BSci 110 Terms
1/148
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terms comprised of learning curve vocab.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Foot In The Door Phenomenon
A psychological phenomenon where people are more likely to agree to a larger request after they have already agreed to a small request. This technique is often used in persuasion and compliance strategies.
Cognitive Dissonance
The mental discomfort experienced when holding two or more contradictory beliefs or values. This often leads individuals to change their attitudes or behaviors to reduce the dissonance.
Role Playing
The acting out of a particular role or scenario to better understand behaviors or to practice skills. Role playing is often used in therapy, training, and educational settings to enhance learning and empathy.
Informational Social Influence
A type of social influence that occurs when individuals conform to others' beliefs or behaviors because they assume those others possess accurate information, especially in uncertain situations.
Normative Social Influence
A type of social influence that leads individuals to conform in order to be accepted or liked by a group, often resulting in public compliance without private acceptance.
Milgram Experiment
A series of psychological experiments conducted by Stanley Milgram in the 1960s to study obedience to authority, where participants were instructed to administer electric shocks to another person. Individual conducting the shocks experienced cognitive dissonance.
Social Facilitation
Improved performance on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others.
Social Loafing
Tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable.
Deindividuation
The loss of self-awareness and self-restrain occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity.
Group Polarization
The beliefs and attitudes we bring to a group grow stronger when we discuss them with like-minded others.
Groupthink
When desire for harmony in decision making overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives.
Microaggression
A subtle, often unintentional, comment or behavior that expresses a prejudiced attitude toward a marginalized group.
Just-World Phenomenon
A cognitive bias where people believe that the world is inherently fair and that individuals get what they deserve.
Ingroup Bias
The tendency for people to favor and give preferential treatment to members of their own group over those in an outgroup.
Scapegoat Theory
A theory that proposes when things go south, finding a group or person to blame can provide a target for negative emotions.
Other-Race Effect
A psychological phenomenon where people are generally better at recognizing and remembering faces of their own race compared to faces of other races.
Mere Exposure Effect
A psychological phenomenon where people tend to develop a preference for things simply because they are familiar with them.
Social Responsibility Norm
A principle in social psychology that suggests individuals have a moral obligation to help others who are dependent on them or in need, without expecting anything in return.
Bystander Effect
A social psychological theory that explains why individuals are less likely to help a person in need when other people are present.
Equity
The idea of fairness in the distribution of resources, responsibilities, and outcomes among individuals or groups.
Social Exchange Theory
A psychological and sociological framework that explains human relationships in terms of costs and benefits.
Reciprocity Norm
A social rule that suggests people should return favors or acts of kindness that others have done for them.
Diffusion of Responsibility
A psychological phenomenon where individuals feel less personal responsibility to take action when others are present.
Fundamental Attribution Error
A common cognitive bias in social psychology where people tend to overemphasize personality traits and underemphasize situational factors when explaining others' behavior.
Altruism
Unselfish concern for others welfare, often involving personal sacrifice.
Mirror Image Perceptions
A psychological phenomenon where two opposing sides in a conflict view each other in similar but opposite ways.
Social Traps
Situations in which individuals or groups act in ways that are immediately rewarding but ultimately harmful to themselves or others in the long run.
Observational Learning
A type of learning that occurs by watching others and imitating their behavior.
Associative Learning
A fundamental type of learning in which an individual forms a connection between two stimuli or between a behavior and a consequence.
Respondent Behavior
Involuntary, automatic responses to specific stimuli.
Shaping
A behavioral technique used in operant conditioning where successive approximations of a desired behavior are reinforced until the target behavior is achieved.
Cognitive Learning
A type of learning that involves active engagement of mental processes such as thinking, memory, problem-solving, and attention.
Classical Conditioning
A type of associative learning where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus, eventually triggering a similar response
Operant Conditioning
A type of learning where behavior is influenced by its consequences.
Conditioned Stimulus
A previously neutral stimulus that, after being repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus (US), begins to trigger a conditioned response (CR) on its own.
Unconditioned Stimulus
A stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response without any prior learning.
Conditioned Response
A learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus (CS) that occurs after the CS has been repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus (US).
Unconditioned Response
An automatic, natural reaction to an unconditioned stimulus (US)—it occurs without any prior learning.
Instinct
An inborn, fixed pattern of behavior that is biologically hardwired and typically emerges in response to specific stimuli.
Central Route Persuasion
A method of persuasion that relies on logical reasoning, critical thinking, and the quality of arguments to influence attitudes and behavior.
Peripheral Route Persuasion
Influences people through superficial cues rather than the strength of the message itself.
Dispositional Attribution
Refers to the tendency to explain someone’s behavior by attributing it to their internal characteristics, such as personality, motives, or attitudes, rather than to external or situational factors.
Situational Attribution
The process of explaining someone’s behavior by pointing to external factors—things in the environment or context—rather than internal traits or personality.
Personal Attribution
Same as dispositional attribution.
Heuristic
A mental shortcut or rule of thumb that people use to make decisions or solve problems quickly and efficiently.
Insight
A sudden realization or understanding of how to solve a problem or grasp a concept.
Algorithm
A step-by-step set of instructions or rules designed to perform a specific task or solve a particular problem.
Fixation
A persistent focus on a specific idea, object, or behavior, often to the point where it interferes with problem-solving or emotional development.
Confirmation Bias
A cognitive bias where people tend to seek out, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms their preexisting beliefs or expectations, while ignoring or dismissing evidence that contradicts them.
Belief Perseverance
A cognitive bias where people cling to their initial beliefs even after those beliefs have been discredited or contradicted by new evidence.
Availability Heuristic
A mental shortcut where people judge the likelihood or frequency of an event based on how easily examples come to mind.
Framing
The way information is presented or structured, which can significantly influence how people perceive, interpret, and respond to it—even if the underlying facts remain the same.
Functional Fixedness
A type of cognitive bias that limits a person’s ability to use an object or concept in a way that’s different from its traditional or intended use.
Source Amnesia
A memory phenomenon where a person can remember information but forgets where or how they learned it.
Misinformation Effect
A memory phenomenon where a person's recollection of an event becomes less accurate due to post-event information, especially if that information is misleading.
Deja Vu
The strange and brief feeling that you've experienced a situation before, even though it's happening for the first time.
Repression
A defense mechanism in which an individual unconsciously pushes threatening thoughts, memories, or desires out of conscious awareness. These repressed elements may influence behavior indirectly.
Encoding Failure
Occurs when information is not effectively processed into memory in the first place.
Proactive Interference
A memory phenomenon where older information interferes with the ability to learn or recall new information.
Retroactive Interference
Occurs when new information interferes with the ability to recall older information. It’s the opposite of proactive interference.
Anterograde Amnesia
A condition where a person cannot form new memories after the onset of the amnesia.
Retrograde Amnesia
A condition where a person loses memories of events that occurred before the onset of the amnesia.
Consolidation
The process by which short-term memories are stabilized and transformed into long-term memories.
Retrieval
The process of accessing and bringing stored information from memory into conscious awareness.
Reconstruction
The process of rebuilding a memory during retrieval, often by filling in gaps with general knowledge, expectations, or other memories.
Reconsolidation
The process by which previously stored memories are recalled and then modified or updated before being stored again.
Iconic Memory
A type of sensory memory that holds visual information for a very brief period—typically less than one second.
Sensory Memory
The initial stage of memory that briefly holds information from the senses (sight, sound, touch, etc.) for a very short duration—typically less than a second.
Automatic Processing
Refers to the unconscious encoding of information such as space, time, frequency, and well-learned material (like word meanings).
Effortful Processing
The active and conscious encoding of information that requires attention and deliberate effort.
Spacing Effect
The psychological phenomenon where information is better retained when learning is spread out over time (spaced) rather than crammed into a single session (massed practice).
Chunking
A memory strategy that involves grouping individual pieces of information into larger, more meaningful units (or "chunks") to make them easier to remember.
Testing Effect
The psychological phenomenon where retrieving information through testing improves long-term memory retention more effectively than simply re-studying the material.
Mnemonics
Memory aids or strategies that help encode, store, and retrieve information more easily, often by linking new information to familiar concepts, patterns, or imagery.
Implicit Memory
A type of long-term memory that influences thoughts and behaviors without conscious awareness.
Primary Appraisal
The initial evaluation a person makes when encountering a situation or event, to determine its significance for their well-being.
Secondary Appraisal
The appraisal that involves the individual determining how much control over the stressor they have.
Type A Personality
Someone who is highly competitive, driven/ambitious, impatient, etc.
Type B Personality
Calm and relaxed, patient, flexible, etc.
Stress
The process by which we perceive and respond to certain events (stressors) that we appraise as threatening or challenging.
Stress Performance Chart
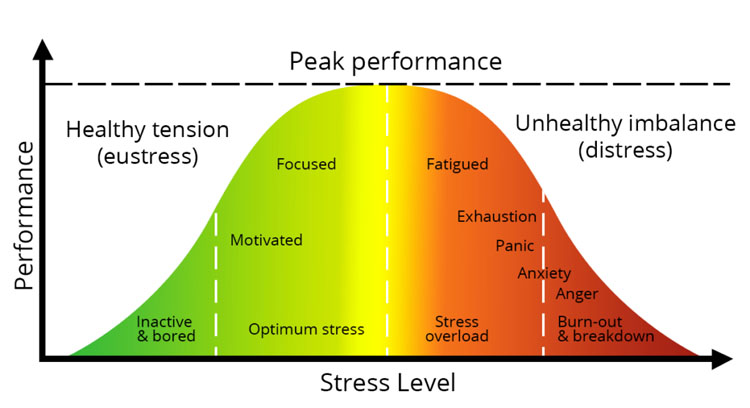
Sympathetic Nervous System
Plays a central role in the body's response to stress, especially in what's known as the "fight-or-flight" reaction.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The counterpart to the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and is often referred to as the "rest and digest" system. Returns the body to a calm and relaxed state.
Mitigating Stress
Waiting, reframing the situation in a positive way, finding a healthy distraction / support system.
Growth Mindset
The belief that abilities, intelligence, and talents can be developed through effort, learning, and persistence.
Phycological Disorder
A clinically significant disturbance in an individual's cognition, emotional regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning.
Major Depressive Disorder
A mental health condition where a person feels sad, hopeless, or loses interest in things they used to enjoy, for at least two weeks. It can affect sleep, appetite, energy, and concentration.
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
A mental health condition that can happen after someone experiences or witnesses a traumatic event—like war, a serious accident, or violence.
Self-Injury
When a person deliberately harms their own body, often as a way to cope with emotional pain, stress, or overwhelming feelings. It’s usually not meant as a suicide attempt.
Epigenetic Model
Describes how biological development unfolds in a staged, sequential manner—where genetic instructions interact with environmental influences to shape outcomes.
Comorbidity
Having two or more medical or mental health conditions at the same time.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
A mental health condition where a person has unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and feels the need to do certain actions repeatedly (compulsions) to reduce anxiety or prevent something bad.
Bipolar Disorder
A mental health condition that causes extreme mood swings, including emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression).
Dissociative Identity Disorder
Mental health conditions where a person feels disconnected from their thoughts, feelings, memories, or identity. It can feel like being outside of oneself or losing time.
Phobia
An intense and irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity that leads a person to avoid it, even if it’s not dangerous.
Somatic Symptom Disorder
A mental health condition where a person has significant physical symptoms—like pain, fatigue, or shortness of breath—and reacts with excessive worry, emotions, or behaviors that cause distress or disrupt daily life, even if the symptom has a medical explanation.
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
A mental health condition where a person is overly concerned with a flaw in their appearance—often something minor or imagined—and it causes distress or affects their daily life.
Social Anxiety Disorder
A mental health condition where a person has intense fear of being judged, embarrassed, or rejected in social situations. It can make everyday interactions feel overwhelming.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
A mental health condition where a person feels constant and excessive worry about many things, even when there’s no clear reason. It lasts for months and can affect sleep, concentration, and daily life.
Panic Disorder
A mental health condition where a person has sudden and repeated panic attacks—intense episodes of fear or discomfort that come on quickly and include physical symptoms like a racing heart, shortness of breath, or dizziness.