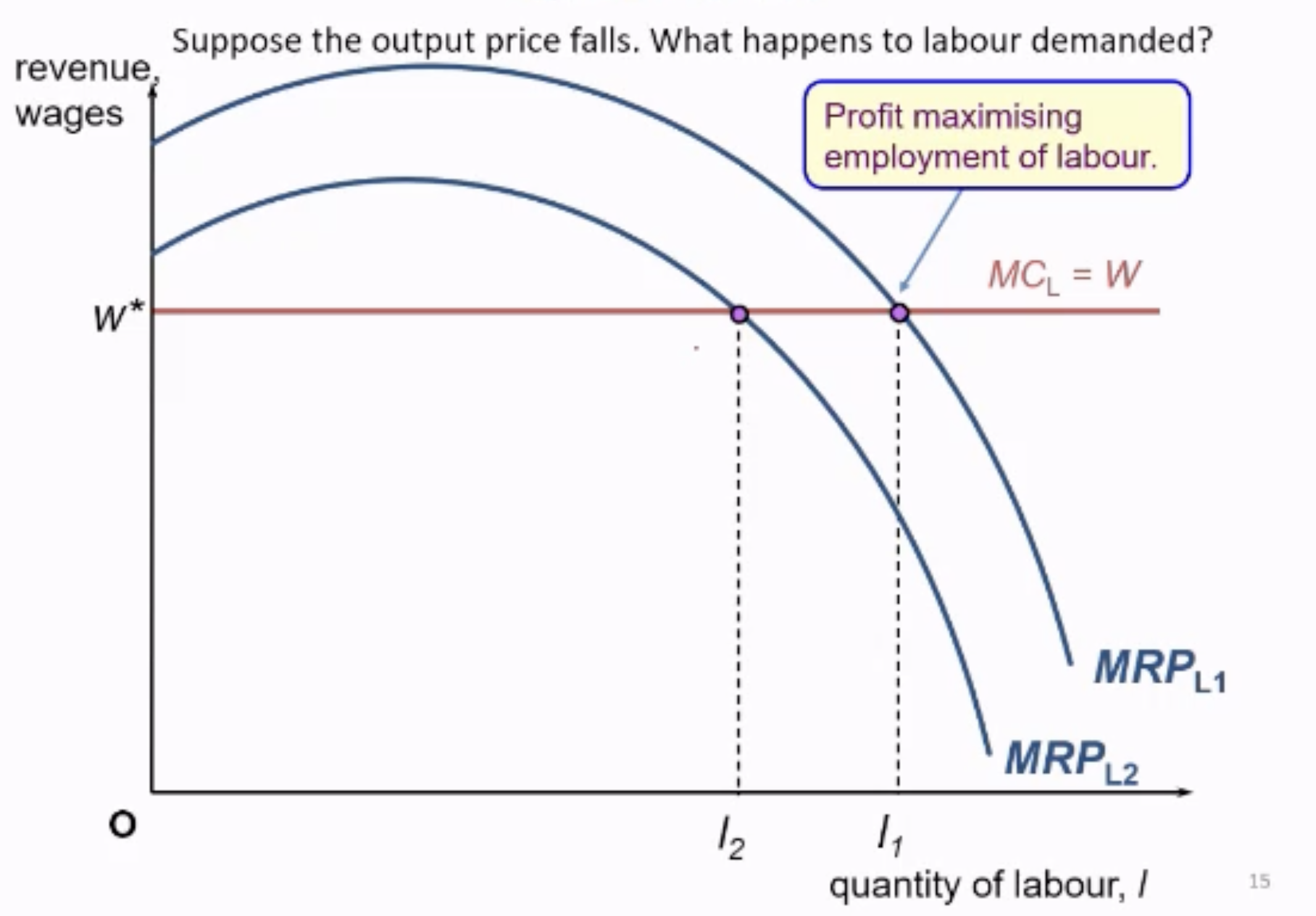
When MCL = MRPL
When output price fall MRPL shifts down, reducing the quantity of labour demanded by firms.
Find SR Equilibrium of PCLM
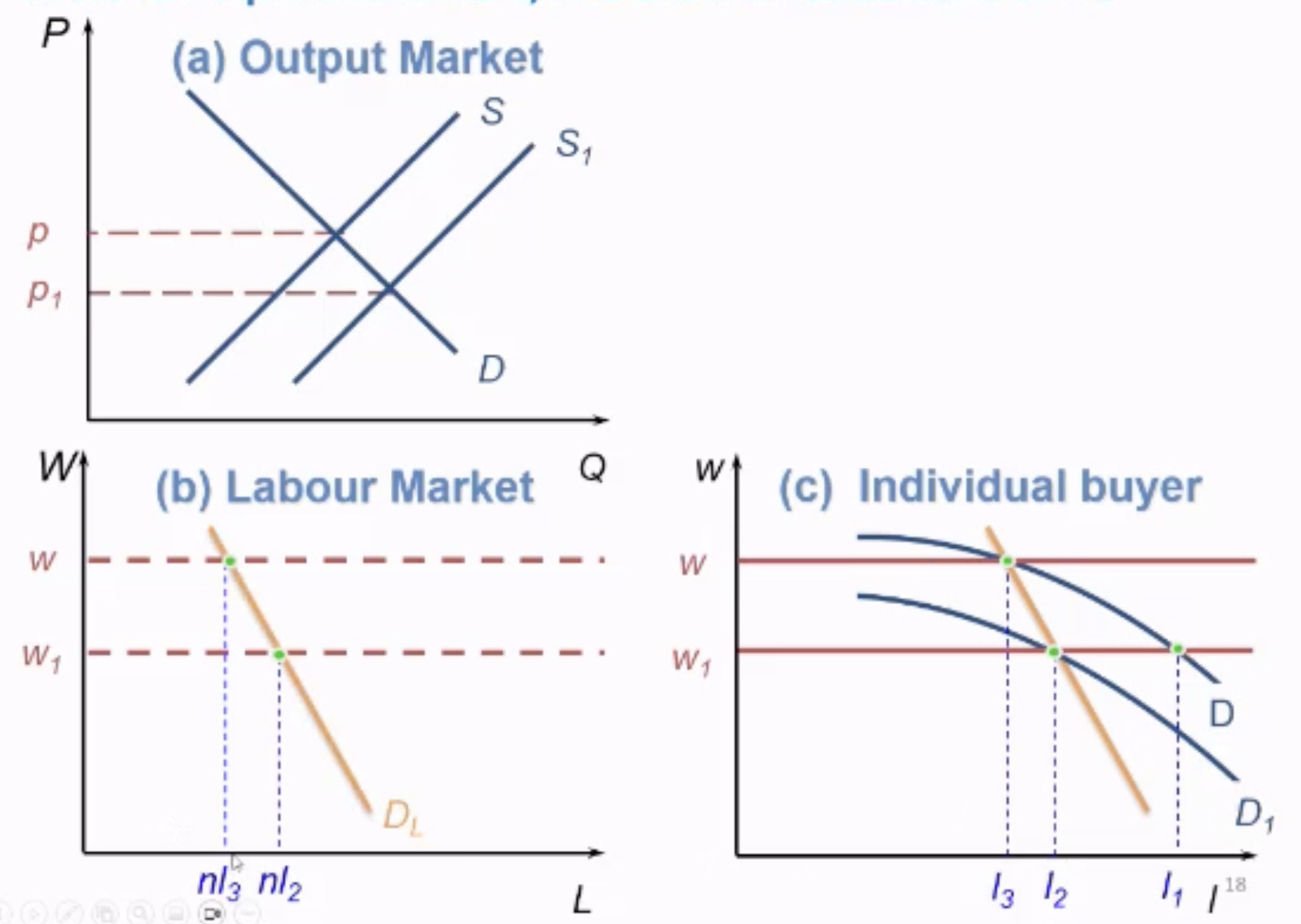
Find Buyers Demand Curve
Find Equil. Price in output market
Given price, draw D, MRPL curve for individual buyer
FInd Labour Market Demand Curve
Find demand of individual buyer at lower wage, shifting D —> D1
Draw a line connecting the 2 points of Equil. Labour of individual buyer at 2 different wages.
This forms labour market Demand Curve
To find E put Labour Supply Curve
Imperfect Labour Market
When employees and/or firms are wage makers
e.g. Monopsony
Monopsony
When there is one large buyers of a particular good or service
Monopolist of labour market
Employees are wage makers when
They have unique talent
Create a union and makes threats if demands aren’t met
Monopsony Assumptions
Similar to Perfect Competition
Firm in Competitive Output Market
Firm is Wage Maker in Labour Market (Only difference)
Higher wages needed for increased labour employment.
Complete Information for workers
Workers are wage takers
Free entry for workers
Market Structure of Monopsony
Remember workers are considered as sellers
S. Many, Small Sellers (Workers)
So change in worker’s supply has luttle effect on wage.
B. One Larger Buyer (Firm)