Large animal nursing: pigs + camelids
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Pig common name
porcine
Wild pig scientific name
sus scrofa
Domestic pig scientific name
sus scrofa domesticus
Domestic pig relatives
warthog *think pumba
pygmy hog (endangered)
Anatomy and physiology of pigs
cannot sweat (pants)
harvesting weight = 250 lbs
milk production: anterior teats > posterior teats

duroc: red pig

chester white
pink, droopy ears
highly susceptible to sun-scald
no free-reign diet

berkshire
black/white, erect ears
resistant to sun-scald
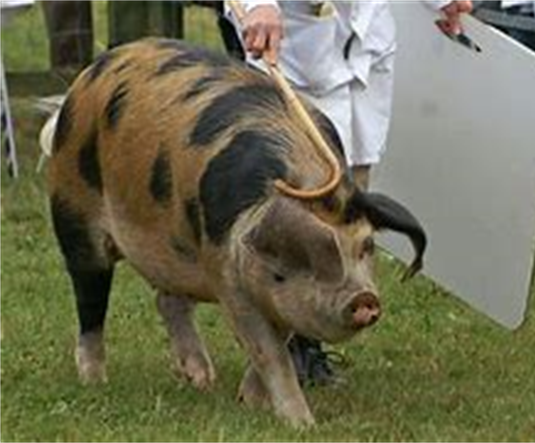

spotted: black/white spots

Pot-belly: black with white straight tail

hampshire
black/white belt
lean muscle, high carcass quality, large loins, minimal backfat

landrace
white, BIG droopy ears
highly susceptible to sun-scald
no free-reign diet

saddleback: black with white band, droopy ears

tamworth
brown, erect ears
resistant to sun-scald
ideal breeders
Farrowing
pig giving birth
Pig gestation
3 months, 3 weeks, 3 days
Piglets per litter
6-14
Barrow
castrated male pig
Boar
intact male pig
Runt
smallest piglet
Shoat/hoag
growing piglet
Gilt
pig reaching sexual maturity at 8 months
Mummification
dead piglets carried to term weighing 2.5 pounds or less
Split-suckle
seperating litter into assigned feeding times
Cross-fostering
reduce weight variation among the piglets
Creep feeding benefits
promote gut + digestive health
improve growth rate
allow for better weaning transition
Maternal line
increased pigs/litter size, milk production, docile temperament
Terminal line
fast growth, meaty, lean, durable
Plastic sorting boards
helps us move pigs
note hold firmly
Rattle pads
visual and auditory aid to help move pigs
Invading pig’s flight zone
will move away from you
Approaching a pig from behind the shoulder
the pig will move forward
Euthanasia in pigs
captive bolt: penetrating(brain)/non-penetrating
electrical stunning: pigs/sheep, tonic/clonic phase
CO2: most common, irritates respiratory tract, 20 seconds to take effect
Piglet processing
tail docking, castration, iron injection, cut umbilical cord, extract needle teeth
Piglet tail docking
clippers: pull skin of tail toward rump and cut
Cauterization: hold tail and cauterize
Piglet castration
no anesthesia
Immunocastration
pros: less invasive, better-quality meat, improves growth
cons: strict administration times, regulations/market acceptance
Ear notching system
left = individual
right = litter number
Pig blood draw sites
lateral auricular vein (marginal ear): 45 degrees angle
jugular vein: most common; 90 degree angle
Types of pig injections
SQ
IM: most common, lateral neck muscles
Porcine congenital splay leg syndrome
aka pcs
one of the most common causes of piglet death
tape legs together to prevent
if front and back legs are affected = euthanasia
PSS
aka malignant hyperthermia, transport myopathy, soft-pale exudative pork
ryanodine receptor (RYR1): large release sustained muscle contraction and increased metabolic rate, excess heat production
Aujeszky’s disease
aka pseudorabies
cns signs in piglets
Exudative edpidermitis
aka greasy pig
Osteomalacia
malnourished bones due to poor diet and waste food (pig swill)
Mastitis
mammary gland inflammation
Metritis
uterine infection
Aglactica
decreased milk production
Sodium chloride toxicity
due to dehydration
Atrophic rhinitis
caused by bordetella bronchiseptica
White scours
caused by e. coli
Tylopoda
calloused foot in pigs
Artiodactyle
even-toed
Huarizo
alpaca and llama hybrid
Kushing
camelid laying down + folding their forelimbs over their hindlimbs
Cria
baby camelid
Camelid GI tract
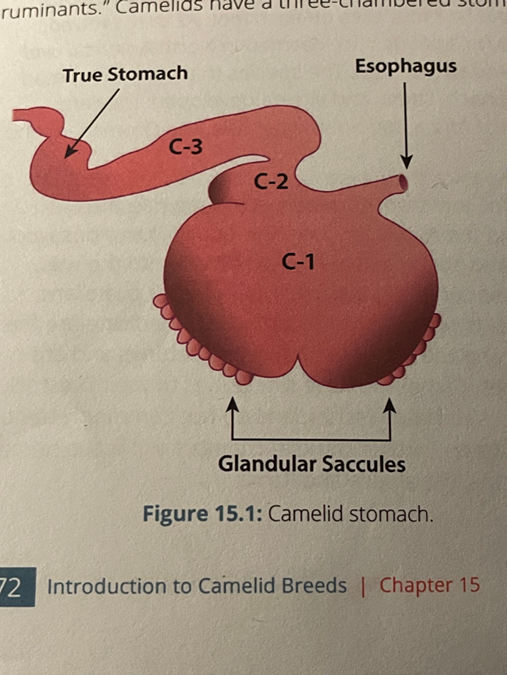
dental pad
regularly scheduled feedings
C1 = rumen, C2 = reticulum, C3 = abomasum
Camelus dromarius
aka dromedary
one-humped camel
Camelus bactranius
aka bactranian
two-humped camel
Wild bacterian
Red blood cells can expand to 240% to allow larger volumes of water
Gestation: 13-15 months
Mature 7 years
aka camelus ferus
Vicuna
smallest camelid
lives in south america
deer-like frame
Llamas appearance
ears: long curved bananas
straight face think emporers new groove
Ulcers in alpacas
signs = teeth grinding, hypersalivation, black stool
Choanal atresia
congenital disease affecting the respiratory tract
Mycoplasma haemolamae
mild to marked anemia in stressed/immunocompromised camelids
Parelaphostrongylus tenuis
aka meningeal or brain worm
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Wry face: jaw displacement
caused by caseous lymphadenitis (bacteria)
Hepatic lipidosis
fatty liver
E. mac
origin: south africa
large cocci, widespread in u.s
Wry face
jaw displacement in camelids