Climate - The Atmosphere
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is the stmosphere?
An envelope of gases consisting of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% other gases.
Explain the atmospheric heat budget
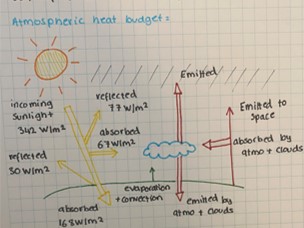
What is incoming solar radiation known as?
insolation
What is the main source of energy driving our weather systems?
The sun
Where is most of the energy from the sun absorbed?
Equator
Where is most of the energy lost?
Polar regions
How is solar radiation redistributed to higher latitides?
Circulation (wind and air)
How is energy recieved?
As short-wave radiation
How much energy does the sun provide in comparison to how much we use?
It provides more energy in an hour than we humans use in a year
Define short-wave radiation
Energy from the sun that enters the atmosphere. They are very short wavelengths like UV and visible light
Define long-wave radiation
Energy leaving the earth as infrared radiation at low energy and contains less energy than short-wave radiation
Define convection
The transfer of heat by movement of gas or liquid
Define conduction
The transfer of heat by contact
What is the greenhouse effect?
The process where water vapour, CO2, CH4, CFCs allow short-wave radiation to pass through the atmosphere and heat the earth.
What is the resultant of the greenhouse effect?
That long-wave radiation gets trapped
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
A result of increased quantities of GHGs in the atmosphere due to human activity and their impact on the fragile atmospheric systems.
What are 5 examples of stores?
Land
Oceans
Clouds
Atmosphere
NOT FINISHED
ugh