B1 - Cell Level Systems
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Define eurkaryotes.
(E.g. Animals and plants) made from complex cells called eukaryotic cells.
Define prokaryotes.
(E.g. bacteria) made of smaller and simpler cells called prokaryotes.
State the 5 main features an animal cell has.
1) Nucleus
2) Cytoplasm
3) Mitochondria
4) Ribosomes
5) Cell membrane
What is the role of the nucleus?
Contains the DNA (genetic material) in the form of chromosomes that control the cells activity.
What is the role of the cytoplasm?
Gel-like substance where most of the chemical reactions happens.
What is the role of mitochondria?
The site of cellular respiration and contain the enzymes needed for the reactions involved.
What is the role of the ribosomes?
The site of protein synthesis.
What two additional features do plant cells have?
1) Cell wall
2) Chloroplasts
What is the role of the cell wall?
gives support for the cell
What is the cell wall made out of?
Cellulose.
What is the role of chloroplasts?
Site of photosynthesis.
What are chloroplasts made of?
Green substance called chlorophyll.
What are the 3 structures that exist within prokaryotic cells?
1) Chromosomal DNA
2) Plasmids
3) Cell membrane
What is chromosomal DNA (say WHAT it is, NOT its role)?
One long circular chromosome.
What is the role of chromosomal DNA?
Controls the cell’s activities and replication. It floats free in the CYTOPLASM.
What is a plasmid?
Small loops of extra DNA that AREN’T part of the chromosomes.
What is the role of a plasmid?
Contain the gene for things like drug resistance, and can be passed between bacteria.
What is the role of a cell membrane>
Controls what goes in and out of a cell.
What do microscopes do?
Use lenses to magnify images (make them look bigger).
Define resolution.
How well a microscope distinguishes between two points that are close together.
What are the two types of microscopes?
1) Light microscopes
2) Electron microscopes
How does electron microscopes differ from light microscopes?
They let us see smaller things in more detail, such as the internal structure of mitochondria, or plasmids and vriuses.
What does TEM stand for?
Transmission electron microscopes.
What are the drawbacks of TEMs?
Expensive, complicated process to prepare specimens (aka can’t be used for living tissue).
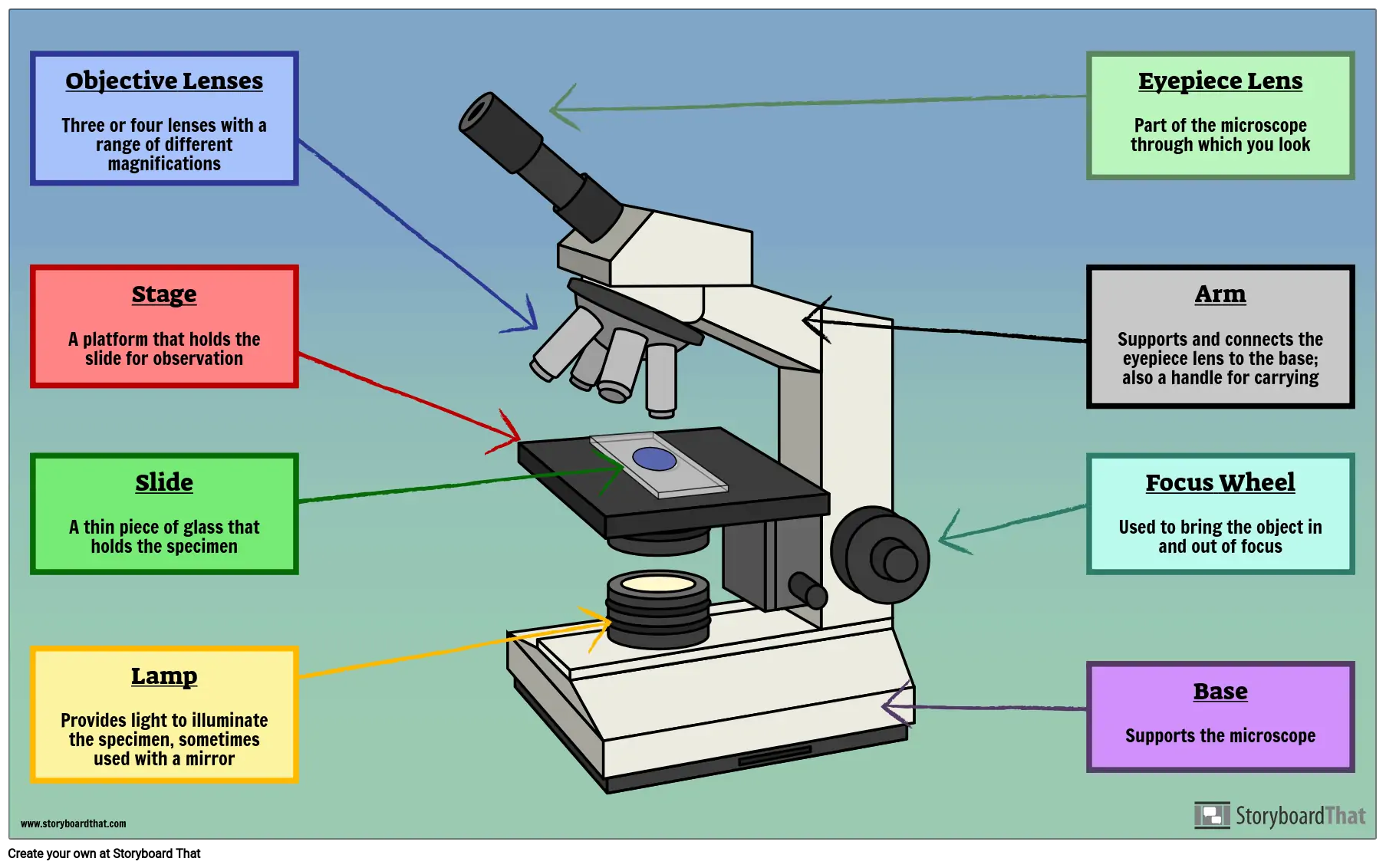
Can you label each part of a light microscope?
Done?
Why does the specimen you use for a light microscope need to be quite thin?
It needs to let light through it.
Describe step by step how you would prepare a specimen?
1) Take a clean slide (a strip of glass or plastic) and use a pipette to put one drop of water or mount ant (a clear, goopy liquid) in the middle of it - this will secure the specimen in place.
2) Use tweezers to place your specimen on the slide.
3) Add a drop of stain if needed.
4) Place a cover slip and one end of the specimen, holding it at an angle with a mounted needle.
5) Carefully lower the cover slip onto the slide. Press it down gently with the needle so that no air bubbles are trapped under it.
Why might you add a stain to a specimen?
If your specimen is colourless or transparent, a drop of stain may make it easier to see. Different stains are used to highlight different structures of tissues.
What are the two types of stains you need to know and what sub cellular structure do they make more visible?
1) eosin - cytoplasm
2) methylene blue - DNA
How do you place your specimen into the light microscope for viewing?
1) Clip the slide containing your specimen to the stage.
2) Select the lowest-powered objective lens (the one that produces the lowest magnification)
3) Use the coarse adjustment knob to move the stage up to just below the objective lens.
4) Then, while looking down at the eyepiece, move the stage downwards (NECESSARY SO U DONT CRASH THE SLIDE INTO THE LENS) until the specimen is just about in focus (doesn’t need to be fully focused, next step is for that)
5) Then, still looking down the eyepiece, adjust the focus with the fine adjustment knob, until you get a clear image of the specimen.
What would you do if you want to see the slide with greater magnification?
Swap to a higher powered objective lens and refocus.
Why isn’t a higher magnification always a good thing?
If your specimen is relatively big, you might not be able to see the whole thing. It can also be difficult to refocus at high magnifications.
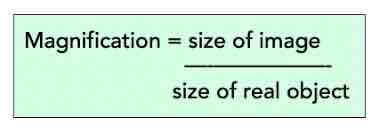
Equation for total magnification in terms of lenses.

Equation for magnification of an image if you dont know the lens used?
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
What does DNA contain?
All of an organisms genetic material.
How is DNA arranged?
In chromosomes.
Define chromosomes.
Long molecules of coiled up DNA.
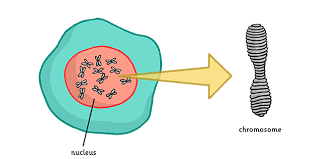
DNA is divided into small sections called…
Genes.
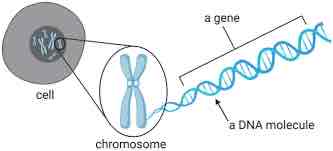
What is the shape of DNA (describe it)?
Double helix (two strands twisted together in a spiral)
What are the 4 names of nucleotide bases?
Adenine
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
A pairs up with…
T
C pairs up with…
G
How is DNA a polymer?
Each of the two DNA strands (that form a double helix) are made up of lots of nucleotides joined up in a long chain.
Define a polymer.
Large, complex molecules composed of long chains of monomers joined together.
Define a monomer.
Small, basic molecular units.
What is the monomer for DNA?
Nucleotides
Explain the effect of base pairing on the structure of DNA.
Each bases forms cross links to a base on the opposite strand, this keeps the two DNA strands tightly wound together.
What is a protein made out of?
Chains of molecules called amino acids.
Why do proteins differ with shape and function.
They have a unique chain of amino acids (particular number or order).
Define triplet code?
Each amino acid is coded for by a sequence of three bases in the gene.
How does each gene code for a different protein?
Each gene contains a different sequence of bases that allow it to code for a particular protein.
Why can’t DNA leave the nucleus?
It is too big.
How does mRNA differ from DNA?
Shorter and is only a single strand.
Describe the step by step process of protein synthesis.
1) The DNA contains the gene coding for the protein in the nucleus.
2) The two DNA strands unzip around the gene. The DNA is then used as a template to make the mRNA. Base pairing ensures it’s complimentary (matches the opposite strand). The step is called transcription.
3) The mRNA molecule then moves out of the nucleus (cause its small enough) into the cytoplasm and joins with the ribosome (site of protein synthesis)
4) Amino acids that match the triplet codes on the mRNA are joined together in the correct order. This makes the protein code for the gene.
5) These amino acids are brought to the ribosome by another RNA molecule called transfer RNA (tRNA). This step is called translation.
Define enzymes.
Biological catalysts that speed up reactions without being used themselves.
What makes up a cell’s metabolism?
The cells chemical reaction.
What is an enzyme (like how is it made)?
A protein coded for by a gene, that folds to form a unique shape which it needs to do its job.
Define substrate.
The molecule changed in the reaction.
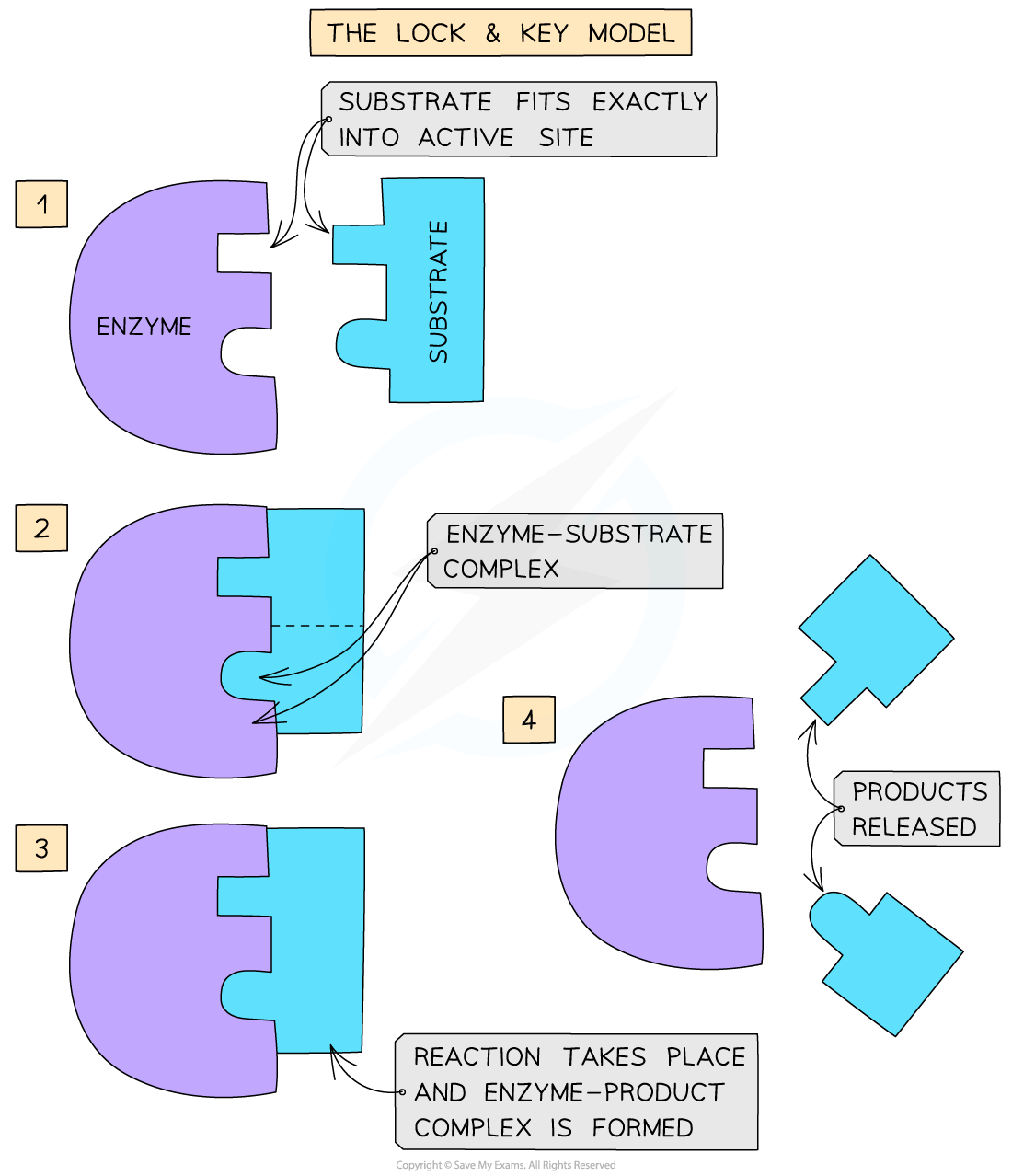
What is an enzymes active site?
The part where it joins on to its substrate to catalyse the reaction.
Explain the lock and key hypothesis,
For the enzyme to work, the substrate has to fit into the active site. If the substrate shape doesn’t match the active sites shape and the reaction won’t be catalysed.
What 4 factors affect enzyme reaction?
Temperature, pH, enzyme concentration and substrate concentration.
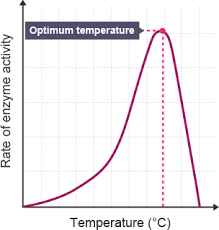
Describe the effect of temperature on enzyme activity.
Higher temperature = faster enzyme activity (enzyme and substrate move about more, so they’re more likely to meet up and react)
But if it gets too hot, the bonds holding the enzyme together will break, denaturing the enzyme.
What does it mean if an enzyme is denatured?
It loses its shape and the substrate doesn’t fit into the active site anymore.
What is the optimum temperature for enzymes?
Around 37 degrees (humans body).
Why is the human body 37 degrees?
Optimum temperature for enzyme activity (reaction goes fastest as it is just before it gets too hot and denatures).
Describe the effect of pH on an enzyme.
If pH is too high or too low, it interferes with the bonds holding the enzyme together, causing it to change the shape of the active site and irreversibly denature.
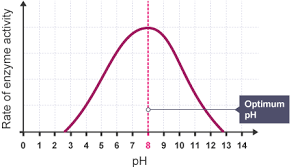
What is the optimum pH for enzyme activity?
Neutral pH of 7.
Why does the enzyme pepsin have an optimum pH of 2?
Pepsin - breaks down proteins in the STOMACH (highly acidic place in body). Therefore it needs to work at a high pH to work well in the acidic conditions of the stomach.
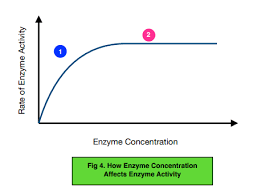
Describe the effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity.
More enzyme molecules = more likely for substrate molecule to meet up and join with one = increases rate of reaction.
But, if the amount of substrate is LIMITED, there comes a point when there are more than enough enzyme molecules to deal with all the available substrate, so adding more enzyme has no further effect.
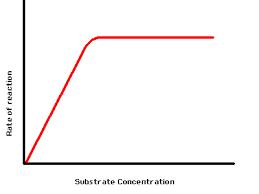
Describe the effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity.
Higher substrate concentration = more likely for enzyme to meet up and react with substrate molecules
Up to a point, when all the active sites of the enzymes are full, which means adding more substrate has no effect.
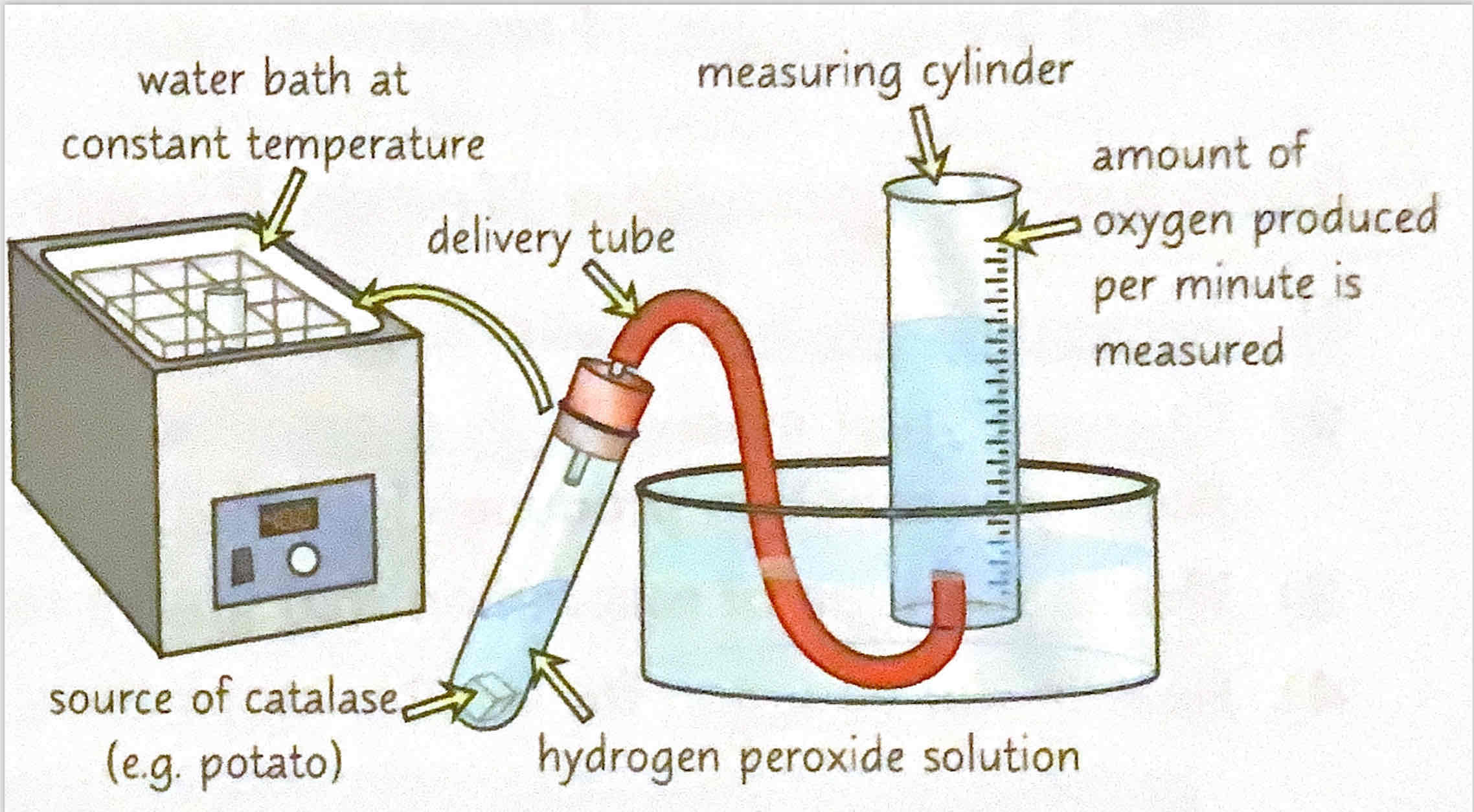
Describe the practical for measuring how fast a product appears.
1) The enzyme catalase catalyses the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
2) You can collect the oxygen and measure how much is produced in the set time.
3) Use a pPierre to add a set amount of hydrogen peroxide to a boiling tube. Put the tube in a water bath at 10°C.
4) Set up the rest of the apparatus as shown at
5) Add a source of catalase (e.g. 1cm³ of potato) to the hydrogen peroxide and quickly attached the bung.
6) Record how much oxygen is produced in the first minute. Repeat three times and calculate the mean.
7) Repeat at 20° 30° and 40°
😎 Control any variable (e.g. pH, potato used or size of potato) to make it a fair test
9) Calculate the mean rate of reaction at each temperature by dividing the mean volume of oxygen produced in centimetres cubed by the time taken ie 60 seconds. The units will be 60 cm³ per second. .
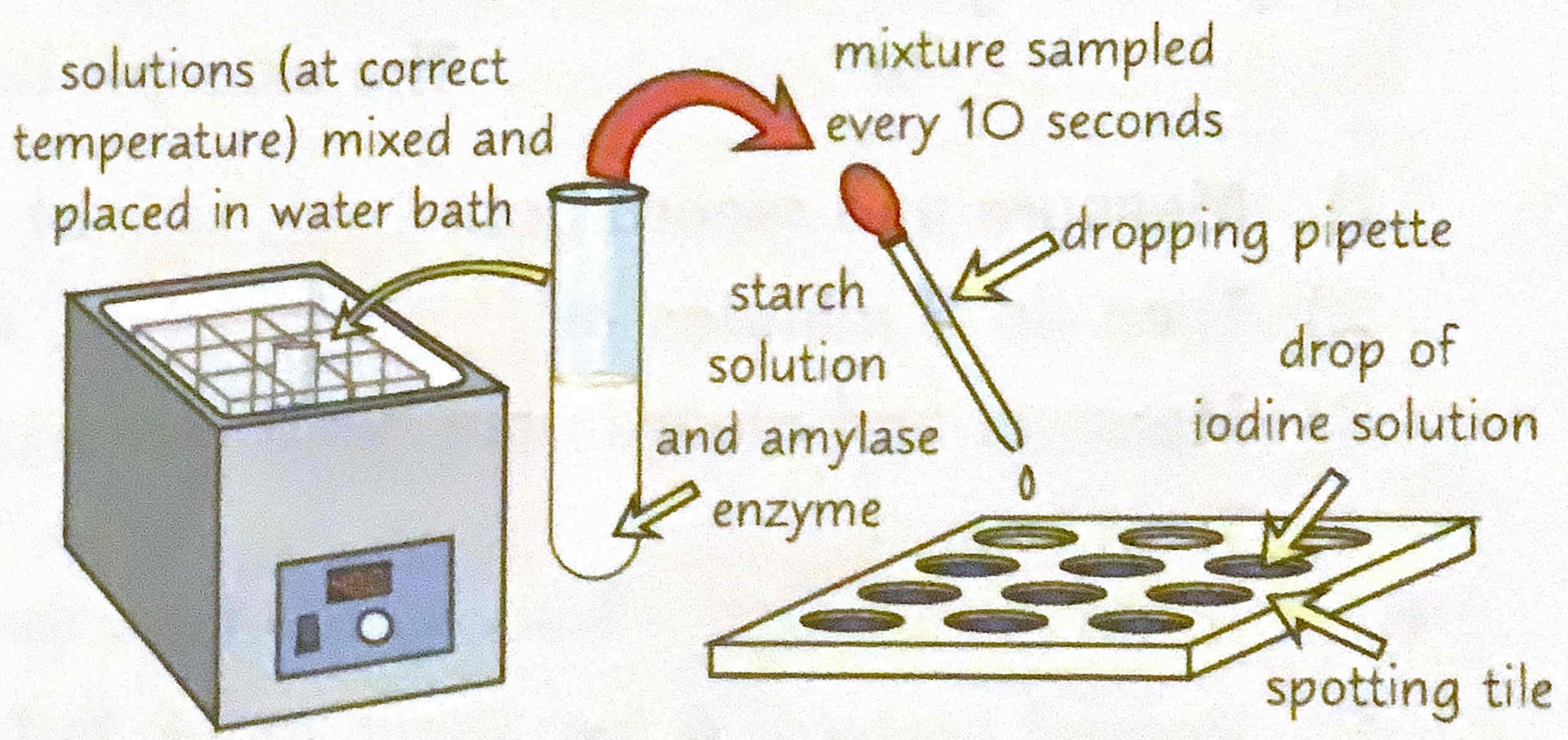
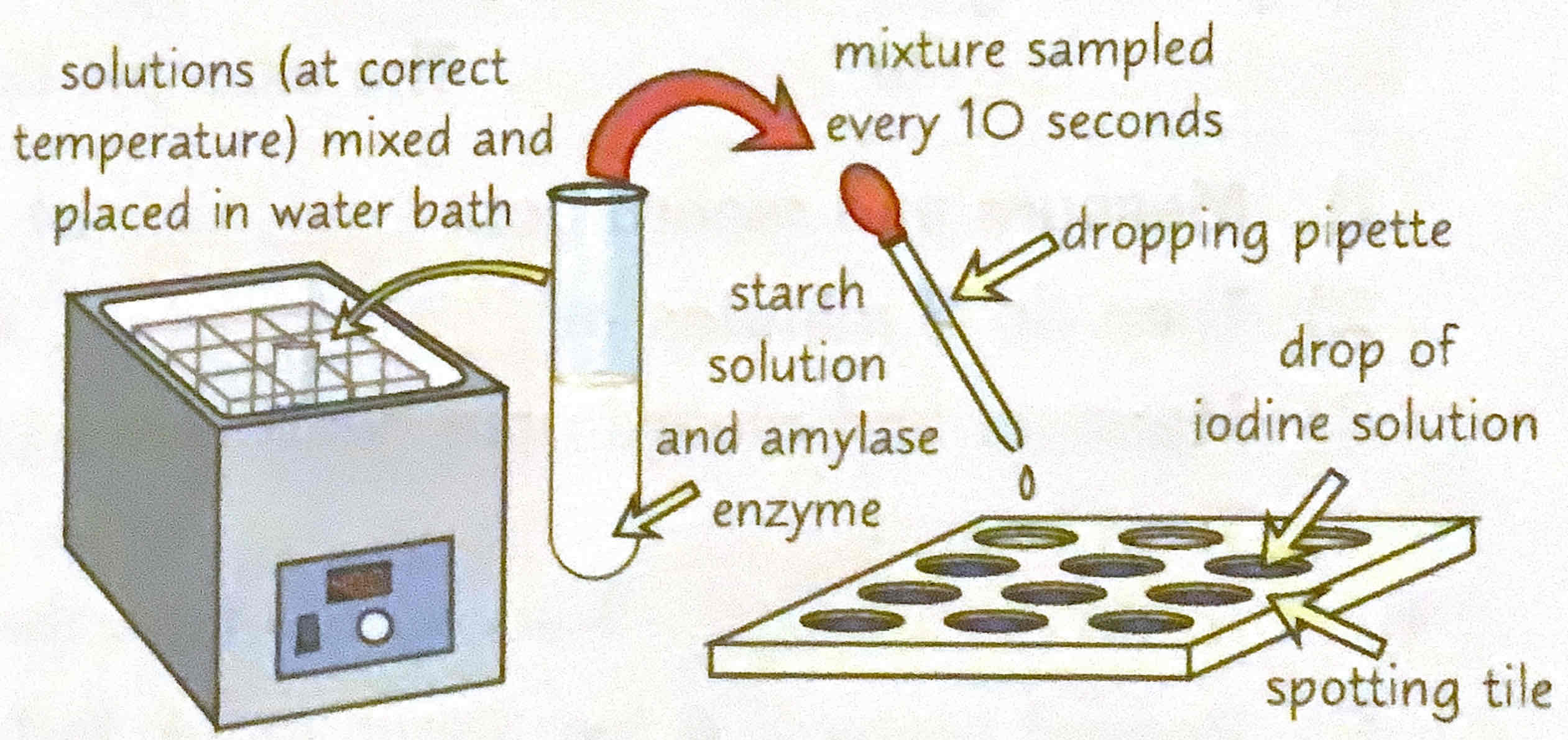
Describe the practical for measuring how fast a substrate disappears.
1) The enzyme amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch and maltose.
2) Set apparatus as shown in the diagram.
3) Put a drop of iodine solution into each well in the spotting tile. Every 10 second drop a sample of the mixture into a well using a pipette. When iodine solution remains browny orange (aka starch is no longer present) record the total time taken.
4) Repeat with the water bath at different temperatures to see how it affects the time taken for the starch to be broken down. Remember to control all of the variables each time.
How could you improve the accuracy of this experiment?
Use a colorimeter
What is a colorimeter?
A piece of electronic equipment that measures the strength of a coloured solution so measurements aren’t unreliably based on somebody’s judgment of when the colour changes.
Define respiration.
The process of transferring energy from the breakdown of glucose (a sugar).
What is meant by universal chemical process?
It happens in every cell, in all living organisms, all the time.
What is the energy transferred by respiration made into?
A substance called ATP.
What is respiration controlled by?
Enzymes.
Is respiration endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic
What are three other examples of substrates for respiration?
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
What are the two types of respiration?
Aerobic and anaerobic.
Why is aerobic respiration the most efficient way to transfer energy from glucose?
It produces lots of ATP.
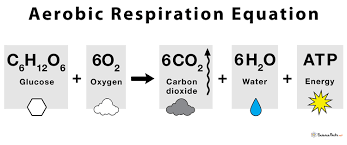
How much ATP is produced in aerobic respiration?
32 molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose.
Equation for aerobic respiration?
Why does your rate of respiration increase when you exercise?
More energy is needed by your muscles so they can contract more.
Why does breathing rate increase with exercise?
Increases to get more oxygen in the blood.
Why does your heart rate increase with exercise?
To get the oxygenated blood around your body faster.
Describe the experiment to investigate the effect of exercise on heart rate.

What is the time it takes for your heart to return to its resting rate called?
Recovery time.
How do you measure your heart rate?
Measure your pulse rate - put two fingers either on the inside of your wrist or the side of your neck and count the number of pulses in 1 minute.
Define anaerobic respiration.
Respiration in the absence of oxygen.
Why is anaerobic respiration less efficient than aerobic respiration?
It’s transfers much less energy per glucose molecule.
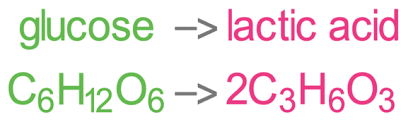
How much ATP is produced during anaerobic respiration?
2 molecules of ATP per glucose molecule.
When would anaerobic respiration occur?
During vigorous exercise.
Why does anaerobic respiration occur?
Because your body cannot supply enough oxygen to your muscles for aerobic respiration.
Equation for anaerobic respiration.
Why do you feel the burn when you do vigorous exercise?
The lactic acid builds up in your muscles, which gets painful and makes your muscles fatigued.
Define oxygen debt.
The extra oxygen you need to break down all the lactic acid you’ve built up and to allow aerobic respiration to begin again.
In what condition would a plant have to resort to anaerobic respiration?
In waterlogged soil (where there is little to no oxygen)