common pool resources and negative externalities
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
common pool resources
resources not owned by anyone
don’t have a price
free to use without payment or other restrictions
eg: clean air, lakes, rivers
common pool resources are…
rivalrous: the consumption by one person reduces the availability for someone else
non-excludable: it is not possible to exclude people from using the resources since there is no price
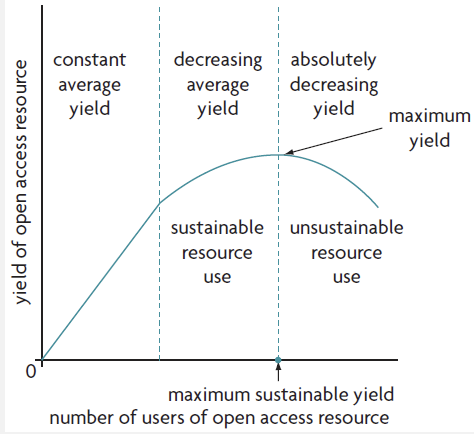
tragedy of the commons
situation in which individuals sharing a common resource act based on self-interest
ultimately, depleting the resource
unsustainable production
production that uses resources unsustainably
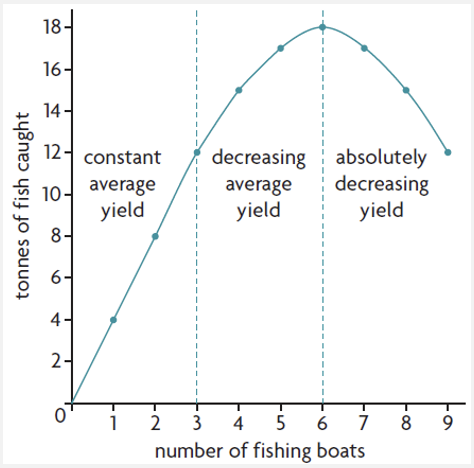
maximum sustainable yield
maximum use that can be made of a resource that is also sustainable, in that the resource can reproduce itself.
market failure
the failure of market to allocate resources efficiently
results in allocative inefficiency
private benefit, external benefit and social benefit
private: the benefit gained directly by the consumer
external: the benefit gained by a third party
social: private + external
private cost, external cost and social cost
private: cost firm pays when producing a good
external: cost incurred by third parties
social: private + external
externality
occurs when the actions of consumers or producers give rise to negative or positive side effects on other people who are not part of these actions and whose interests aren’t taken into consideration
MSB>MPB
MSC>MPC
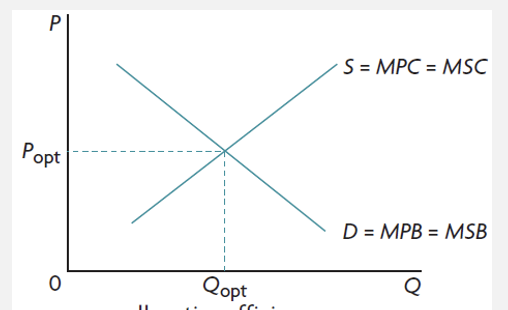
allocative efficiency
when MSC=MSB
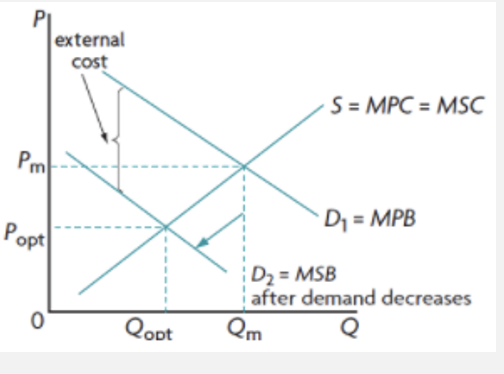
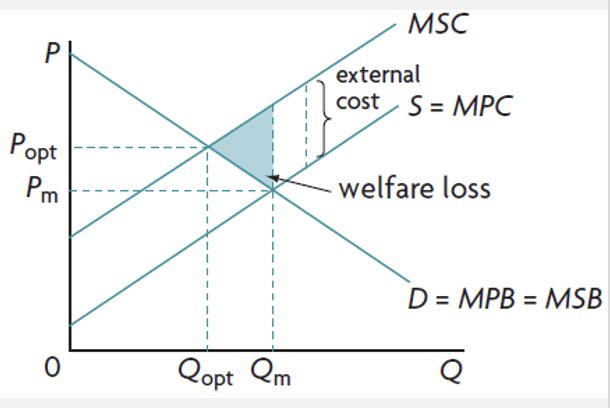
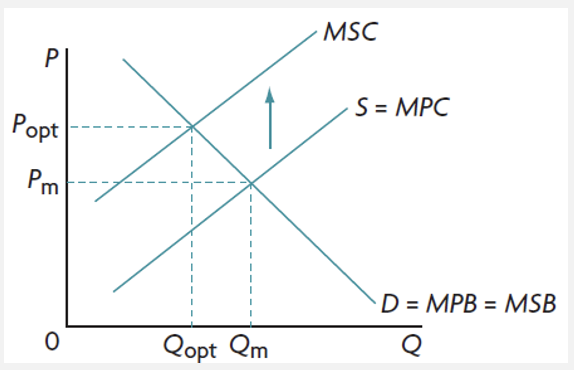
negative production externalities
costs created by producers, in the form of pollution as a side-effect of production
the free market overallocates resources to the production of a good and more produced than what is socially optimal
negative production externalities graph
when Qm > Qopt
MSC > MSB at Qm
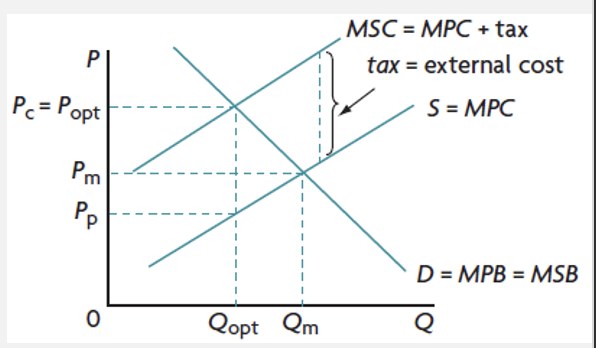
indirect tax to correct NPE and overuse of CPR
increases the cost of production and results in a shift of the supply curve to the left, reducing supply
if tax is same as the external cost, externality will be corrected and will result in allocative efficiency
consequences of an indirect tax
advantages: internalise the externality (polluter pays principle), generate govt revenue, lower pollution at a lower overall cost to society
disadvantages: difficult to design, politically difficult to impose taxes high enough to make a difference, administrative costs, regressive
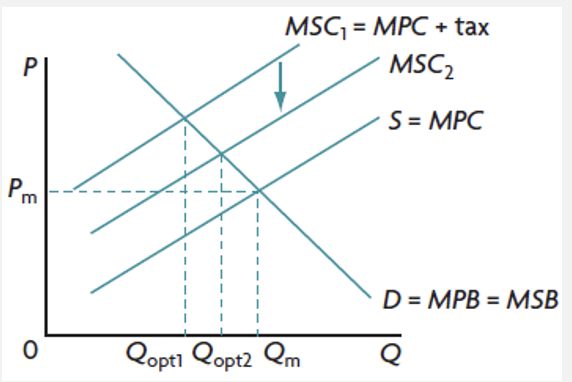
carbon tax to correct NPE and overuse of CPR
designated to deal with emissions of greenhouse gasses
tax/unit of carbon emitted, so the more carbon emitted the higher the tax
since there are substitutes for carbon, firms may be incentivised to switch to less polluting sources to lower their costs
Qopt increases because the external cost of production will be smaller
consequences of carbon taxes
advantages: provides an incentive for firms to switch to less polluting resources, makes energy prices more predictable, internalises the externality, directly targets emissions, govt revenue
disadvantages: regressive, political pressures to be set too low to make a difference, can’t target a particular level of carbon reduction
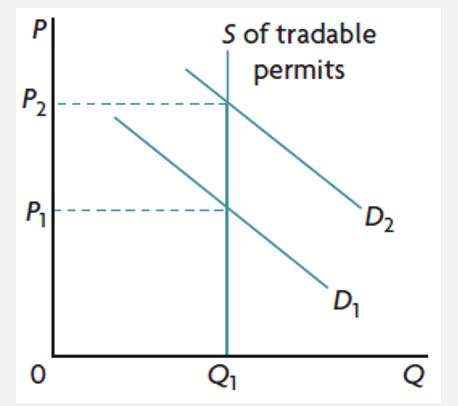
tradable permits to correct NPE and overuse of CPR
involve a system of permits to pollute issued to firms by the government
permits can be traded in a market, so firms that can produce using less of the permits, can sell them for a profit
supply of permits is perfectly inelastic and is set at a level lower than what would be the level of pollution without the permits
As the economy grows, the number of permits demanded increases, increasing their price
consequences of tradable permits
advantages: internalise the externality, governments can manipulate the distribution, gives the market some freedom, if it’s set at the right level pollution will be lower, exact amount is set
disadvantages: cap may be set too high due to political pressures so will be ineffective, firms may abuse market power, trading costs
government legislation and regulation
the government uses its authority to enact legislation and regulations in the public’s interest. Could involve: emission standards, quotas, licenses, permits
examples:
banning of harmful substances
prohibiting construction in protected areas
restrictions in the form of quotas
requirement for firms to install smokestack scrubbers to reduce emissions
consequences of legislation and regulation
advantages: simple to put into effect and reinforce, easier to implement compared to market-based policies, force firms to comply
disadvantages: don’t always offer incentive to reduce emissions, no ability to distinguish between firms with lower/higher pollution levels, partially effective since they don’t have specific knowledge on the cause, monitoring costs
collective self-governance
Users take control of the common pool resources and use them in a sustainable manner.
Communities that can come together to discuss the best use and allocaiton of resources with future generations in mind, but if the communities cannot communicate or if the cost of self-organizaion are too high, there will be failures.
education and awareness creation
Provision of information regarding the polluting activities of firms may turn consumers away from their products- negative impact on their sales. Companies are forced to take the consumer’s opinions into consideration
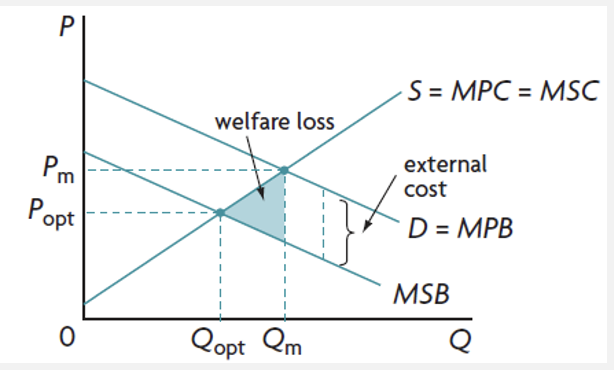
negative consumption externalities
costs created by consumers in the form of externalities on third parties
the free market overallocates resources to the provision of the good and more is consumed than what is socially optimal
negative consumption externalities graph
when Qm > Qopt
MSC > MSB at Qm
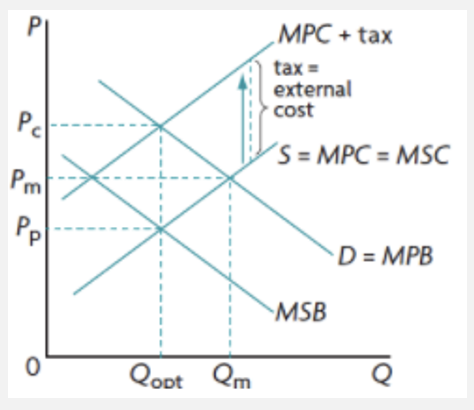
indirect taxes to correct NCE and prevent overuse of CPR
internalise the externality
difficult to estimate the external cost
inelastic demand so increase in price doesn’t reduce consumption by much but increases govt revenue- can be reinvested in education programmes to discourage consumption
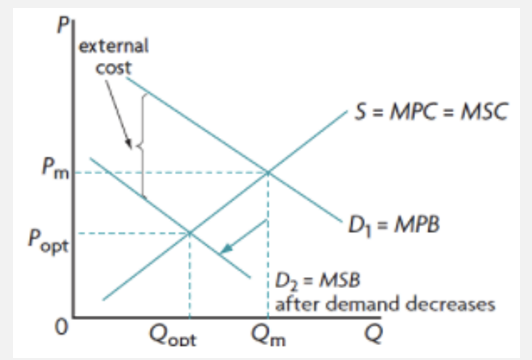
government legislation and education to correct NCE and prevent overuse of CPR
used to prevent/limit activities by consumers
restrictions on activities such as in public places or age restrictions
education and awareness is simple but costly to the govt
may be ineffective
nudges to correct NCE and prevent overuse of CPR
designing methods to influence consumer behaviour
unhealthy foods can be placed in less accessible places or graphic pictures can be used to discourage consumption
desirable behaviour can be stimulated through incentives