BIO 201: Chapter 4.1 Neurohistology and Neurophysiology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
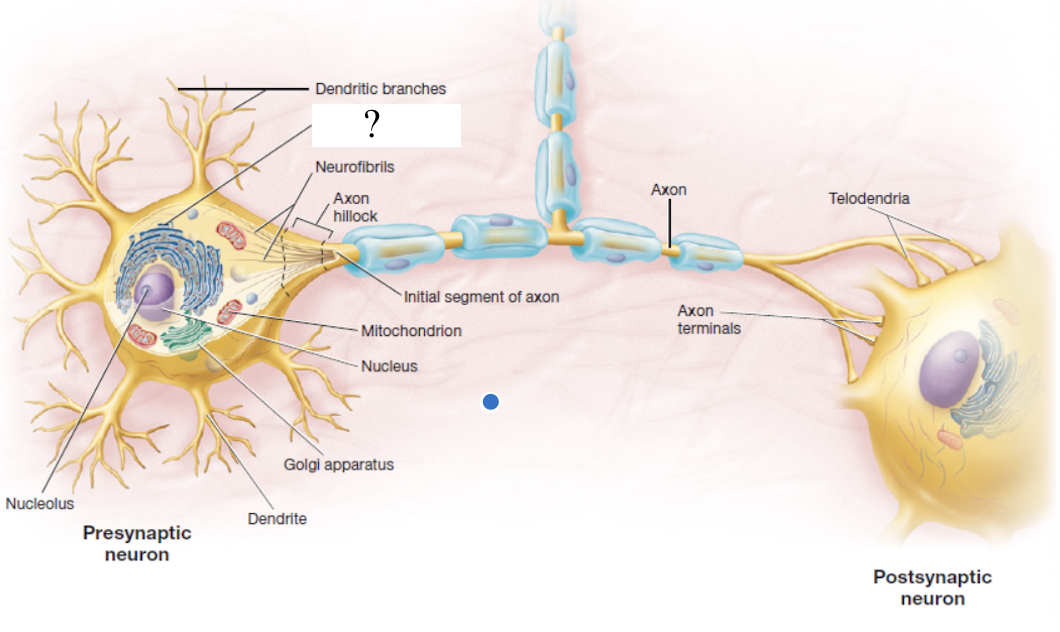
nerve cell/neuron
basic functional unit of the nervous system
neurosoma
cell body and control center of a neuron which contains the nucleus and organelles
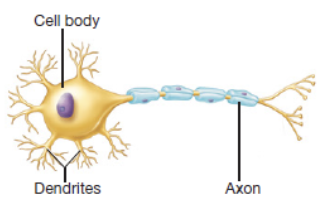
axon
slender and long projection that rapidly conducts signals away from the neurosoma
dendrite
primary site for receiving signals from other neurons that is named for resembling tree branches
dendritic branches
smaller branches arising from big and thicker dendrites
epineurium
dense irregular connective tissue that covers the whole nerve branch
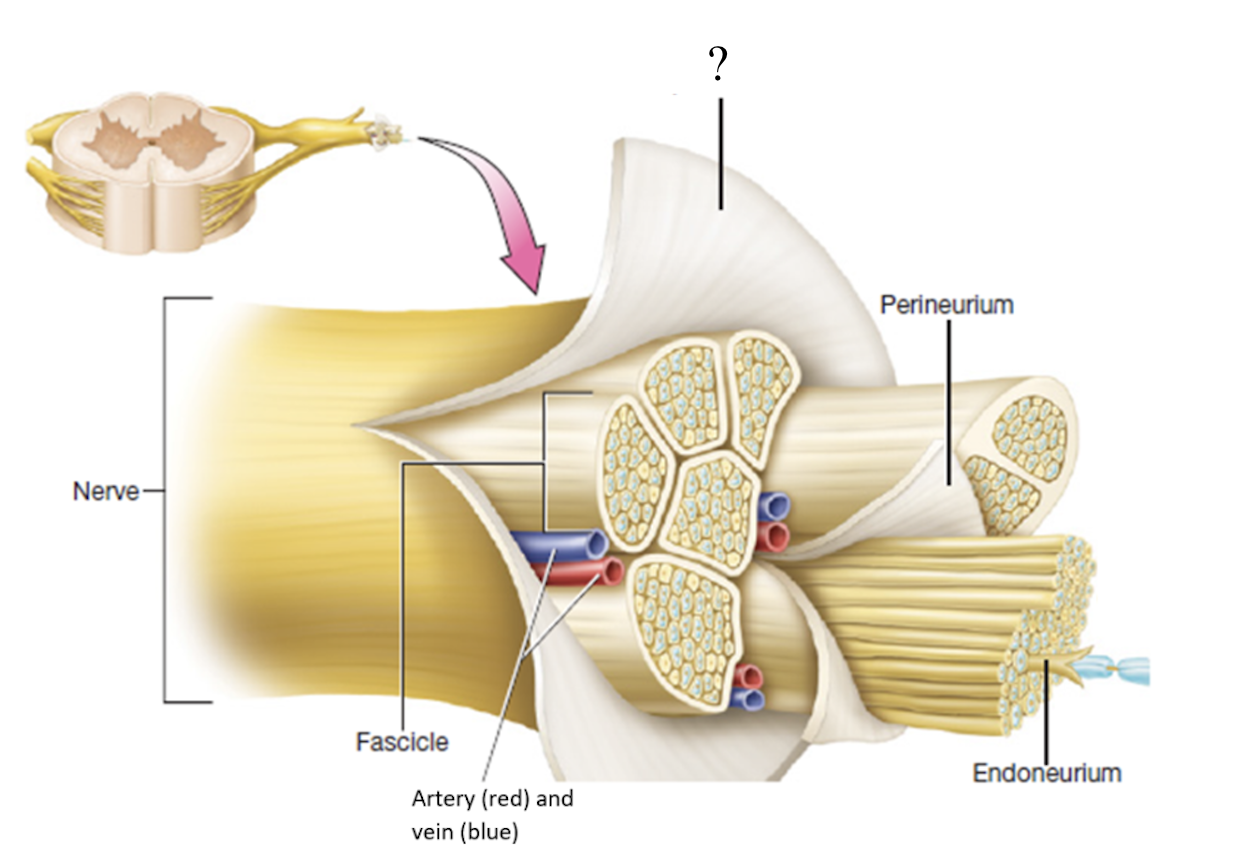
fascicles
bundles or group of neurons
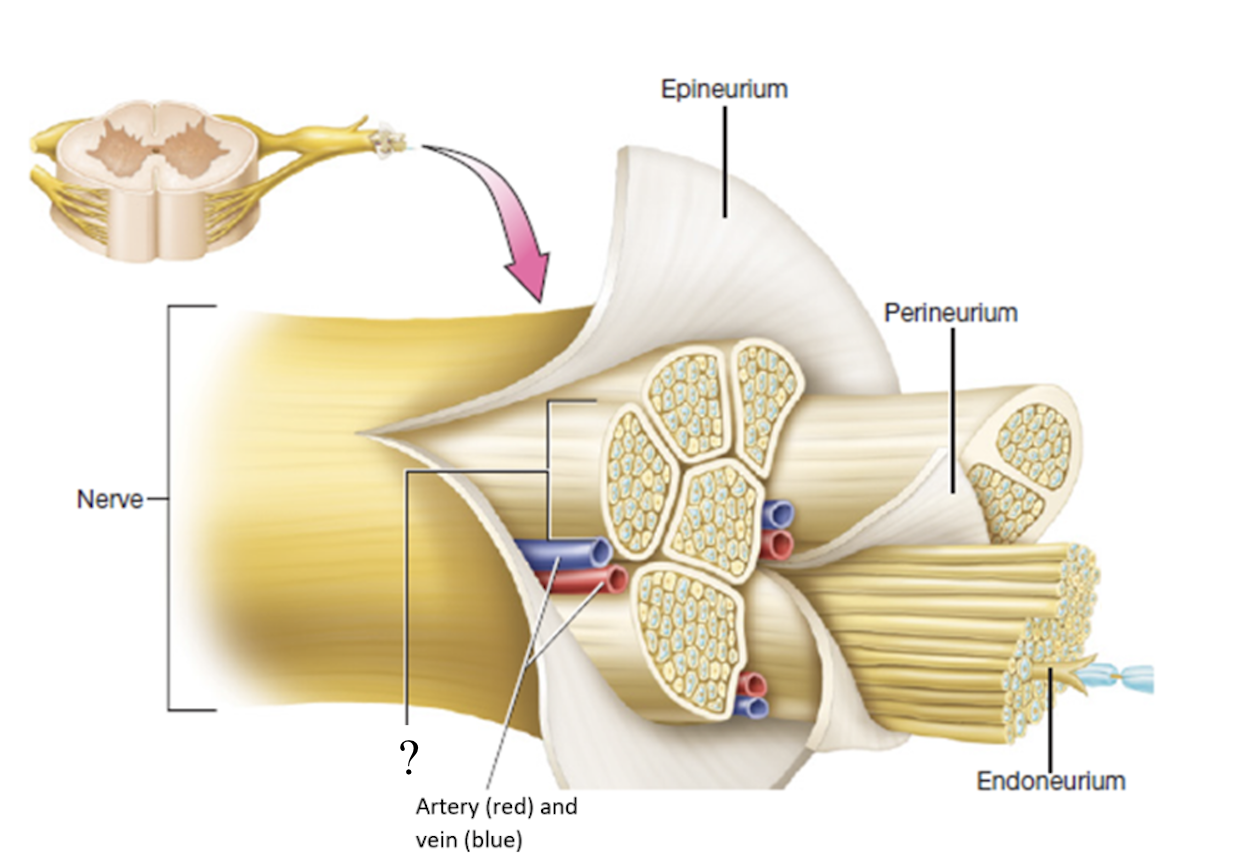
perineurium
connective tissue that covers fascicles
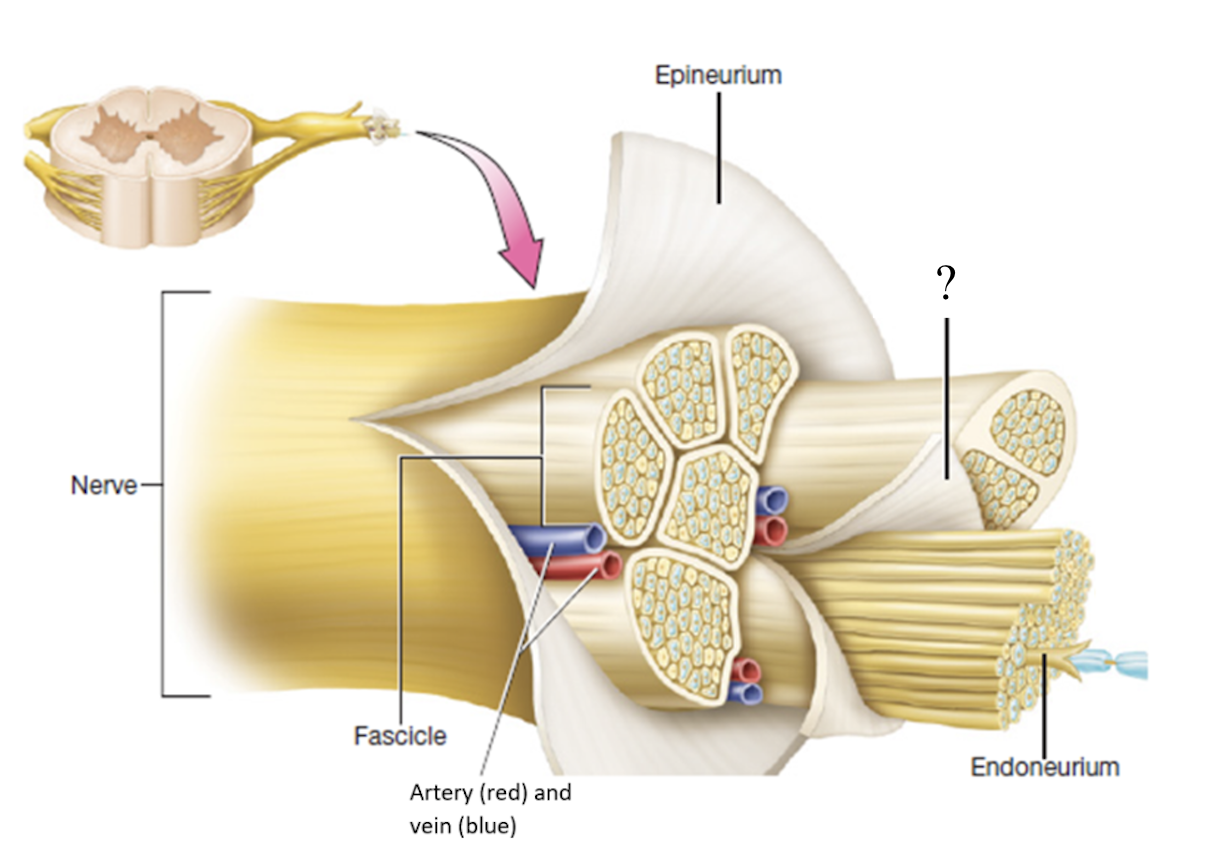
endoneurium
delicate thin layer of connective tissue that covers each separate neuron
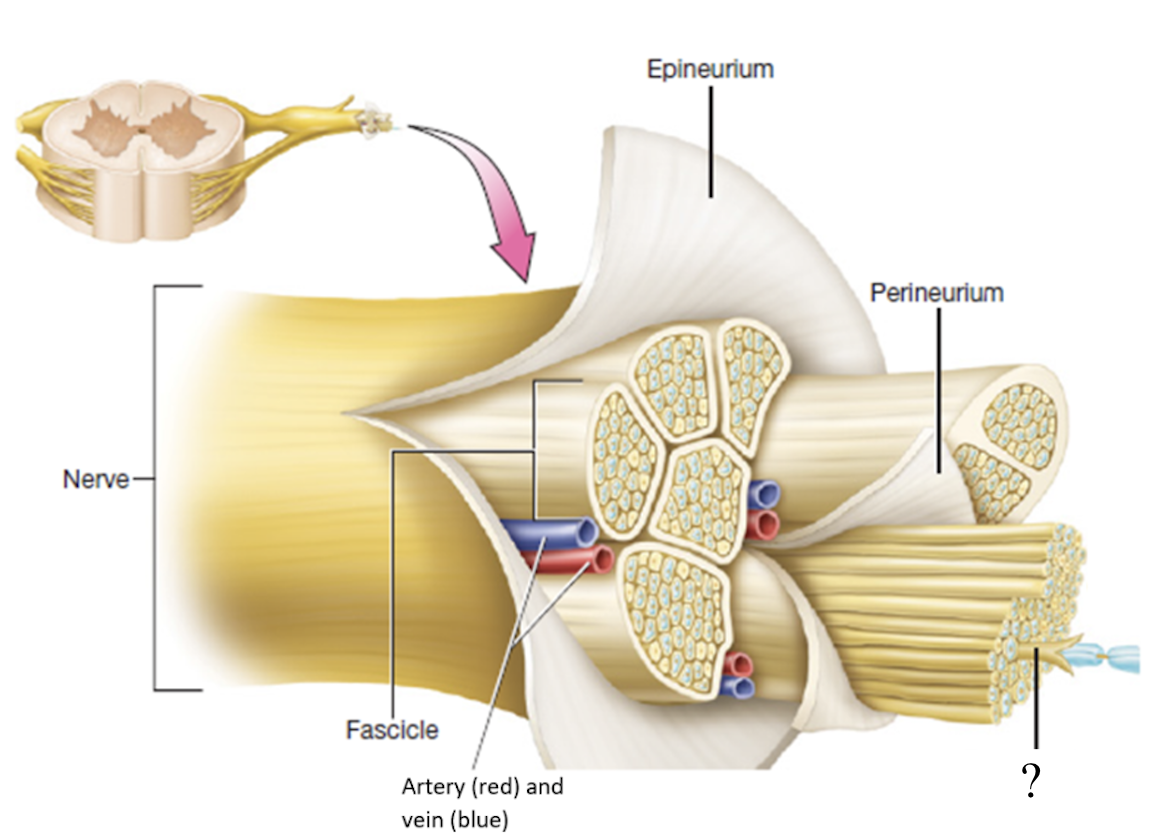
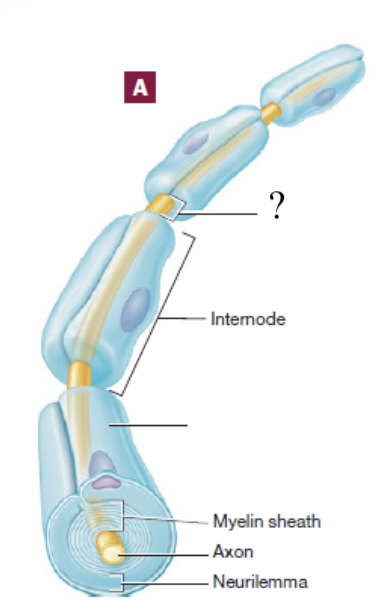
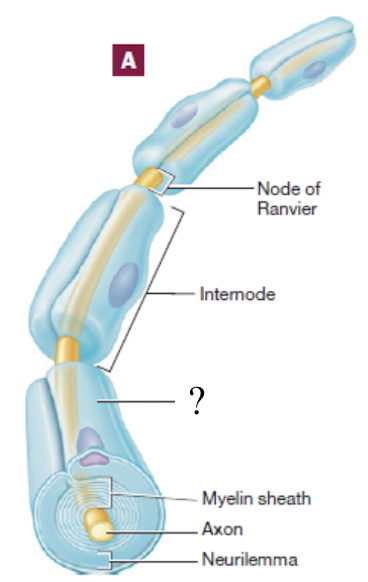
myelin sheath
spiral layer of insulation around the nerve fiber that is production through myelination
functions of myelin sheath
insulates the nerve axon from surround tissue and increases the speed and efficiency of conduction
axon terminal
distal end of an axon that is a synapse
synapse
location where a neurotransmitter, like acetylcholine, epinephrine, and serotonin, are released
multipolar neurons
most common type of neuron that has multiple dendrites and one axon
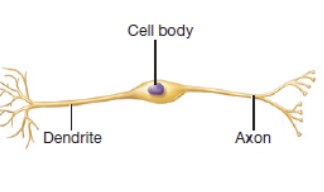
bipolar neurons
found in the nerves of the retina, have one long dendrite and one axon
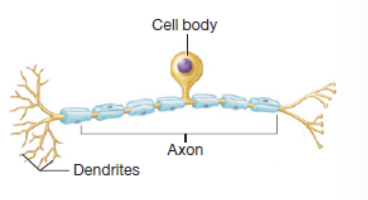
pseudounipolar neurons
appears to have two branches and shaped like a T but actually only had a single axon with dendrites at one end and a synapse at the other
axon hillock
mound where the axon originates
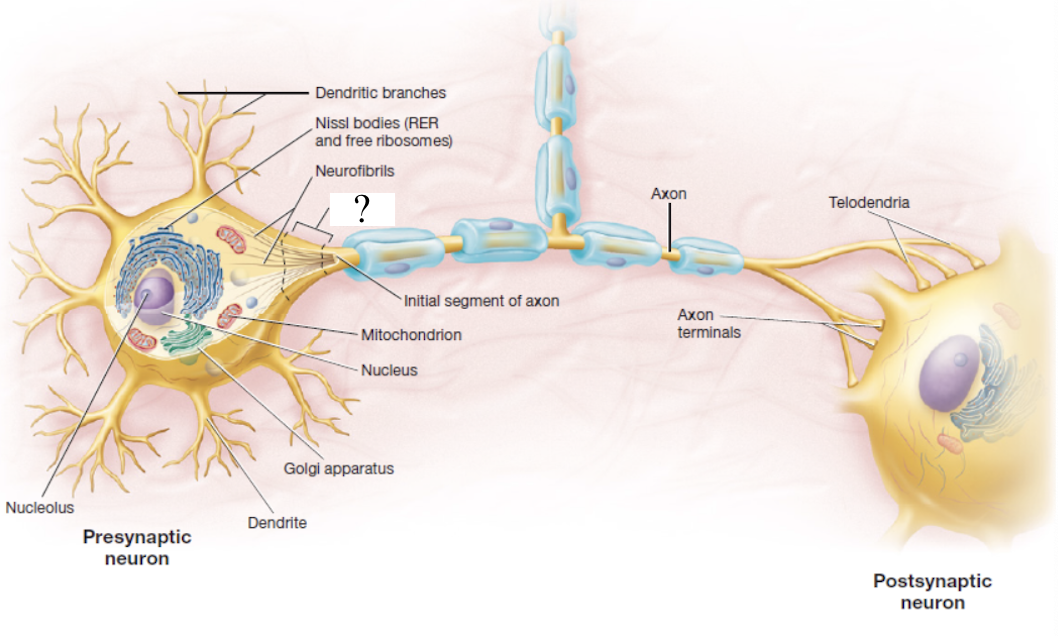
initial segment of axon
very first part of the axon coming out of the axon hillock
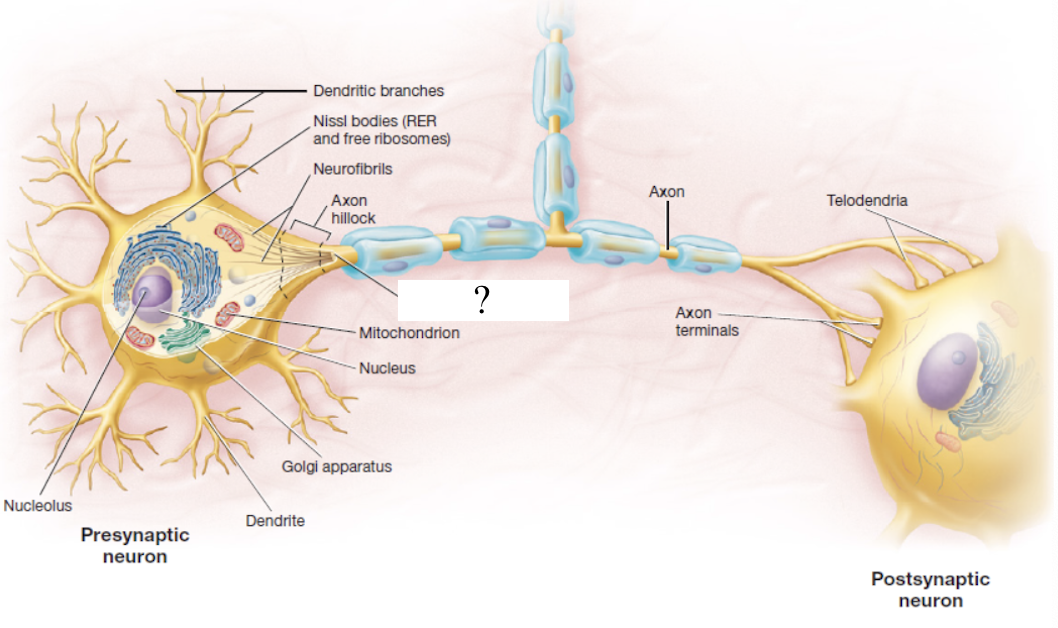
neurofibrils
part of the cytoskeleton made up of bundles of actin filaments
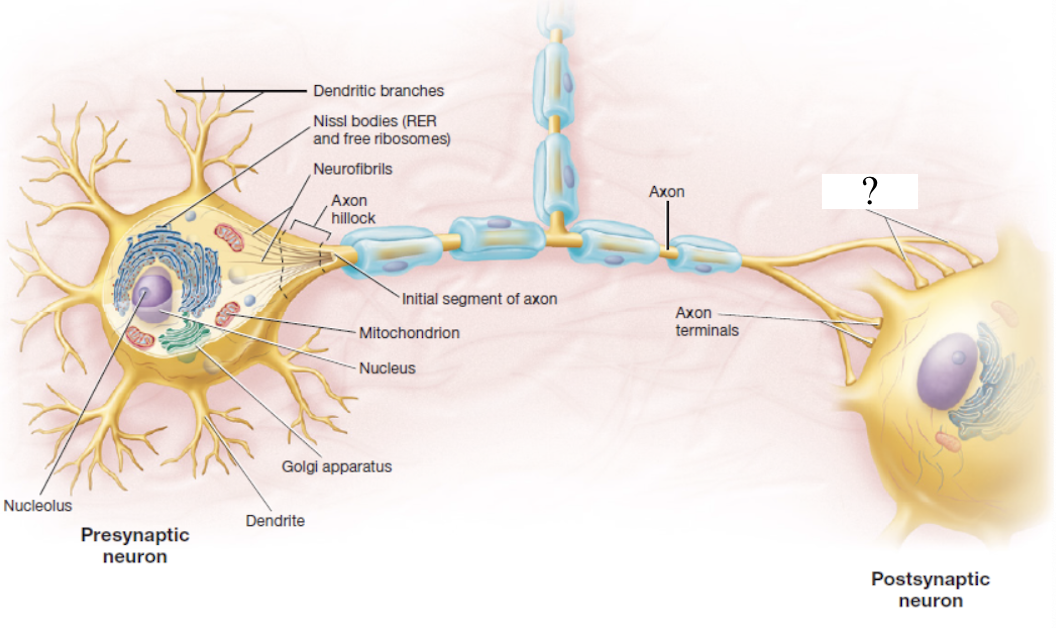
telodendria
extensive complex fine branches that give rise to axon terminals
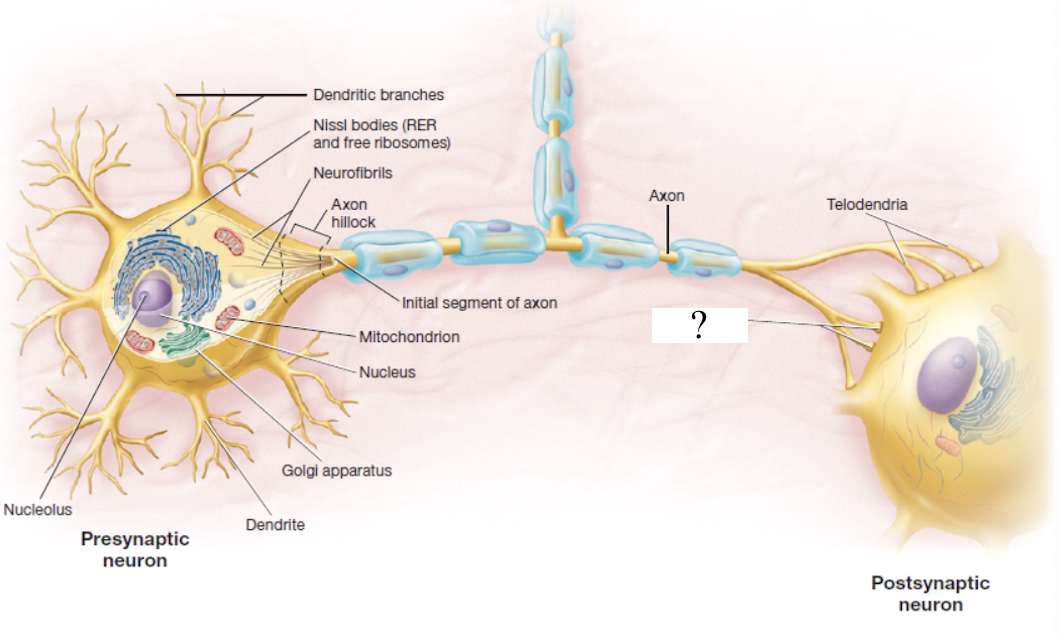
axon terminal
bulbous end that forms the synapse to the next nerve
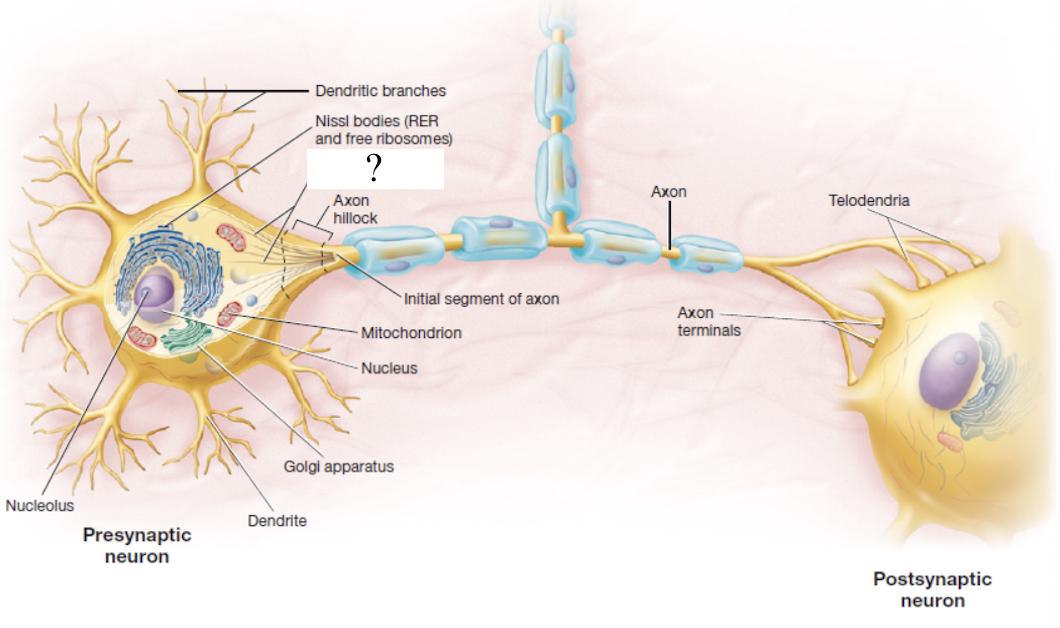
nissl bodies
dark staining regions made up of rough ER and free ribosomes that help to identify them
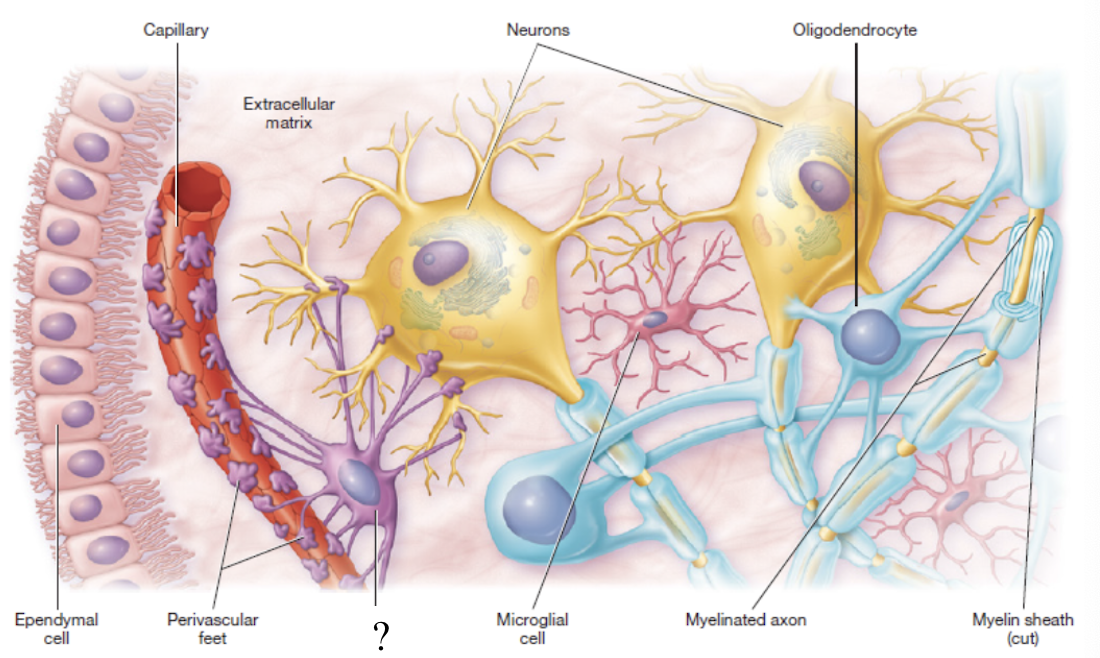
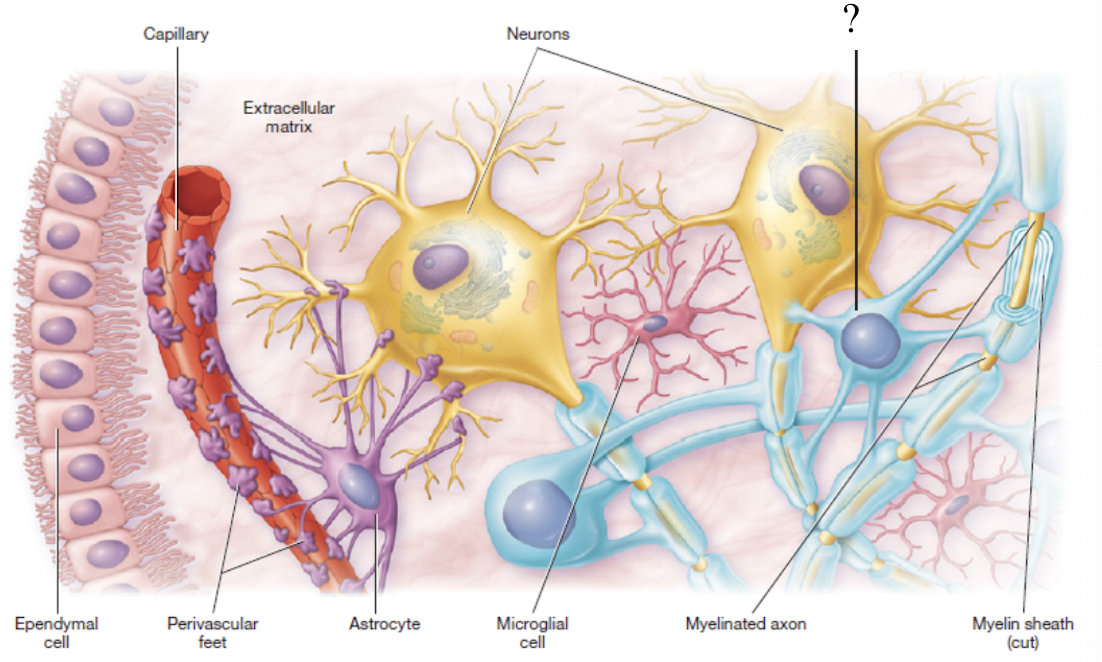
neuroglia
5 types of glial cells that make up majority of the cells in the nervous system
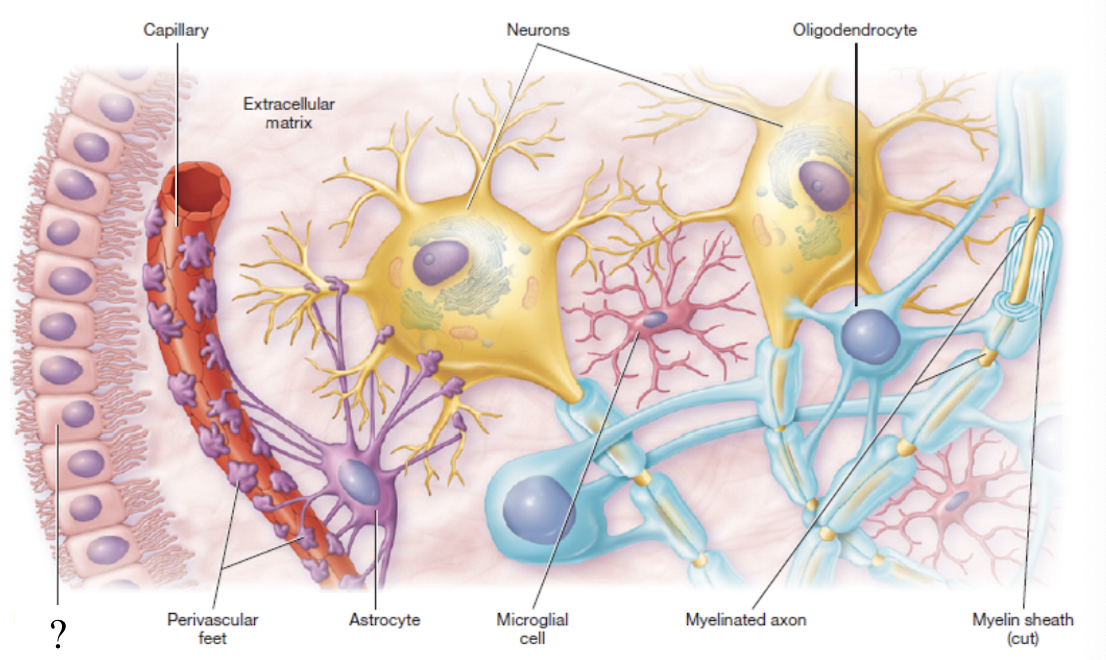
astrocytes
star-shaped with long projections that wrap around blood vessels of the brain
form a blood-brain barrier to control what enter nerve tissue
true
true or false: astrocytes are the most abundant glial cell in the central nervous system
ependymal cells
resemble cuboidal epithelium
produce cerebrospinal fluid
cover the choroid plexus that lines the brain ventricles
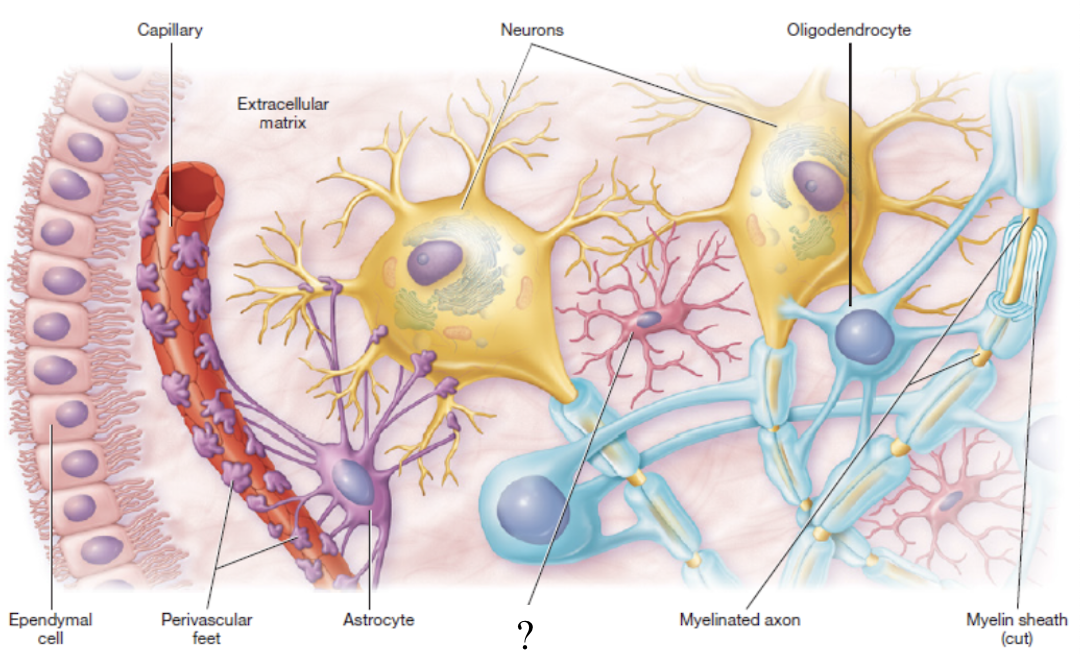
microglia
small macrophages that act as phagocytes to remove damaged neurons and infections
macrophages: immune system cells that wander
phagocytes: cell eaters
oligodendrocytes
produce myelin sheath in the CNS only
resemble an octopus due to its bulbous body and arm-like processes
nodes of ranvier
gaps between myelin sheaths
schwann cells
produce myelin sheath in the PNS only and assist in the regeneration of damaged fibers
excitability
ability of a nerve cell to respond to a stimulus that may be mechanical, chemical, or electrical
conductivity
ability of the cell to carry the excitation response along the length of the nerve cell axon
resting membrane potential
nerve cell at rest with (-70 mV)
action potential
electrochemical change that disturbs the resting membrane potential of a cell
depolarization
wave that a action potential travels down an axon
post-synaptic neuron
target cell that a neurotransmitter will bine to in order to activate a cell
asymmetric distribution
the voltage difference across the cell membrane arises from _____ of ions in extracellular and intracellular compartments
neurophysiology step 1
resting membrane potential maintained by the sodium-potassium pump
extracellular compartment has high concentration of Na+ and low concentration of K+
intracellular compartment has high concentration of K+ and low concentration of Na+
neurophysiology step 2
depolarization: Na+ gates open and Na+ rushes from area of high concentration to area of low concentration, making nerve cell more positive and less polarized
threshold: depolarization reaches irreversible point or threshold (-55 mV) that initiates the action potential or nerve impulse which travels down the length of the axon
repolarization: membrane shifts permeability and K+ ions move out of the cell to shift the voltage back into negative numbers
neurophysiology step 3
action potential reaches the end of the presynaptic cell’s axon and enters the terminal region
triggers the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels which then triggers the exocytosis of acetylcholine from synaptic vesicles traveling through the synaptic cleft
acetylcholine binds to neurotransmitter receptors on post-synaptic cell