Punnett Squares, Dihybrid, Sex-linked, Pedigrees, Non-Mendelian
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Genotype
A set of alleles that are responsible for a certain trait. (letters)
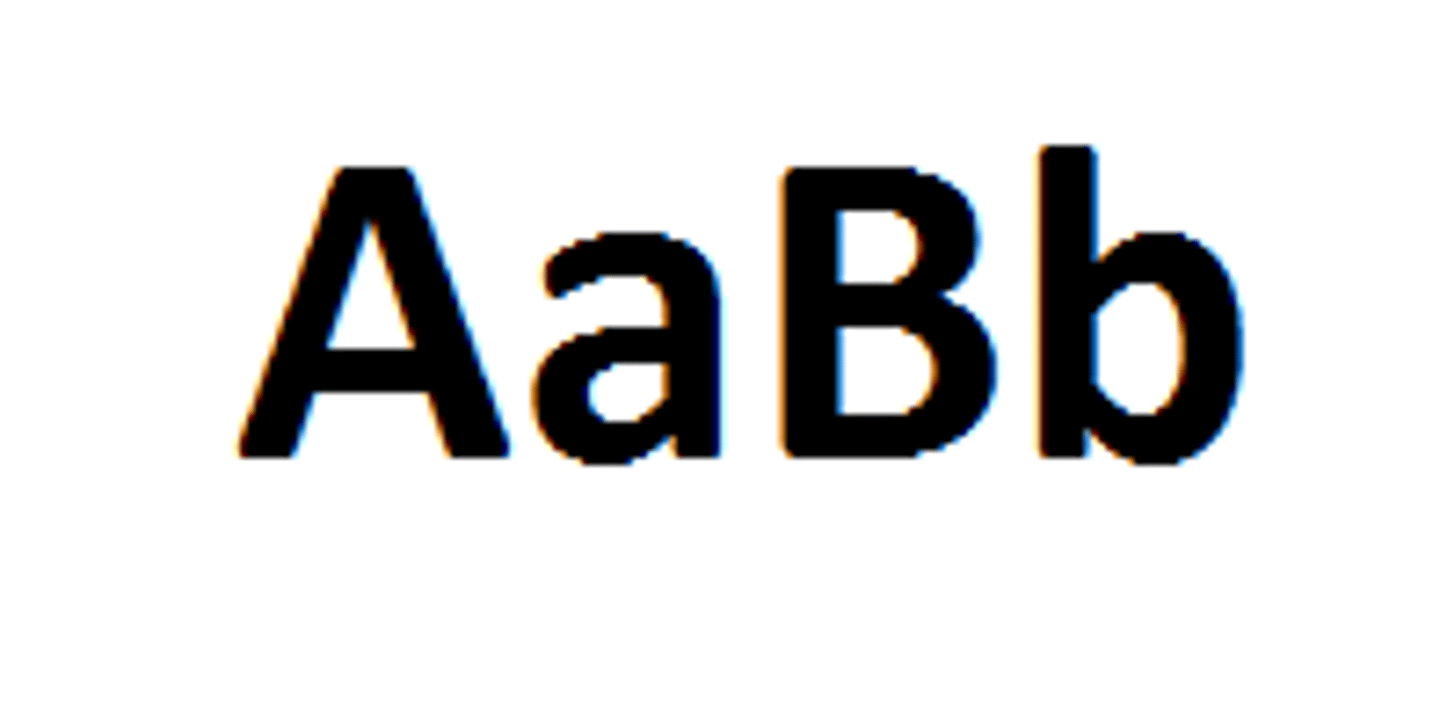
Phenotype
A observable set of characteristics
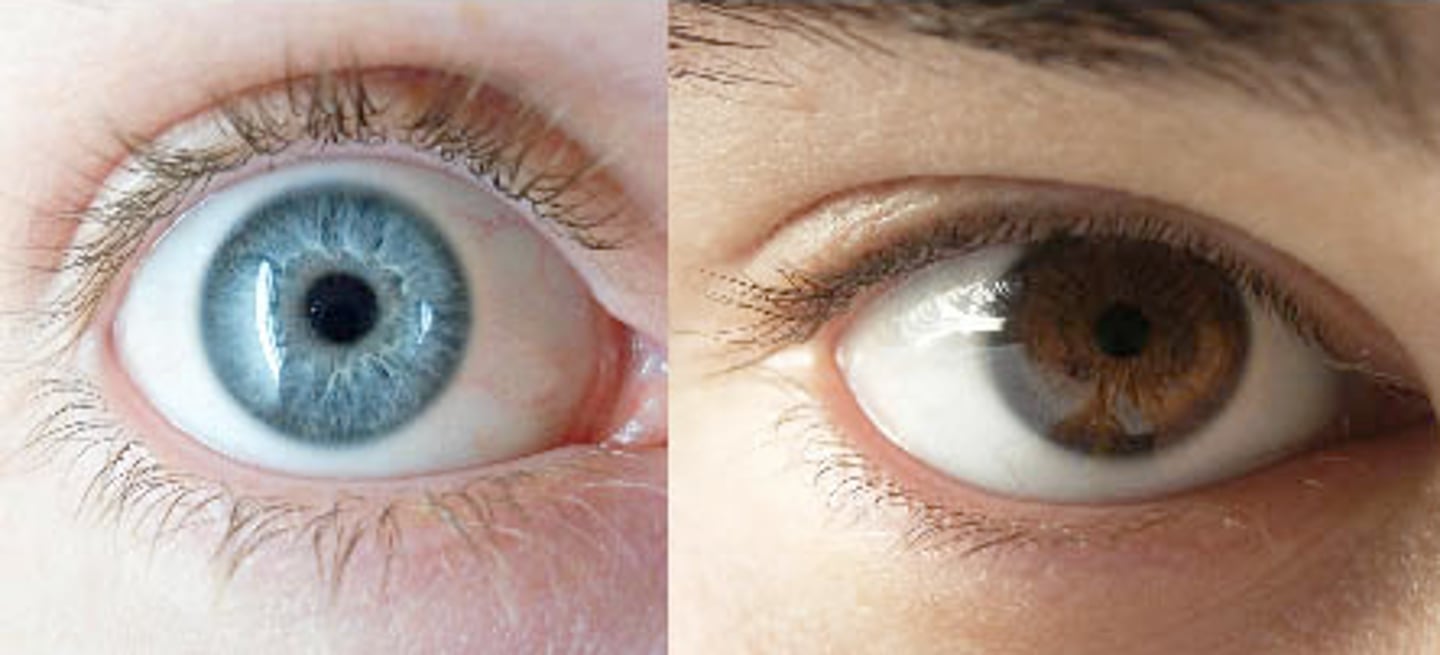
Allele
The pairs of genes occupying a specific spot on a chromosome; different forms of a gene
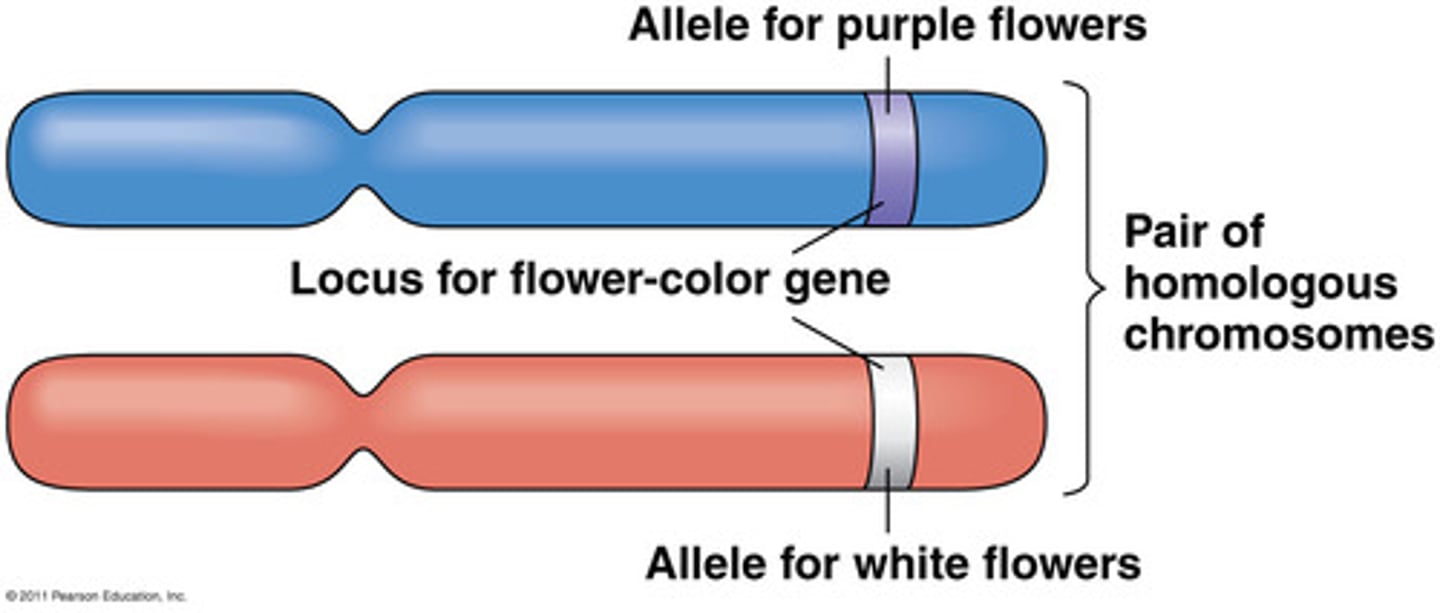
Dominant
Stronger gene

Recessive
Weaker gene
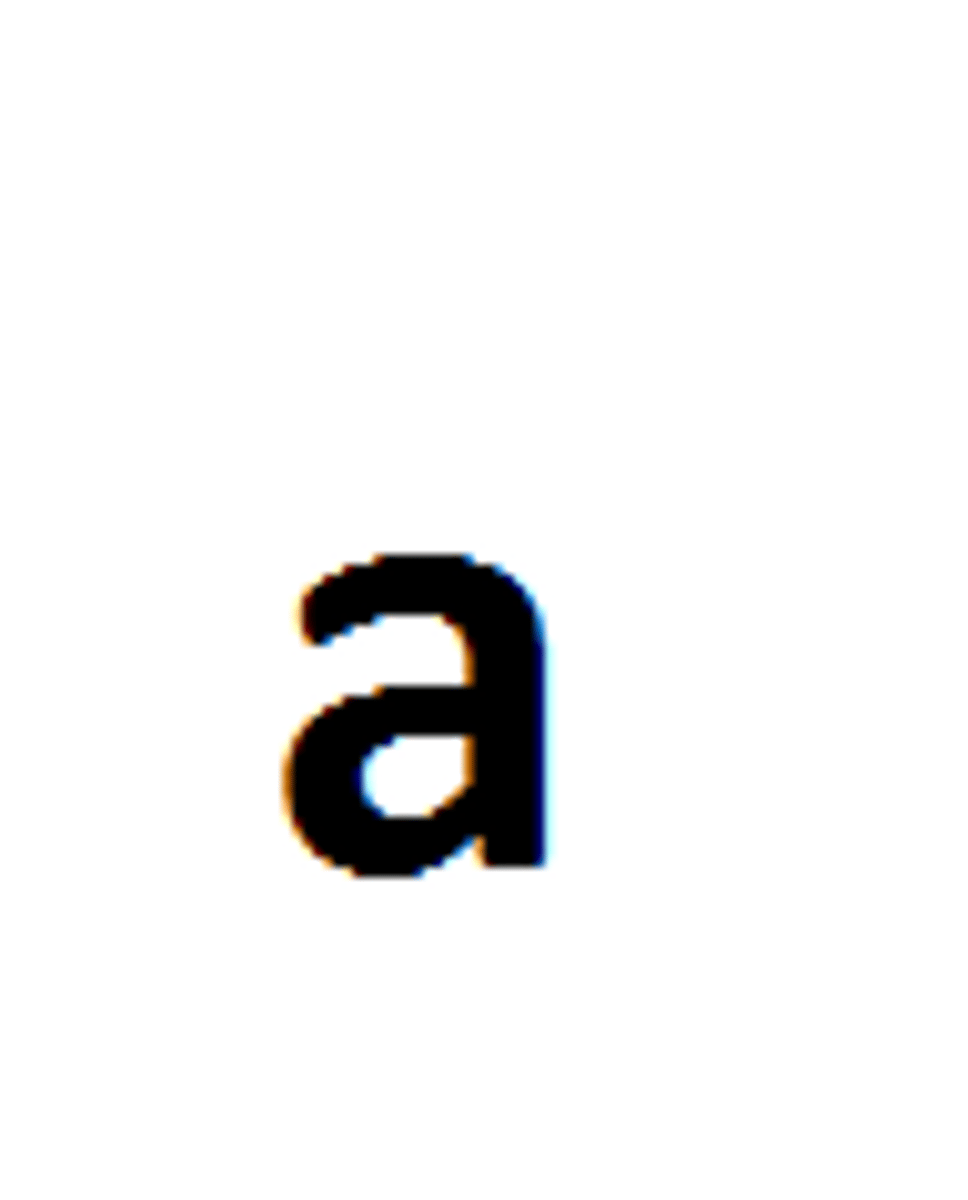
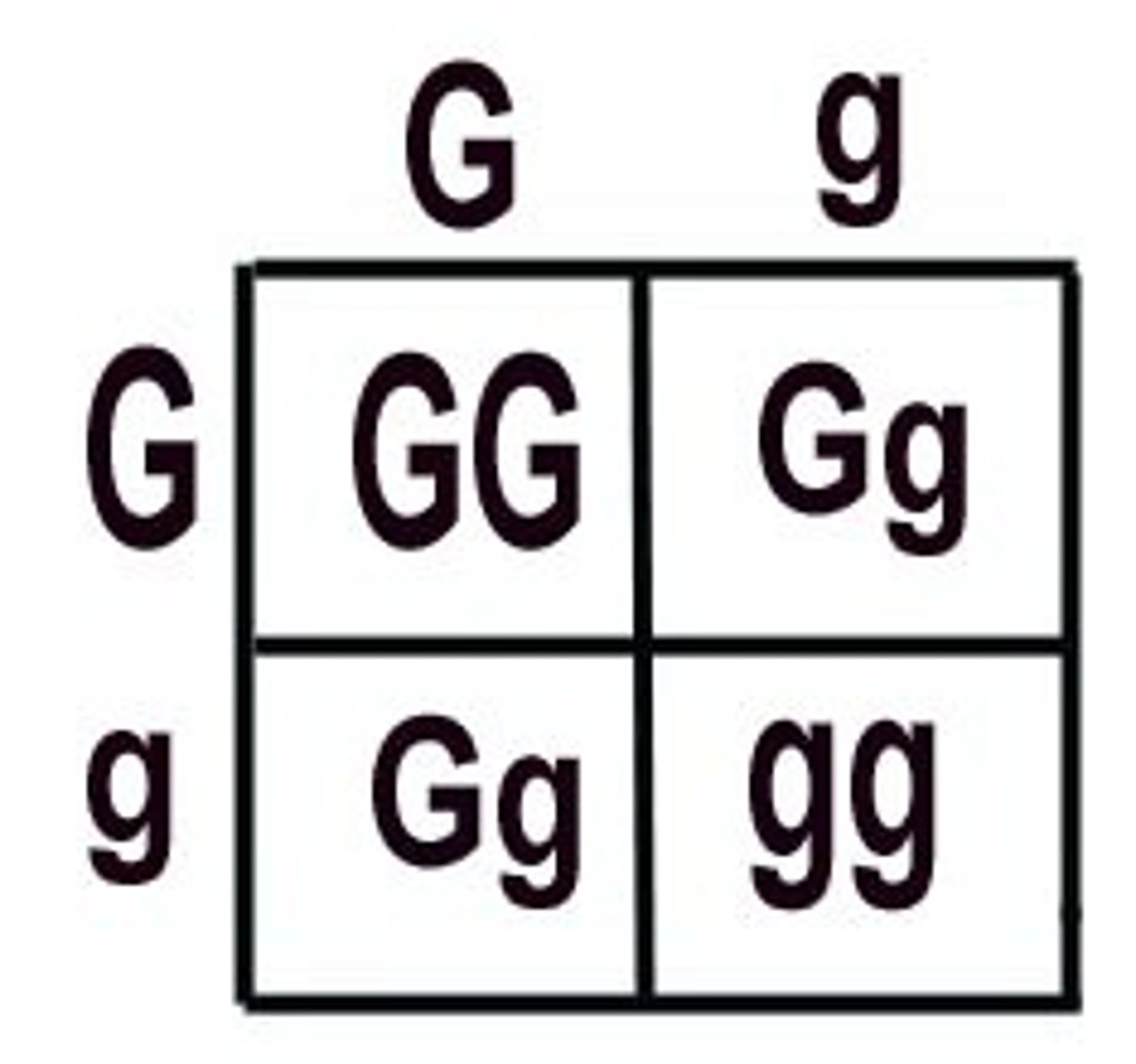
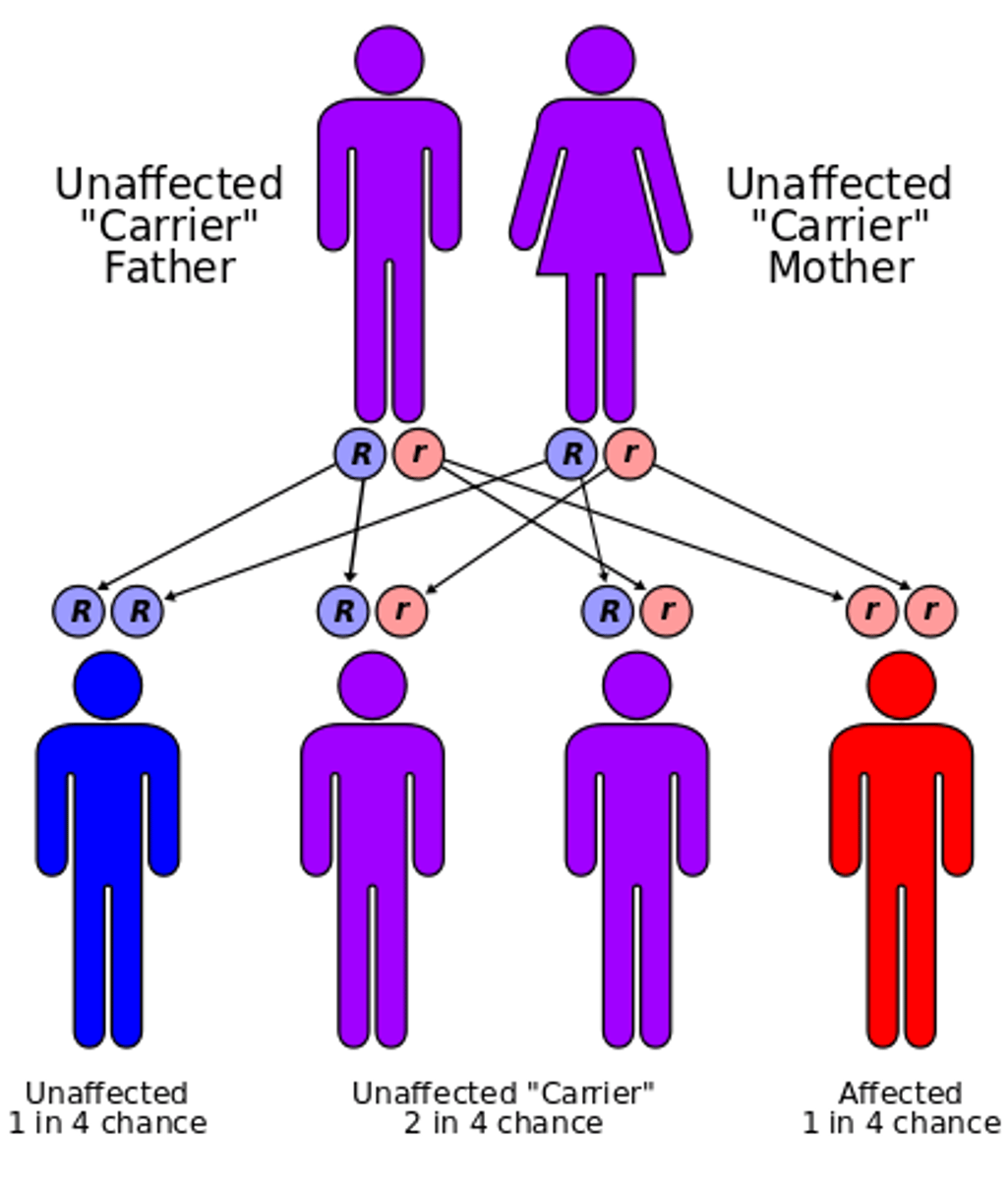
Punnett Square
used to predict results in genetics
Heredity
passing the traits from parents to children
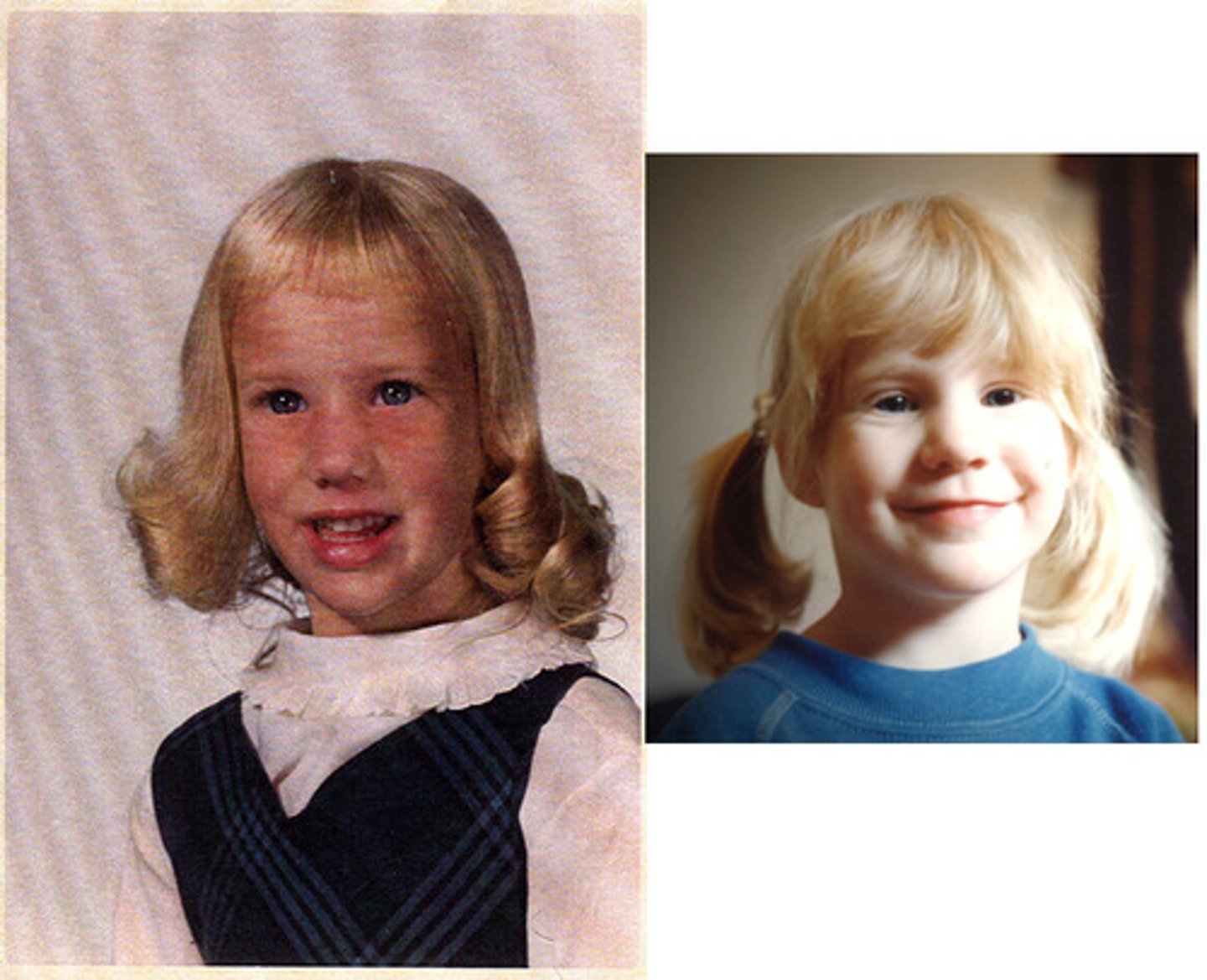

Genetics
the scientific study of heredity.
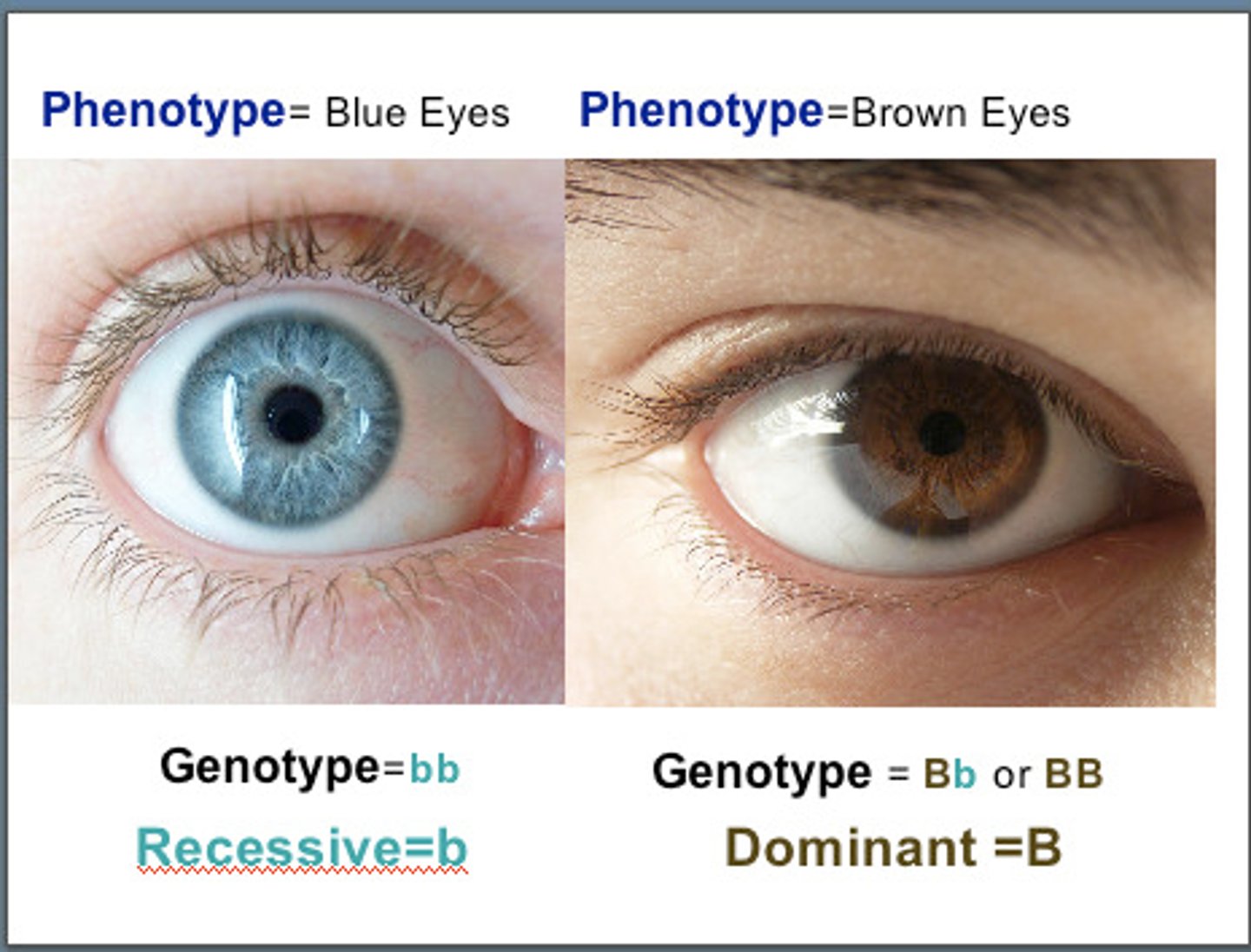
Heterozygous
Two different alleles (Dominant and recessive)

Homozygous
Two of the same alleles
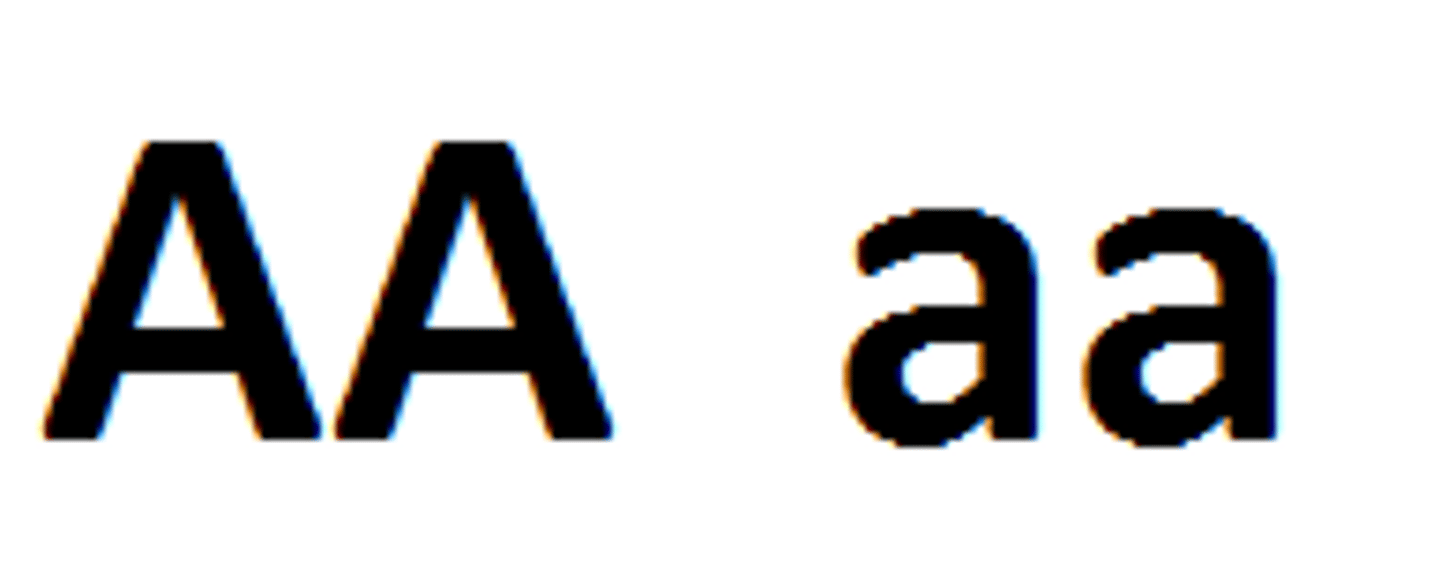
Homozygous Recessive
Two recessive alleles (lower case)

Homozygous Dominant
Two dominant alleles (capital)

Gregor Mendel
The scientist that discovered how traits were passed down from one generation to the next while he was studying garden peas.

Hybrid
Two different alleles, another name for heterozygous
Purebred
Two of the same alleles; Another name for homozygous

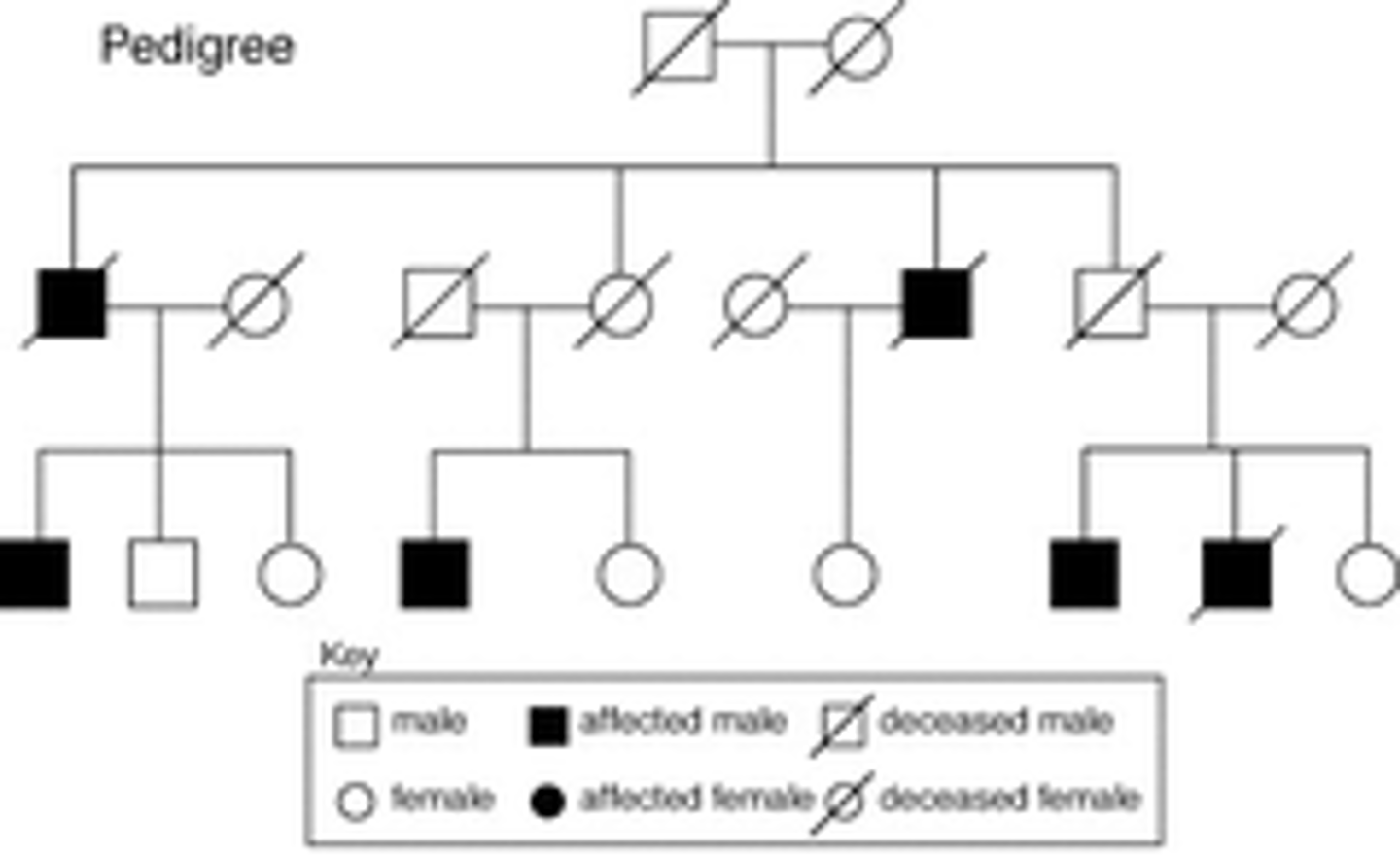
Pedigree
A chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance or phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors from one generation to the next
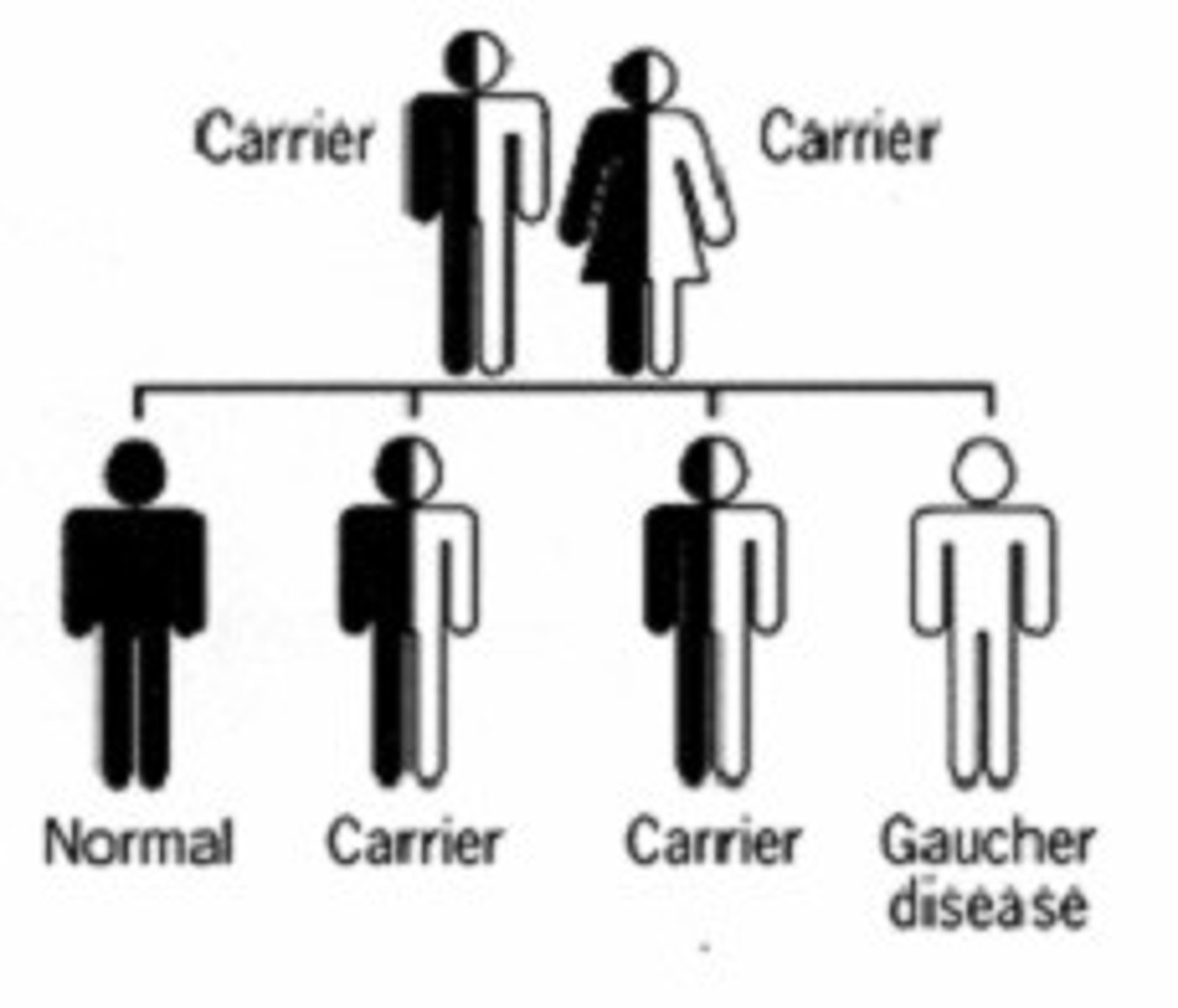
Carrier
is a person or organism that is heterozygous for a trait
sex-linked trait
A trait associated with a gene that is carried on the X or Y chromosome
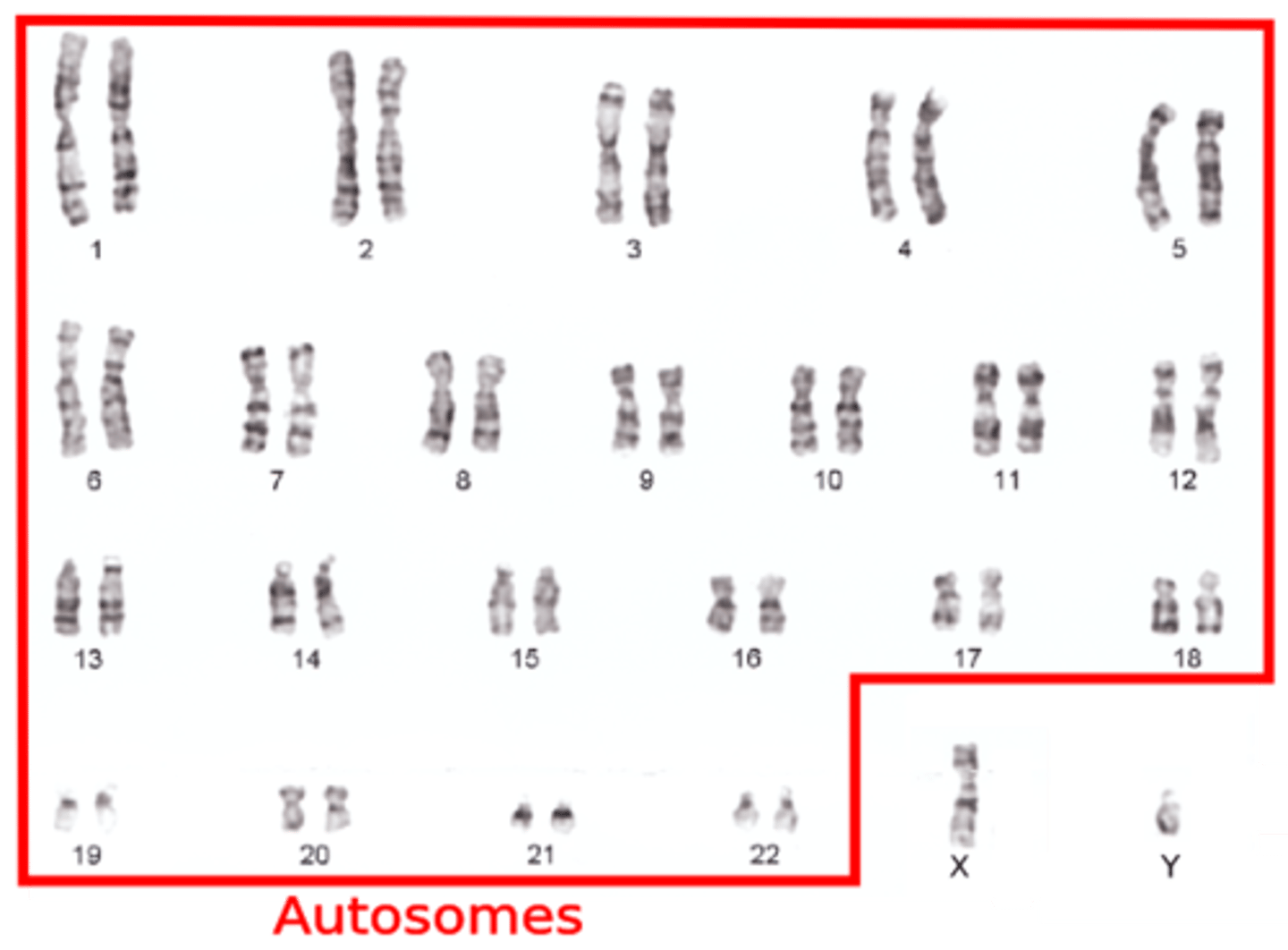
Autosomal
Any of the numbered chromosomes, doesn't include the sex chromosomes
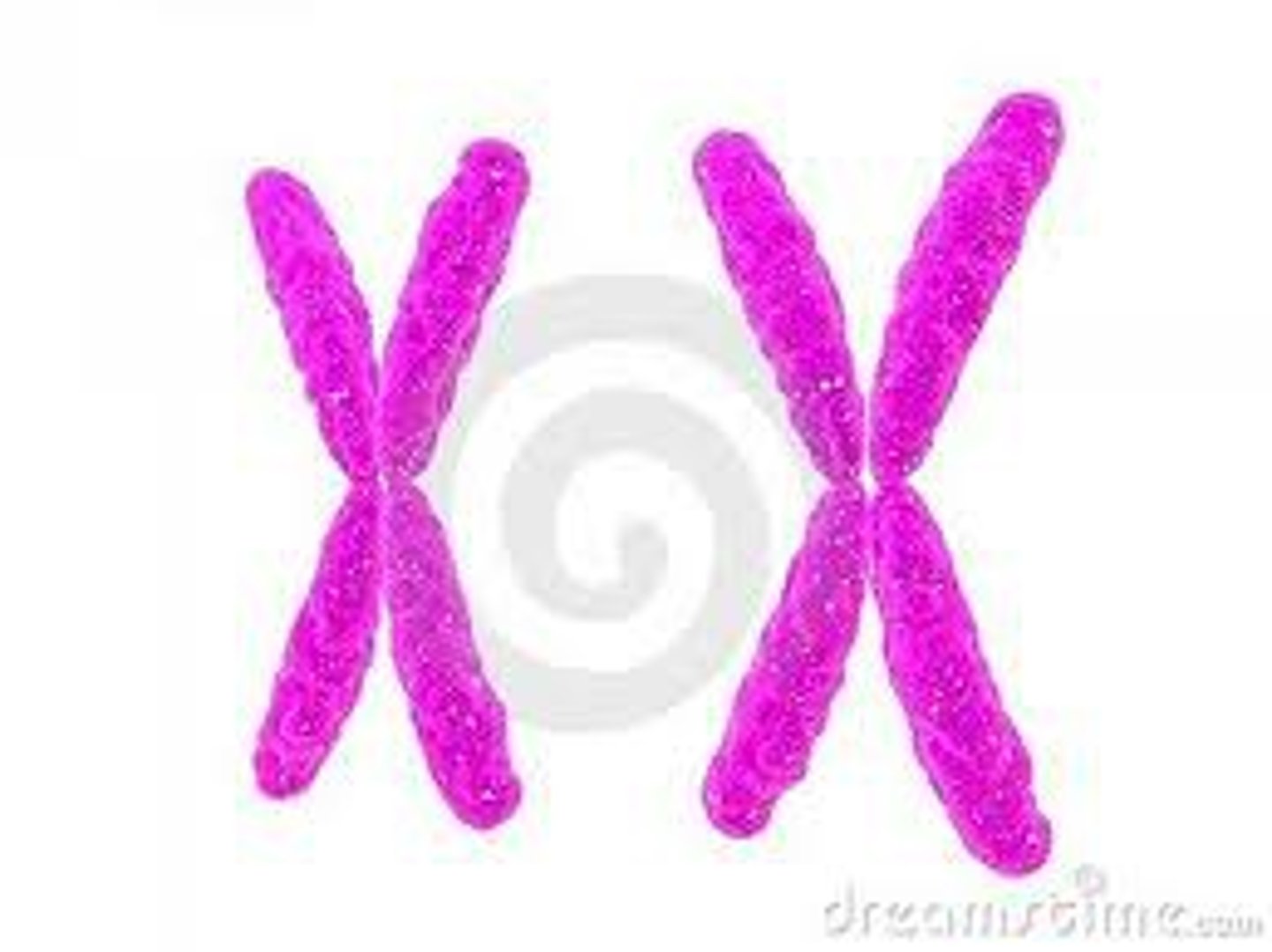
XX
Girl

XY
Boy

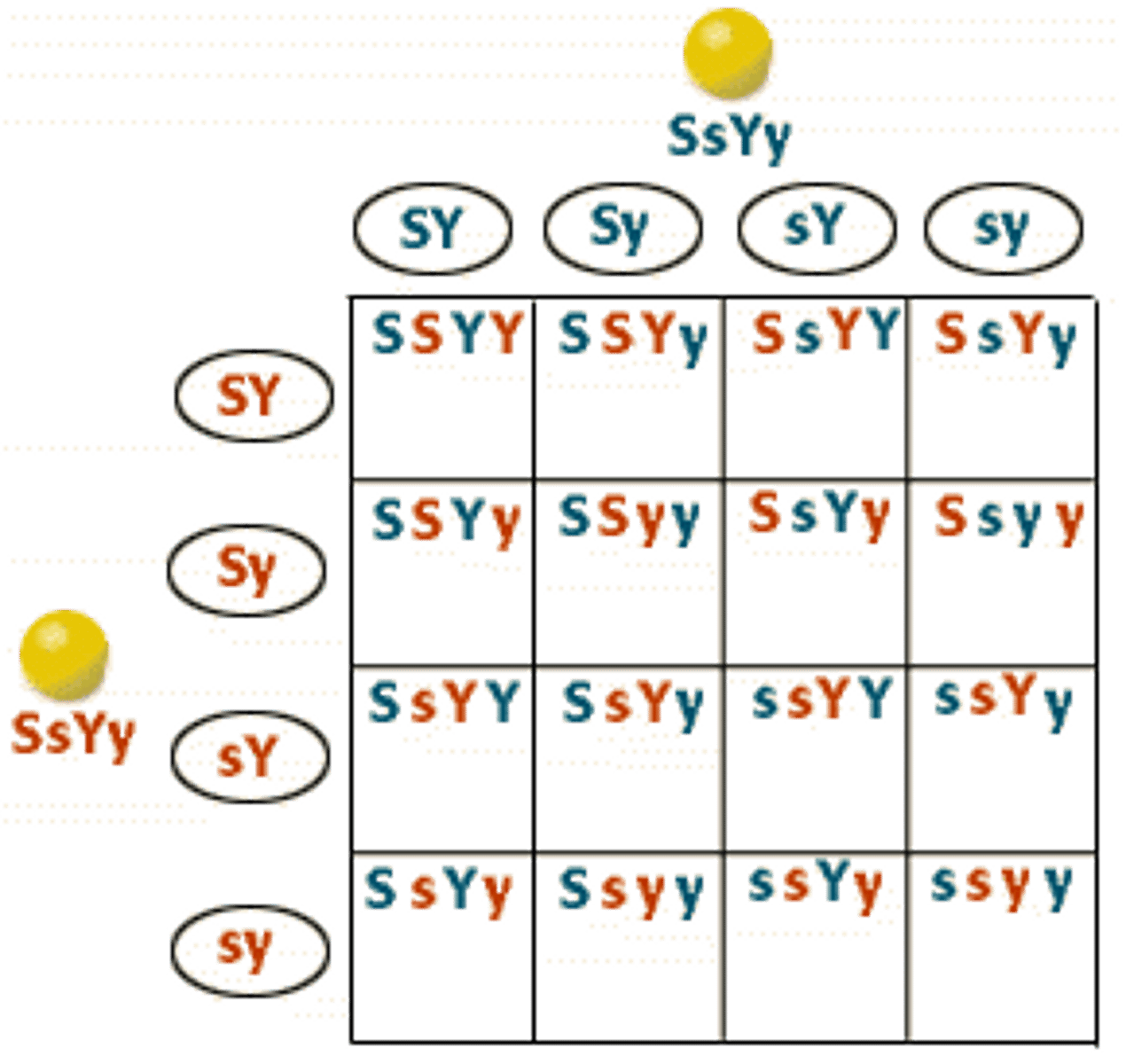
9:3:3:1
Ratio when two heterozygous parents were crossed
Dihybrid
crossing two traits in a punnett square
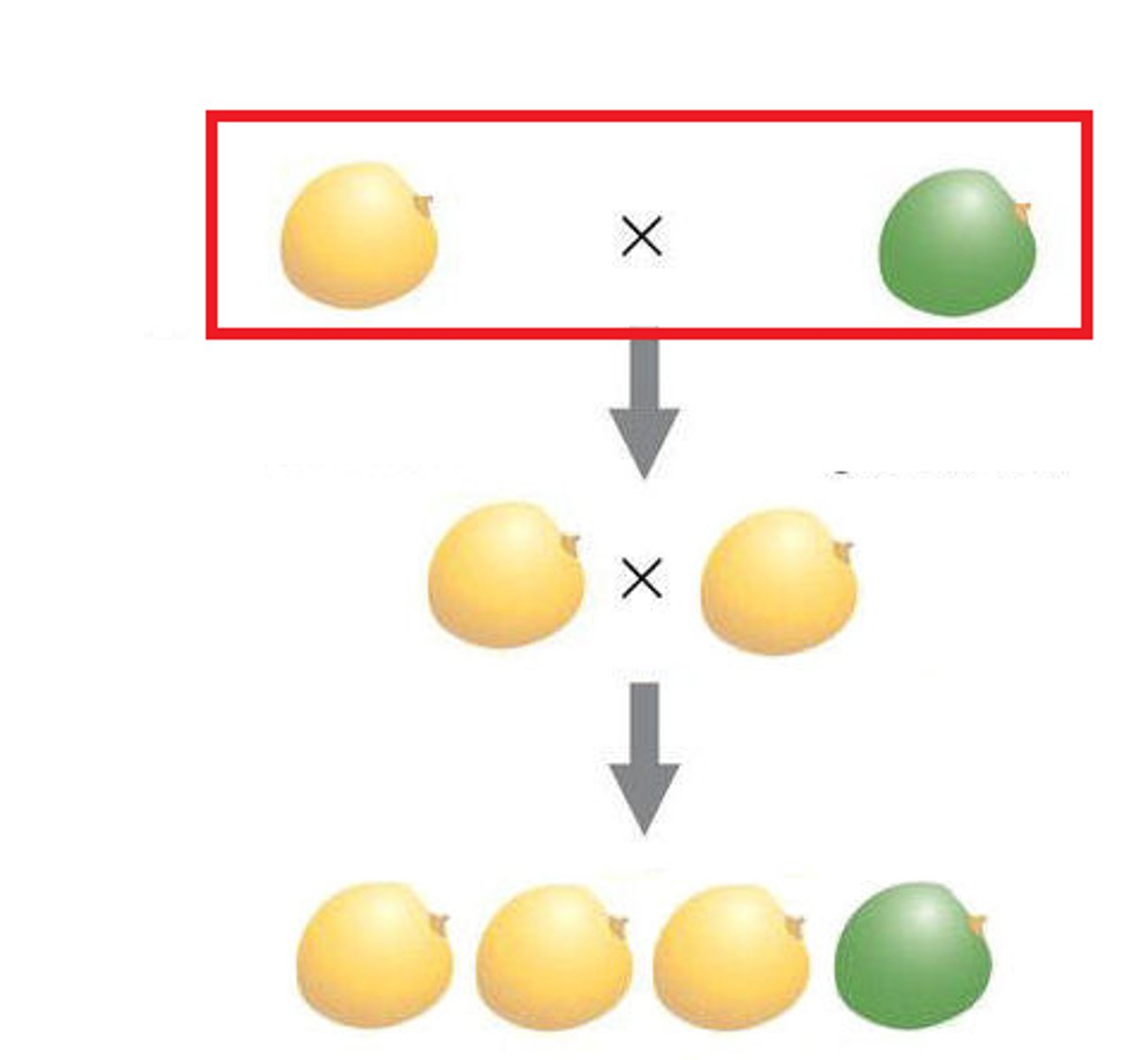
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
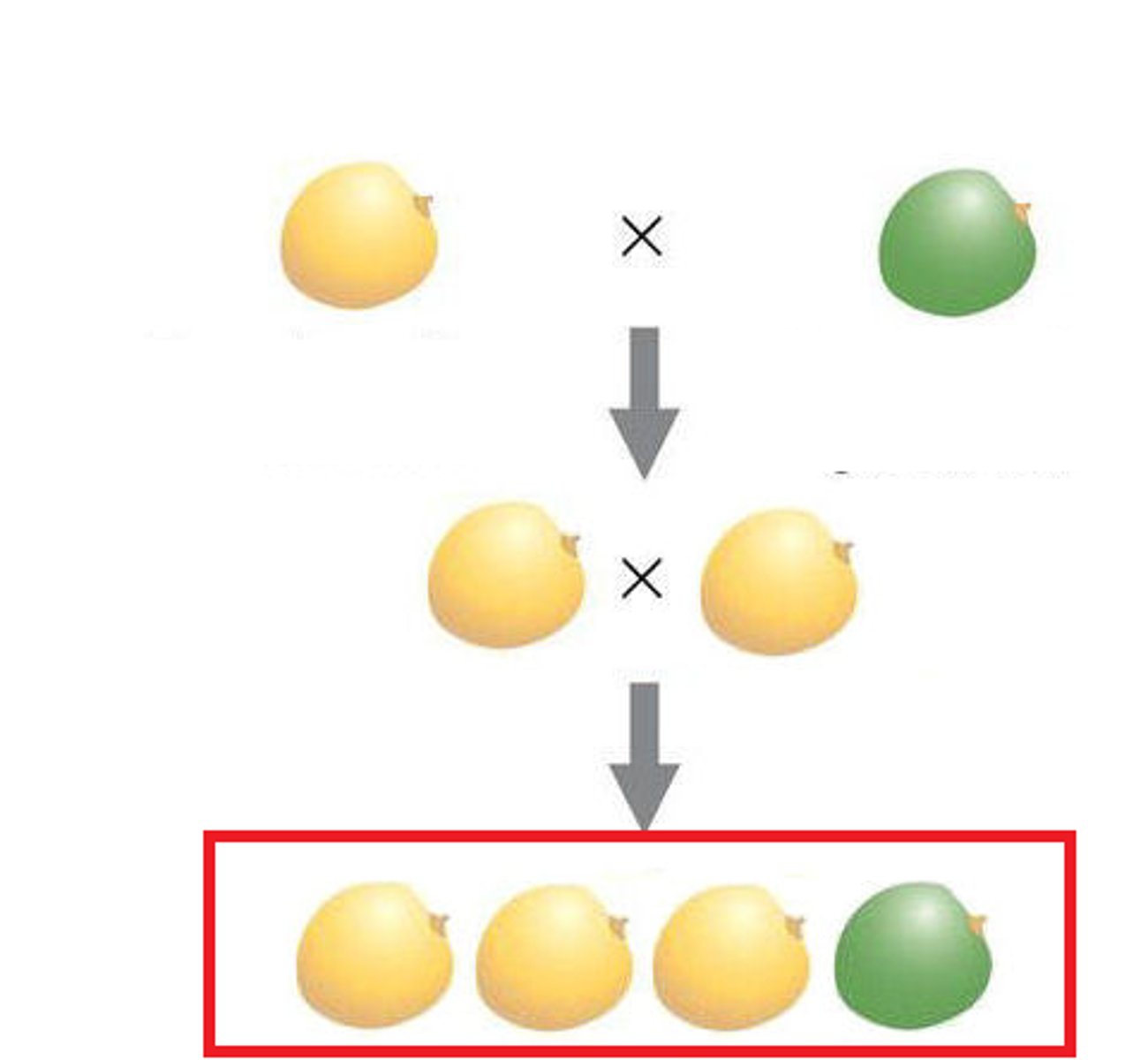
F2 generation
offspring of the F1 generation
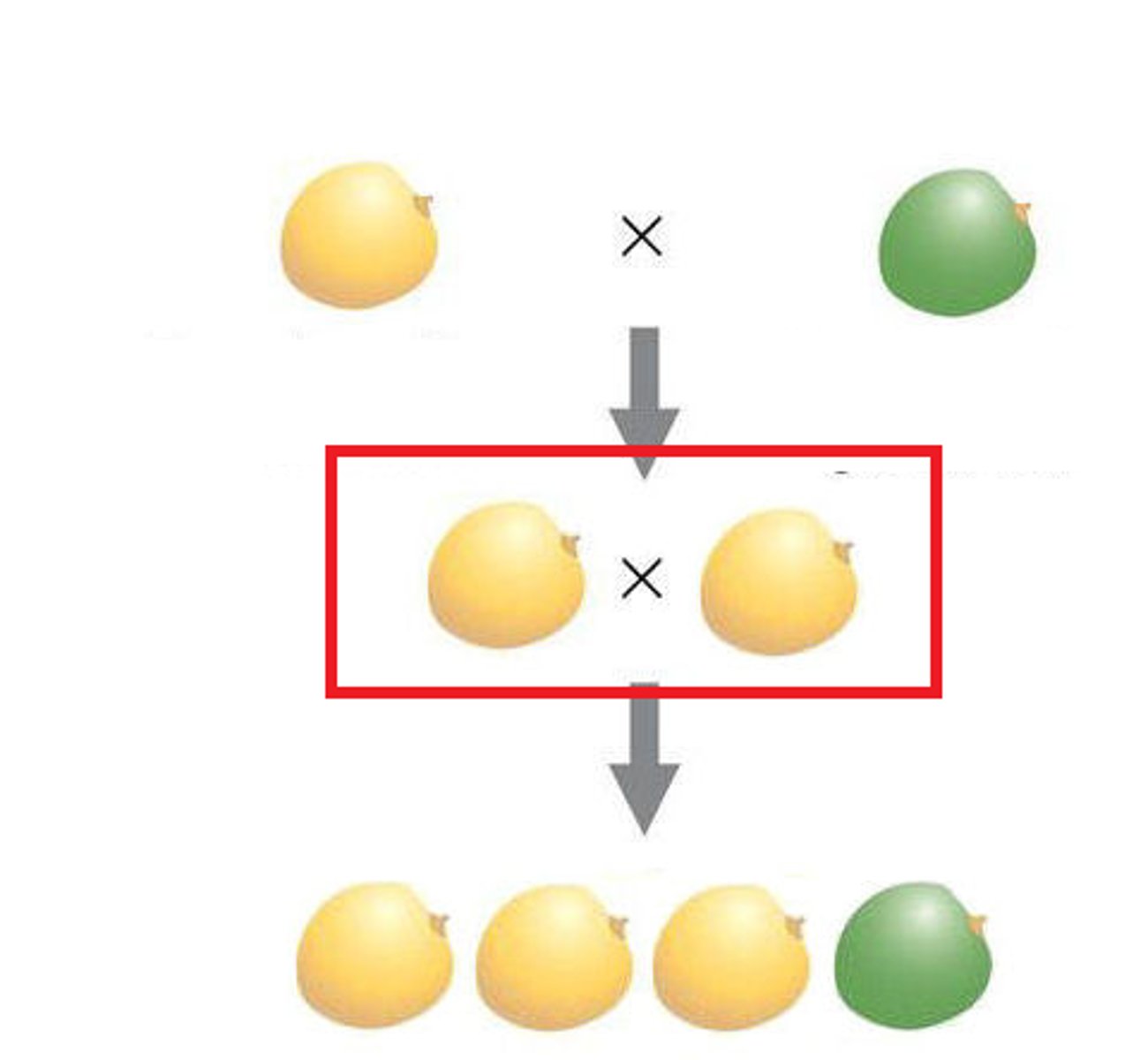
P generation
Parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
Law of Dominance
In many traits one allele is dominant over the other allele. The "weaker (recessive" allele is only expressed when it is paired with another recessive allele
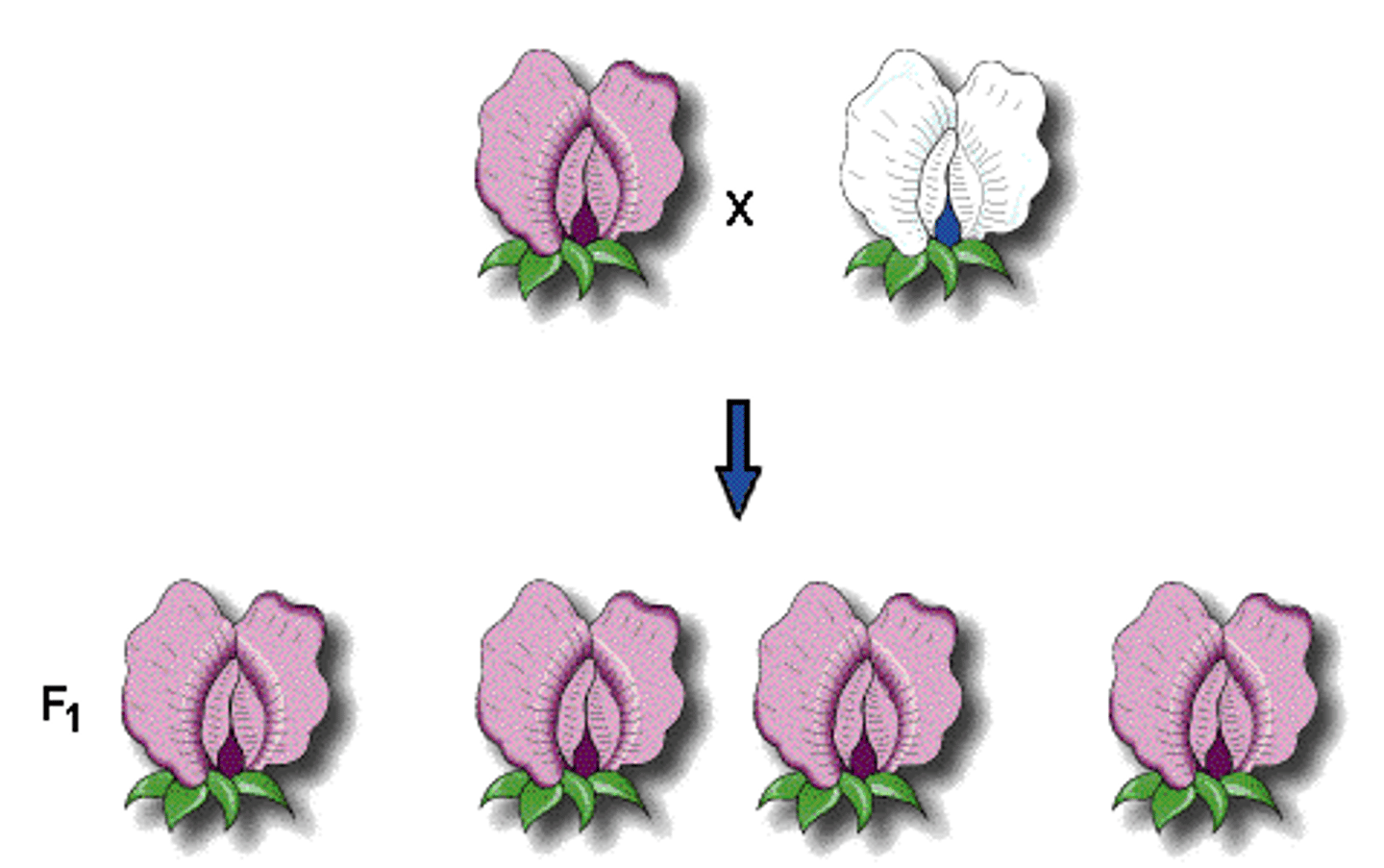
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
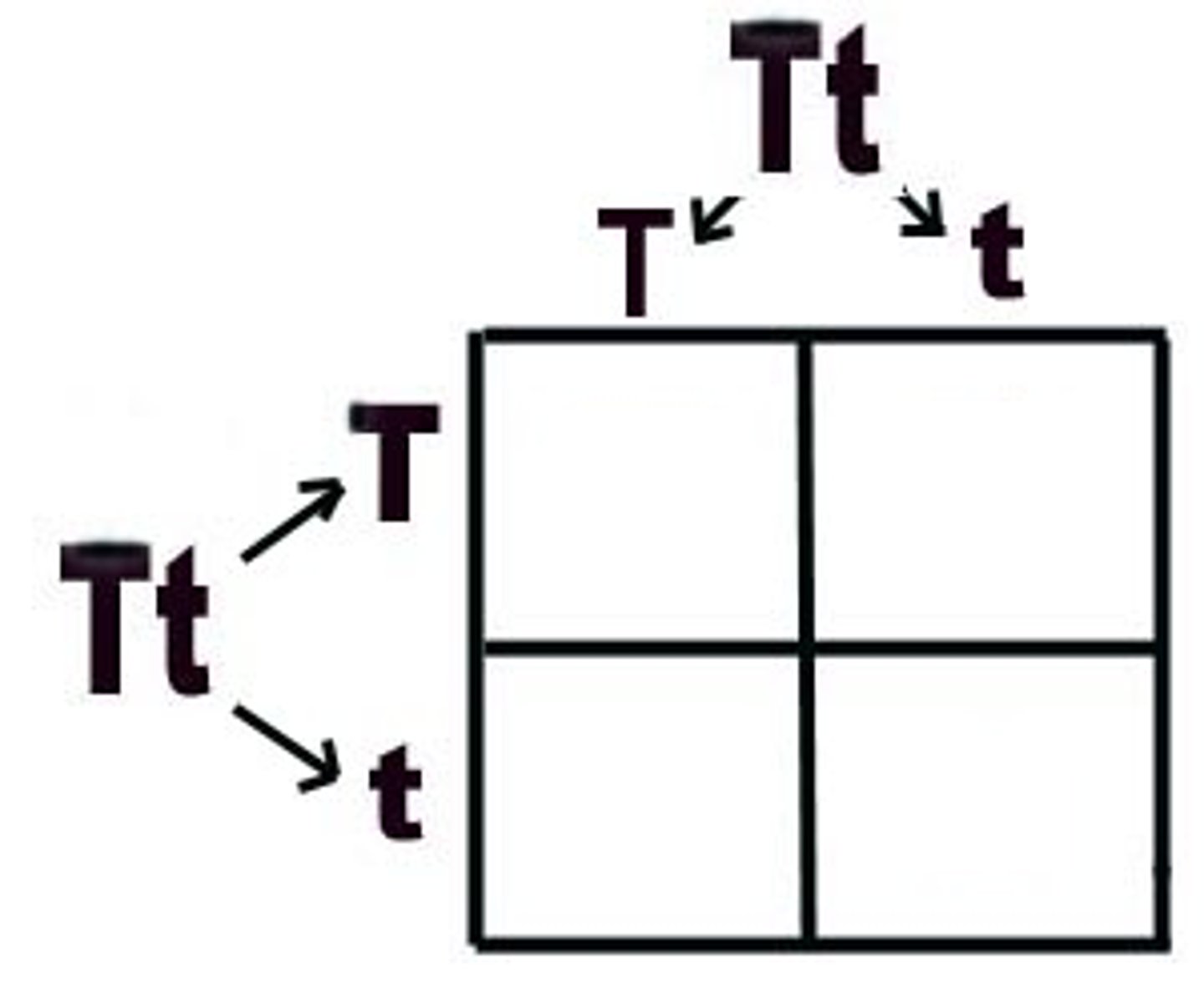
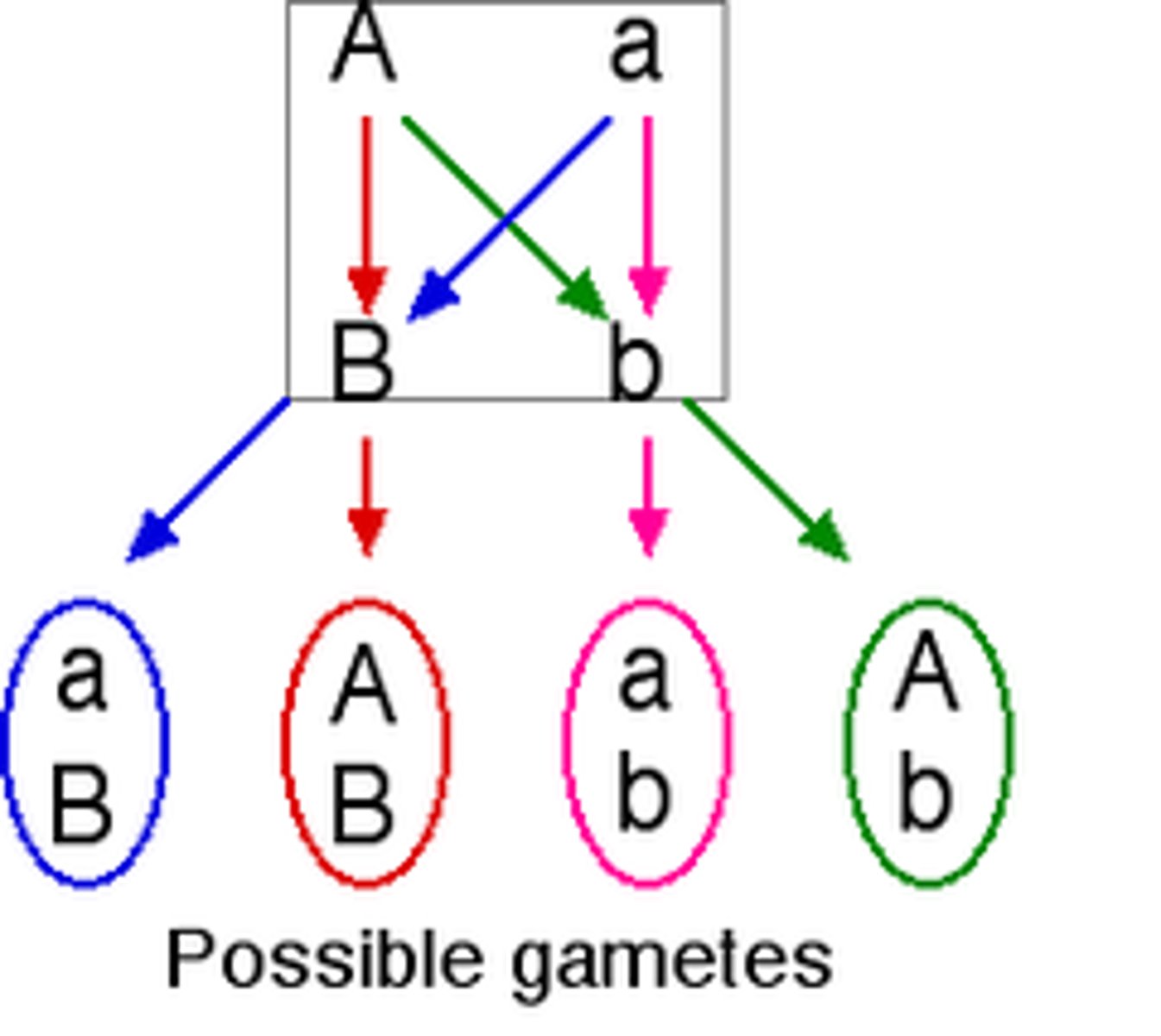
law of independent assortment
the law that states that genes separate independently of one another in meiosis
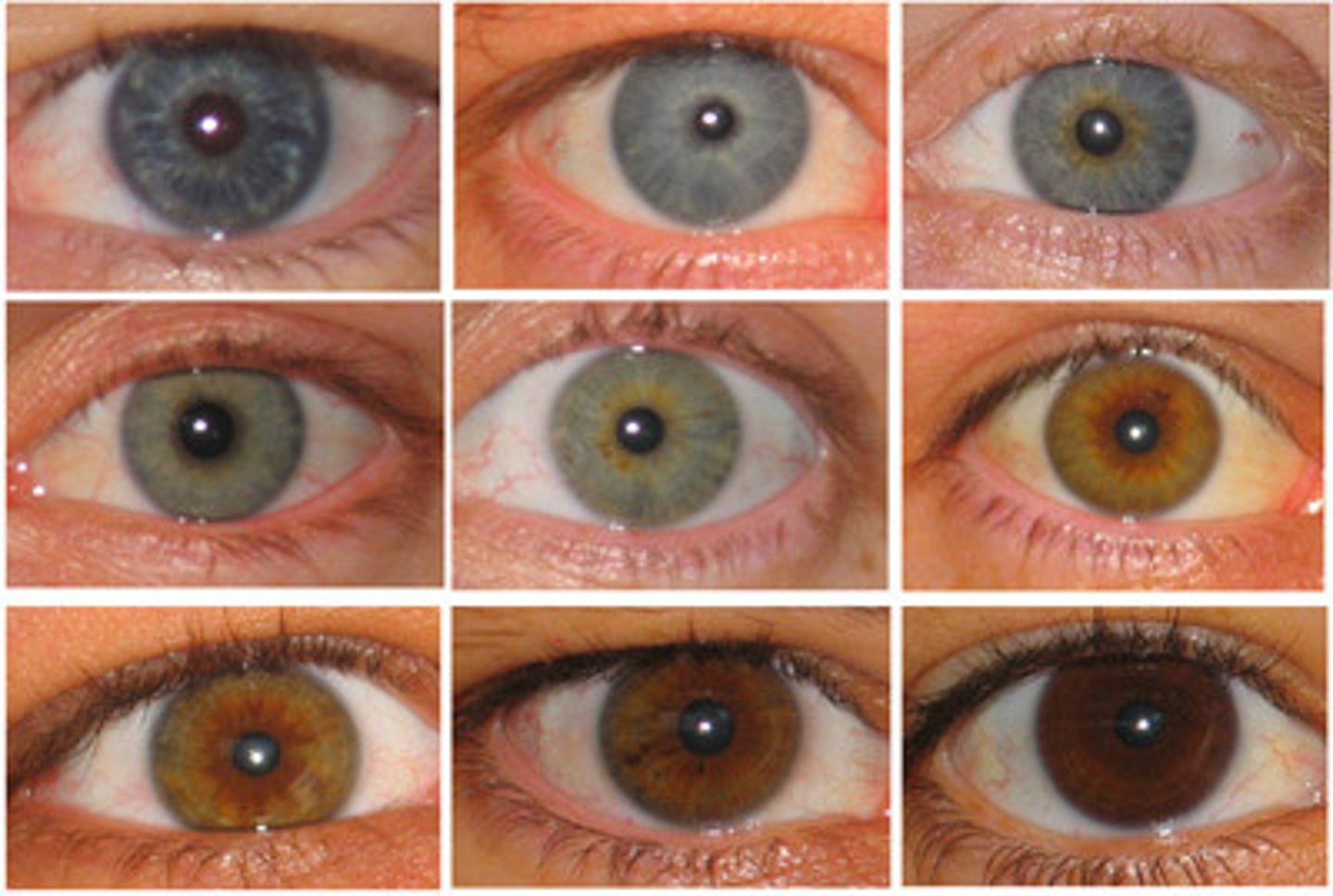
Trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
true-breeding
term used to describe organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self-pollinate
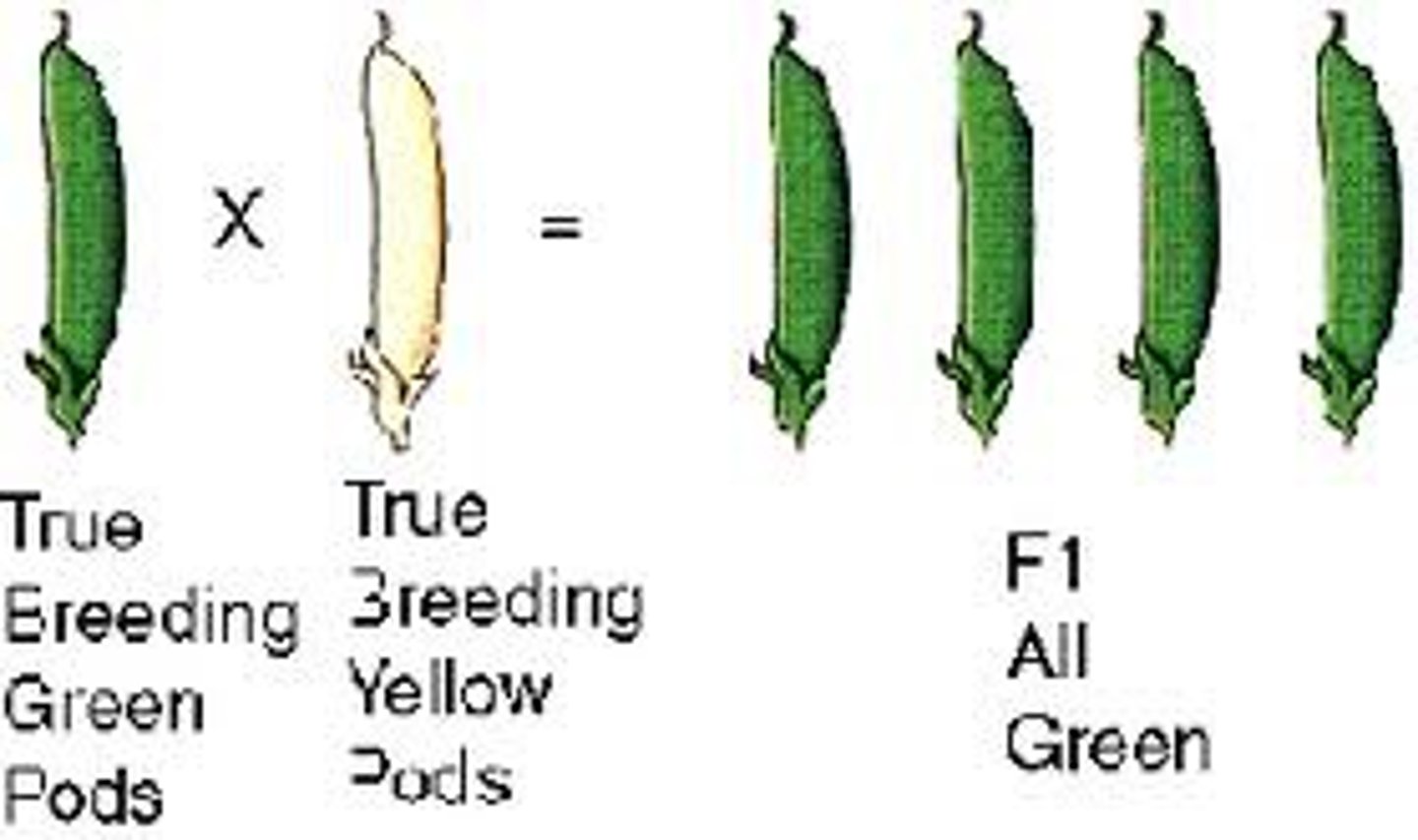
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele, results in a neither allele showing when heterozygous
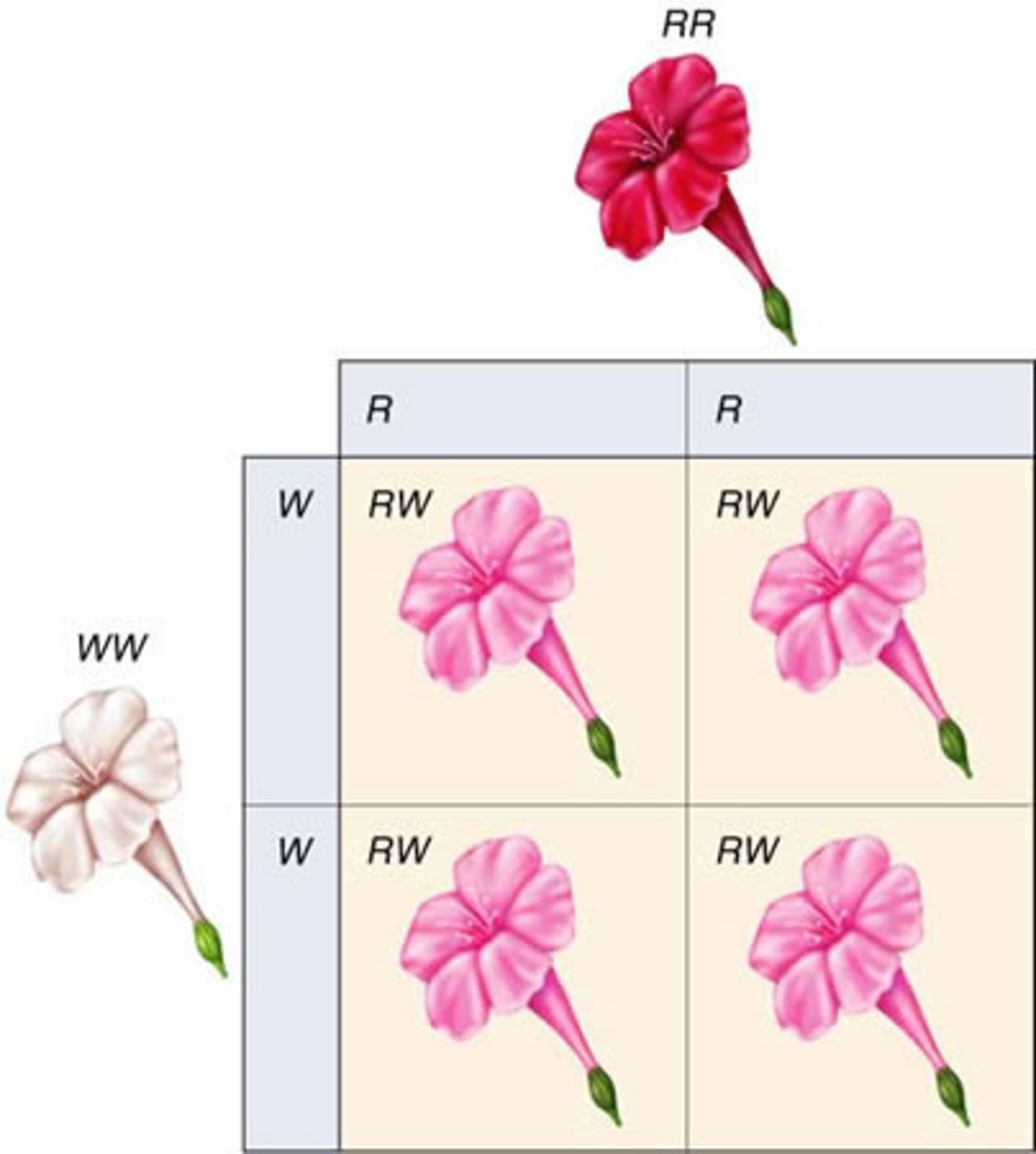
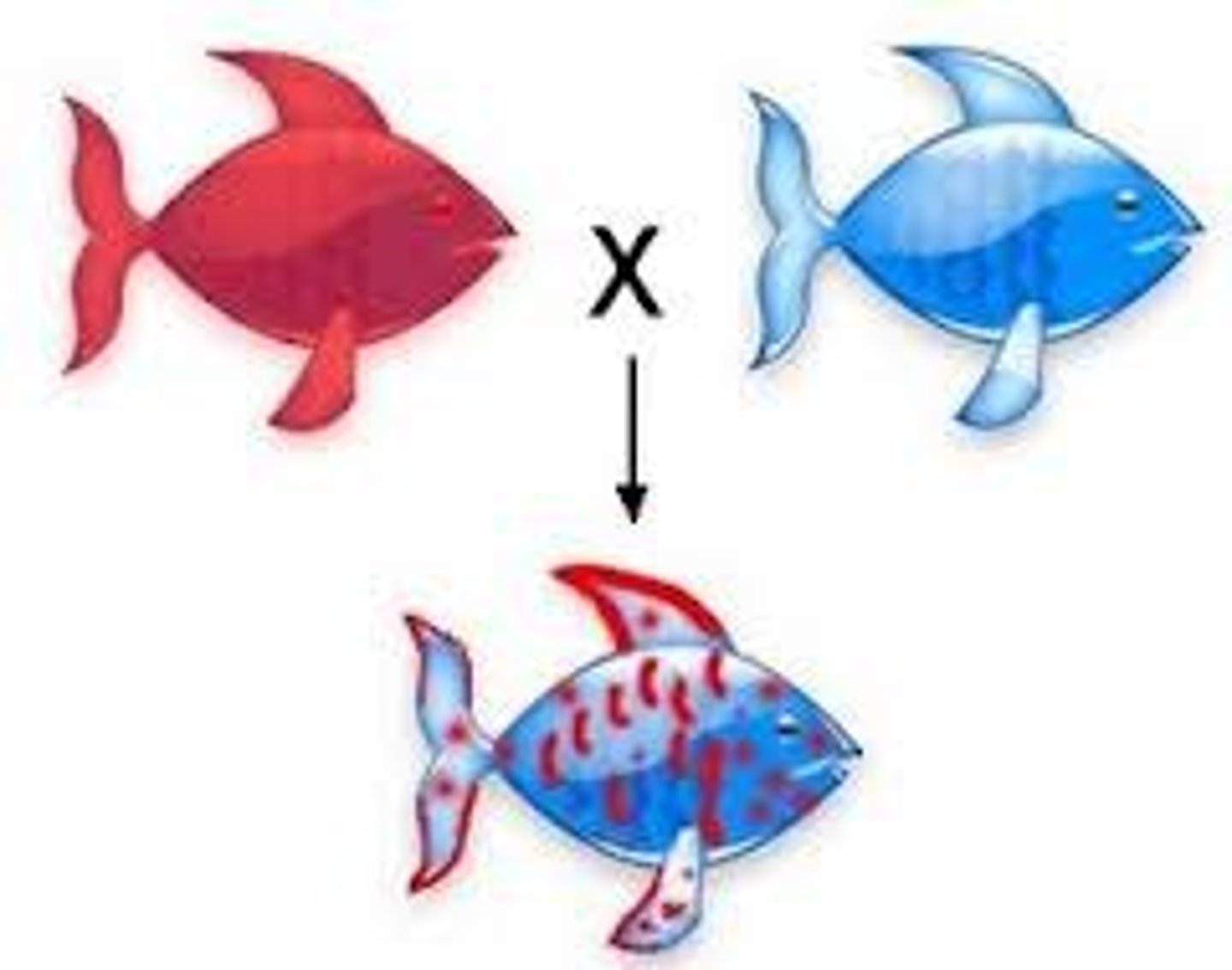
Codominance
A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive. Results in both alleles showing when heterozygous
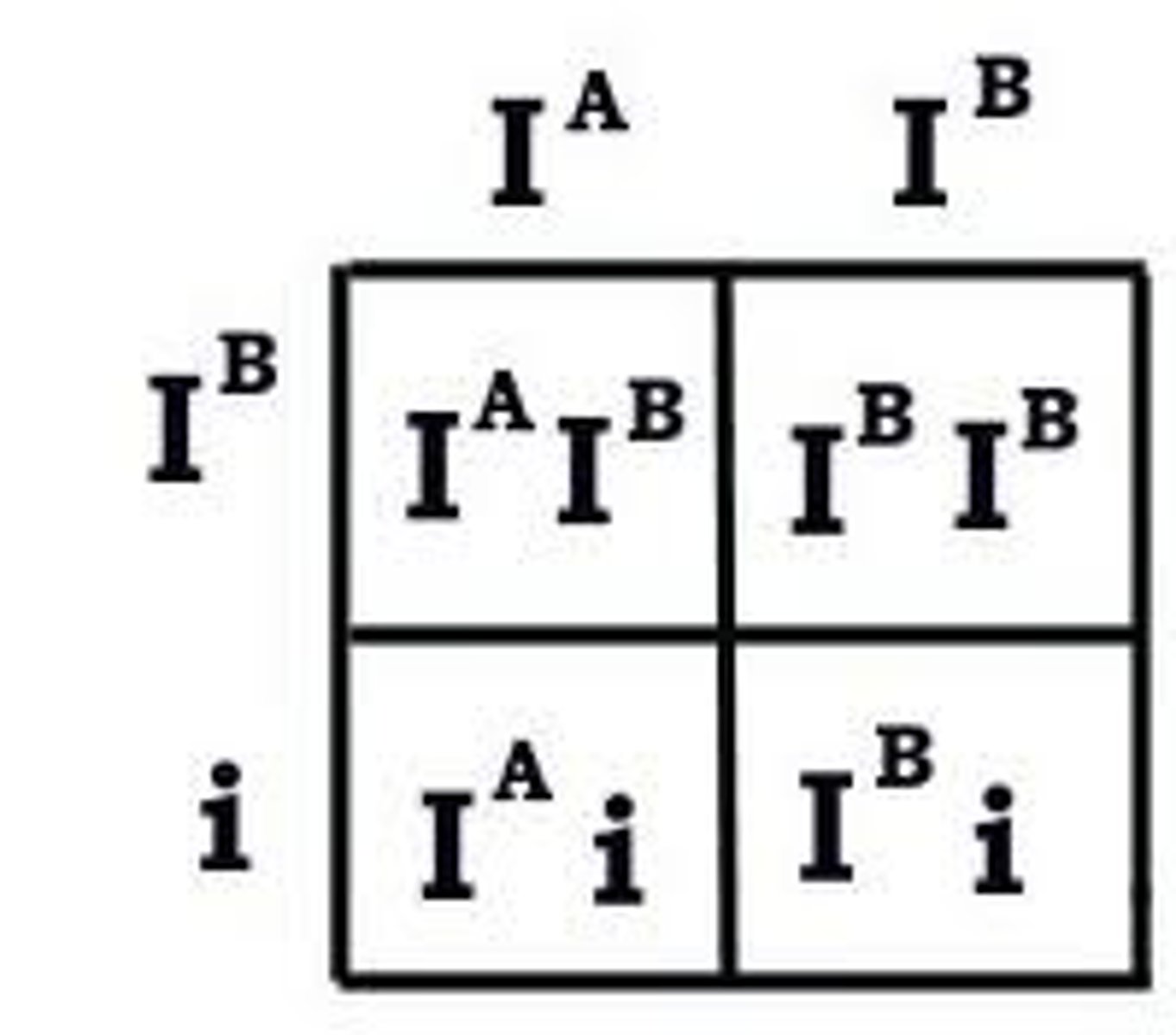
multiple alleles
A gene that has more than two alleles
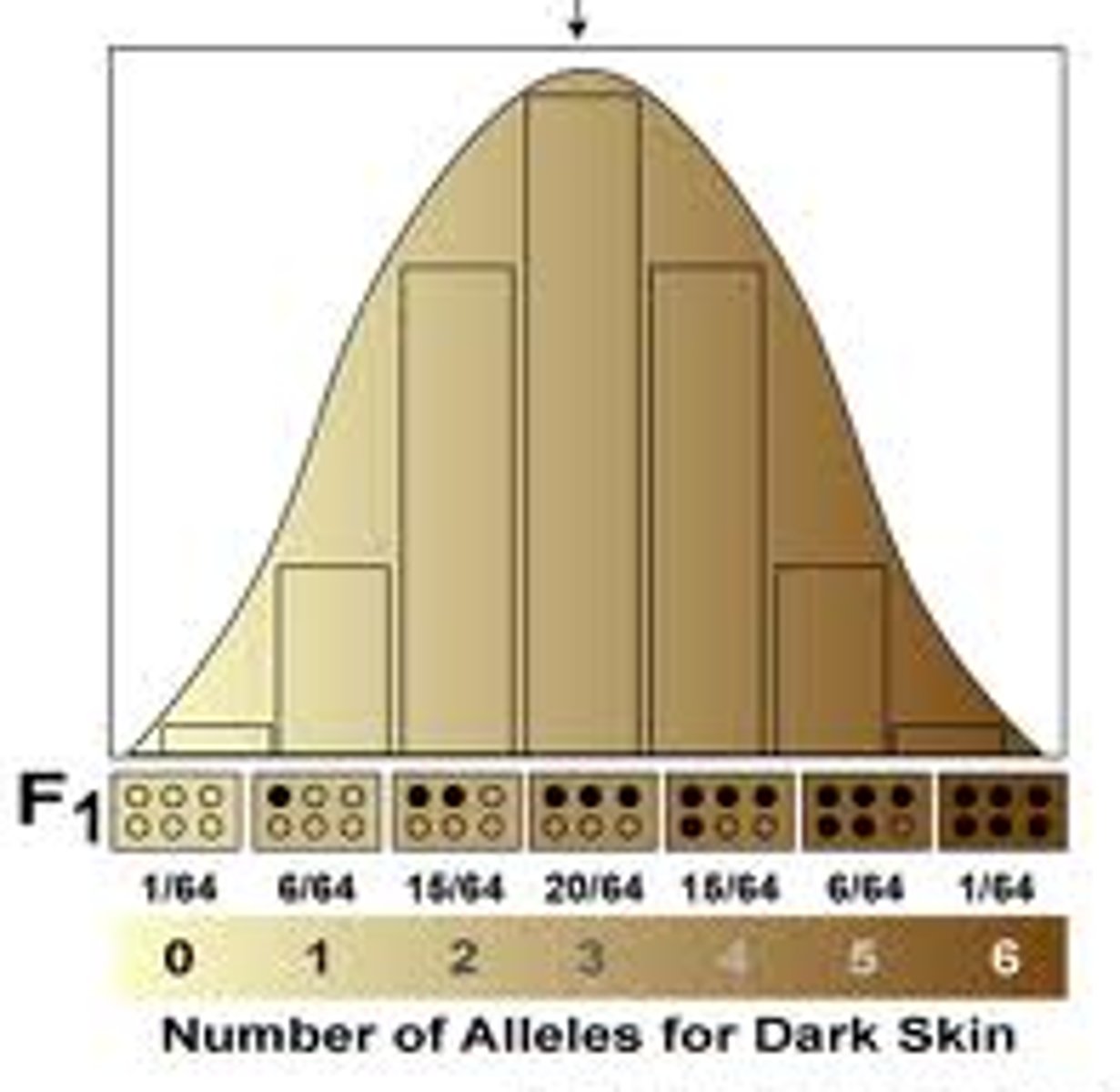
polygenic inheritance
multiple genes influencing one trait
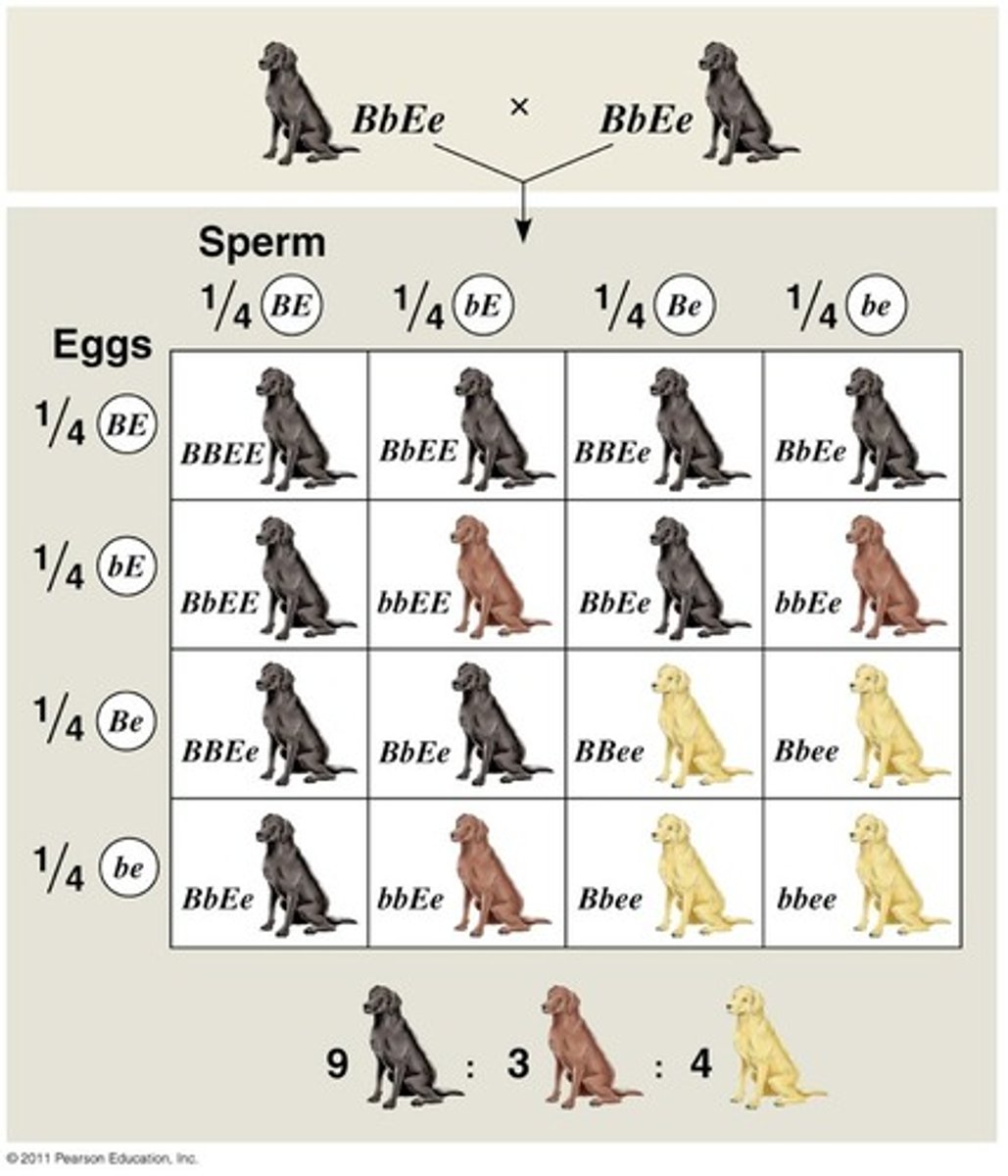
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
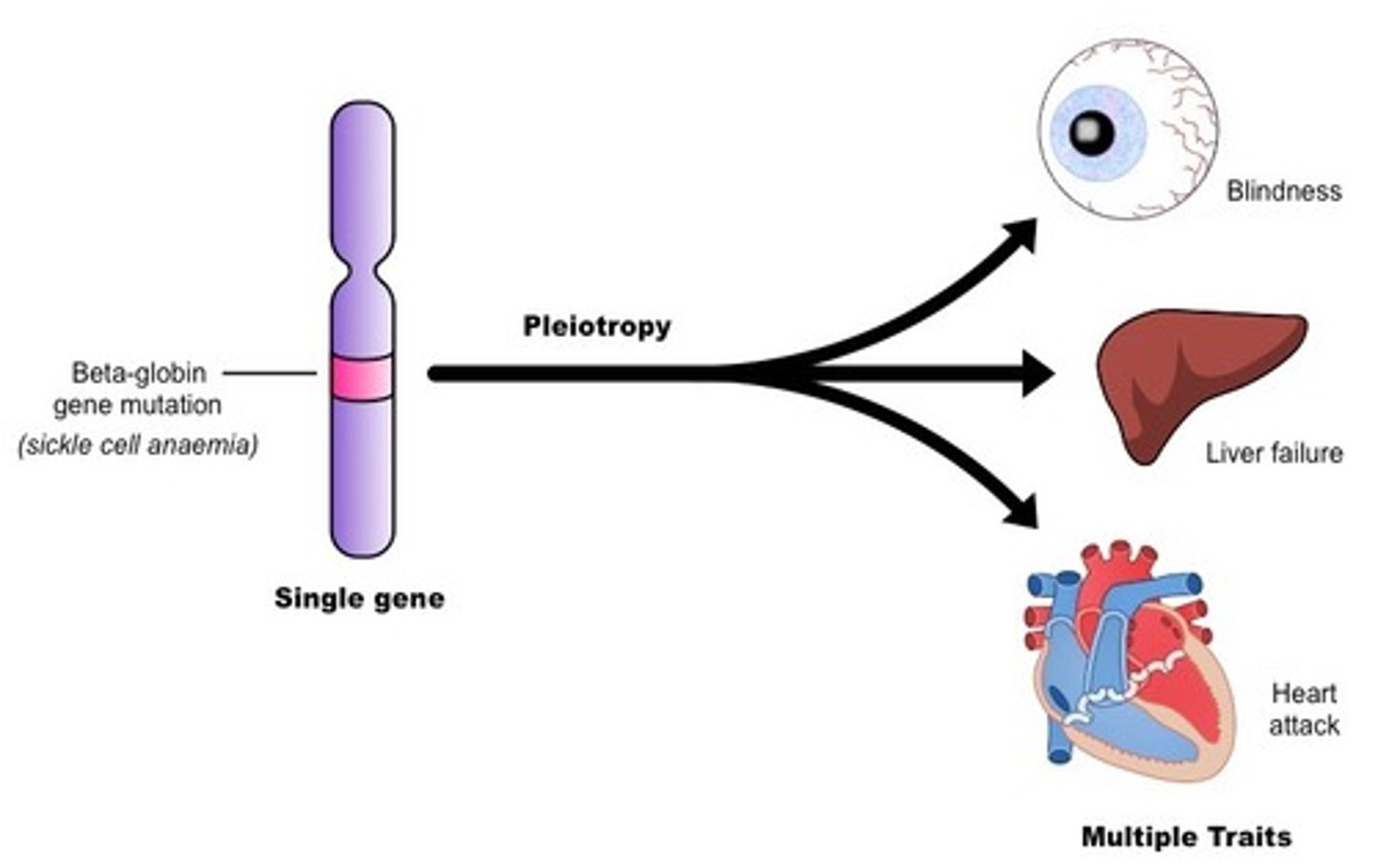
Pleiotropy
A single gene to have multiple effects.
AA, AO
Type A blood
BB, BO
Type B blood
OO
Type O blood
AB
Type AB blood
autosomal dominant
inheritance pattern of a dominant allele on an autosome
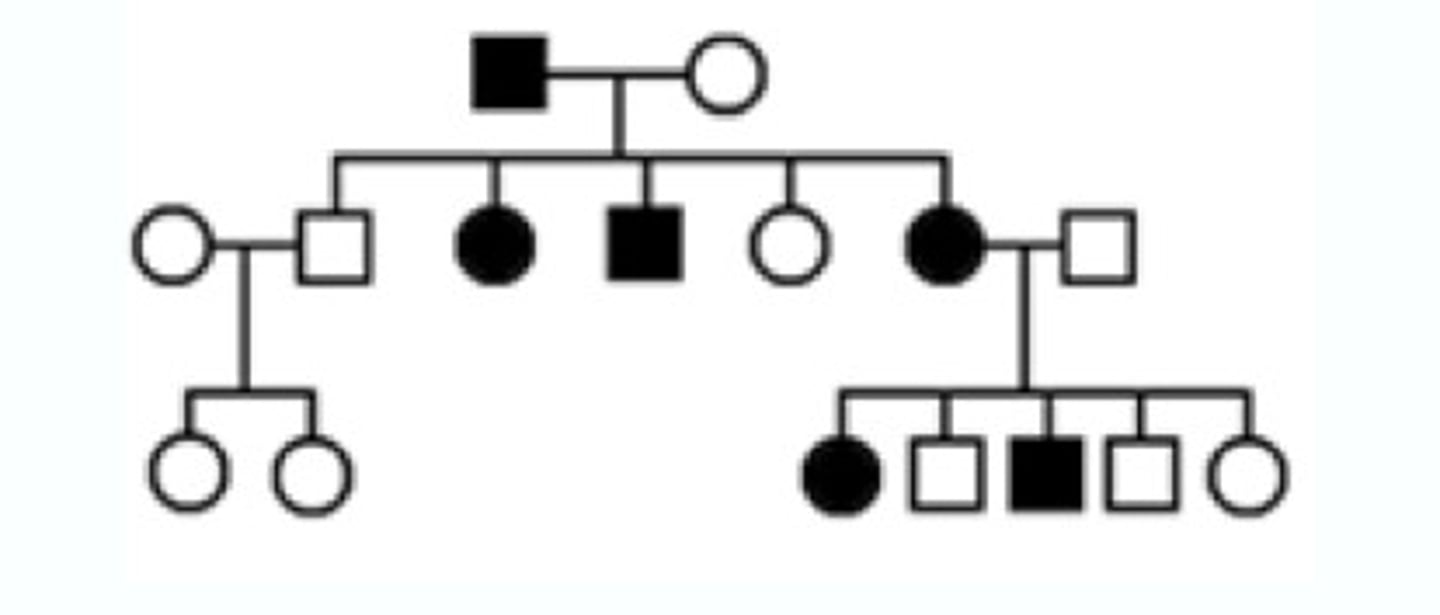
autosomal recessive
inheritance pattern of a recessive allele on an autosome
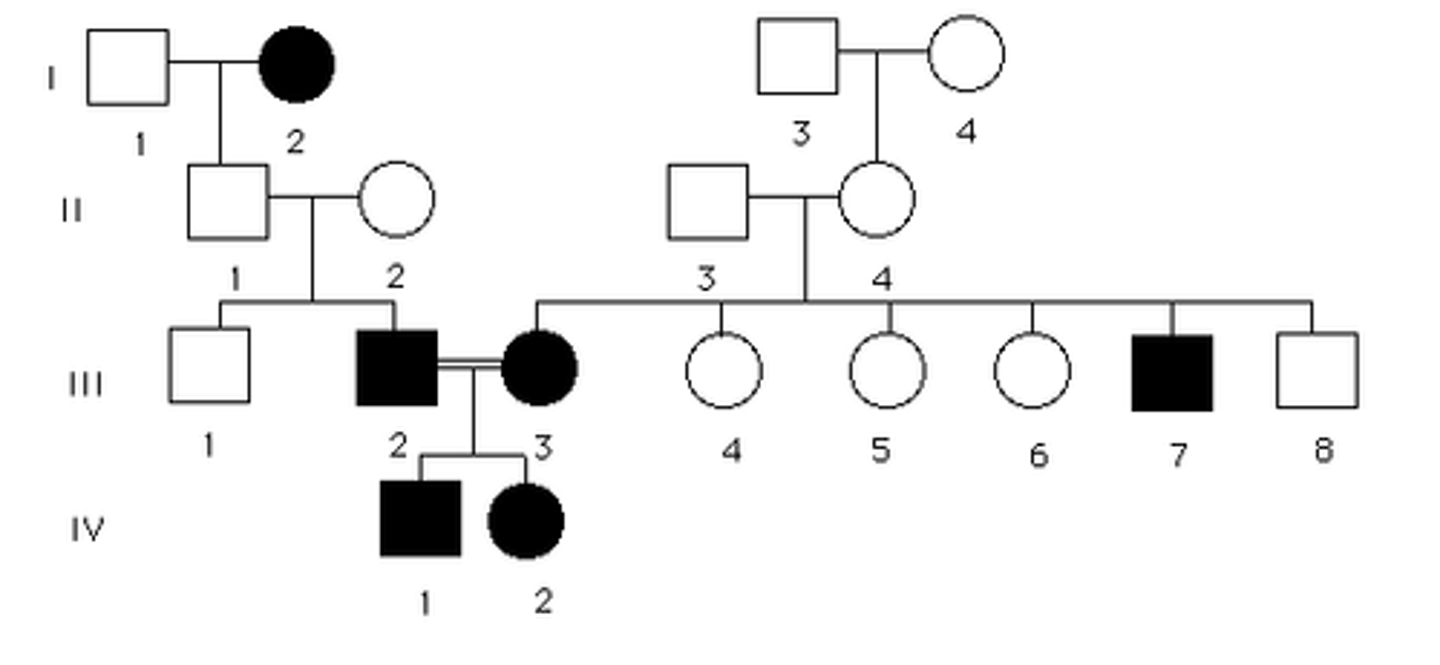
sex-linked recessive
recessive gene on a sex chromosome