2.1 Cell origin
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Why are viruses not considered to be living organisms?
they are unable to reproduce outside of the host cell.
they cannot keep themselves in a stable state
They rely on the host cell for most life processes, including nutrition and growth, and they do not possess a metabolism
Why are cells considered to be living?
they contain all the components necessary to carry out all eight processes of life at some point in their life cycle.
Individual cells use energy to maintain their state. They can also divide to produce more cells. They can be taken from the body and cultured.
What is the spontaneous generation theory and why was it rejected?
Describe how Pasteur’s experiments provided convincing evidence to falsify the concept of spontaneous generation.
a. spontaneous generation is life appearing from nothing / from non-living / cells only come from pre-existing cells/life
b. broth/culture medium (for bacteria) (used/placed) in flasks
c. broth boiled/sterilized «in some flasks» to kill microbes
d. no clouding/signs of bacterial growth/reproduction / microbes did not appear «in flasks of boiled broth»
e. after necks of flasks were snapped boiled broth became cloudy/growth of microbes
f. because microbes from the air contaminated the «boiled» broth
(curved necks allowed indirect exposure to air but prevented entry of microbes)
What are the 8 processes of life?
Mr GRENHM
Metabolism
reproduction
homeostasis
movement
growth
respond to stimuli
excretion
nutrition
Conditions of the early earth
High atmospheric temperature
High levels of CO2 and CH4 (green house gases hence trapped infrared radiation increasing surface temp)
this ment it had a reducing atmosphere
The reducing gases in the atmosphere would have been able to donate electrons to other molecules, enabling chemical reactions to take place.
No ozone layer
due to lack of oxygen (Ozone is O3 which is formed when UV radiation from the sun interacts with O2)
led to UV radiation penetrating to the surface of Earth
UV radiation cause DNA damage and increases the rate at which mutations occur
Liquid inner core (rather than the solid current one)
increased motion within the liquid core would have resulted in a smaller protective magnetic fields than existing today, exposing the plannet to much solar higher radiation and cosmic rays
Intense volcanic acitivty and meteorite bombardment
Lead to high concentration of CO2 and methane which are both heat trapping energy hence increasing the temperature of the earth.
What led to the formation of carbon compounds in the early years?
Early Earth conditions may have allowed the spontaneous formation of carbon compounds through unique chemical processes which do not occur now.
Adding energy (heat or UV radiation) to the early atmosphere's gas mixture could have produced organic molecules like amino acids, simple sugars, nucleotides, and fatty acids.
These organic molecules served as the building blocks for early cells.
High levels of UV radiation on early Earth might have catalyzed the formation of larger polymers such as proteins, complex sugars, mRNA, and phospholipids from these simpler molecules.
What are the intermediate stage required for evolution of the first cells?
Catalysis - Provides control over which chemical reactions occur
Self-assembly - carbon compounds such as amino acids have to form polymers
Compartmentalization- a membrane must develop to enclose cell contents
Self replication of molecules- Molecules replicate to form the basis of inheritance and the persistence of successful variants .
Discuss the limitations in testing hypothesis about the cells origin.
Billions of years ago the conditions of earth was very different. Whilst scientists have attempted to model conditions on prebiotic earth, it is not possible to replicate the conditions with certainty.
What is the hypothesis for the necessary steps for the origin of cell?
simple organic compounds such as amino acids and hydrocarbons were formed.
chemical reactions were accelerated in the process of catalysis
larger organic molecules including RNA and phospholipids were assembled from smaller molecules
some of these molecules including RNA were able to self replicate
formation of a membrane bound compartment (the cell surface membrane) allowed the internal chemistry of the cell to become different from that of outside compartment
The methodology of the Miller Urey experiment set
Sealed Glass Apparatus with Gases:
Reasoning: Represents the Earth's primitive atmosphere, consisting of methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen (H2), and water vapor (H2O).
Electric Discharge Apparatus:
Reasoning: Simulates lightning strikes, providing the energy needed to drive chemical reactions in the atmosphere, similar to the conditions on the early Earth.
Condenser:
The condensed water droplets formed on the side of the apparatus and collected at the bottom, representing the primordial soup of the early oceans.
Allowed to Run for a Week:
Reasoning: Provides sufficient time for the simulated processes to occur, allowing the accumulation of organic compounds.
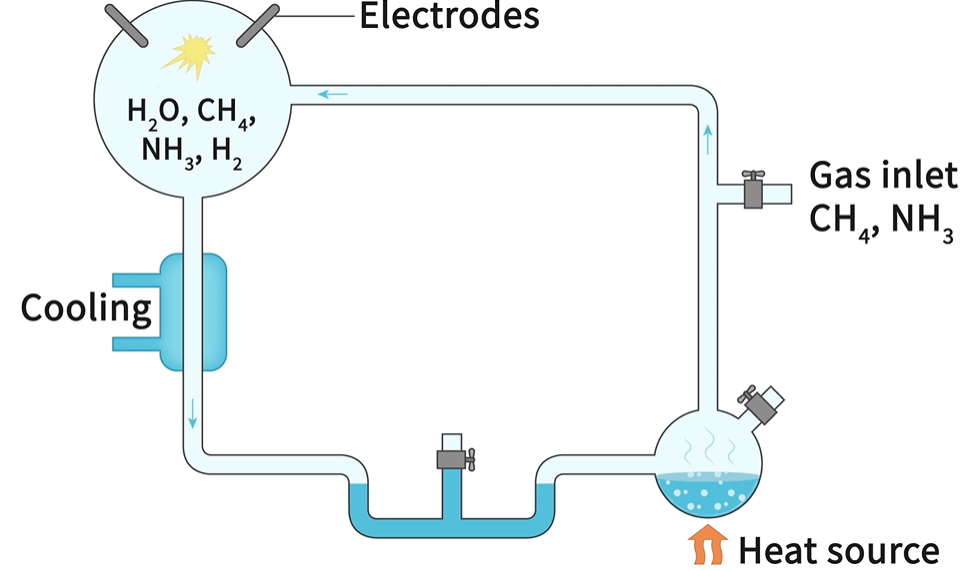
Outline the results and conclusion drawn from the Miller Urey experiment
Day 1: Pink water
Week 1: Dark red water
-proved that it was possible for carbon compounds to spontaneously form prior to the formation of life (as long as the experiment stimulated conditions were correct)
produced some simple organic molecules. Complex oily hydrocarbons were synthesised and Amino acids.
Evaluate the Miller and Ureys experiment in 1952
Methane availability
At the time Miller and Urey performed their experiment, it was believed that they simulated the early atmosphere accurately by including high levels of methane
It is now believed however, that methane may have been in low supply in the atmosphere of early Earth
The energy source
Miller and Urey used an electrical discharge as a source of energy instead of UV light
For the synthesis of organic molecules, however, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water require nuclear and UV radiation along with electrical discharges
The presence of water
In a watery environment amino acids tend to remain as monomers rather than joining to form proteins
Given that water is needed to form the 'primordial soup', this contradicts the idea that complex molecules could have formed in this environment
Nucleotides
Miller and Urey were unable to generate nucleotides with their experiments
Nucleotides have since been chemically synthesised using a different approach
What’s an amphipathic cell?
A molecule comprised of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic cells
What is the primordial soup
A hypothetical mixture of organic compounds formed in the conditions present on pre-biotic Earth.
What do modern cells use as their genetic components?
DNA as the genetic material
Enzyme proteins as catalyst of metabolism
How did the formation of a membrane-bound compartment occur and what is its importance?
When fatty acids spontaneously coalesced to form a spherical bilayer, a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses a space.
This physical separation provided a chemical environment with a different chemistry to the external environment allowing the cells to control and maintain a precise set of conditions for proper cell functioning, including pH and solute concentration.
Why is RNA presumed as the first genetic material?
Short RNA sequences have been shown to be able to duplicate other molecules of RNA, demonstrating that RNA can self-replicate
.
RNA has some catalytic activity so it may have acted initially as both the genetic material and the enzymes of the earliest cells.
ribosomal Ribozymes in the ribosome are still used to catalyse peptide bond formation during protein synthesis.
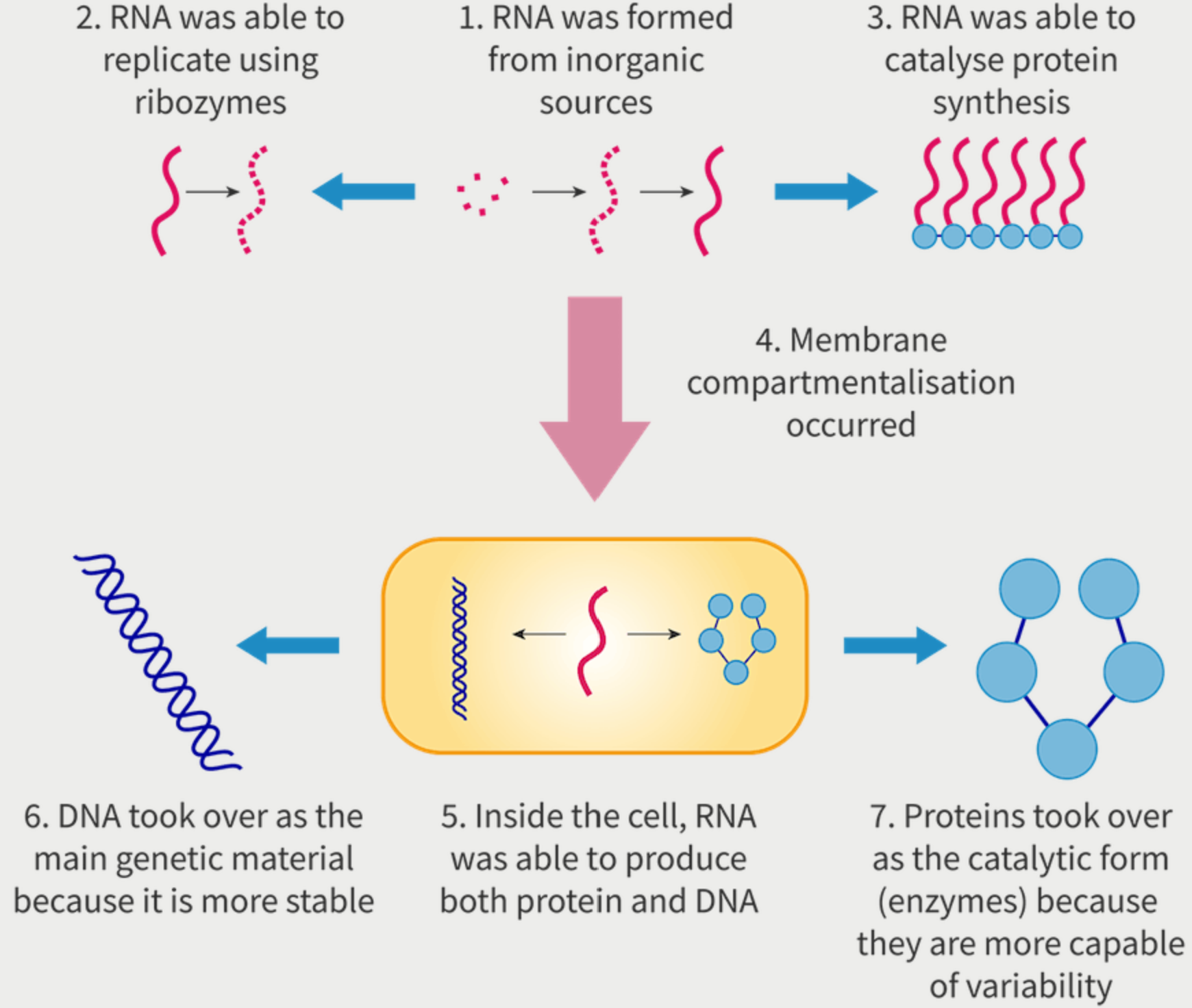
Explain the RNA first hypothesis and outline how life may have originated on earth. PRovide a diagram.
(from virus topic as well) (not very important but just to look over)
RNA was formed from inorganic sources.
RNA was able to replicate using ribozymes.
RNA was able to catalyse protein synthesis.
Membrane compartmentalisation occurred.
Inside the cell, RNA was able to produce both protein and DNA.
DNA took over as the main genetic material because it is more stable.
Proteins took over as the catalytic form (enzymes) because they are more capable of variability.
Compare the genetic stability between RNA and DNA
DNA generally exhibits higher genetic stability compared to RNA due to its double-stranded structure, accurate replication mechanisms, and greater resistance to chemical and enzymatic degradation. DNA is optimized for the stable storage of genetic information,
while RNA, with its dynamic and versatile nature, is more prone to changes and mutations, allowing for rapid adaptation and evolution.
What is the evidence of the Last Universal Common Ancestor in the vicinity of hydrothermal vents
existed deep in the ocean in alkaline hydrothermal vents.
These hydrothermal vents would have been rich in hydrogen and dissolved minerals, including sulfur, methane and iron, which could have been used by LUCA as an energy source.
Hydrothermal vents have high temperatures, which could have provided the energy necessary for the formation of complex organic molecules required for cellular formation
Explain the use of deductive reasoning to predict what genes were present in the LUCA cells
Characteristic and features of LUCA
existed between 2.5 and 3.5 billion years ago
existed deep in the ocean in alkaline hydrothermal vents. These hydrothermal vents would have been rich in hydrogen and dissolved minerals, including sulfur, methane and iron, which could have been used by LUCA as an energy source.
Hydrothermal vents have high temperatures, which could have provided the energy necessary for the formation of complex organic molecules required for cellular formation
was anaerobic, which fits with the lack of oxygen in the early atmosphere of the Earth
was autotrophic, combining inorganic carbon with hydrogen, to produce carbon dioxide and formic acid, which could then be used for other processes.
What are stromatolites?
fossils found within rocks that are thought to have been formed by layered communities of microorganisms.
Describe the conditions present in a white-smoker hydrothermal vent
emerge at temperatures of 60-90 degrees
contained high concentrations of hydrogen, methane, ammonia and sulphides
what is phylogenetic analysis?
Studying genomes and characteristics of organisms to infer genetic relatedness and evolutionary history.