Bio 2B - Final Exam Review
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Adaptation
permanent change in any trait over time due to changes in environment
How bacterial cells exchange genes
Transformation - living cells take in DNA from dead bacteria cell
Transduction - bacteriophage packages host genome instead of viral genome, inject bacterial DNA into another bacterium (transferred DNA)
Antibiotics
produced as a means to compete with other microorganisms
heavy antibiotic use can select for rapid evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
Major ecosystem services: Provisioning
things we harvest from ecosystems
ex: food, water, genetic resources(all dec), biofuel (inc), wood (stable), coal
Probiotics
aid in re-colonization of the patient’s body by beneficial bacteria
Bacteriophages
infects and replicates within bacteria, but doesn’t infect invertebrates. Targets other bacteria
Pierce’s Disease
plants along creeks are affected by sharpshooters, causing this disease
ecosystem disservice for native vegetation growing along creeks
Short-term threats to ecosystem
degradation of water supply
climate change
invasive species
species extinction
Biodiversity
full diversity of life on earth, diversity of all organisms in all habitats across all levels of organization
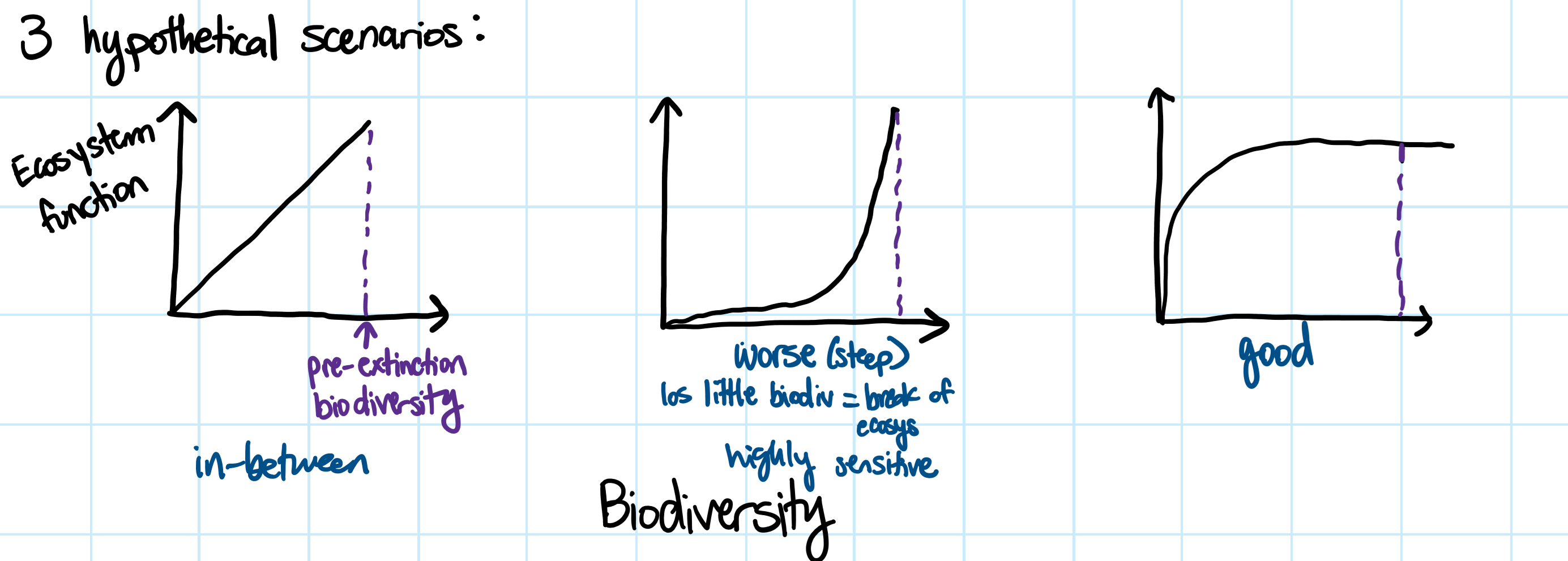
Relationship between Biodiversity & Ecosystem function
Pathogens
virus, bacterium that can cause disease
Abiotic environmental conditions
non-living part of an ecosystem that shapes its environment
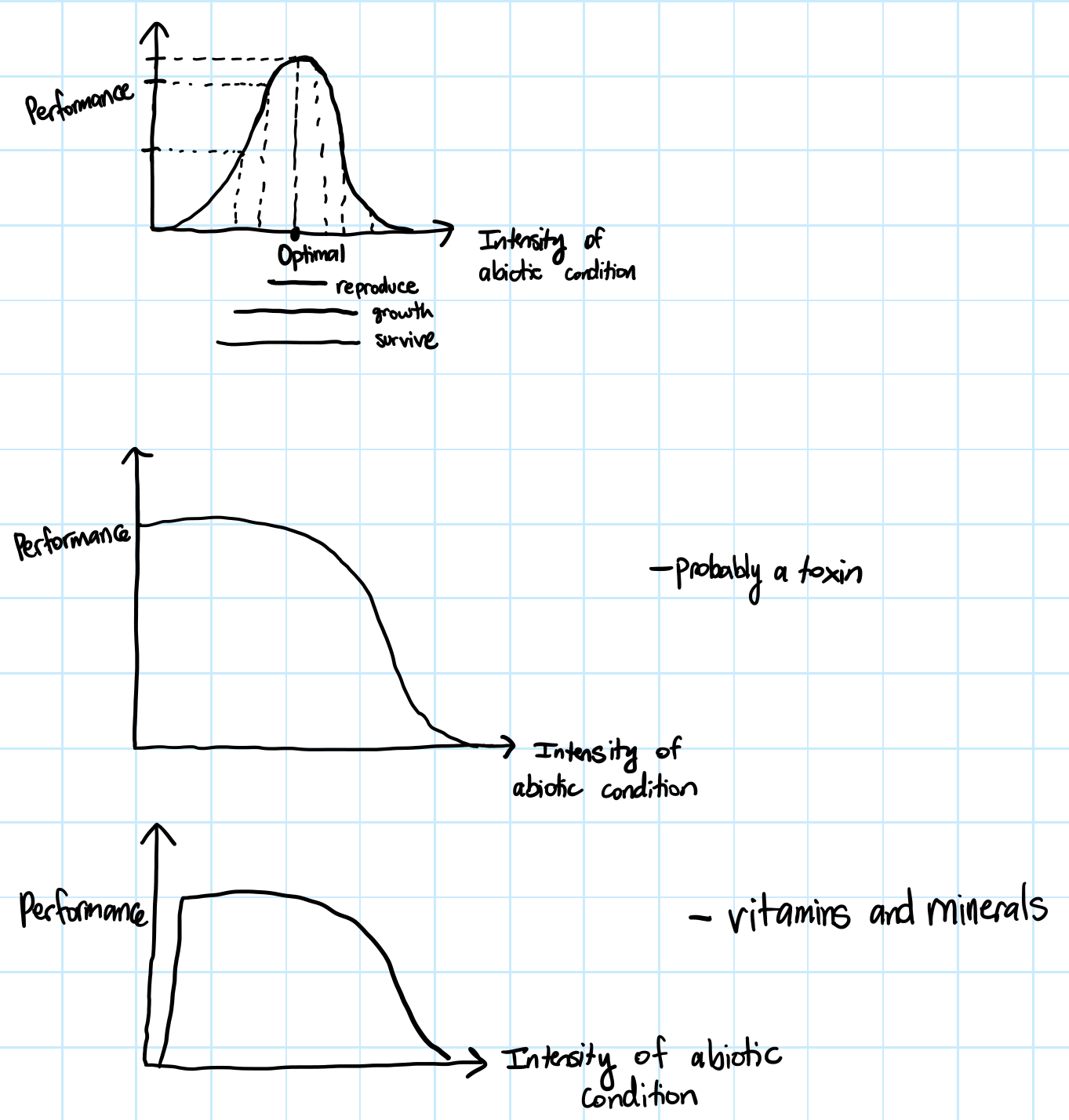
Organism’s niche
Environmental conditions and the availability of key resources that must be satisfied simultaneously to allow an organism to grow, reproduce, and survive
Endotherm vs Ectotherm
Endotherm relies on metabolically-generated heat as predominant source of warmth
Enzymes
need to maintain proper shape and to work they need the right amount of flexibility
Cooler environment = fewer bonds needed = more flexible
Warmer environment = kinetic energy is greater = stronger chemical bonds = more rigid
Too high temperature (exceeds optimal range) —> becomes denatured
Photoinhibition
too much light intensity for the plant; prevented by holding leaves at an angle to “dilute” radiation and keep it at optimum level for photosynthesis
CO2
increase in CO2 concentrations induced by industrial revolution (burning fossil fuels; can’t be recaptured by plants)
increasing more rapidly than we’ve known in history of earth
stomata - CO2 diffuses in; open stomata=loss of H2O
CO2 lets energy and not out, energy is trapped in the form of heat
Photosynthesis
visible light 400-700nm
Macronutrients vs micronutrients
macronutrients - uptake in large amounts
micronutrients - uptake in small amounts
roots branch to take in valuable nutrients; amino acids are NOT essential resource for plants
R0
R0 - basic reproductive rate

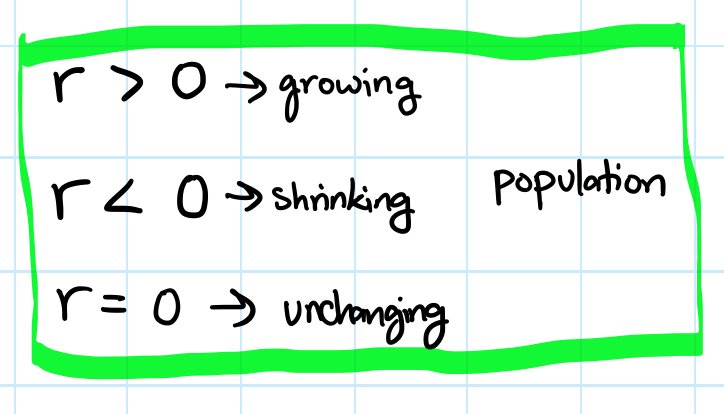
r
r - intrinsic rate of increase
(b-d+i-e)
senescence
“deterioration” with age
somatic cell lineages (sex cells, eggs, seeds, spores, etc.)
age-independent mortality factors favor senescence because benefit outweighs cost of repairing/avoiding senescence
freezes, fires, predation
NO SENESCENCE - fission, budding (any cell could be passed onto future generations, thus maintained w/out senescence)
Trade offs
between current and future reproduction
between reproduction and somatic maintenance
Exploitative competition
indirect
scramble competition: more or less evenly
overcompensating density-dependence
very strong influence on population growth rates
Interference competition
interaction between competing individuals (one prevents other)
contest competition: unequal division of resources (winners/losers)
exactly compensating density-dependence
occurs when # of individuals surviving competition is constant across a range of high values of initial # of competitors
resource-weighted density vs consumer-weighted density

Essentialism - Plato
in natural world, # of unchanging essences that are discrete
constancy (opp of change)
discontinuity
variation
Great chain of being (Scala Naturae) - Plato
all things on earth can be arranged in linear sequence (topology)
Jean Baptiste de Lamarck
theory:
spontaneous generation
intrinsic tendency to strive towards perfection
inheritance of acquired characteristics
Darwin and Wallace
common descent (common ancestor)
causation of adaptive evolution - natural selection
inheritance, variation in traits, variation in fitness
evolution could occur as automatic process that produces adaptation
DONE WITH MIDTERM 1 CONTENT BIO
Lec 1-11
Mendel’s first law
segregation; genes are particulate or discrete
every individual has 2 alleles, and only one allele is passed onto offspring
genes, chromosome, gametes
common garden experiment: keep environmental conditions stable/constant, then diff in traits shows that genes is the reason
Mendel’s second law
independent assortment
genes located on different pairs of homologous chromosomes assort independently during meiosis
autosomal linkage and crossing over
Autosomal linkage
any chromosome other than sex chromosome 2 genes located on same chromosome (and close)
2 or more genes being carried on same autosome
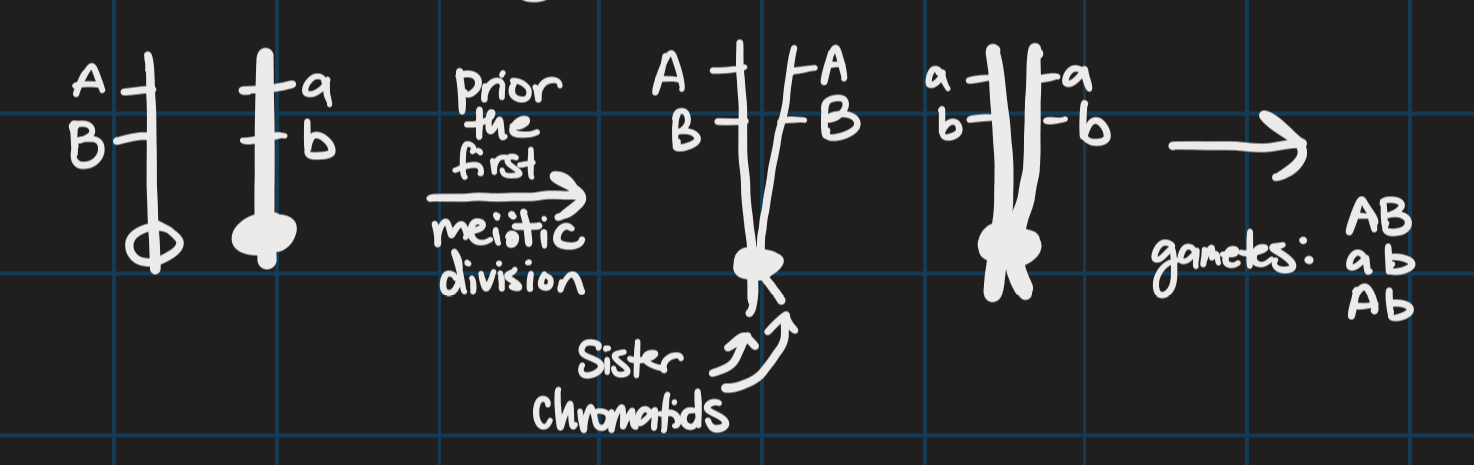
Crossing over
chromosomes of same type are lined up
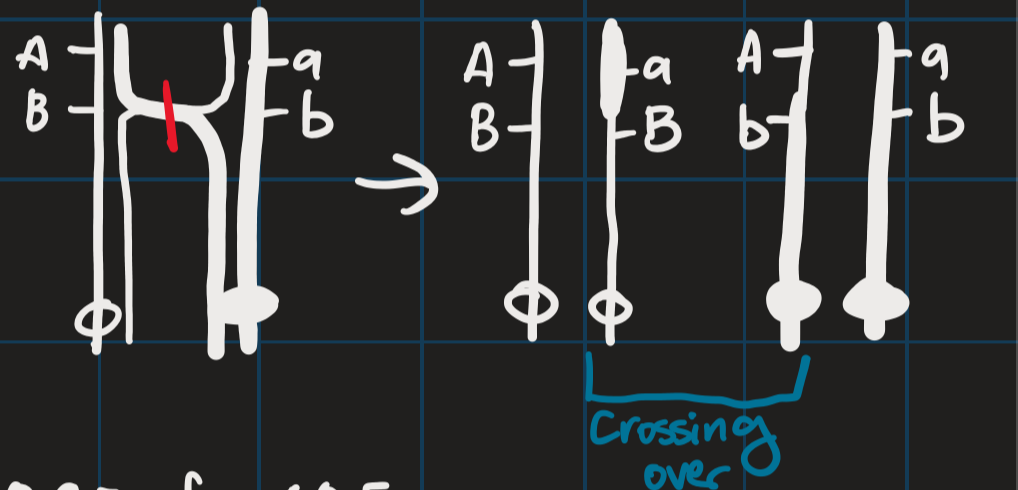
Genetic recombination
when two molecules of DNA exchange pieces of their genetic material with each other
occurs within chromosomes, through crossing over
occurs across chromosomes, through meiosis and fertilization (normal sexual reproduction)
Darwin’s lack of understanding mechanism of inheritance
NO BLENDING MECHANISM
natural selection would be ineffective in producing evolutionary change
Genetic variation
mutation
immigration - gene flow
genetic recombination - new combination of genetic variations
withing (crossing over) and across chromosomes (normal sexual diploid gamete)
Mutation
often occurs during DNA replication
most important source of genetic variance
point mutations
chromosomal mutations
insertions/deletions
Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium
if:
very large population (infinite)
random mating
no gene flow (immigration)
no mutation
no selection
then: NOT EVOLVING
allele frequencies will stay same across generations
genotype frequencies
p² + q² + 2pq
if expected frequency = actual frequency —> NO EVOLUTION
Selection
Tay-Sachis
an enzyme that doesn’t metabolize lipids (lethal if defective) ←recessive alleles expressed
Genetic drift
process by which allele frequency change due to chance events (survival) in finite populations
smaller population = more changes in allele frequencies
drift is more important than selection
1/N > S
Traits with continuous variation
control by many genes
polygenic
environmental effects
P = G + E
phenotype = genotype + environment
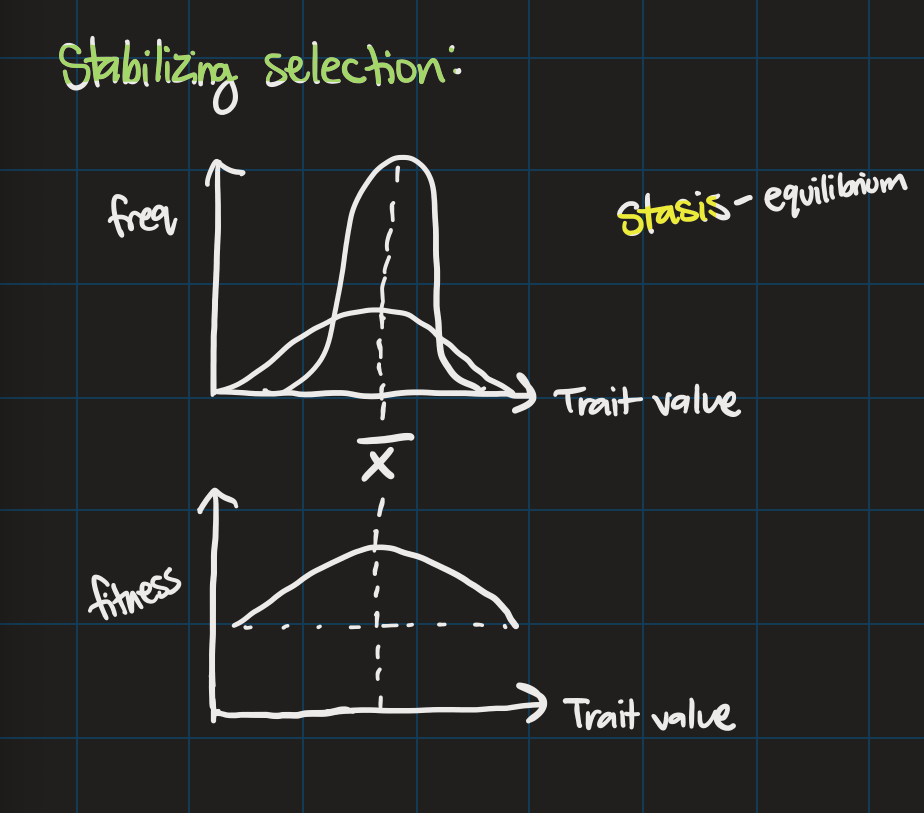
Stabilizing selection
mean doesn’t change
variance DECREASES
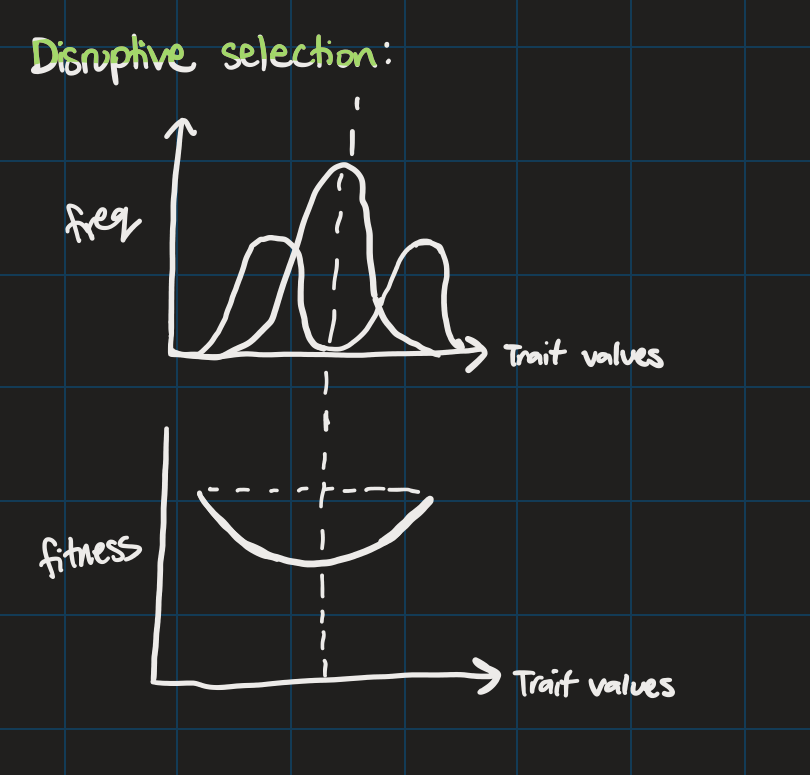
Disruptive selection
mean doesn’t change
variance INCREASES
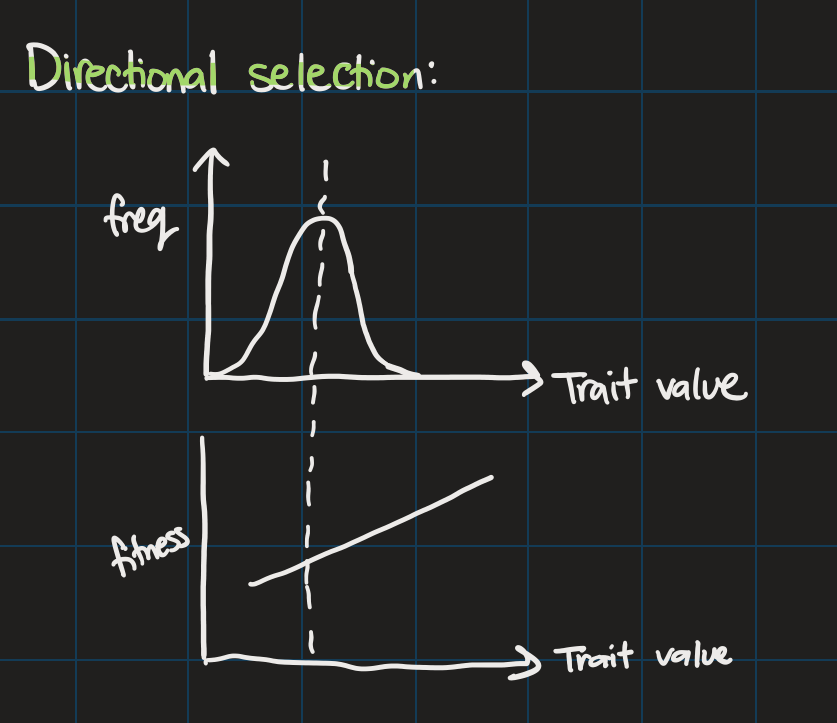
Directional selection
mean continues to rise
variance doesn’t change
Bacillus thuringiensis
part-time pathogen
kills host by producing protein toxin in gut
receptor-cadherin (kills cell)
highly selective
toxic to insects but not to mammals
mechanisms of resistance
detoxication - dominant alleles
toxin is broken down before lethal dose reaches host
target site insensitivity
4 things to know about resistance evolution + management
resistance proceeds through discriminating with individuals with different genotypes
mortality does not equal effective selection
functional dominance - environment determines if trait looks dominant/recessive
fitness costs of resistance (R)
dilution of resistance by immigration
resistance management
low dose strategy
high-dose, refuge strategy
Lotka-Volterra Model of Interspecific Competition

Zero-growth isocline
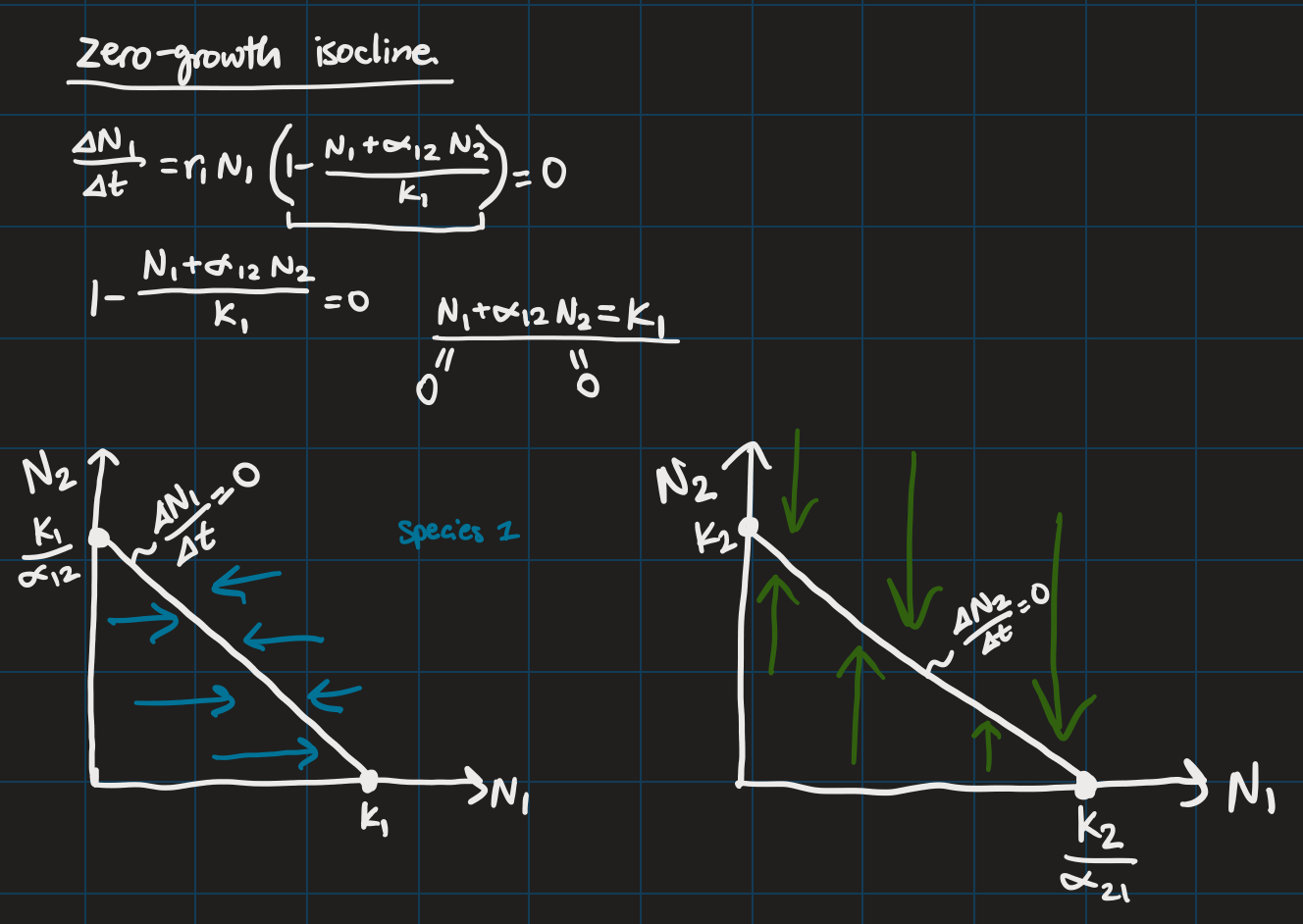
Predation + prey tactics
effects all: birth, death, immigration, emigration
Prey tactics:
refuge in time - not around when predator is around
refuge in space - not being in same place as predator
refuge in body size - being too big/small for predator
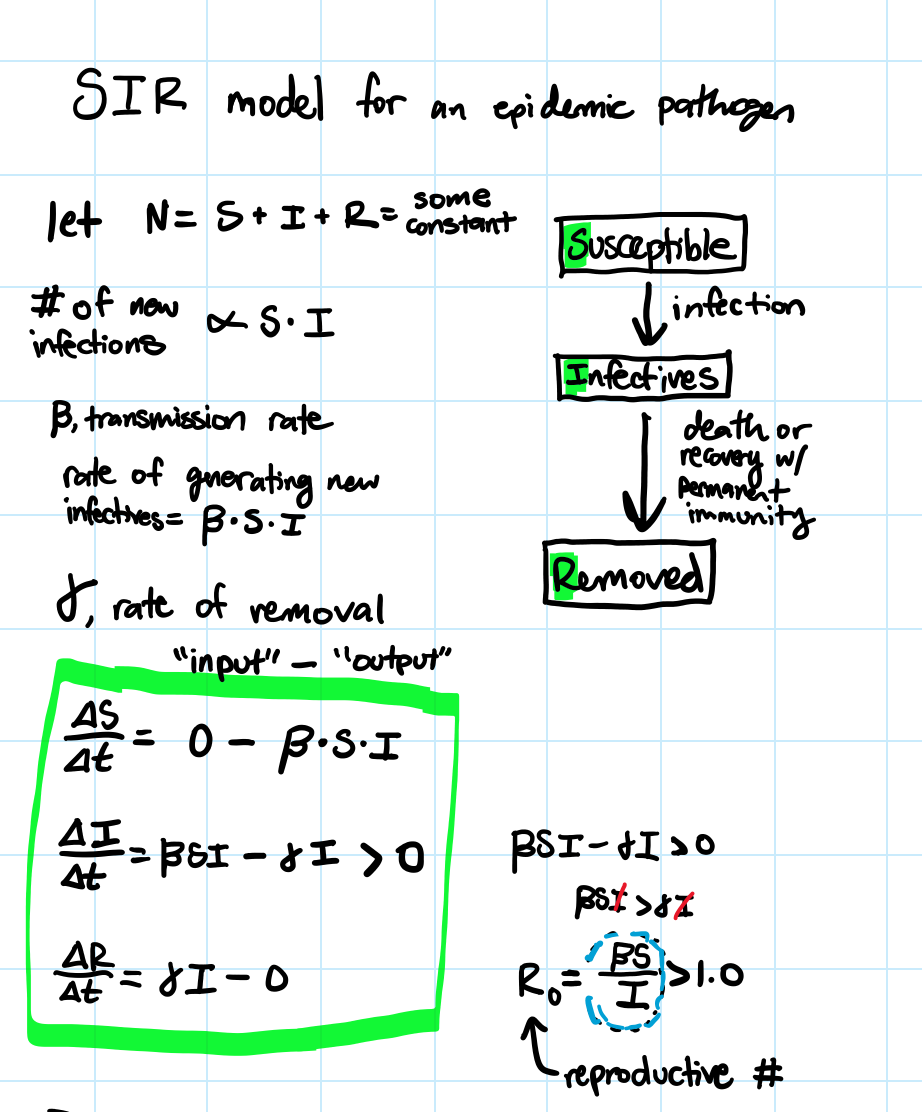
SIR model for an epidemic
Susceptible
Infectives
Removed
1/y is the mean time that an infected individual has the disease and can infect other individuals within the host population
S is # of susceptible hosts present
Herd immunity + mandatory immunization
big enough proportion of population vaccinated, protect all population (even unvaccinated)
ex: pertussis (whooping cough)
mandatory immunization is important where 100% immunization of the host population isn’t possible
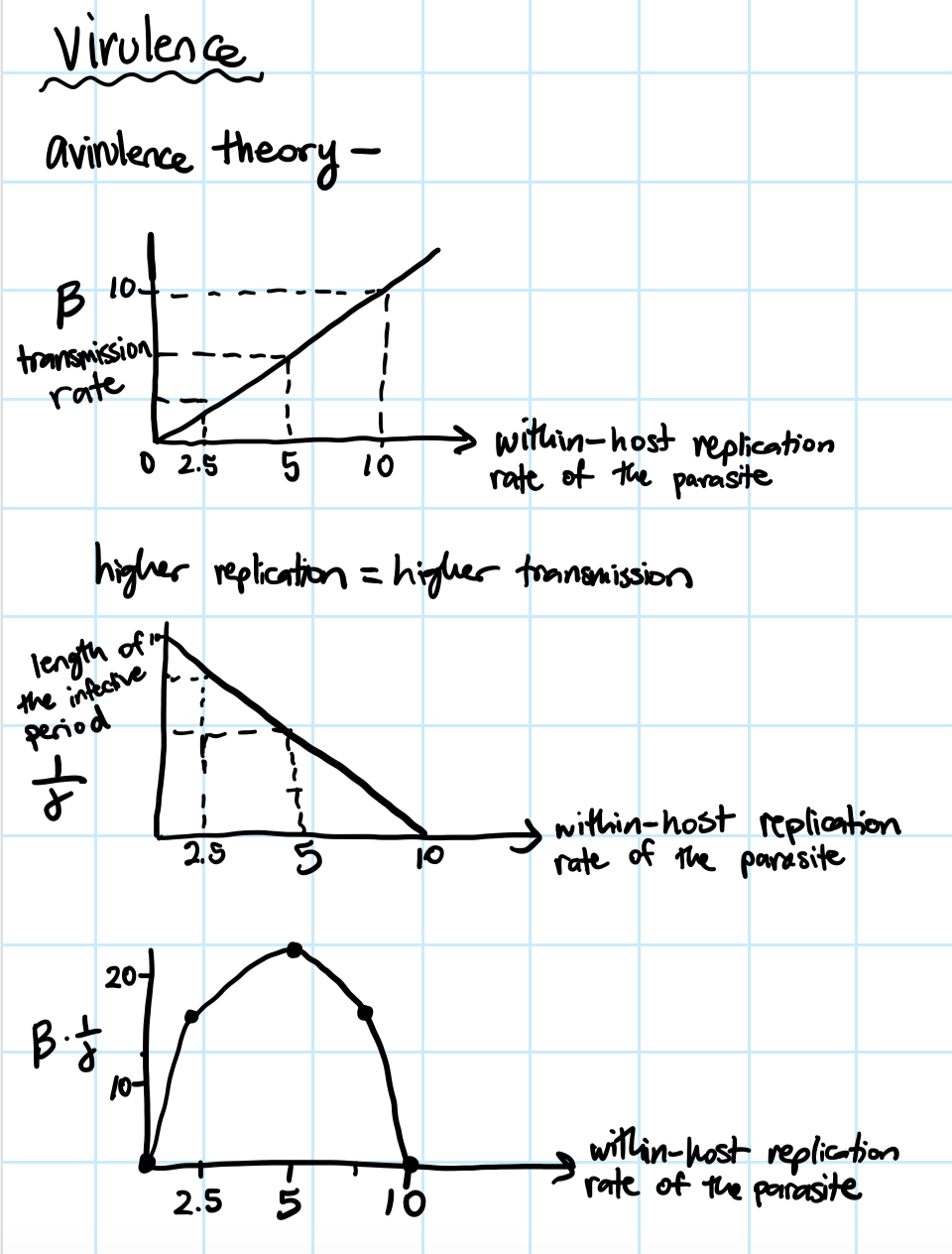
Virulence
severity or harmfulness of a disease/poison
avirulence theory - pathogens have no effect on host
Mutualism
interaction between 2 species that’s beneficial to both
exchange of service/resources
Major classes of mutualism:
protective services
ants + plant (nectar for ants, ants protect)
dispersal services
plant + human/animal (produces fruit/nectar, seed spreads)
digestive services
build population by eating
biosynthesis services
allow insects to survive via eating microbes
resource exchanges
trade sugar for another resource (ex: corals, lichens)
Food Web - trophic cascade
direct and indirect effects
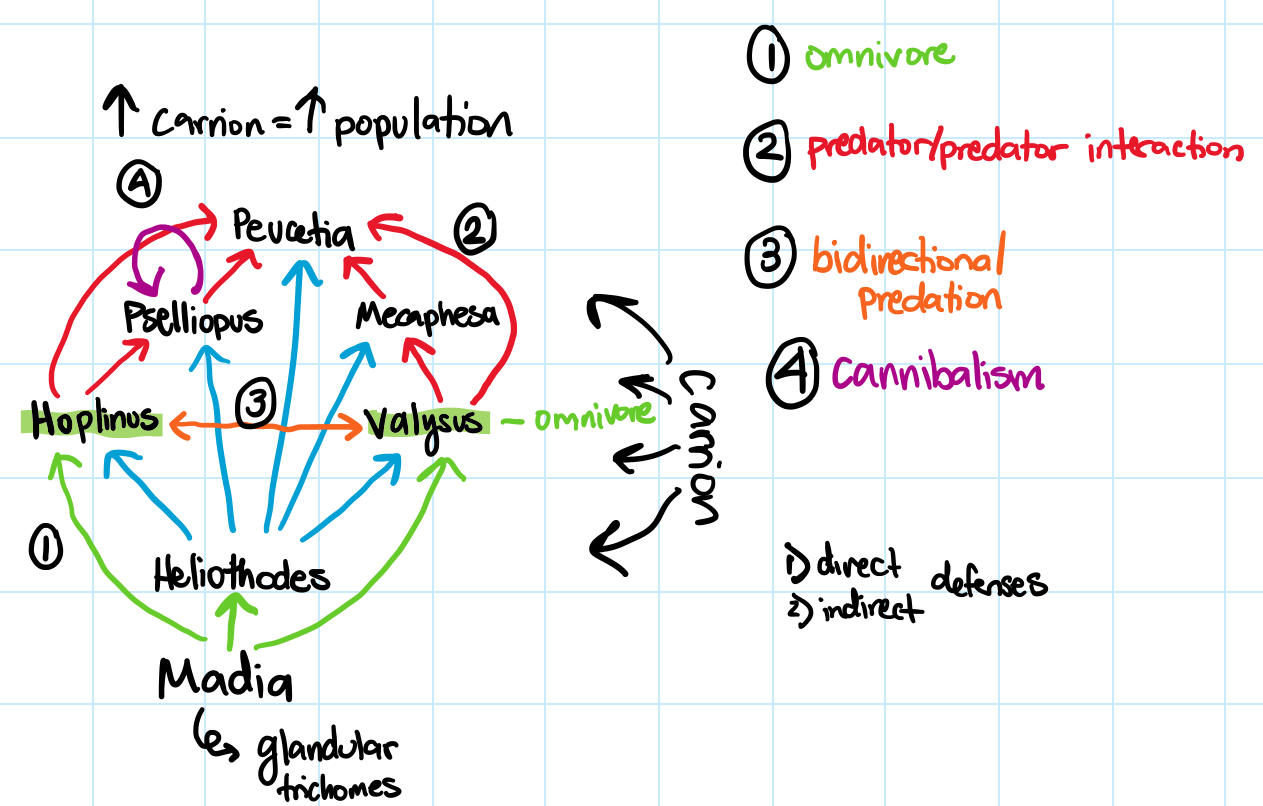
Density-mediated indirect effect
Trait-mediated indirect effect
occurs because of predator effects on prey traits rather than prey density
predator effects behavior
ex: aquatic system
prey refuge strategies
Biological species concept
species are groups of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations which are reproductively isolated from other such groups
measured reproductive components
Morphological/Phenetic species concept
individuals are grouped into species based on their similar physical appearance
appearance/grouping
Reproductive isolating mechanisms
post-zygotic
hybrid sterility - hybrid can’t make gametes (no mating)
hybrid inviability - hybrid zygote dies early on

allopatry
a population or species that is physically isolated from other similar groups by an extrinsic barrier to dispersal
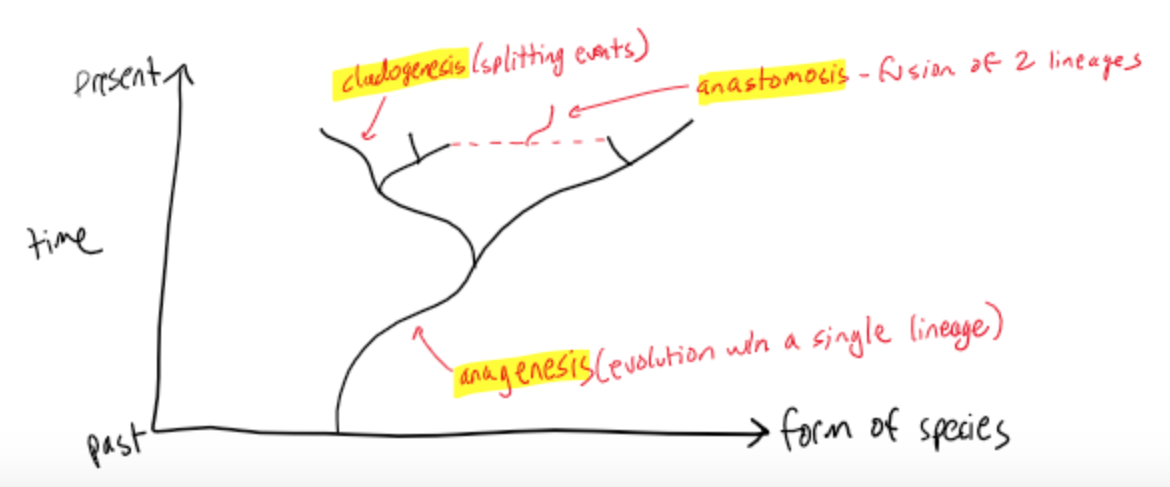
Anagenesis
microevolution
evolutionary change within an evolutionary lineage
Cladogenesis
speciation
splitting events
Anastomosis
fusion of two lineages
Ring species
set of populations whose distribution is shaped like a doughnut
one location around the ring, there’s a clear absence of gene flow between two classes of individuals
shows the idea that what makes two species different is often the amount of genetic divergence, rather than some fundamental difference in the type of genetic differences that exist
Modes of Speciation
Allopatric - geographic isolating at the initiation of the divergence event
Sympatric - splitting of an ancestral species into two or more reproductively isolated groups without geographical isolation of those groups
Polyploidy
genome duplicated (diploid gamete)
initial mutation occurs when cells that have replicated their DNA in prep for cell division have failed to divide properly
Symbiosis (and anastomosis)
basis for evolution of plants and eukaryotic cell
explains why mitochondria and chloroplast has own DNA
can cause two independently evolving lineages to fuse into a single lineage (anastomosis)
key evolutionary innovation
favored by ability of two organisms to exchange needed nutrients
may lead to eventual fusion
NO it is NOT ultimate source of all genetic variation because it’s different from mutational event
Mutualistic symbiosis
two species with different metabolic needs (waste product from one is a key resource for other)
reduction in overall genome size of symbiont
trend towards increasingly strict dependence of symbiont and host on each other
increased number of genes within the symbiont’s genome
ex: mitochondrion has own DNA because it descended from proteobacterium that formed mutualistic symbiosis with a host cell
Macroevolutionary history
How to generate new genes
gene duplication
meiosos: alignment of homologous chromosomes
misalignment: mistake, can lead to mutation
differentiation of the multiple B genes
major changes in gene copy number occurs rapidly - little as 10yrs
Gene death
Deletion - unequal crossing over, or DNA replication error (lose part of gene)
Mutational damage (pseudogene - dead gene)
damage to promoter
insertion/deletion
nonsense mutation
other
2-fold cost of sexual reproduction
cost of securing the mate
and
risk of not finding a mate
Muller’s ratchet
accumulation of harmful mutations in a generation
evolutionary consequences of the absence of recombination
can lead to long-term cost of asexual reproduction
HIV-AIDS
relies on host to replicate, intracellular
is in the immune system, incapasitates immune system (susceptible to other infections that harm human)
mutation rate is HIGH
low dose, and high dose refuge won’t work
Disease
human population is EXTREMELY LARGE
become much more mobile
serious new disease epidemics in the future
Gene-centric
purpose of offspring is to project copies of genes into future generations
reproduce yourself
help relative to reproduce
Hamilton’s Rule
altruistic allele (donor/recipient) will be favored
not always right because it doesn’t take into account genes

male sex
produces smaller gametes
broadcast spawning
large # of gametes released in ocean and have to find each other to fertilize
HARD
Isogamy
sexual reproduction involving haploid gametes that are all the same size
found in diverse organisms (algae, yeasts, fungi, etc)
Anisogamy
idea of how it evolved:
small male gametes are parasites of the larger female gametes
Intersexual selection
females are picky when choosing male
Intrasexual selection
competition among males