Skull Anatomy and Brain Structures: Key Landmarks and Functions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the learning objectives for studying the skull?
Identify the bones of the skull and their articulations, label the suture lines, identify key points like bregma, lambda, pterion, asterion, and describe the bones contributing to the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossa.
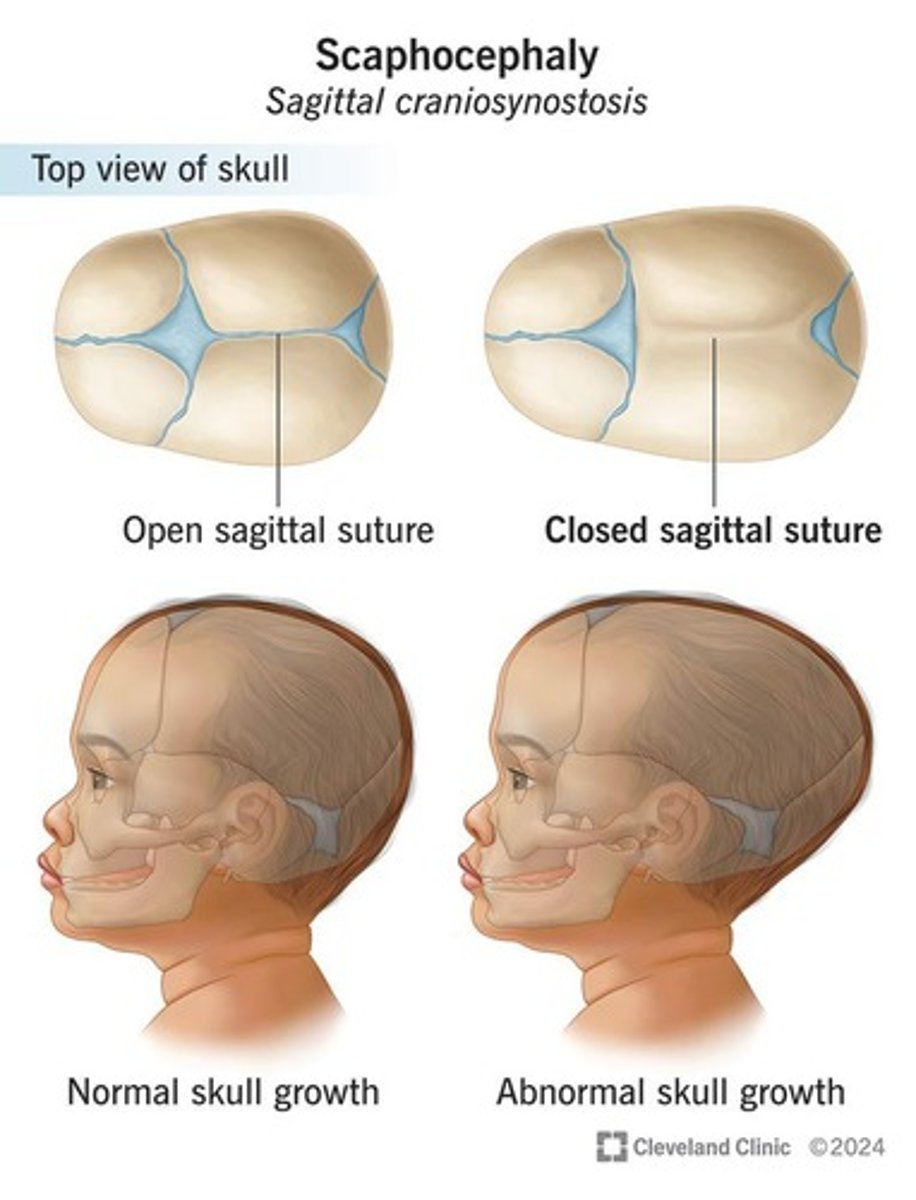
What is craniosynostosis?
Premature closure of cranial sutures, which are joints where skull bones form and fuse, typically occurring around age 2.
What is the definition of the cranium?
The cranium refers to the skull without the mandible.
What bones make up the calvaria or skull cap?
The calvaria includes the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones.
What is the function of the skull?
The skull protects the brain and special senses such as vision, hearing, smell, and taste.
How many bones are in the skull?
The skull consists of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones (neurocranium) and 14 facial bones (viscerocranium).
List the cranial bones of the skull.
Occipital (1), Sphenoid (1), Ethmoid (1), Frontal (1), Parietal (2), Temporal (2).
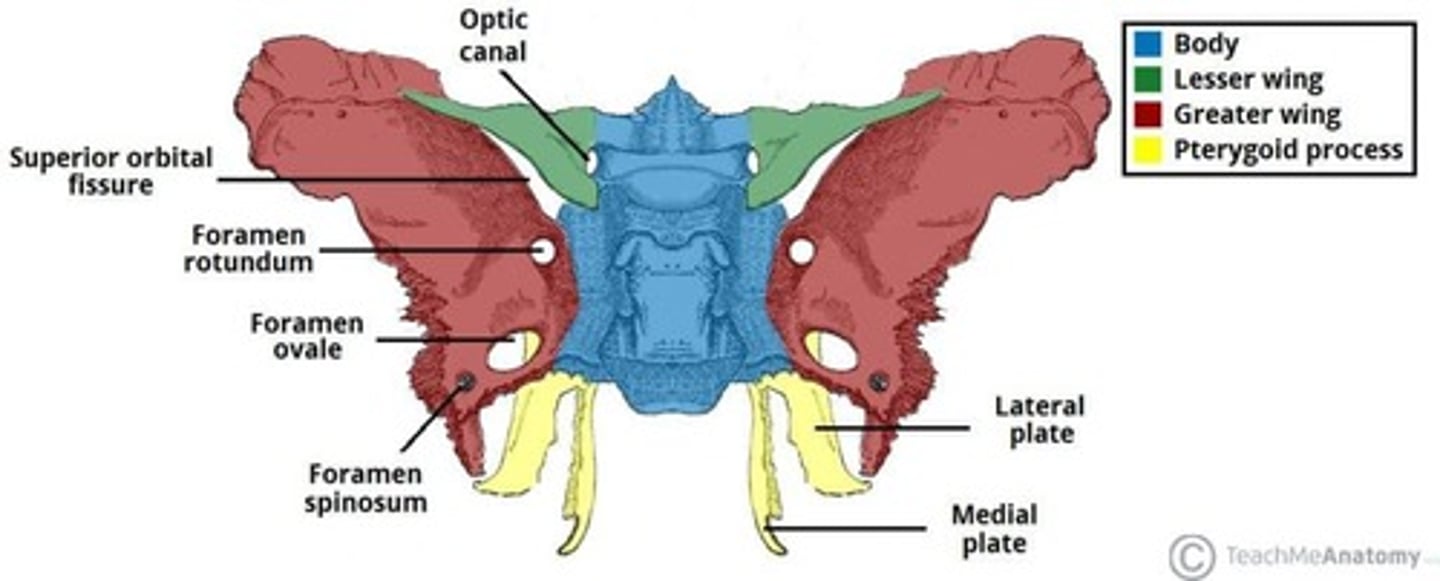
What are the components of the sphenoid bone?
The sphenoid bone includes the body (containing sphenoid sinuses), greater wings (forming parts of the middle cranial fossa), lesser wings (forming parts of the anterior cranial fossa), and pterygoid processes (attaching muscles involved in mastication).
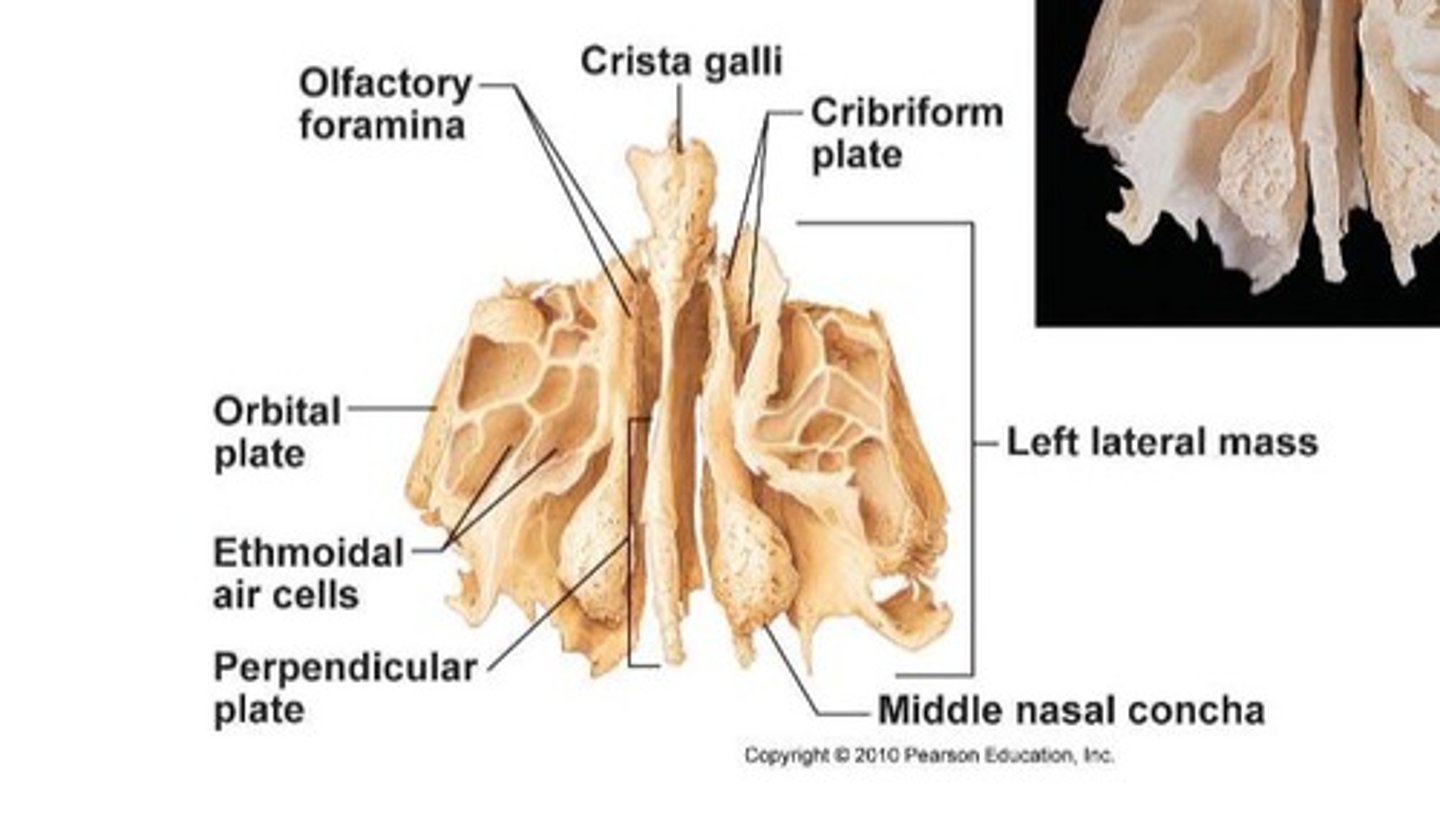
What is the role of the ethmoid bone?
The ethmoid bone is a complex bone located deep within the skull, contributing to the anterior cranial fossa and the upper two-thirds of the nasal septum.
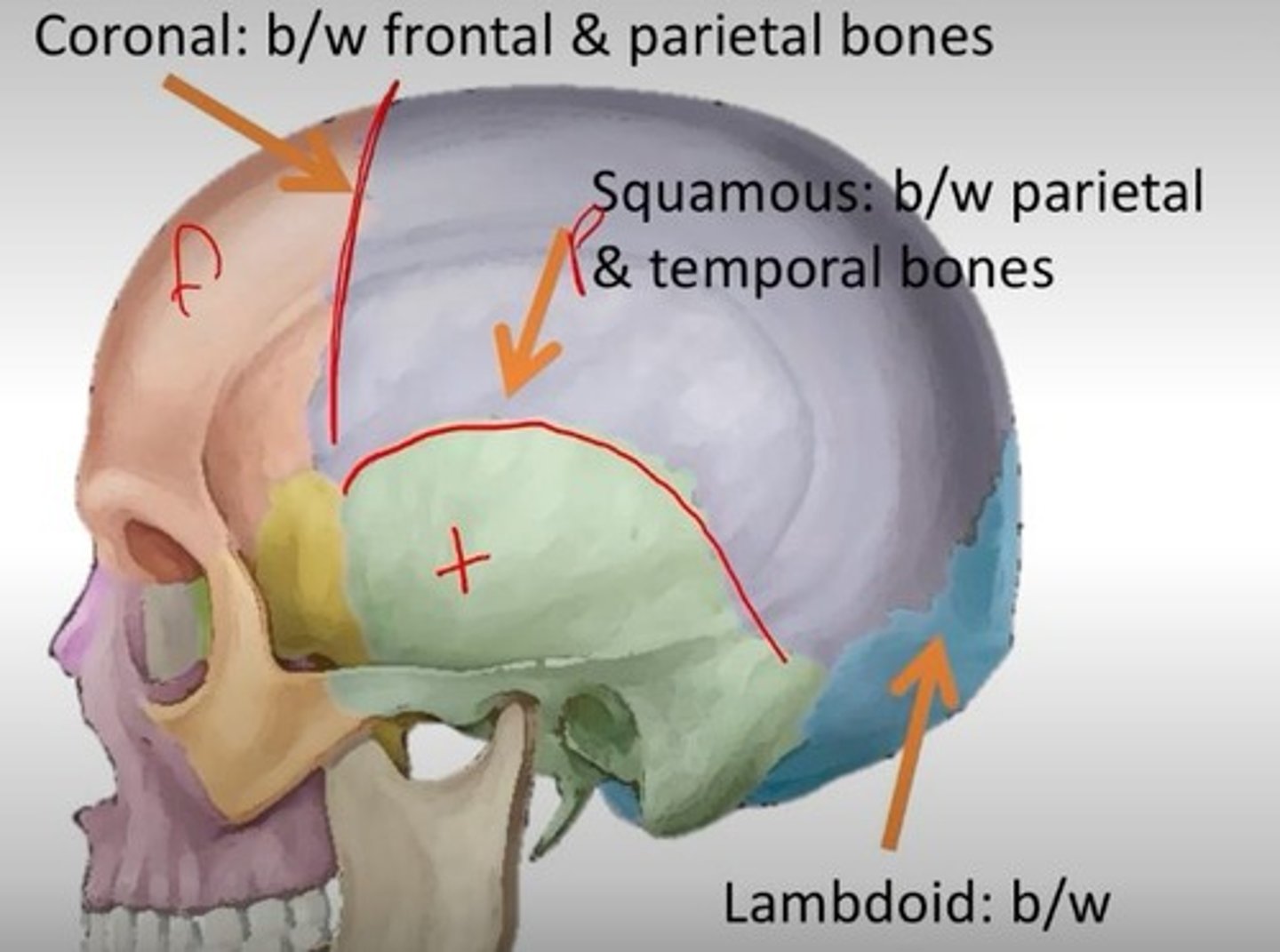
What are the sutures of the skull?
Sutures are solid fibrous joints connecting skull bones, including the coronal, squamous, lambdoid, sagittal, and occipitomastoid sutures.
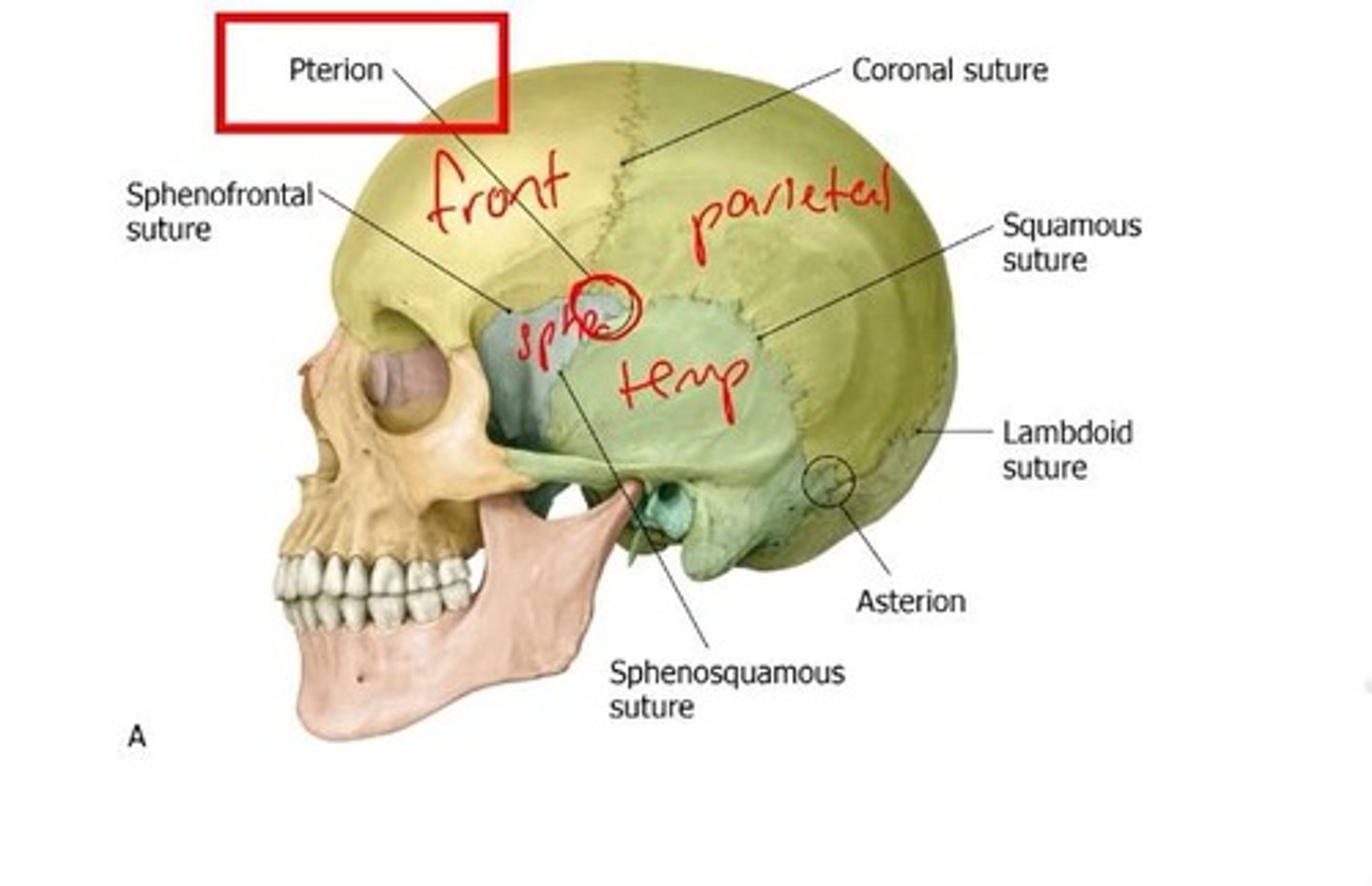
What is the significance of the pterion?
The pterion is the intersection of the frontal, sphenoid, parietal, and temporal bones, with the middle meningeal artery lying underneath.
What bones contribute to the anterior cranial fossa?
The anterior cranial fossa is formed by the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones.
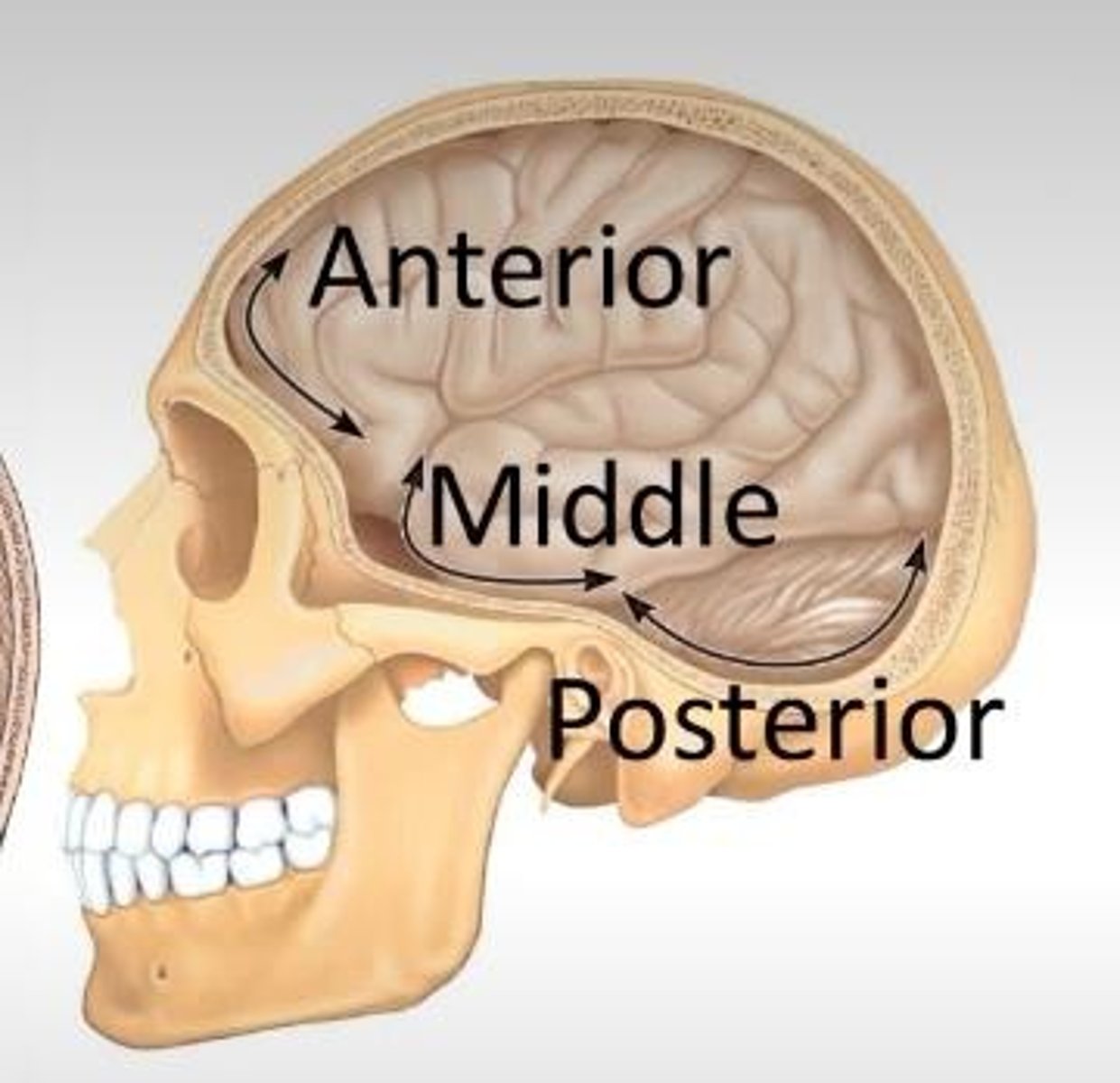
What structures are found in the middle cranial fossa?
The middle cranial fossa contains the sphenoid and temporal bones, houses the temporal lobes, and includes the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland.
What bones form the posterior cranial fossa?
The posterior cranial fossa is formed by the occipital, temporal, and parietal bones.
What are the major anatomical planes of the brain?
The major anatomical planes are sagittal (divides right and left), coronal (divides anterior and posterior), and transverse (divides upper and lower portions).
What are the directional terms used in neuroanatomy?
Rostral (towards the front), caudal (towards the tail), ventral (towards the belly), dorsal (towards the back).
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobe contains the primary motor cortex, responsible for voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
The parietal lobe contains the primary sensory cortex, responsible for the perception of touch, pressure, pain, vibration, taste, and temperature.
What is the function of the occipital lobe?
The occipital lobe is responsible for the visual cortex and the perception of visual stimuli.
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe contains the auditory and olfactory cortex, responsible for the perception of auditory and olfactory stimuli.
What is the role of the corpus callosum?
The corpus callosum connects the right and left sides of the brain through white fiber tracks.
What are gyri and sulci?
Gyri are ridges on the brain's surface, while sulci are grooves or depressions.
What is the significance of the central sulcus?
The central sulcus separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
What are the major sulci and gyri of the brain?
Major sulci include the central sulcus, lateral sulcus, parieto-occipital sulcus, and calcarine sulcus. Major gyri include the precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, and cingulate gyrus.
What structures are located on the ventral side of the brain?
The ventral side of the brain contains the olfactory bulbs, pons, medulla, and cerebellum.
What is the function of the gustatory cortex?
The gustatory cortex is responsible for the conscious perception of taste and smell.