NHM 361 - Lipid Metabolism
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
What are lipoproteins?
A group of molecules that contain lipids (phospholipids, cholesterols, and triglycerides) and proteins.
What is the function of lipoproteins in the bloodstream?
They act as transport vehicles that transport lipids to various parts of the body.
What are apolipoproteins?
The protein portions of lipoprotein particles.
What are lipoproteins classified by?
Density
What is the biggest type of lipoprotein?
Chylomicron
What percentage of triglycerides do chylomicrons contain?
Over 85%
What type of lipoprotein contains high levels of triglycerides over 50%?
Very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
What type of lipoprotein contains high levels of cholesterols?
Low density lipoprotein (LDL)
What type of lipoprotein contains high levels of protein?
High density lipoprotein (HDL)
What enzyme breaks down lipoproteins?
Lipoprotein lipase
What is the order of lipoproteins by proportion of triglyceride from highest to lowest?
Chylomicron > VLDL > LDL > HDL
What is the order of lipoproteins by density from lowest to highest?
Chylomicron < VLDL < LDL < HDL
What are dietary triglycerides hydrolyzed into during digestion?
Glycerol, monoglycerides, and free fatty acids
What enzyme hydrolyzes dietary triglycerides during digestion?
Intestinal lipase
Where are triglycerides resynthesized in the body?
Inside small intestine enterocytes
What do triglycerides combine with to form chylomicrons?
Proteins, phospholipids, cholesterol, and fat-soluble vitamins
What do chylomicrons contain?
Lipids from the diet (mostly triglycerides) and a small amount of protein.
Where are chylomicrons synthesized?
In the intestinal cells.
What happens to chylomicrons after they are synthesized?
They enter the lymph or the bloodstream.
What enzyme hydrolyzes chylomicrons?
Lipoprotein lipase.
What are chylomicron remnants taken to?
The liver.
What is Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)?
A type of lipoprotein produced in the liver.
What does VLDL contain a high proportion of?
Lipids, including those synthesized in the liver and dietary lipids from chylomicron remnants.
What is the primary function of VLDL in circulation?
To deliver lipids, mostly triglycerides, to tissue.
What enzyme hydrolyzes VLDL in circulation?
Lipoprotein lipases.
What is Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)?
A type of lipoprotein that delivers cholesterol to tissues.
What percentage of LDL particles is cholesterol?
~45% cholesterol
What percentage of LDL particles is triglyceride?
10% triglyceride
What percentage of LDL particles is protein?
25% protein
How is VLDL converted to LDL?
VLDL can be converted to LDL by lipoprotein lipases.
What can high circulating LDL cause?
High circulating LDL can cause plaque, leading to atherosclerosis.
What is atherosclerosis?
A condition where plaque clogs arteries.
What can result from a clot blocking a narrowed artery?
A heart attack or stroke can result.
What is LDL cholesterol often referred to as?
Bad cholesterol.
What does HDL stand for?
High Density Lipoprotein
Why are HDL particles considered to have the greatest density among lipoproteins?
Because they contain the most protein and the least triglyceride.
What is one of the main functions of HDL?
It helps remove cholesterol from tissues and transports it back to the liver.
What is cholesterol carried within HDL particles commonly referred to as?
Good cholesterol
What is the relationship between high circulating levels of HDL and heart disease?
High circulating levels of HDL are associated with reduced risk of heart disease.
What happens to triglycerides during glycogen depletion?
Triglycerides are broken down and used as an energy source.
What occurs to triglycerides when glycogen is present?
Triglycerides are still broken down to conserve glycogen.
What can glucose from glycogen be used for?
It can be used by brain cells and red blood cells.
Why can't fatty acids cross the blood-brain barrier?
The blood-brain barrier precludes entry of fatty acids.
Why can't red blood cells perform β-oxidation?
Red blood cells lack mitochondria.
What is hydrolysis of fat?
It is the breaking down of triglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol.
What hormones stimulate the hydrolysis of fat?
Epinephrine and glucagon.
Which enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of fat?
Hormone-sensitive lipase.
How are fatty acids transported to target tissues after hydrolysis?
They bind to albumin.
How is glycerol transported to target tissues after hydrolysis?
It is dissolved in the blood stream and is hydrophilic.
Lipid Catabolism
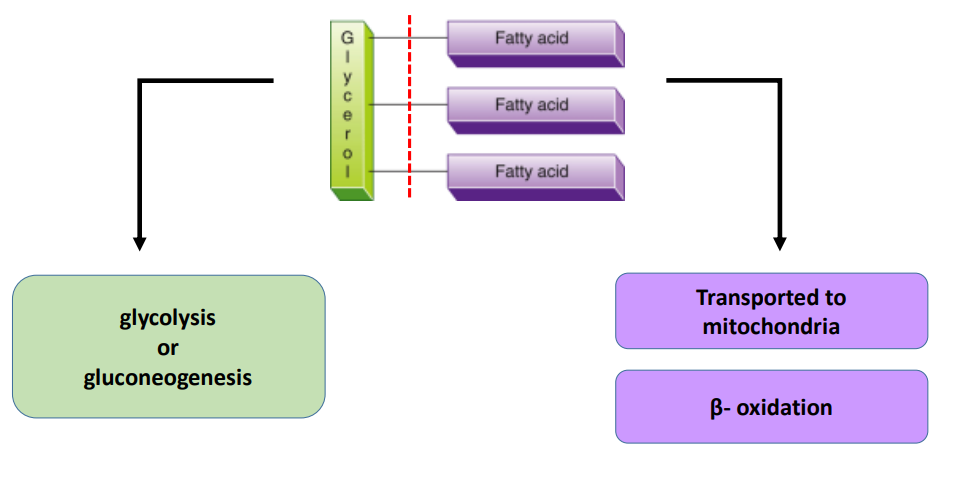
What can glycerol from hydrolyzed triglycerides enter?
Glycolysis
What is glycerol converted to in the cytoplasm?
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Which enzyme converts glycerol to glycerol 3-phosphate?
Glycerol kinase
Which enzyme converts glycerol 3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate?
Glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
What two metabolic pathways can glycerol enter?
Glycolysis or gluconeogenesis
Can fatty acids directly pass through the mitochondrial membrane?
No, fatty acids cannot directly pass through the mitochondrial membrane.
What enzyme catalyzes the conversion of fatty acids to fatty acyl-CoA in the cytosol?
Acyl-CoA synthetase
What is required for the conversion of fatty acids to fatty acyl-CoA?
ATP
What is the reaction for the conversion of fatty acid to fatty acyl-CoA?
Fatty acid + CoA + ATP ↔ Fatty acyl-CoA + AMP + PPi
What shuttle does fatty acyl-CoA enter to be transported into mitochondria?
Carnitine shuttle
What is β-Oxidation?
The pathway by which a fatty acyl-CoA is broken down into molecules of acetyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix.
What is the process of β-Oxidation?
The process of 2 carbon unit removal from fatty acyl-CoA.
What is the end product of β-Oxidation?
Acetyl-CoA, FADH2, and NADH.
What happens to a 16 carbon fatty acid during β-Oxidation?
It is broken down into 14 carbon fatty acids, then 12 carbon fatty acids, and so on.
What is the role of Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase in β-Oxidation?
Transfers electrons from fatty acyl-CoA to FAD, producing FADH2 for the electron transport chain.
What does Enoyl-CoA hydratase do in β-Oxidation?
Adds water to produce β-hydroxyacyl-CoA.
What is the function of β-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (HAD) in β-Oxidation?
Removes hydrogen to form ketoacyl-CoA, with NAD+ as the electron acceptor producing NADH for the electron transport chain.
What is the role of Acyl-CoA acetyl-transferase (thiolase) in β-Oxidation?
Incorporates with free CoA and cleaves the ketoacyl-CoA.
What does Acetyl-CoA produce when it enters the citric acid cycle?
3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP
What do FADH2 and NADH enter after being produced in β-Oxidation?
The electron transport chain
What happens to fatty acyl-CoA during β-Oxidation?
It becomes 2 carbons shorter and re-enters β-Oxidation
What are the products of each cycle of β-Oxidation?
Acetyl-CoA, FADH2, and NADH
What is the process called where fatty acyl-CoA is converted to Acetyl-CoA repeatedly?
Fatty acid spiral
What is produced by β-oxidation that can lead to ketone body synthesis?
Acetyl-CoA
Where does ketone body synthesis mainly occur?
In the liver mitochondria
What are the two main types of ketone bodies?
Acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate
How are ketone bodies utilized by extrahepatic tissues?
They are converted to acetyl-CoA and enter the citric acid cycle to produce energy.
Which organ can use ketone bodies as an alternative energy source?
The brain
What is the primary ketone body?
Acetoacetate
What is the secondary ketone body?
β-hydroxybutyrate
How are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate transported in the body?
They are transported by the blood to other tissues.
What do acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate convert back to in tissues?
Acetyl-CoA
What is acetone in relation to ketone bodies?
It is a secondary ketone body produced in smaller quantities.
How is acetone eliminated from the body?
It is volatile and exhaled.
What is ketogenesis?
A metabolic process that occurs during very low carbohydrate levels in the body.
What conditions can lead to ketogenesis?
Overnight starvation, low carb diet, or uncontrolled diabetes.
What is the primary energy source used during ketogenesis?
Fat.
What is produced when fat is broken down during ketogenesis?
Acetyl-CoA.
What enhances the formation of ketone bodies during ketogenesis?
Accumulation of acetyl-CoA.
What is a possible result of ketogenesis in urine?
Ketone bodies (ketonuria).
What is ketosis?
High levels of ketone bodies in blood.
What is ketonuria?
The presence of ketone bodies in the urine.
What causes ketonuria?
Ketone bodies in circulation spill over into the urine.
What is ketoacidosis?
A condition caused by elevated levels of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, which are acidic.
What is the effect of ketoacidosis on blood pH?
It causes low blood pH due to elevated levels of ketone bodies.
What are the potential dangers of acute ketoacidosis?
It can lead to coma or death.
What is lipogenesis?
The synthesis of triglycerides.
What is the starting material for fatty acid synthesis?
Acetyl-CoA.
What is the process of converting Acetyl-CoA to triglycerides?
Acetyl-CoA → Fatty acids → Triglycerides.
What type of pathways do fatty acids participate in?
Anabolic pathways.