4.2.2.2 + 4.2.2.3 - The heart and blood vessels
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Does the heart have a double or singular circulatory system?
Double circulatory system
What is meant by a double circulatory system?
Two circuits joined together
Describe the double circulatory system in the heart?
The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to take in oxygen. The blood then returns to the heart.
The left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood around all the other organs of the body. The oxygen from the blood is transferred to the body cells. The deoxygenated blood returns to the heart so it can be pumped to the lungs again.
What are the use of valves in hearts?
To make sure blood flows in the right direction - prevent it from flowing backwards
What are the heart walls mostly made out of?
Muscle tissues
What is the order of blood flow through the heart?
The blood needs its own supply of oxygenated blood - which artery gives the heart this?
Coronary arteries branch off the aorta and surround the heart.
Describe the location and explain the importance of the coronary arteries
provide oxygenated blood and glucose for respiration in the heart.
Surround the heart and are found at the surface
Describe and explain the difference in thickness in the walls of the right and left ventricles
The left ventricle has a thicker wall as it pumps blood at higher pressures as the blood needs to be transported around the body.
Describe and explain how the resting heart rate is controlled
It is controlled by a group of cells in the right atrium wall that produces a small electric impulse which spreads to the surrounding muscle cells, causing them to contract. It acts like a pacemaker
What are the 3 types of blood vessels?
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
What are the role of Arteries?
Carry blood away from the heart
What is the role of Capillaries?
Involved in the exchange of materials at the tissues (glouc
What is the role of Veins?
Carry blood to the heart
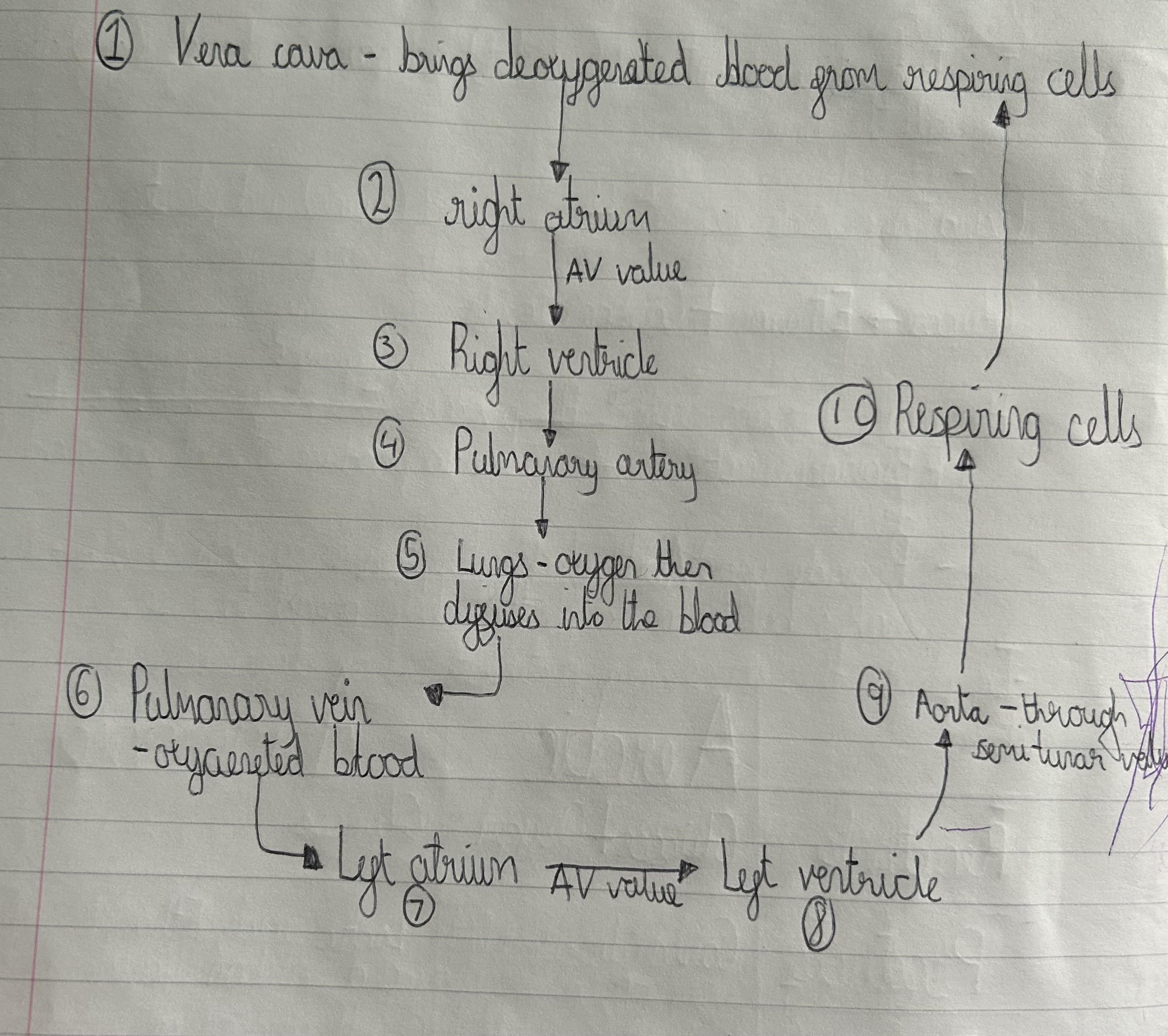
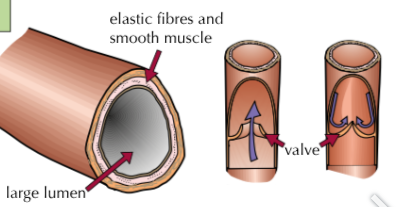
What are the characteristics of Arteries?
Walls are strong and elastic - because it pumps blood at high pressures.
Walls are thick compared to the lumen
Walls contain thick layers of muscle and elastic fibres
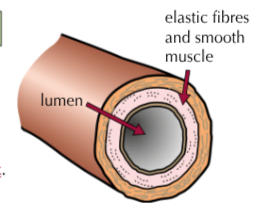
What are the characteristics of Capillaries?
Are really small - they carry blood really close to every cell in the body to exchange substances with them.
Have permeable walls - substances can diffuse in and out
Walls are usually one cell thick - increasing the rate of diffusion by decreasing the distance
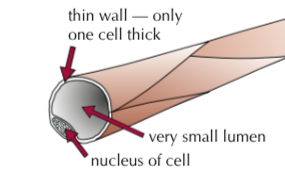
What are the characteristics of Veins?
Have valves to keep blood flowing in the right direction
Have a bigger lumen to aid with blood flow.
How to calculate the rate of blood flow?
Rate of blood flow = volume of blood/number of minutes
What is the role of Red blood cells?
To carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells in the body
What happens when there is less red blood cells in the blood? And why?
Fatigue:
Less oxygen transported to respiring cells
Less respiration occurs
So less aerobic respiration
But more anaerobic respiration - lactic acid produced so there is muscle fatigue
Adaptations of red blood cells?
Their shape is a biconcave disc - gives a large surface area for absorbing oxygen
Don’t have a nucleus - allows more room to carry oxygen
Contain a red pigment called haemoglobin - binds to oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin
What is the role of white blood cells?
To kill unwanted microorganisms to prevent infection
What happens when there is less white blood cells? And why?
Frequent infections:
Fewer phagocytes/lymphocytes
So fewer phagocytosis and antibodies/antitoxins occur
So less pathogens killed/neutralised
Adaptation of white blood cells?
Phagocytes can change shape to engulf pathogens
Lymphocytes produce antibodies and antitoxins
Role of platelets?
They help the blood to clot at a wound - to stop microorganisms getting in and blood pouring out
What are platelets?
small fragments of cells - have no nucleus
What happens when there is less platelets? And why?
More bleeding and more frequent infections:
Less platelets so less blood clotting at wounds therefore microorganisms can enter
What is plasma
Pale - straw coloured which carries just about everything
What do plasma carry?
Red and white blood cells + platelets
Nutrients (glucose and amino acids)
Carbon dioxide
Urea
Hormones
Proteins
Antibodies and antitoxins