Unit 4 - Traumatic Brain Injury
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Traumatic brain injury
is defined as evidence of brain pathology as a result of an external force. This force may vary widely from gunshot wounds, motor vehicle accidents, or falls to the head
Traumatic brain injury: Consequences
Long-standing disability
Financial burdens
Changing family dynamics
Premature death
Mechanisms of Injury
Primary Injury
Blast Injury
Secondary Injury
Primary Injury
Where contact was made
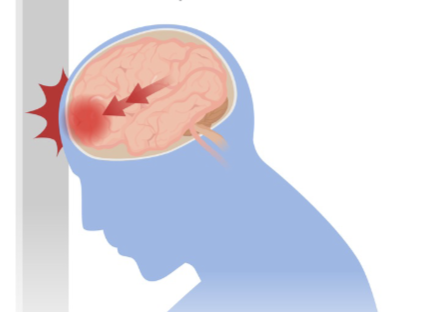
Coup-Contrecoup Injuries
result in a contusion at the area of contact, in addition to the damage or laceration created by whatever that external force was
usually localized to the site of the injury
Coup-contrecoup injuries
occur with rapid acceleration and deceleration as the brain floats within the cranium
The brain essentially bounces off of one aspect of the cranium
Coup
the frontal aspect if the collision is in a forward direction
ContreCoup
reverts backward to hit the posterior aspect of the cranium
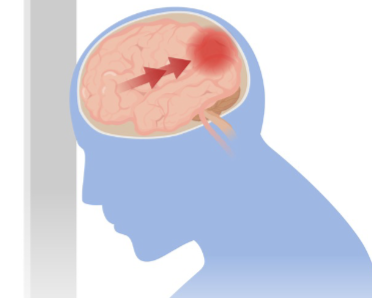
Blast Injury
No “direct” hit
Overpressure = edema
Secondary Injury
Inflammatory Response
Histamine
Micro/Macronutrients
Edema
Increased ICP
Normal Intracranial pressure
5-20 mmhg
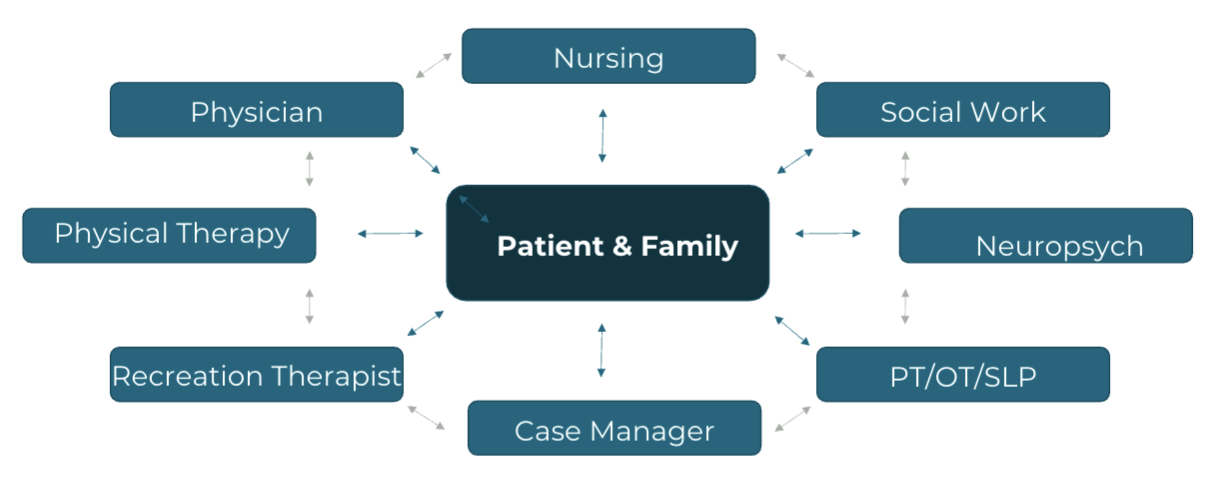
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Early Medical Management
Stabilize
Minimize complications
Identify injuries
Monitor
Minimize secondary complications by…
restoring cerebral blood flow, identifying all injuries, and monitor continuously
LOC
loss of consciousness
AOC
alteration of consciousness
PTA
post-traumatic amnesia
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Eye Opening
Motor Response
Verbal Response
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Eye Opening
Spontaneous (4)
To Speech (3)
To Pain (2)
No Response (1)
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Motor Response
Follows commands (6)
Localizes to pain (5)
Withdraws from pain (4)
Decorticate Posturing (3)
No Response (1)
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Verbal Response
A & O x 3 (5)
Confused (4)
Inappropriate words (3)
Incomprehensible sounds (2)
No Response (1)
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Mild TBI
LOC: 0-30 min
AOC: brief >24 hr
PTA: 0-1 day
GCS: 13-15
IMAGING: norm
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Moderate TBI
LOC: >30 min & <24 hrs
AOC: >24 hrs
PTA: >1 & <7 days
GCS: 9-12
IMAGING: norm or abnorm
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Severe TBI
LOC: >24 hrs
AOC: >24 hrs
PTA: > 7 days
GCS: <9
IMAGING: norm or abnorm
Galveston Orientation and Amnesia Test, or GOAT
can be used to detect orientation in amnesia post TBI
set of 14 questions pertaining to person, place, time, and situation
Imaging
necessary in cases of traumatic brain injury prior to medical intervention
First line is usually a CT scan
Causes of elevated ICP
Increase in Brain Volume
Mass Effect
Increase in CSF
Decreased Resorption of CSF
Increase in Blood Volume
Other causes
Mass effect
can also be a cause related to hematomas, tumors, abscesses, or other infarcts of brain tissue
Subfalcine herniation
characterized by the cingulate gyrus herniating against the falx cerebri
Central herniation
herniation of both temporal lobes through the tentorial notch
Transcalvarial herniation
occurs when the brain tissue is squeezed through a fracture in the skull or a surgical incision
Uncal herniation
occurs as the medial temporal lobe is squeezed by a mass under and across the tentorium
Upward herniation
occurs when a mass in the posterior cranium causes superior displacement of the cerebellum through the tentorial notch
Downward, or tonsillar herniation
caused when a mass forces the cerebral tonsils down through the foramen magnum
Management of Elevated Intracranial Pressure
Evacuation of the mass
Pharmaceutical management
Positioning
Ventilation
CSF Drainage
Hyperventilation
Hypothermia
Coma
Decompressive Hemicraniectomy/Craniotomy
Communication/Speech, Swallowing
Aphasia, Dysarthria, Dysphagia
Cognitive Impairments
Coma
Vegetative state
Minimally conscious state
Stupor
Obtunded
Coma
No arousal
may be placed into a medically-induced coma in order to decrease cerebral edema and allow for healing to occur
Vegetative state
Unaware of surroundings
the higher brain centers are not integrated fully with the brainstem. So wakefulness and consciousness are not one and the same
Minimally conscious state
Mild awareness
Behavior and responses such as reaching toward objects may be demonstrated and reproduced but are very inconsistent
Patients can also localize to stimuli
So instead of withdrawing from noxious stimuli, they may withdraw but turn their head toward that stimulus
Visual pursuit is also possible in this stage, as is sleep and wakefulness cycle
Stupor
Arousal with vigorous stimuli
Obtunded
Sleepiness/Delayed reaction
Visual/Perceptual Deficits
Similar to those seen with acquired brain injury (CVA)
General hemispheric differences
Similar to those seen in ABI
Frontal Lobe Dysfunction
executive decision making and behavioral deficits may arise
Additional Clinical Presentations
Seizure activity
Dysautonomia
Posturing
Dysautonomia
deficits in functioning of the sympathetic nervous system
may demonstrate an overactive response to stimuli, including elevated heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure, and diaphoresis
decerebrate and decorticate posturing
Decorticate posturing
an abnormal flexion posturing where the
shoulders, elbows, and wrists and fingers are flexed
lower extremities are extended and internally rotated
ankles plantar flexed
toes hyperextended
can also be termed decorticate rigidity or response
occurs with more rostral injuries to the cerebrum, including lesions to the forebrain, diencephalon, or rostral midbrain

Decerebrate posturing
an abnormal extensor posturing where the
head and neck extension
upper extremities extended
forearms pronated
fingers flexed
lower extremities also extended, internally rotated
ankles plantarflexed
toe hyperextension
This type of posturing results from a disconnect with the higher brain modulating centers with the vestibular nuclei
Animal studies have indicated that it only occurs with noxious stimuli, passive hyperextension of the head, or with metabolic abnormalities from hypoxia
This specific type of posturing is usually associated with a severe destructive cerebral lesion

Posturing can present asymmetrically…
decorticate unilaterally and decerebrate on the contralateral side.
Asymmetrical patterning, such as this, has been suggested to indicate a less severe form of injury, the anatomical divide between decorticate and decerebrate posturing being the intercollicular line at this level of the red nucleus
Lesions above the red nucleus tend to cause…
decorticate posturing
Lesions below the red nucleus tend to cause…
decerebrate posturing
Rancho Los Amigos (RLAS - R) Scale - Revised
Describes cognitive/behavioral patterns after BI
Developed in 1972 – Included 8 stages
Revised in 1997 – Included 10 stages
Level I: No response
Level X: Purposeful and Appropriate: Modified Independent
Discussed at length in an additional lecture
Activity and Participation Restrictions
Walking
Upper extremity handling
Activities of Daily Living
Return to work
Return to family
Caregiver roles
Comorbid Factors Post-TBI
Seizure
Bowel & Bladder
Cardiopulmonary Deficits
DVT & PE
Osteoporosis
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Specifically for individuals with brain injury
Describes behavioral characteristics
Original had 8 levels
Revised version (RLAS – R) includes 10 levels
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level I
No response
Unresponsive to stimuli
Equates to “coma” state
No Sleep/Wake cycles
Physical therapy indicated to decrease effects of immobility
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level II
Generalized Response
Responds only “Generally”
Vegetative state
Eyes may be open
Reflexive reactions
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level III
Localized Response
Responds inconsistently
“Minimally conscious state”
Non-verbal
Slowed processing time
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level IV
Confused/Agitated
Agitated state/combative/restlessness
Difficulty focusing on tasks
No new memories/confabulation
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level V
Confused Inappropriate
Agitation resolved
Unable to recognize insight into deficits
Deficits with memory and new learning
Post-Traumatic Amnesia
Highly Distractible
Perseveration
Likely to wander
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level VI
Confused Appropriate
General memory available
Alert and Orientation x 3 with cues
Excess time required to attend to tasks
Emotional lability/pseudobulbar affect
Keeping calendars/logs
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level VII
Automatic Appropriate
Day-to-Day memory recall
Able to complete simple routines
Robotic-like with recall
Difficulty with unfamiliar tasks
Decreased insight
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level VIII
Purposeful Appropriate (Stand by assist)
May begin transitioning to life
Continue to present with difficulties with executive functioning and memory
May become frustrated due to memory deficits
Improving awareness
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level IX
Purposeful Appropriate (Stand by on Request)
Awareness of deficits
Some abilities to multi-task
Able to request assistance
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLAS)
Level X
Purposeful Appropriate (Modified Independence)
Completely Independent
Return to Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs)
May require more time for complex tasks
Factors in Prognosis Development
A variety of factors assist in clinical decision-making poststroke
Extent of recovery versus compensation
Clinical tests and measures
Physical therapy practice setting
Principles of neuroplasticity
Clinical Tests Used in Predicting Outcomes
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Scale helps define and classify severity of brain injury
Three response scores:
Motor response
Verbal response
Eye opening
Scores
8 or less- Severe TBI
9-12- Moderate TBI
13-15- Mild TBI
Glasgow Outcome Scale: 5 Levels
Good recovery
minor deficits with full independence
Moderately Disabled
may require work accommodations
Severely Disabled
need help with daily activities
Vegetative
unresponsiveness with no higher mental functions
Dead
Glasgow Outcome Scale: Predictive Poor Recovery
Low initial GCS scores
Pupillary reactivity
Age
CT showing mass lesion
Raised ICP
CRASH
Developed by the Medical Council
Corticosteroid randomization after significant head injury
Web based calculator for TBI prognosis
Inputs: Age, GCS score, pupil reactivity, extracranial injury, CT findings
Outputs: 14-day mortality risk, 6-month outcome prediction
Galveston Orientation and Amnesia Test (GOAT)
Evaluates cognition during the subacute stage of recovery
Used during the inpatient rehabilitation to predict the following:
Functional independence
Employment
Good overall recovery
Independent living 1 year after injury
Impact of Recovery and Compensation on Prognosis
Recovery is fastest in the first 6 months post TBI but can continue months to years after Chronic traumatic brain injury recovery
Initial GCS Score
CT showing mass lesion
Personal factors
Impact of Physical Therapy Setting on Prognosis
Continuum of Care
Long-Term Care vs. Inpatient Rehab:.
Specialized Intensive Rehab:
Time-sensitive for functional recovery, especially in disorders of consciousness (DoC) (Zhang et al., 2023)
Interdisciplinary Team
Outpatient Transition
Application of Neuroplasticity to Prognosis
Use it or lose it and use it to improve it
Specificity, intensity, and repetition
Salience
Timing
Age
Interference
TBI EDGE Outcome Measures
The task force reviewed 88 outcome measures covering the domains of body structure and function, activities and participation evaluating each for psychometrics and clinical utility for patients with traumatic brain injury
TBI EDGE Outcome Measures
Recommendations were formulated for outcome measures that are:
Highly recommended (Excellent Psychometric and clinical utility)
Recommended (Good Psychometric and clinical utility)
Reasonable to use (Good or excellent Psychometric and clinical utility BUT insufficient study in target group)
Do not Recommend (Poor Psychometric and/or clinical utility)
Types of TBI EDGE Outcome Measures
for inpatient and outpatient rehab
for acute care
for research
for entry-level education
TBI EDGE Outcome Measures:
Highly Recommended (Inpatient only)
Coma Recovery Scale-Revised
Moss Attention Rating Scale (MARS)
Coma Recovery Scale-Revised
Used to establish diagnosis, monitor behavioral recovery, predict outcome, and assess treatment effectiveness.
It can be used in all life span age ranges.
ICF Domain: Body Structure & Body Function.
Time to administer: 15-30 minutes
Moss Attention Rating Scale (MARS)
Used to measure attention-related behaviors after TBI
ICF Domain: Body Structure & Body Function
Time to administer: 5 minutes
TBI EDGE Outcome Measures:
Highly Recommended (Outpatient only)
High Level Mobility Assessment (Hi-MAT)
High Level Mobility Assessment (Hi-MAT)
Assesses the high-level motor performance in TBI patients
The minimum mobility requirement independent walking over 20 meters without gait aids (orthoses are permitted).
ICF Domain: Body Structure & Body Function and Activity.
It can be used in all age ranges staring from 13 y/o or older.
Time to administer: 5-10 minutes
TBI EDGE Outcome Measures:
Recommended Measures (Inpatient only)
Disorders of Consciousness Scale (DOCS)
Agitated Behavioral Scale (ABS)
Cog-Log and Orientation-Log
Barthel Index
Functional Independence measures (FIM)
Disorders of Consciousness Scale (DOCS)
Used to monitor recovery of consciousness.
Evaluate the effects of interventions in adults following a severe traumatic brain injury
DOCS-25 is the most up-to-date and current version
Agitated Behavioral Scale (ABS)
It measures the behavioral aspects of agitation during the acute phase of recovery from acquired brain injury including aspects of aggression, disinhibition, and lability.
14-item instrument, Minimum score is 14; maximum score is 56.
Each item is rated on a scale from 1 to 4:
1 = NO agitated behavior
2 = Mild agitated behavior
3 = Moderate agitated behavior
4 = Extreme/severe agitated behavior
TBI EDGE Outcome Measures:
Recommended Measures (Outpatient only)
Action Research Arm Test
Global Fatigue Index
Apathy Evaluation Scale
Sydney Psychosocial Reintegration Scale
Balance Error Scoring Scale (BESS)
Community Integration Questionnaire
Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI)
Community Integration Questionnaire
Used to assess the social role limitations and community interaction of people with acquired brain injury.
Can be self-administered or administered over the phone
Recommended measures (Both inpatient and outpatient)
6-minute walk
10-meter walk
Berg Balance Scale
Community Balance and Mobility Scale
Disability Rating Scale
Functional Assessment Measure (FAM)
Modified Ashworth Scale
Patient Health Questionnaire
Quality of Life after Brain Injury
Rancho Levels of Cognitive Function
Community Balance and Mobility Scale (CB&M)
evaluates balance and mobility skills necessary for full participation in the community in ambulatory adolescent and adult patients.
All tasks are performed without ambulation aides, except (descending stairs) for which a cane can be used.
Orthoses are permitted
Functional Assessment Measure (FAM)
Adjunct to the FIM (can't be used alone).
Includes functional areas:
Community access
Reading and writing
Safety
Employability
Acute Hospital: LOS, STG, LTG, Considerations
LOS: 7.9 days
STG time: <1 wk
LTG time: Expected LOS
considerations: Discharge Disposition: Post Acute Rehab vs Home
Post Acute Rehab: LOS, STG, LTG, Considerations
LOS: 17 days
STG time: 1 wk
LTG time: Expected LOS (2-6 wks)
considerations: Recovery vs Compensation
Outpatient: LOS, STG, LTG, Considerations
LOS: 2-6 mo
STG time: 1 mo
LTG time: Expected LOS (2-3 mo)
considerations: LOS dependent on dx and insurance; once d/c from OP, therapy is complete
Home Health: LOS, STG, LTG, Considerations
LOS: 1-2 mo
STG time: 2 wks
LTG time: 1-2 mo
considerations: D/c disposition = OP vs completed therapy
Creating “Task / Activity” Specific Goals
Review your Outcome / Objective Statement from your Task Analysis
Identify the measurable aspects of the statement
Based on setting (post-acute rehab) & clinical reasoning, you progress the measurable aspects of the statement and connect to a participation restriction.
Outcome Measure Goals – Activity & Beyond
What to do with the higher level patients in outpatient?
Consider Higher Level OMs from the TBI EDGE recommendations